Abstract
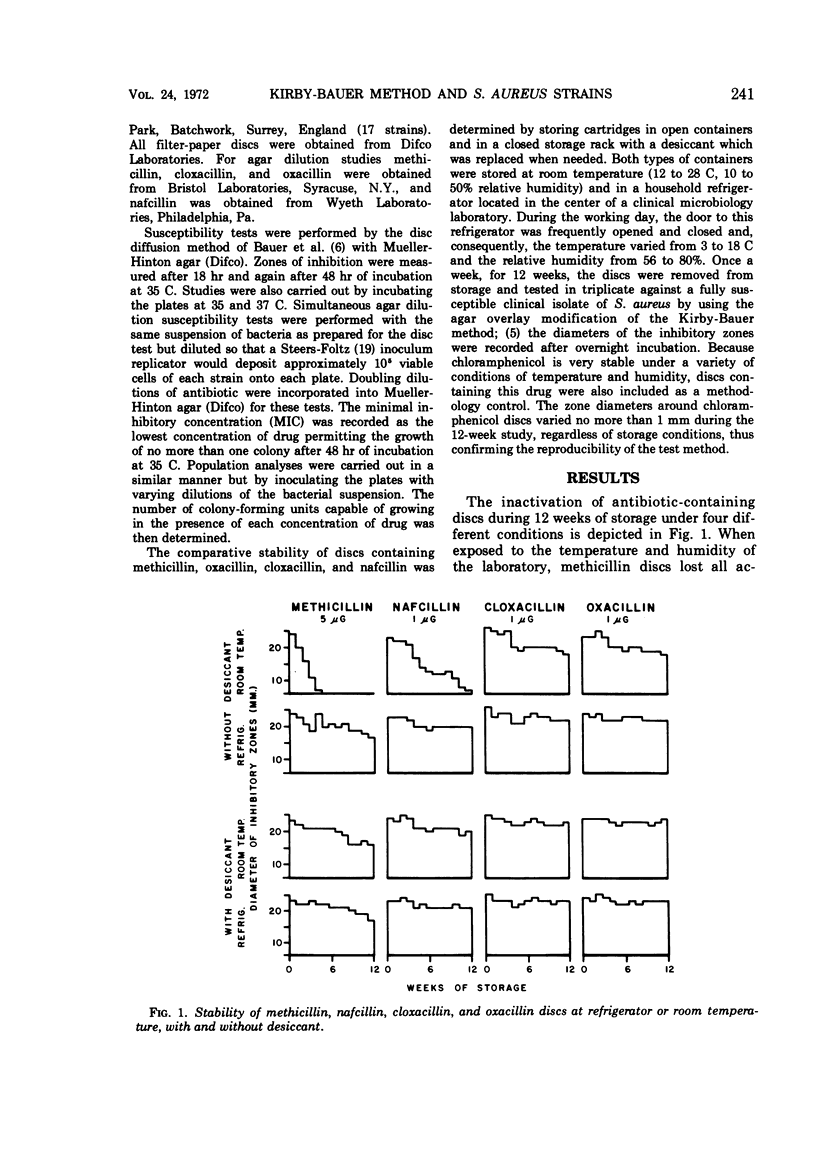
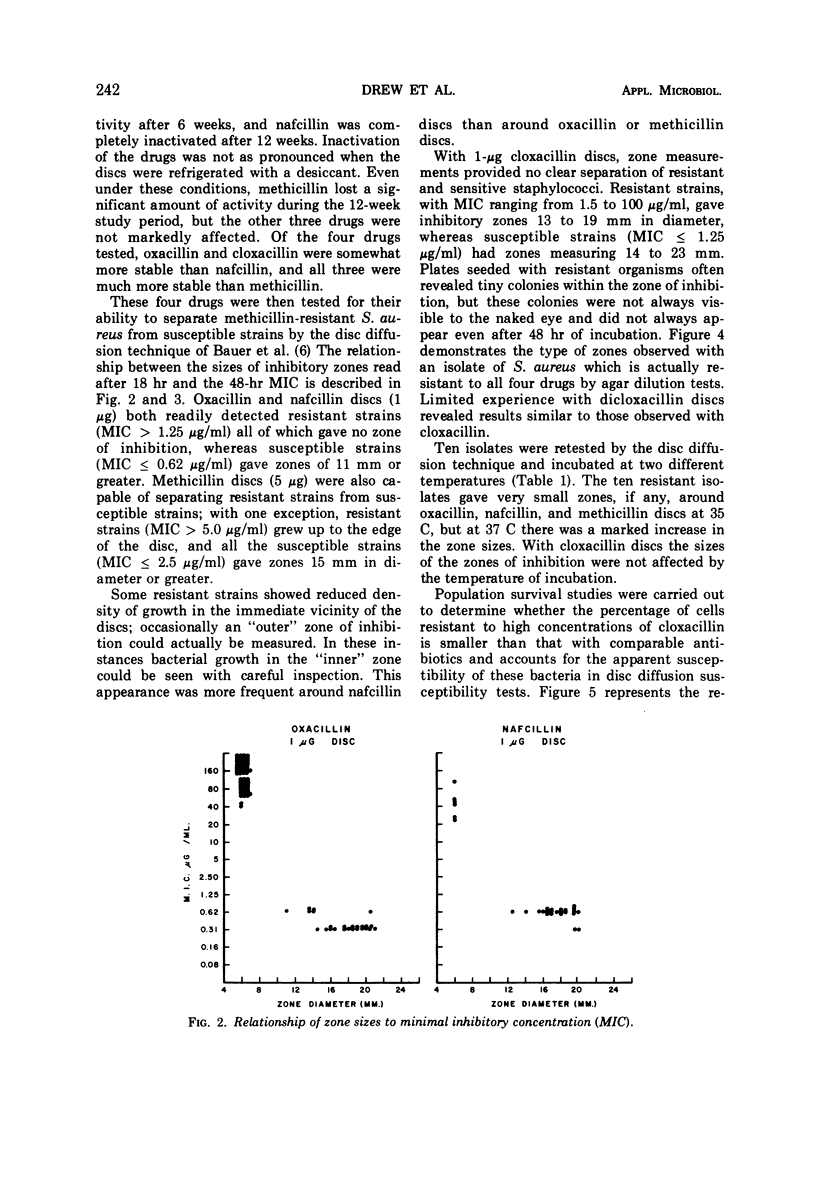
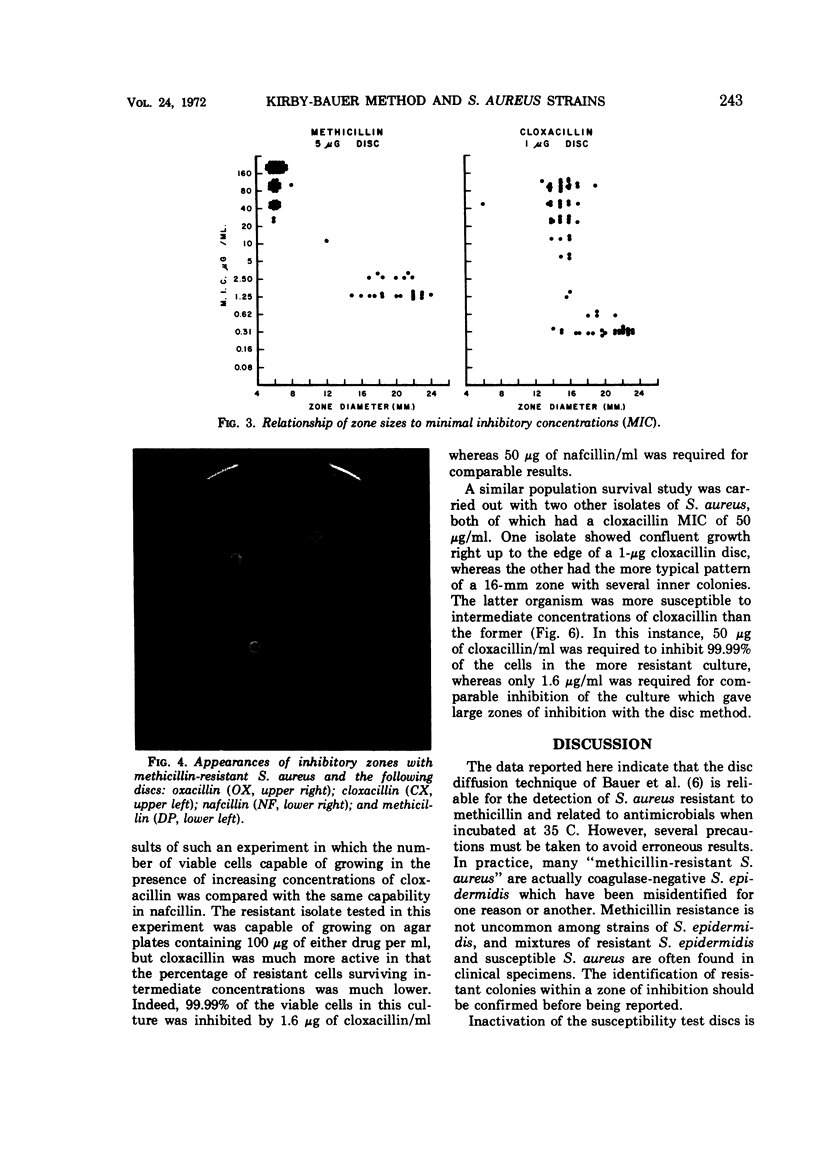
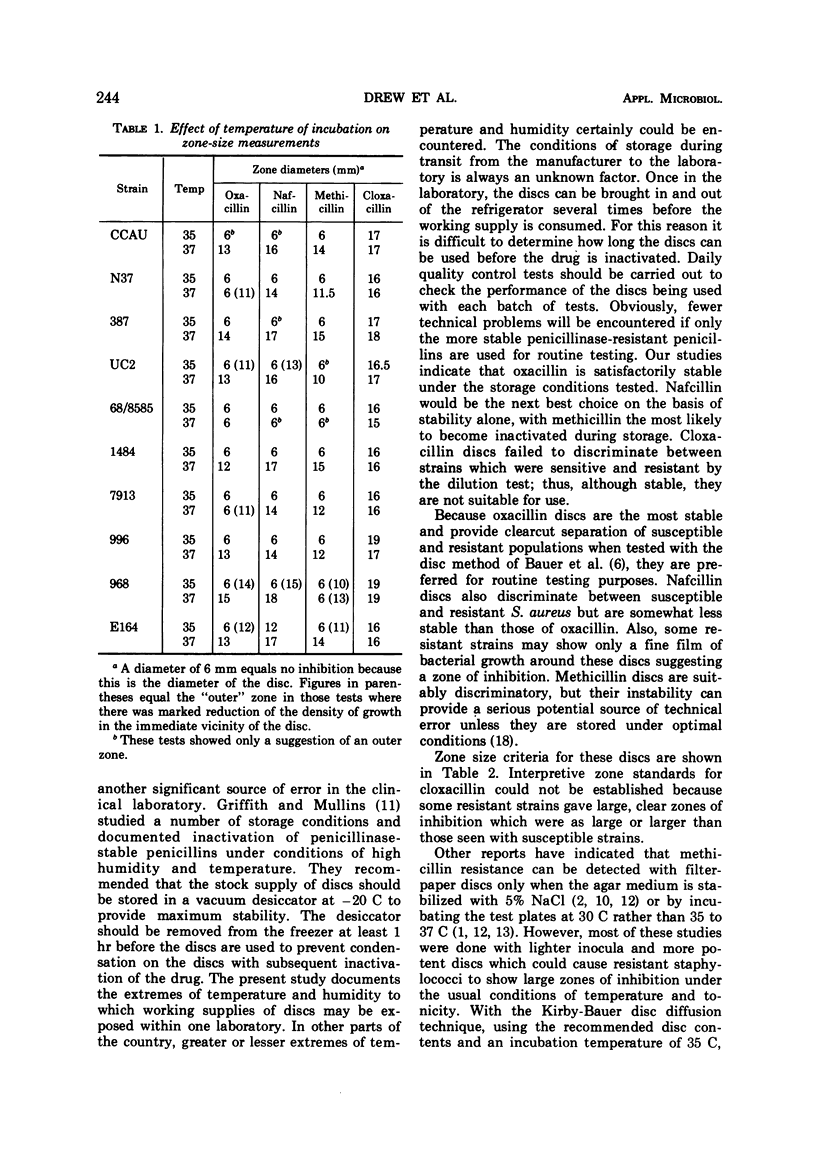
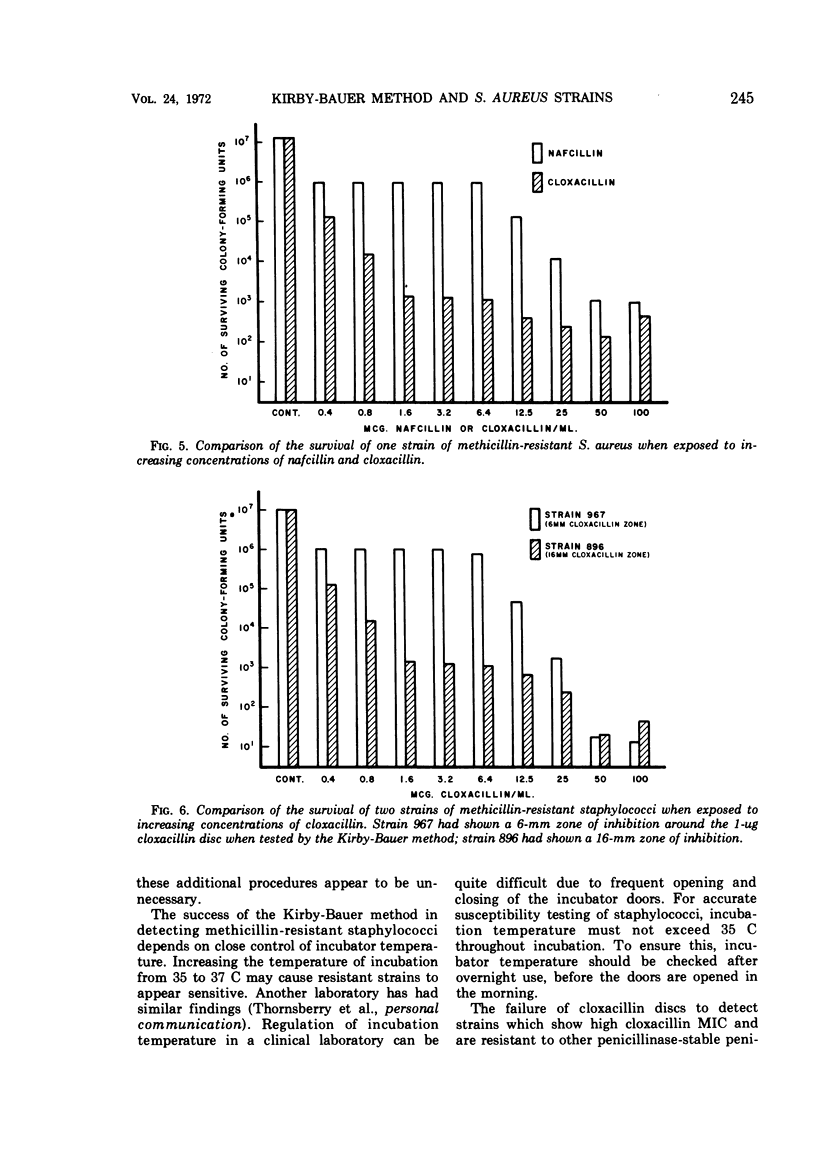
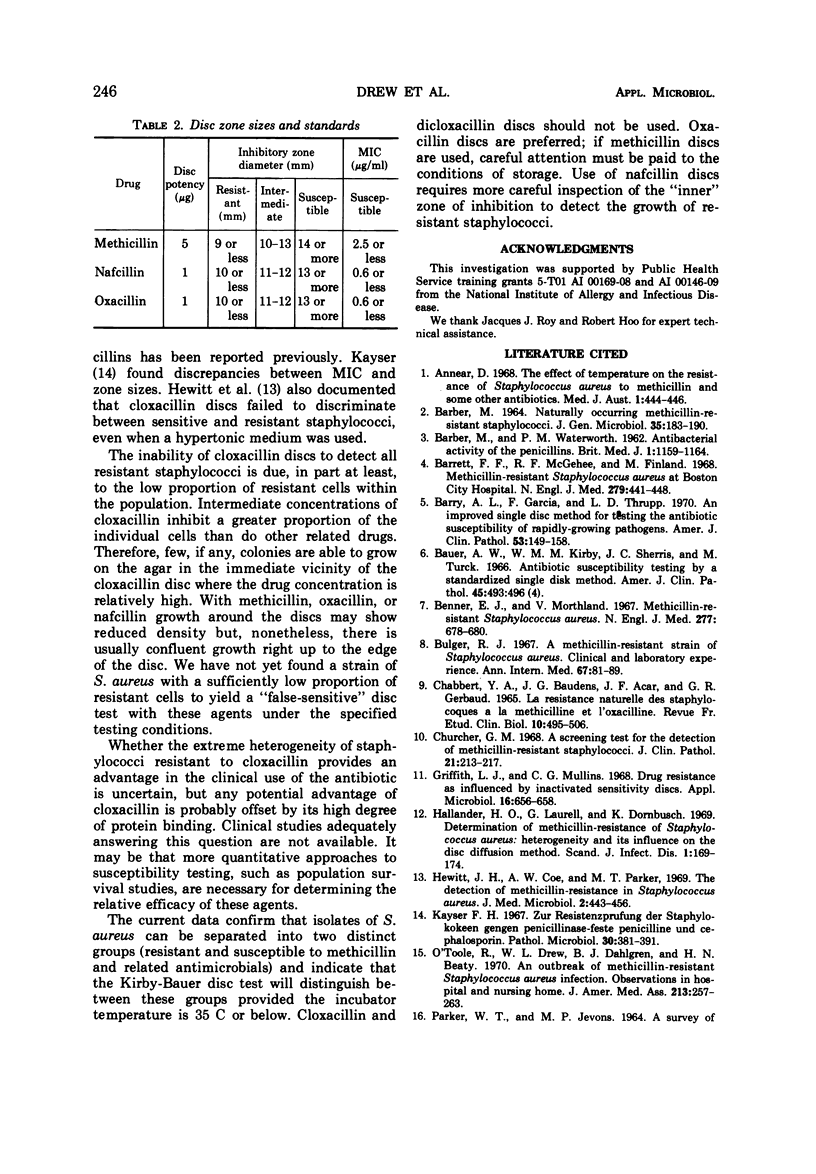
The resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and related drugs can be reliably determined by using the Kirby-Bauer method of susceptibility testing if the incubation temperature is 35 C or below, but resistance may be missed at 37 C. The 1-μg discs of oxacillin and nafcillin or the 5-μg discs of methicillin may be used for this purpose but not the 1-μg discs of cloxacillin. The latter fail to discriminate between sensitive and resistant staphylococci by zone measurement; some resistant strains of staphylococci may show larger zones of inhibition than sensitive strains. Stability of these antibiotic-containing discs was studied under conditions of temperature and humidity variation that might be encountered in a clinical laboratory refrigerator. Oxacillin discs were the most stable and are to be preferred for susceptibility testing. Nafcillin discs were less stable, and methicillin discs lose their potency rapidly unless carefully stored in a refrigerator with a desiccant.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M. NATURALLY OCCURING METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:183–190. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., WATERWORTH P. M. Antibacterial activity of the penicillins. Br Med J. 1962 Apr 28;1(5286):1159–1164. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5286.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett F. F., McGehee R. F., Jr, Finland M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at Boston City Hospital. Bacteriologic and epidemiologic observations. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 29;279(9):441–448. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808292790901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Garcia F., Thrupp L. D. An improved single-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of rapidly-growing pathogens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):149–158. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner E. J., Morthland V. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrobial susceptibility. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 28;277(13):678–680. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709282771303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulger R. J. A methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. Clinical and laboratory experience. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jul;67(1):81–89. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Baudens J. G., Acar J. F., Gerbaud G. R. La résistance naturelle des staphylocoques à la méthicillin et l'oxacilline. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1965 May;10(5):495–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher G. M. A screening test for the detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):213–217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. J., Mullins C. G. Drug resistance as influenced by inactivated sensitivity discs. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):656–658. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.656-658.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallander H. O., Laurell G., Dornbusch K. Determination of methicillin resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Heterogeneity and its influence on the disc diffusion method. Scand J Infect Dis. 1969;1(3):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. H., Coe A. W., Parker M. T. The detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Nov 4;2(4):443–456. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-4-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser F. H. Zur Resistenzprüfung der Staphylokokken gegen Penicillinase-feste Penicilline und Cephalosporine. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1967;30(3):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole R. D., Drew W. L., Dahlgren B. J., Beaty H. N. An outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Observations in hospital and nursing home. JAMA. 1970 Jul 13;213(2):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND R., ROLINSON G. N. CHARACTERISTICS OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:887–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.887-899.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
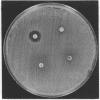
- Seligman S. J. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: genetics of the minority population. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherris J. C., Rashad A. L., Lighthart G. A. Laboratory determination of antibiotic susceptibility to ampicillin and cephalothin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):248–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]