Abstract
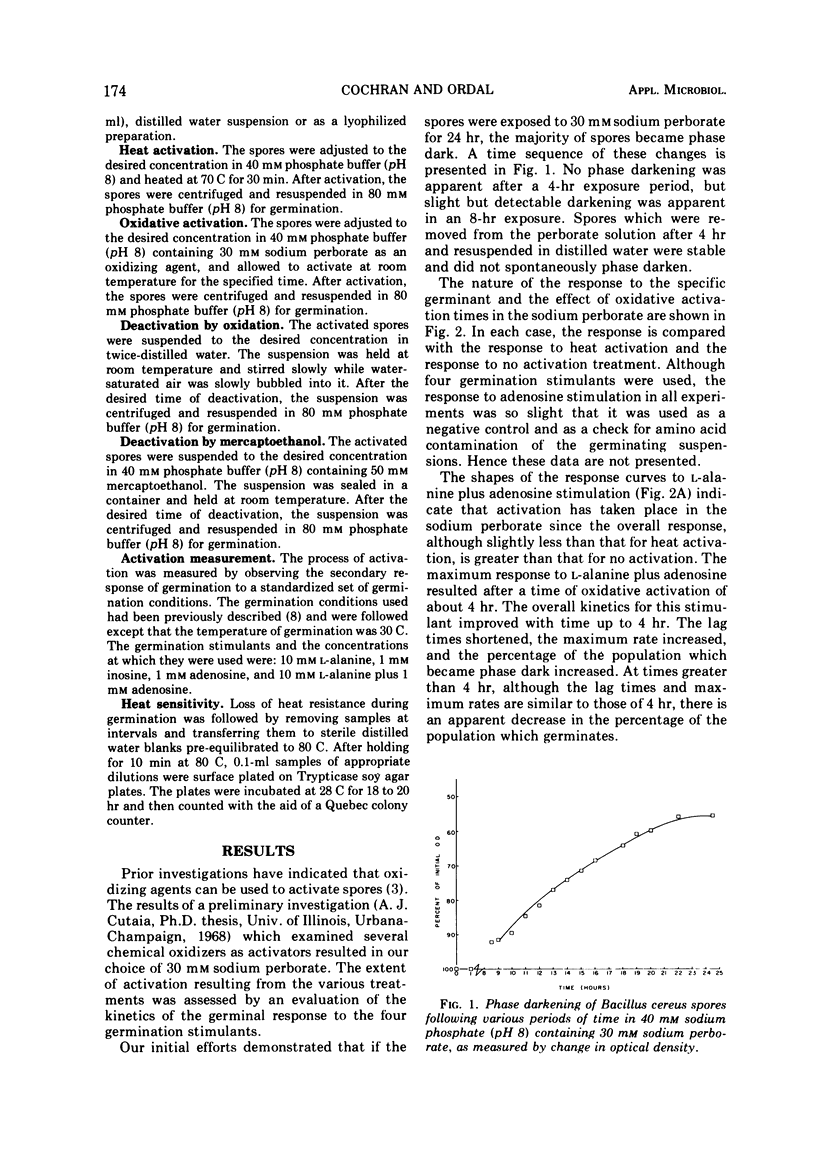
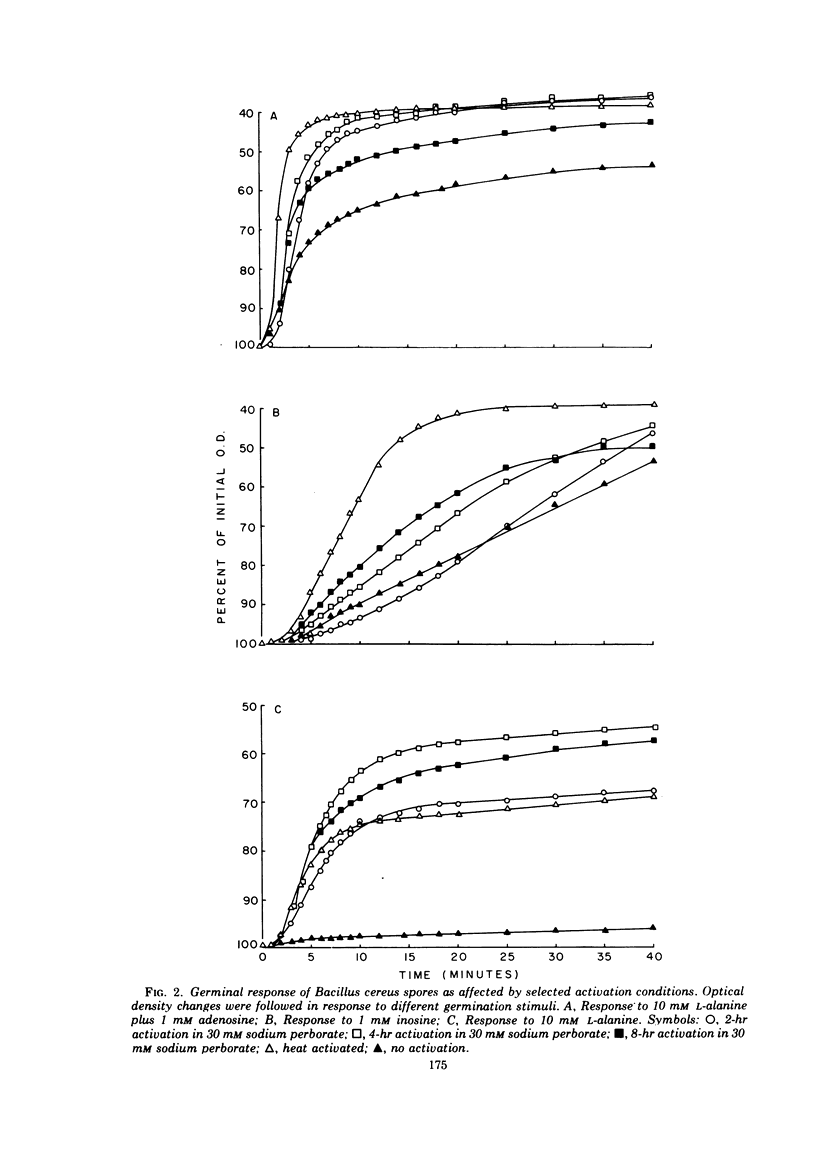
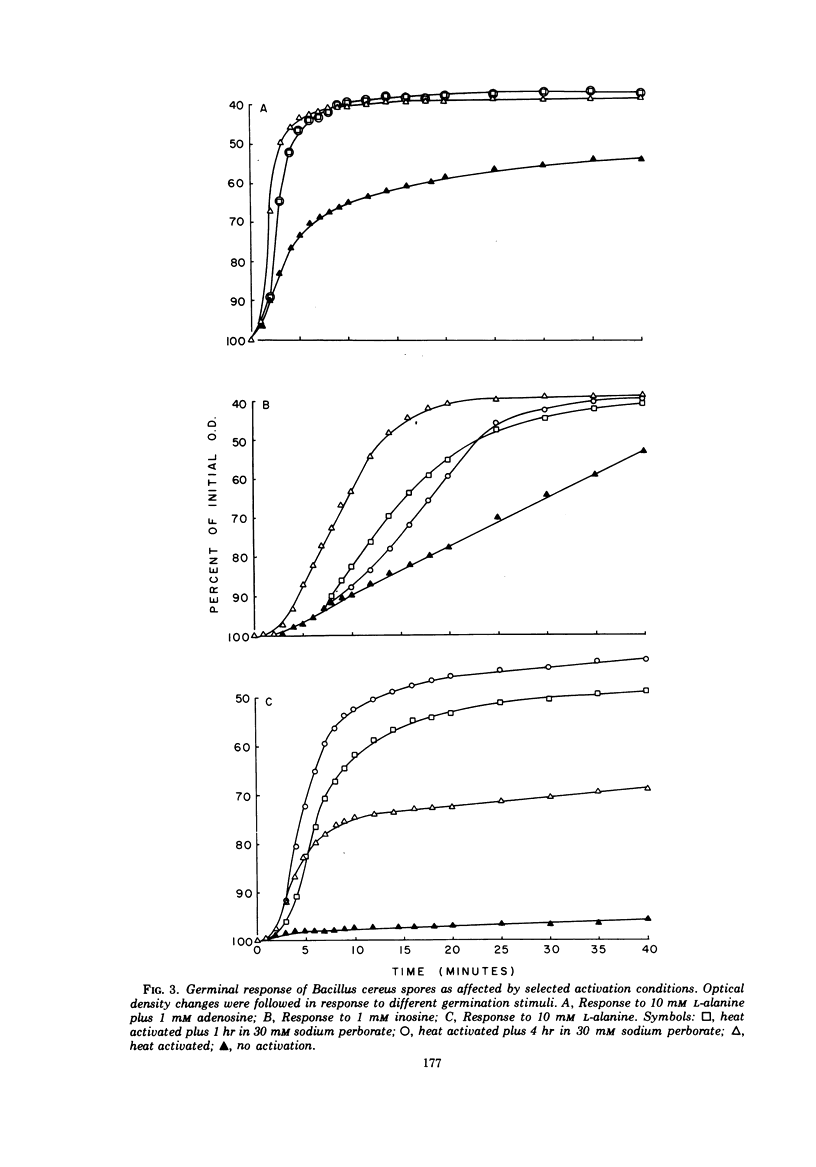
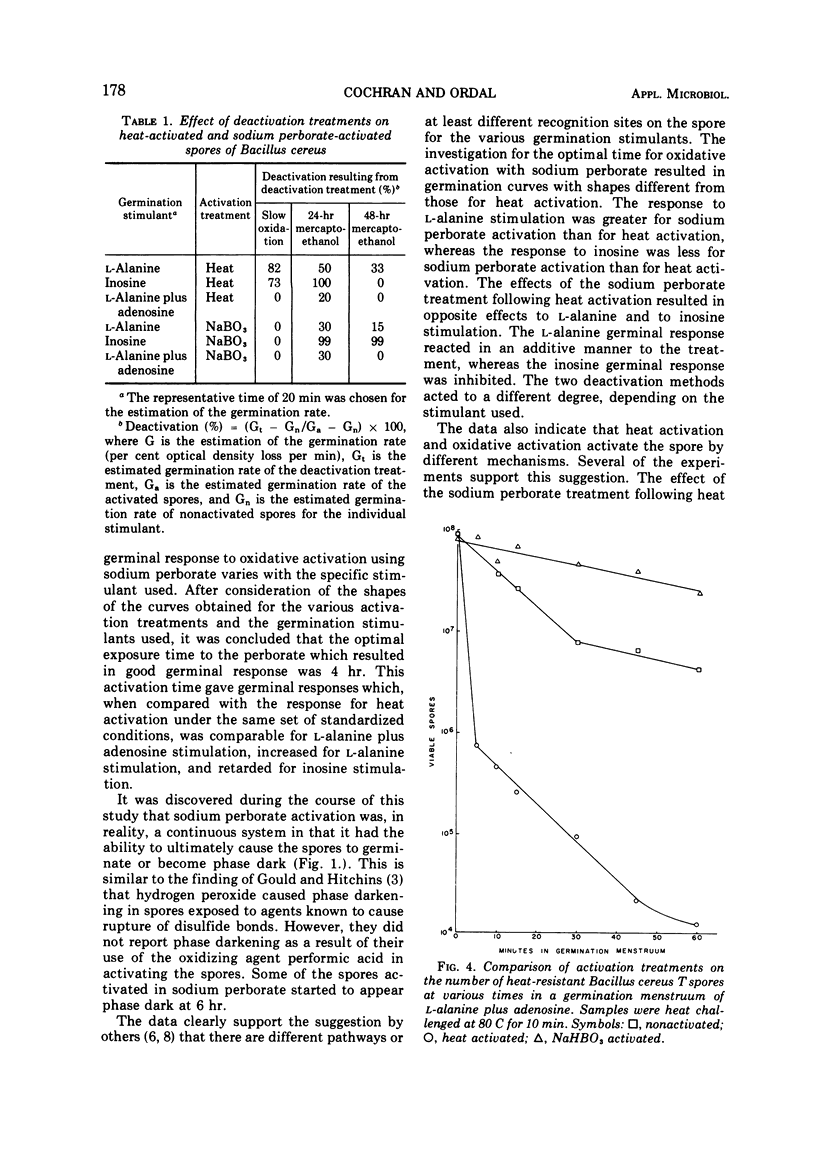
A study was made of the activation of Bacillus cereus strain T spores by using the oxidizing agent sodium perborate. The degree of activation was measured with constant germination conditions by using L-alanine, inosine, adenosine, and L-alanine plus adenosine as germination stimulants. The germinal response following the various treatments was compared with the responses obtained with heat activation. It was concluded that the optimal time for activation with 30 mM sodium perborate at room temperature was about 4 hr. If the exposure time was greatly extended, the spores would germinate spontaneously. When the perborate treatment followed heat activation, the germinal response to L-alanine was stimulated, to inosine retarded and without apparent effect for adenosine or L-alanine plus adenosine. Results of experiments designed to demonstrate deactivation by slow oxidation showed that spores activated with sodium perborate were not deactivated by slow oxidation, whereas those activated by heat were. A deactivation study using mercaptoethanol as the deactivation agent showed that both methods of activation could be deactivated after a 24-hr exposure, but this deactivation was reversible by extending the exposure to mercaptoethanol. The results of heat-sensitivity studies revealed that about 70% of the sodium perborate-activated spores were heat sensitive after 60 min in a germination menstruum of L-alanine plus adenosine, whereas similarly treated heat-activated and nonactivated spores were about 99.99% heat sensitive, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curran H. R., Evans F. R. Heat Activation Inducing Germination in the Spores of Thermotolerant and Thermophilic Aerobic Bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1945 Apr;49(4):335–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.49.4.335-346.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD G. W., HITCHINS A. D. SENSITIZATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES TO LYSOZYME AND TO HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WITH AGENTS WHICH RUPTURE DISULPHIDE BONDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:413–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Jones A., Wrighton C. Limitations of the initiation of germination of bacterial spores as a spore control procedure. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;31(3):357–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNAN A., EVANCHIK Z., HALVORSON H. O., HASTINGS J. W. ACTIVATION OF BACTERIAL ENDOSPORES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.313-318.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


