Abstract
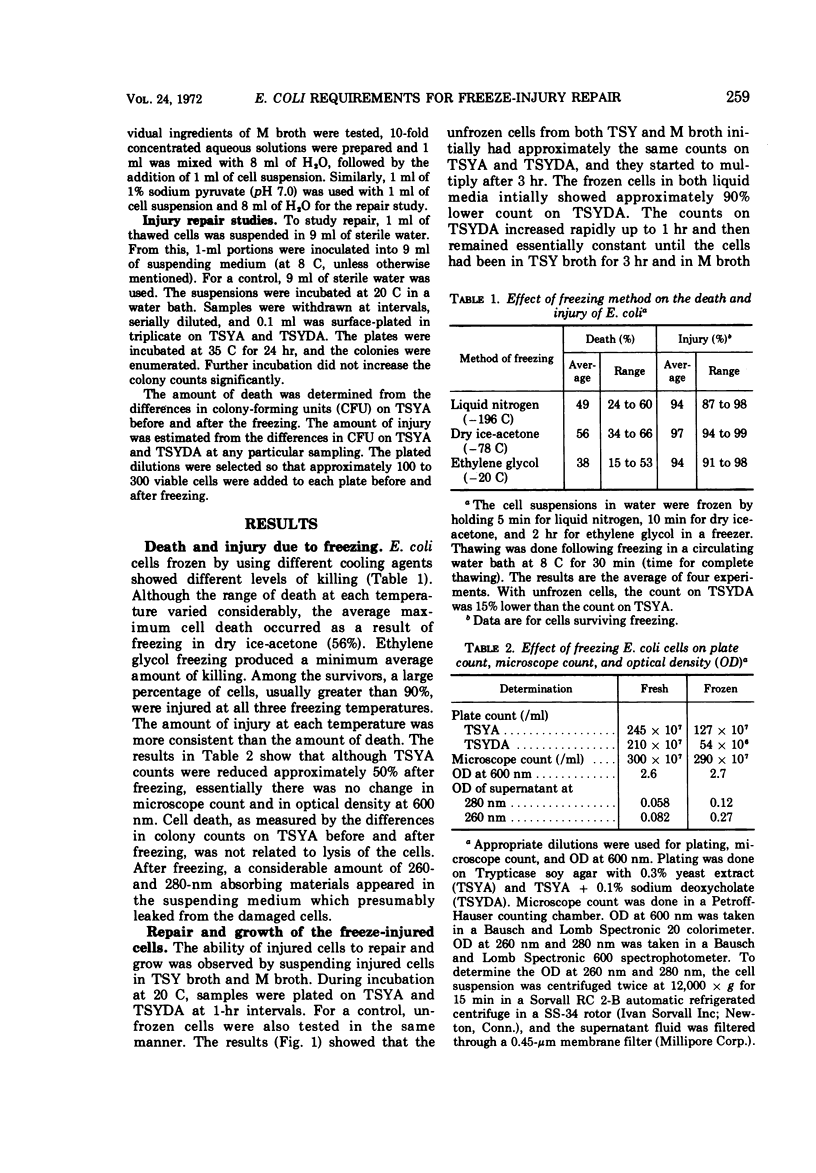
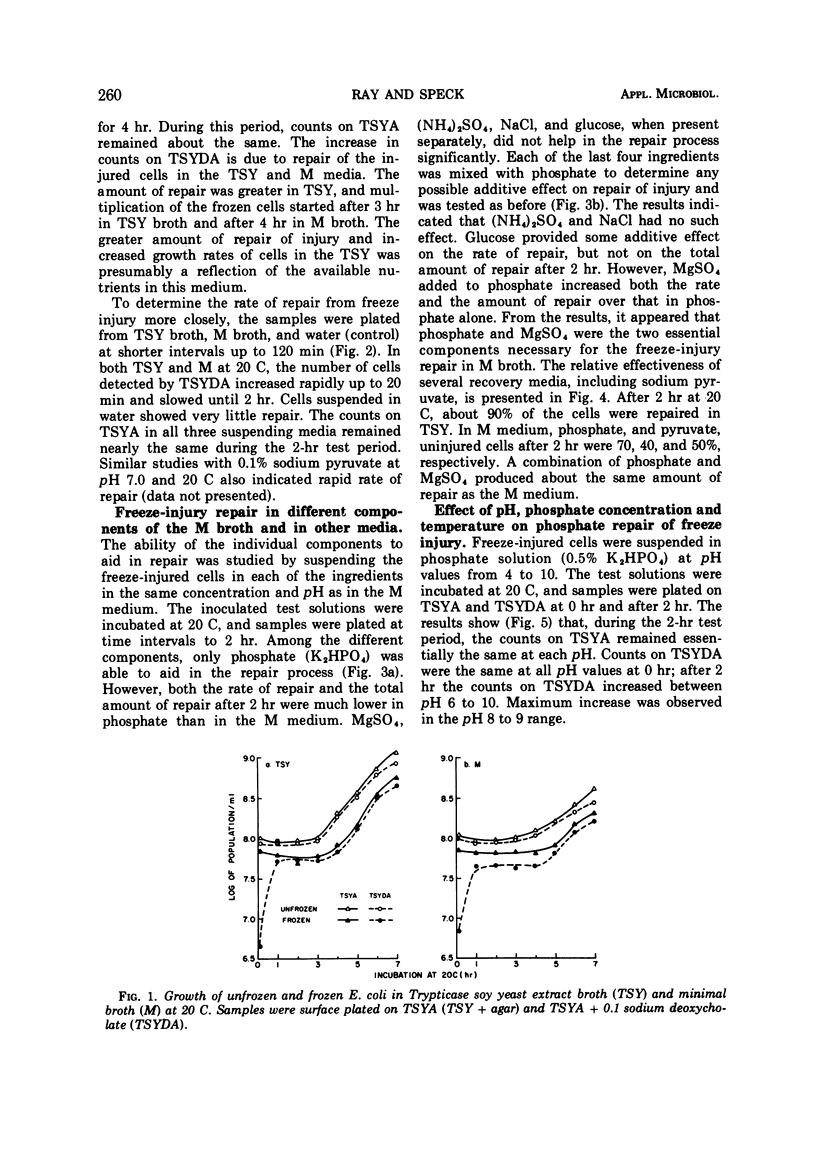
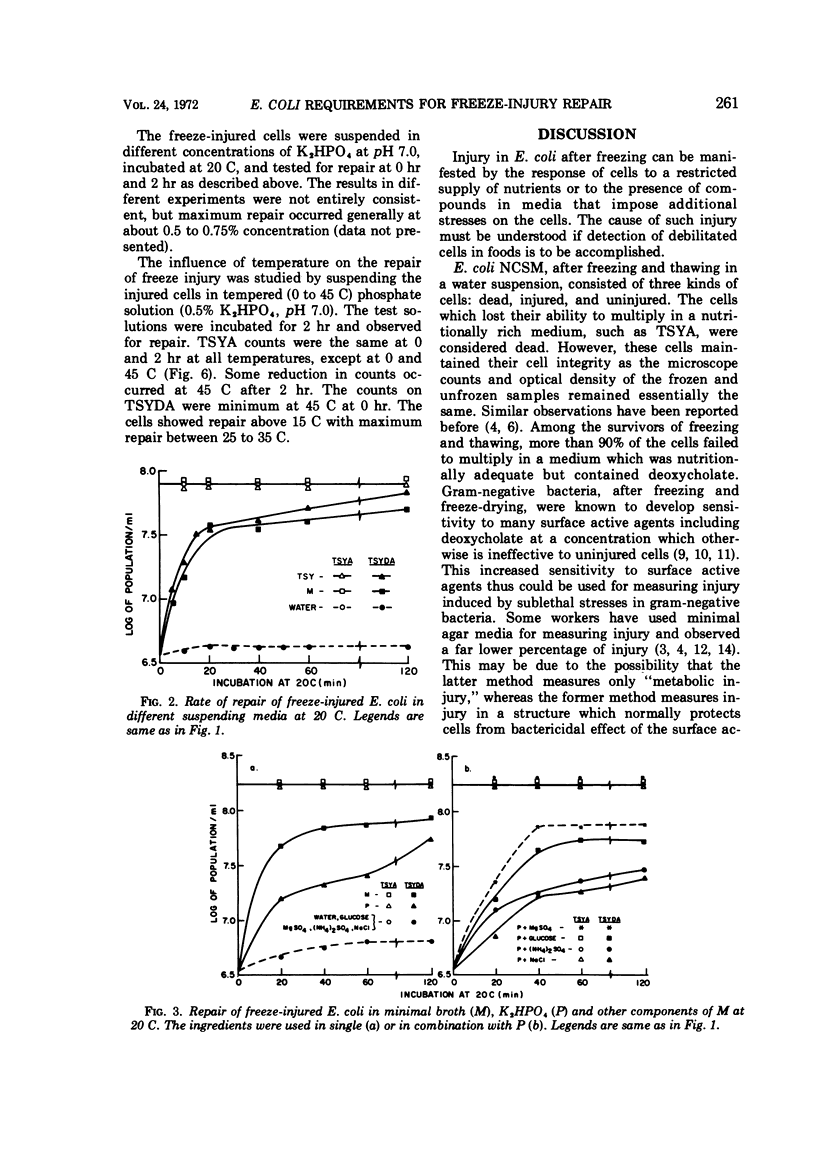
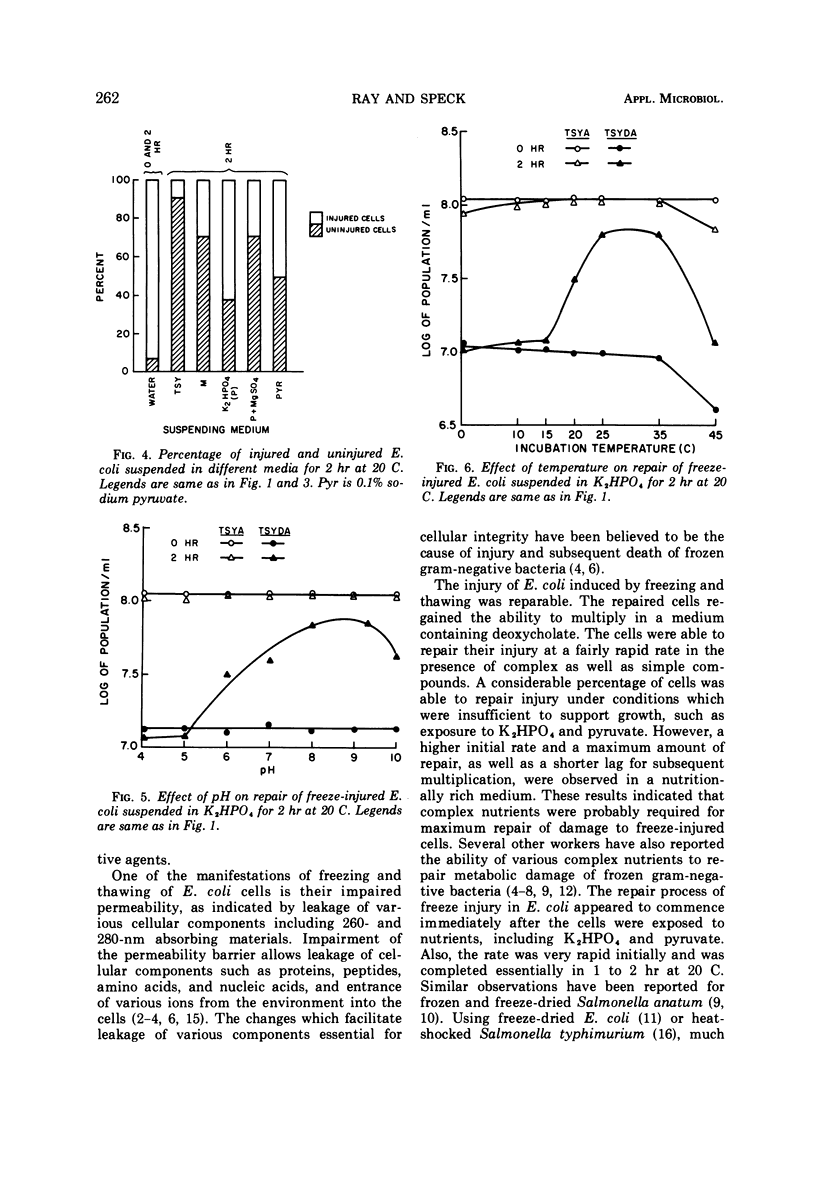
Freezing an aqueous suspension of Escherichia coli NCSM at -78 C for 10 min, followed by thawing in water at 8 C for 30 min, resulted in the death of approximately 50% of the cells, as determined by their inability to form colonies on Trypticase soy agar containing 0.3% yeast extract (TSYA). Among the survivors, more than 90% of the cells were injured, as they failed to form colonies on TSYA containing 0.1% deoxycholate. Microscope counts and optical density determinations at 600 nm suggested that death from freezing was not due to lysis of the cells. Death and the injury were accompanied by the loss of 260- and 280-nm absorbing materials from the intracellular pool. Injury was reversible as the injured cells repaired in many suitable media. The rate of repair was rapid and maximum in a complex nutrient medium such as Trypticase soy broth supplemented with yeast extract. However, inorganic phosphate, with or without MgSO4, was able to facilitate repair. Repair in phosphate was dependent on the pH, the temperature, and the concentration of phosphate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. The role of multivalent cations in the organization and structure of bacterial cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):664–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretz H. W., Kocka F. E. Resistance to actinomycin D of Escherichia coli after frozen storage. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Jul;13(7):914–917. doi: 10.1139/m67-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. A., Smith L. D., Gelinas R. Metabolic injury to bacteria. I. Effect of freezing and storage on the requirements of Aerobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli for growth. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):61–72. doi: 10.1139/m66-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Speck M. L. Identification of nutritional components in trypticase responsible for recovery of Escherichia coli injured by freezing. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1098–1104. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1098-1104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Speck M. L. Release of biologically active peptides from Escherichia coli at subzero temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1105-1111.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA M., DAWSON D. A. Role of suspending and recovery media in the survival of frozen Shigella sonnei. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jan;10:40–43. doi: 10.1128/am.10.1.40-43.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B., Janssen D. W., Busta F. F. Characterization of the repair of injury induced by freezing Salmonella anatum. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):803–809. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.803-809.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B., Jezeski J. J., Busta F. F. Repair of injury in freeze-dried Salmonella anatum. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):401–407. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.401-407.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAKA R. P., STOKES J. L. Metabolic injury to bacteria at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:181–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.181-185.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., DARK F. A. Effect of chilling on Aerobacter aerogenes in aqueous suspension. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Dec;29:719–730. doi: 10.1099/00221287-29-4-719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E. EFFECT OF MAGNESIUM ON PERMEABILITY CONTROL IN CHILLED BACTERIA. Nature. 1964 Sep 19;203:1304–1305. doi: 10.1038/2031304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., POSTGATE J. R. PENETRATION OF SUBSTANCES INTO COLD-SHOCKED BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Sep;36:393–403. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-3-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinskey T. J., Silverman G. J. Characterization of injury incurred by Escherichia coli upon freeze-drying. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):429–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.429-437.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins R. I., Ordal Z. J. Requirements of Salmonella typhimurium for recovery from thermal injury. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):512–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.512-518.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



