Abstract
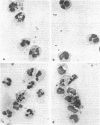
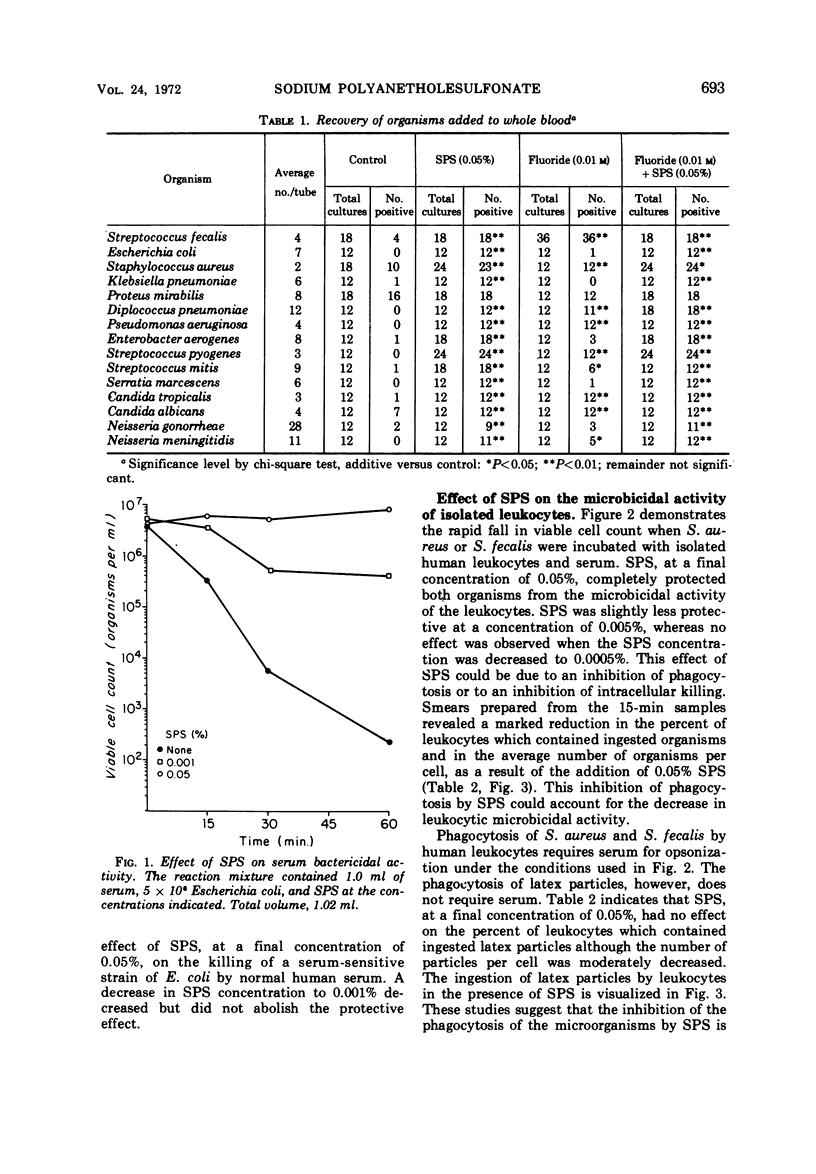
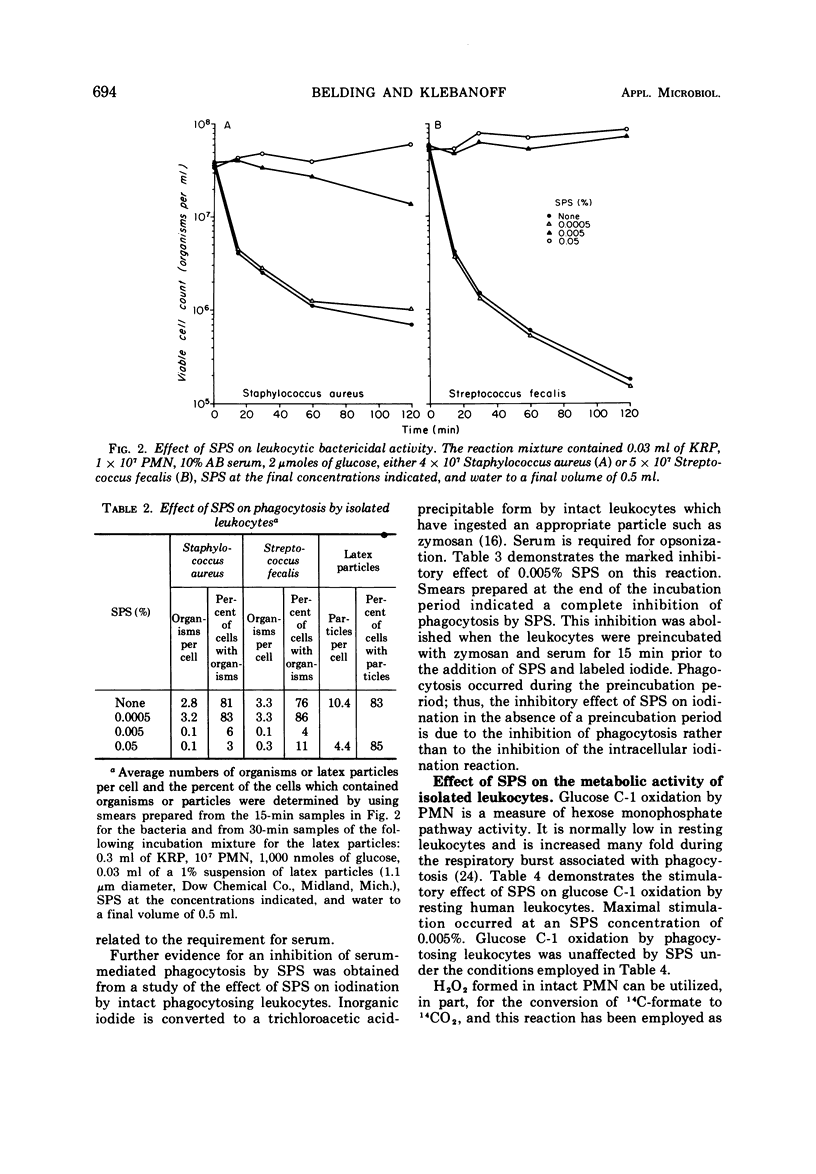
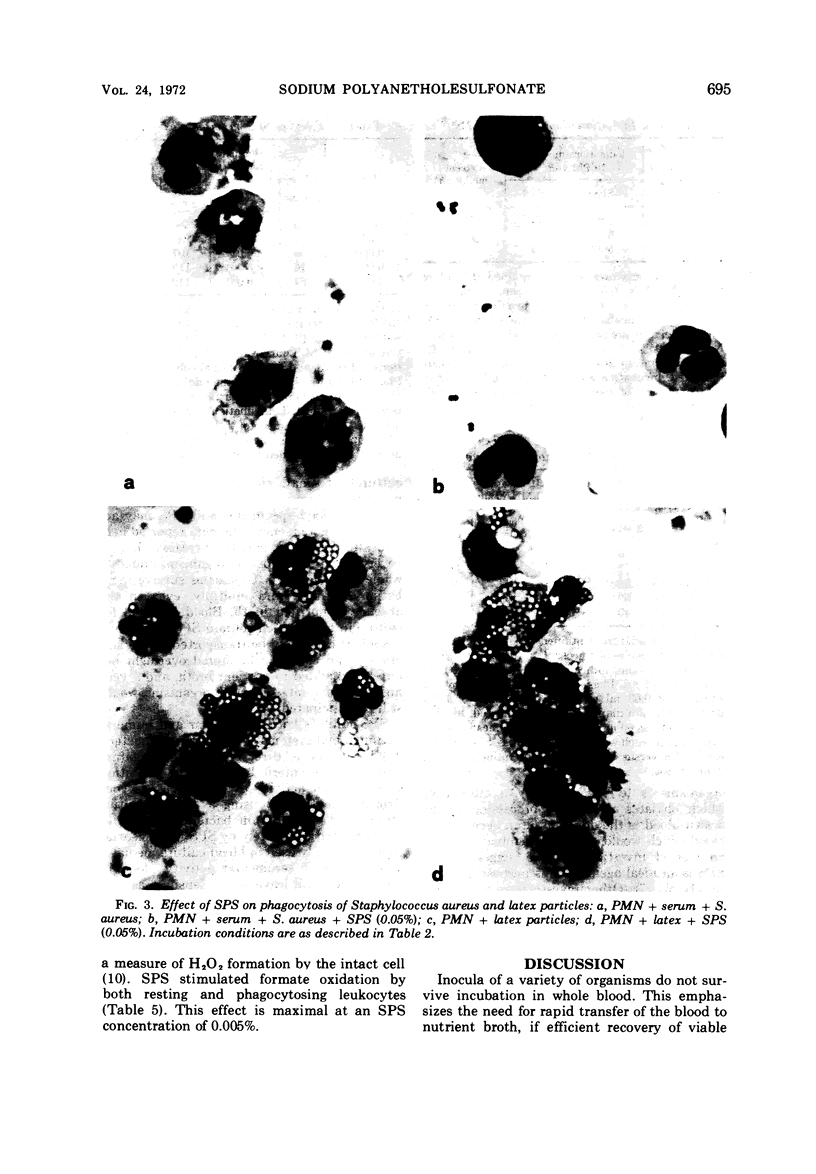
Sodium polyanetholesulfonate (SPS), an anticoagulant which inhibits the antimicrobial systems of blood, is used widely in blood culture media. The addition of SPS to experimental blood cultures inoculated with small numbers of a variety of organisms caused a striking increase in recovery of these organisms. Sodium fluoride also increased the incidence of positive blood cultures with some organisms. SPS completely inhibited serum antibacterial activity and serum-dependent phagocytosis (and killing) by isolated leukocytes at a concentration usually employed in blood culture media. SPS also stimulated both glucose C-1 oxidation in resting leukocytes and formate oxidation in both resting and phagocytosing leukocytes in serum-free systems. These in vitro studies support the concept that SPS is a useful additive to blood culture media and further elaborate on the mechanism of its inhibition of the microbicidal activity of blood.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A., MORSE S. I. Functional and metabolic properties of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. I. Observations on the requirements and consequences of particle ingestion. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:667–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Stoessel C. J. The role of temperature and anticoagulant on the in vitro survival of bacterial in blood. J Infect Dis. 1966 Apr;116(2):238–242. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D. System for inoculation of blood in the laboratory. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1892–1894. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1892-1894.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. L., Cekoric T., Jr, Searcy R. L. Comparative effects of anticoagulants on bacterial growth in experimental blood cultures. Am J Med Technol. 1968 Feb;34(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Ziment I., White M. L., Winn W. R., Carter W. T. Evaluation of polyanethol sulfonate (liquoid) in blood cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:692–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrod P. R. The growth of Streptococcus viridans in sodium polyanethyl sulphonate ("Liquoid"). J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):621–623. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Shafer A. W., Glass E. A., Karnovsky M. L. Metabolic and morphological observations on the effect of surface-active agents of leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):629–647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Pincus S. H. Hydrogen peroxide utilization in myeloperoxidase-deficient leukocytes: a possible microbicidal control mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2226–2229. doi: 10.1172/JCI106718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance B. L., Traub W. H. Inactivation of the bactericidal activity of human serum by liquoid (sodium polyanetholsulfonate). Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jun;17(6):839–842. doi: 10.1128/am.17.6.839-842.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkus R., Moffet H. L. Detection of bacteremia in children with sodium polyanethol sulfonate: a prospective clinical study. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):805–808. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.805-808.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello J. A., Ellner P. D. New medium for blood cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jan;17(1):68–70. doi: 10.1128/am.17.1.68-70.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTIERI G. M., PLESCIA O. J. A COMPARISON OF METHODS FOR THE INACTIVATION OF THIRD COMPONENT OF GUINEA-PIG COMPLEMENT. Experientia. 1965 Feb 15;21:81–82. doi: 10.1007/BF02144753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Zatti M., Cramer R., Rossi F. Stimulation of the respiration of polymorphonuclear leucocytes by phospholipase C. Life Sci I. 1970 Aug 1;9(15):841–849. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Klebanoff S. J. Quantitative leukocyte iodination. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 8;284(14):744–750. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104082841402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roome A. P., Tozer R. A. Effect of dilution on the growth of bacteria from blood cultures. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Nov;21(6):719–721. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.6.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner R. Comparison of a blood culture system containing liquoid and sucrose with systems containing either reagent alone. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Feb;19(2):281–282. doi: 10.1128/am.19.2.281-282.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner R. Effect of various anticoagulants and no anticoagulant on ability to isolate bacteria directly from parallel clinical blood specimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Feb;49(2):216–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Zatti M. Mechanism of the respiratory stimulation in saponine-treated leucocytes. The KCN-insensitive oxidation of NADPH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 15;153(1):296–299. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Zatti M., Patriarca P., Cramer R. Effect of specific antibodies on the metabolism of guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jan;9(1):67–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R. D. The Value of Liquoid for Blood Culture. J Clin Pathol. 1948 Nov;1(5):311–314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Lowrance B. L. Anticomplementary, anticoagulatory, and serum-protein precipitating activity of sodium polyanetholsulfonate. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):465–468. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.465-468.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. S., STUART R. D. STAPHYLOCOCCUS ALBUS IN WOUND INFECTION AND IN SEPTICEMIA. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Jul 3;93:8–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatti M., Rossi F. Relationship between glycolysis and respiration in surfactant-treated leucocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]