Abstract
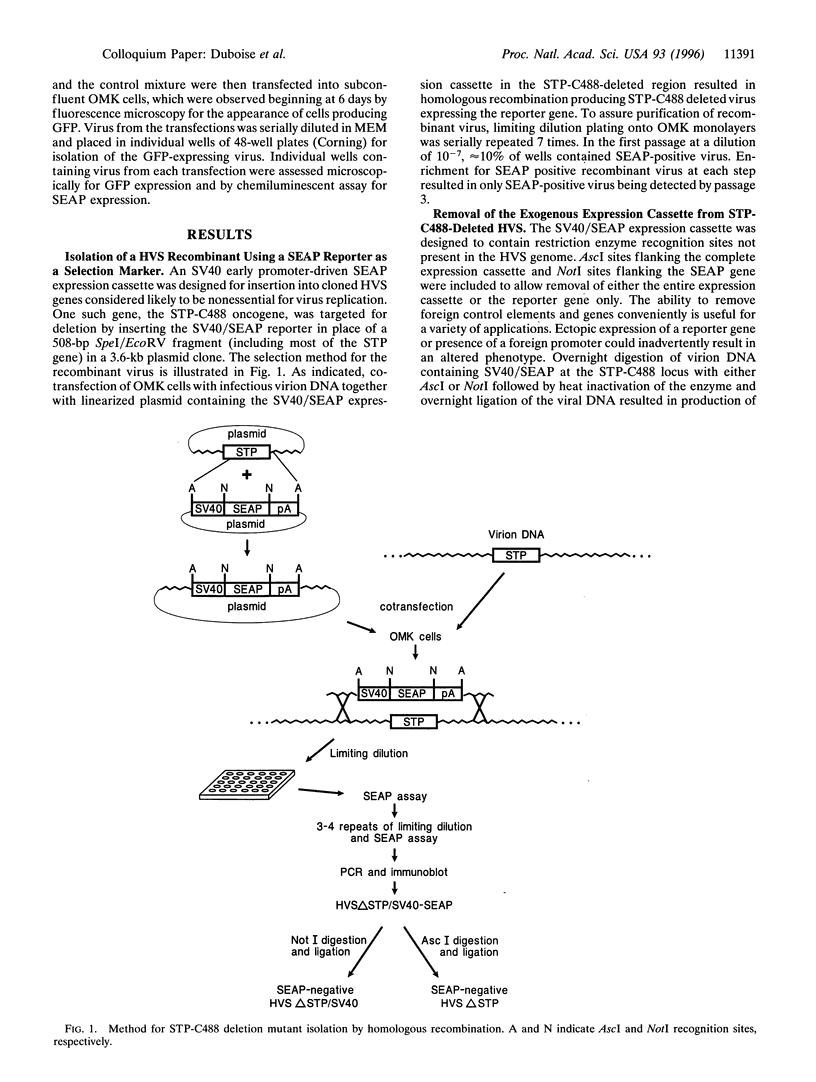
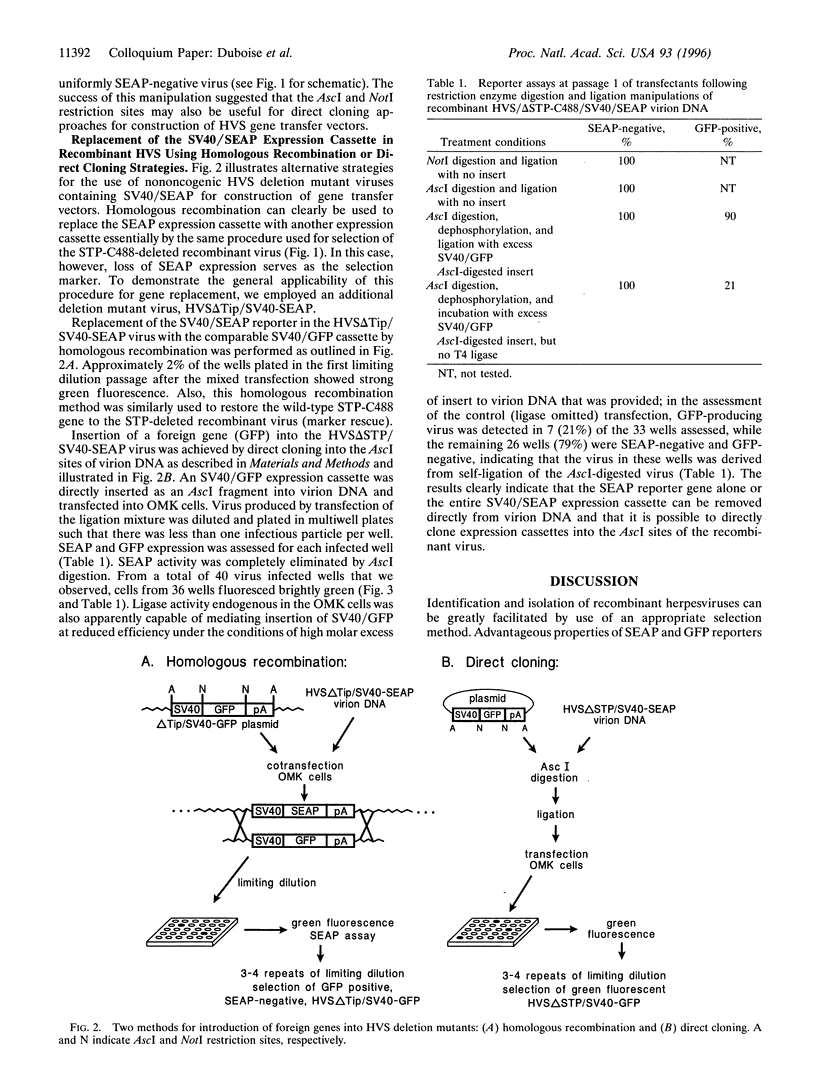
We have developed improved procedures for the isolation of deletion mutant, point mutant, and recombinant herpesvirus saimiri. These procedures take advantage of the absence of NotI and AscI restriction enzyme sites within the viral genome and use reporter genes for the identification of recombinant viruses. Genes for secreted engineered alkaline phosphatase and green fluorescent protein were placed under simian virus 40 early promoter control and flanked by NotI and AscI restriction sites. When permissive cells were cotransfected with herpesvirus saimiri virion DNA and one of the engineered reporter genes cloned within herpesvirus saimiri sequences, recombinant viruses were readily identified and purified on the basis of expression of the reporter gene. Digestion of recombinant virion DNA with NotI or AscI was used to delete the reporter gene from the recombinant herpesvirus saimiri. Replacement of the reporter gene can be achieved by NotI or AscI digestion of virion DNA and ligation with a terminally matched fragment or, alternatively, by homologous recombination in cotransfected cells. Any gene can, in theory, be cloned directly into the virion DNA when flanked by the appropriate NotI or AscI sites. These procedures should be widely applicable in their general form to most or all herpesviruses that replicate permissively in cultured cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja S. K., Murphy P. M. Molecular piracy of mammalian interleukin-8 receptor type B by herpesvirus saimiri. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20691–20694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht J. C., Nicholas J., Biller D., Cameron K. R., Biesinger B., Newman C., Wittmann S., Craxton M. A., Coleman H., Fleckenstein B. Primary structure of the herpesvirus saimiri genome. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5047–5058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5047-5058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesinger B., Müller-Fleckenstein I., Simmer B., Lang G., Wittmann S., Platzer E., Desrosiers R. C., Fleckenstein B. Stable growth transformation of human T lymphocytes by herpesvirus saimiri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3116–3119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesinger B., Trimble J. J., Desrosiers R. C., Fleckenstein B. The divergence between two oncogenic Herpesvirus saimiri strains in a genomic region related to the transforming phenotype. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90020-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesinger B., Tsygankov A. Y., Fickenscher H., Emmrich F., Fleckenstein B., Bolen J. B., Bröker B. M. The product of the Herpesvirus saimiri open reading frame 1 (tip) interacts with T cell-specific kinase p56lck in transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4729–4734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman E., Chang Y., Moore P. S., Said J. W., Knowles D. M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995 May 4;332(18):1186–1191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199505043321802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalfie M., Tu Y., Euskirchen G., Ward W. W., Prasher D. C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):802–805. doi: 10.1126/science.8303295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Cesarman E., Pessin M. S., Lee F., Culpepper J., Knowles D. M., Moore P. S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1865–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7997879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crameri A., Whitehorn E. A., Tate E., Stemmer W. P. Improved green fluorescent protein by molecular evolution using DNA shuffling. Nat Biotechnol. 1996 Mar;14(3):315–319. doi: 10.1038/nbt0396-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubitt A. B., Heim R., Adams S. R., Boyd A. E., Gross L. A., Tsien R. Y. Understanding, improving and using green fluorescent proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Nov;20(11):448–455. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Malim M. H. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase as a eukaryotic reporter gene. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:362–368. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16033-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva M. P. Cuidados de enfermagem nos pacientes com "shunt" e fistula artério-venosa. Rev Enferm Nov Dimens. 1976 Nov;2(5):290–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Bakker A., Kamine J., Falk L. A., Hunt R. D., King N. W. A region of the Herpesvirus saimiri genome required for oncogenicity. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):184–187. doi: 10.1126/science.2983431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Burghoff R. L., Bakker A., Kamine J. Construction of replication-competent Herpesvirus saimiri deletion mutants. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):343–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.343-348.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Falk L. A. Herpesvirus saimiri strain variability. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):352–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.352-356.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Silva D. P., Waldron L. M., Letvin N. L. Nononcogenic deletion mutants of herpesvirus saimiri are defective for in vitro immortalization. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):701–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.701-705.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst W. J., Grabherr R. M., Katinger H. W. Direct cloning into the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus for generation of recombinant baculoviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 25;22(14):2855–2856. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.14.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L. A., Wolfe L. G., Deinhardt F. Isolation of Herpesvirus saimiri from blood of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 May;48(5):1499–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein B. Oncogenic herpesviruses of non-human primates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 30;560(3):301–342. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., DeLuca N. A., Fink D. J. Development and application of herpes simplex virus vectors for human gene therapy. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:675–710. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.49.100195.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim R., Tsien R. Y. Engineering green fluorescent protein for improved brightness, longer wavelengths and fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Curr Biol. 1996 Feb 1;6(2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00450-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Lang S. M., Friedrich U., Jun T., Roberts T. M., Desrosiers R. C., Biesinger B. Identification of Lck-binding elements in tip of herpesvirus saimiri. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20660–20667. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Lang S. M., Jun T., Roberts T. M., Veillette A., Desrosiers R. C. Downregulation of Lck-mediated signal transduction by tip of herpesvirus saimiri. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7814–7822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.7814-7822.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Stäger M., Desrosiers R. C. Virus-encoded cyclin. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7235–7244. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Trimble J. J., King N. W., Biesinger B., Fleckenstein B. W., Desrosiers R. C. Identification of transforming genes of subgroup A and C strains of Herpesvirus saimiri. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7051–7055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melendez L. V., Daniel M. D., Hunt R. D., Garcia F. G. An apparently new herpesvirus from primary kidney cultures of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). Lab Anim Care. 1968 Jun;18(3):374–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittrücker H. W., Müller-Fleckenstein I., Fleckenstein B., Fleischer B. CD2-mediated autocrine growth of herpes virus saimiri-transformed human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):909–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. S., Gao S. J., Dominguez G., Cesarman E., Lungu O., Knowles D. M., Garber R., Pellett P. E., McGeoch D. J., Chang Y. Primary characterization of a herpesvirus agent associated with Kaposi's sarcomae. J Virol. 1996 Jan;70(1):549–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.1.549-558.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. C., Trimble J. J., Desrosiers R. C. Deletion mutants of herpesvirus saimiri define an open reading frame necessary for transformation. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3307–3314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3307-3314.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J., Cameron K. R., Honess R. W. Herpesvirus saimiri encodes homologues of G protein-coupled receptors and cyclins. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):362–365. doi: 10.1038/355362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renne R., Zhong W., Herndier B., McGrath M., Abbey N., Kedes D., Ganem D. Lytic growth of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in culture. Nat Med. 1996 Mar;2(3):342–346. doi: 10.1038/nm0396-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto R., Brini M., De Giorgi F., Rossi R., Heim R., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Double labelling of subcellular structures with organelle-targeted GFP mutants in vivo. Curr Biol. 1996 Feb 1;6(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother R. P., Rollins S. A., Fodor W. L., Albrecht J. C., Setter E., Fleckenstein B., Squinto S. P. Inhibition of complement-mediated cytolysis by the terminal complement inhibitor of herpesvirus saimiri. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):730–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.730-737.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said W., Chien K., Takeuchi S., Tasaka T., Asou H., Cho S. K., de Vos S., Cesarman E., Knowles D. M., Koeffler H. P. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV or HHV8) in primary effusion lymphoma: ultrastructural demonstration of herpesvirus in lymphoma cells. Blood. 1996 Jun 15;87(12):4937–4943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A. A novel viral homologue of Bcl-2 and Ced-9. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;5(9):344–344. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Moss B. Infectious poxvirus vectors have capacity for at least 25 000 base pairs of foreign DNA. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulier J., Grollet L., Oksenhendler E., Cacoub P., Cazals-Hatem D., Babinet P., d'Agay M. F., Clauvel J. P., Raphael M., Degos L. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1276–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. L., Roizman B. Herpes simplex genes: the blueprint of a successful human pathogen. Trends Genet. 1994 Aug;10(8):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90009-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z., Fanslow W. C., Seldin M. F., Rousseau A. M., Painter S. L., Comeau M. R., Cohen J. I., Spriggs M. K. Herpesvirus Saimiri encodes a new cytokine, IL-17, which binds to a novel cytokine receptor. Immunity. 1995 Dec;3(6):811–821. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z., Maraskovsky E., Spriggs M. K., Cohen J. I., Armitage R. J., Alderson M. R. Herpesvirus saimiri open reading frame 14, a protein encoded by T lymphotropic herpesvirus, binds to MHC class II molecules and stimulates T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1996 May 1;156(9):3260–3266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z., Painter S. L., Fanslow W. C., Ulrich D., Macduff B. M., Spriggs M. K., Armitage R. J. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 15;155(12):5483–5486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




