Abstract
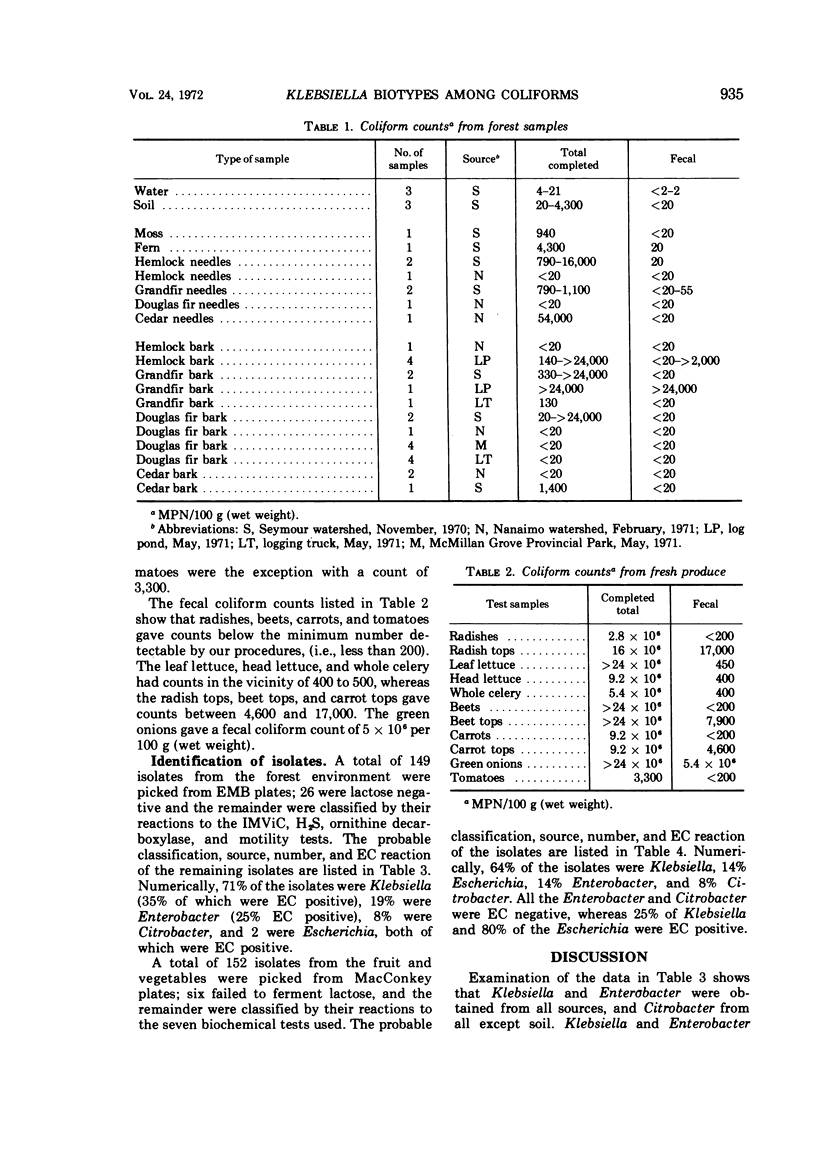
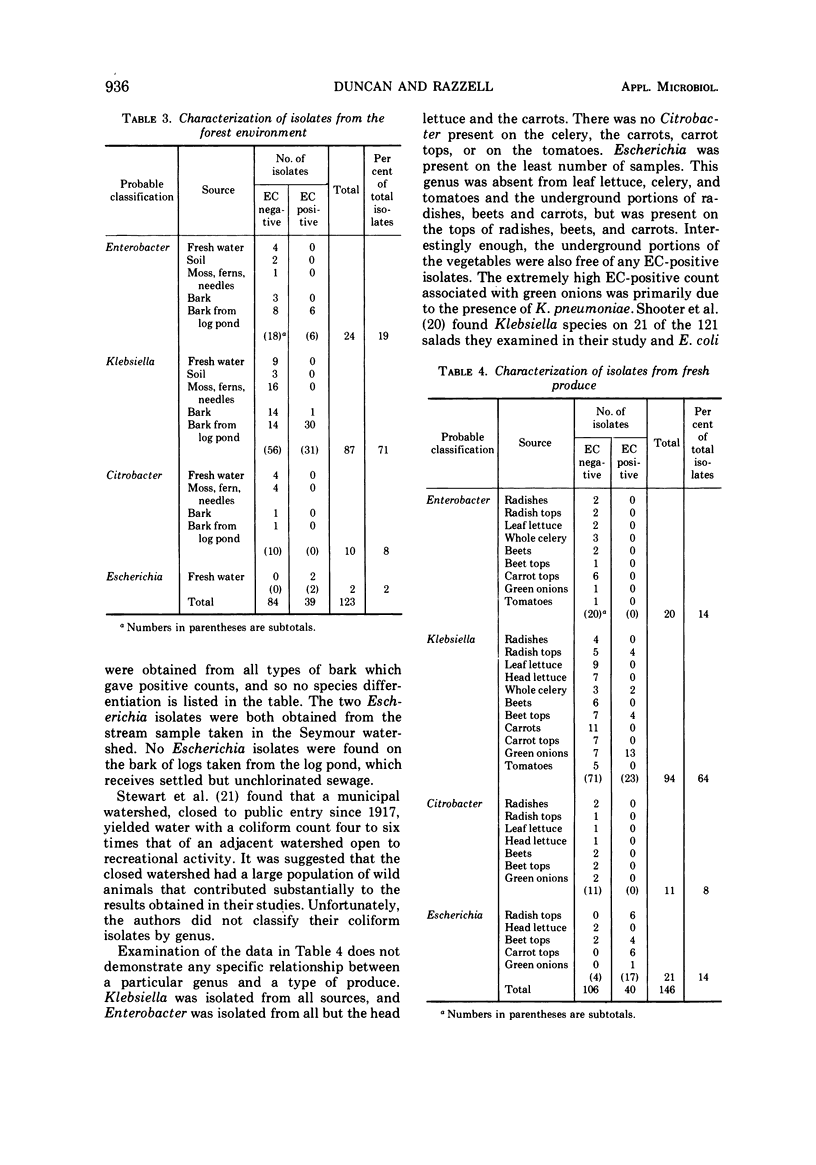
Samples of water, soil, needles, and bark were collected from three different forest environments and from a pulp and paper mill. In addition, samples of fresh produce were obtained from a local supermarket. All samples were examined for total and fecal coliforms. The counts obtained from the forestrelated samples did not correlate with sample type or location. When 123 isolates were identified biochemically, 71% were Klebsiella, 19% Enterobacter, 8% Citrobacter, and 2% Escherichia. All the Citrobacter, 75% of the Enterobacter, and 65% of the Klebsiella were negative for growth in elevated coliform (EC) broth. All the Escherichia were EC positive. The counts obtained from the fresh produce were generally higher than the forest counts, but the distribution of biotypes was similar. Of the 146 isolates examined 64% were Klebsiella, 14% were Escherichia, 14% were Enterobacter, and 8% were Citrobacter. All the Enterobacter and Citrobacter were EC negative, whereas 25% of the Klebesiella and 80% of the Escherichia were EC positive.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bascomb S., Lapage S. P., Willcox W. R., Curtis M. A. Numerical classification of the tribe Klebsielleae. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jun;66(3):279–295. doi: 10.1099/00221287-66-3-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN S. T., STEEL K. J., SHAW C., DUGUID J. P. A classification of the Klebsiella group. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:601–612. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Digranes A. Rapid identification of prompt lactose-fermenting genera within the familyh Enterobacteriaceae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. R. RELATIONSHIPS OF THE ENCAPSULATED BACILLI WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO BACT. AEROGENES. J Bacteriol. 1929 May;17(5):339–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.17.5.339-353.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELDREICH E. E., KENNER B. A., KABLER P. W. OCCURRENCE OF COLIFORMS, FECAL COLIFORMS, AND STREPTOCOCCI ON VEGETATION AND INSECTS. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jan;12:63–69. doi: 10.1128/am.12.1.63-69.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Yu P. K., Washington J. A., 2nd Epidemiologic significance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. A 3-month study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Dec;46(12):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez W. J., Colmer A. R. Differentiation of Aerobacter-Klebsiella isolated from sugarcane. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1875–1878. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1875-1878.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavassiliou J., Tzannetis S., Leka H., Michopoulos G. Coli-aerogenes bacteria on plants. J Appl Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;30(1):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1967.tb00291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shooter R. A., Cooke E. M., Faiers M. C., Breaden A. L., O'Farrell S. M. Isolation of Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella from food in hospitals, canteens, and schools. Lancet. 1971 Aug 21;2(7721):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., Bissonnette G. K., Goodrich T. D., Walter W. G. Effects of multiple use on water quality of high-mountain watersheds: bacteriological investigations of mountain streams. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Dec;22(6):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/am.22.6.1048-1054.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


