Abstract
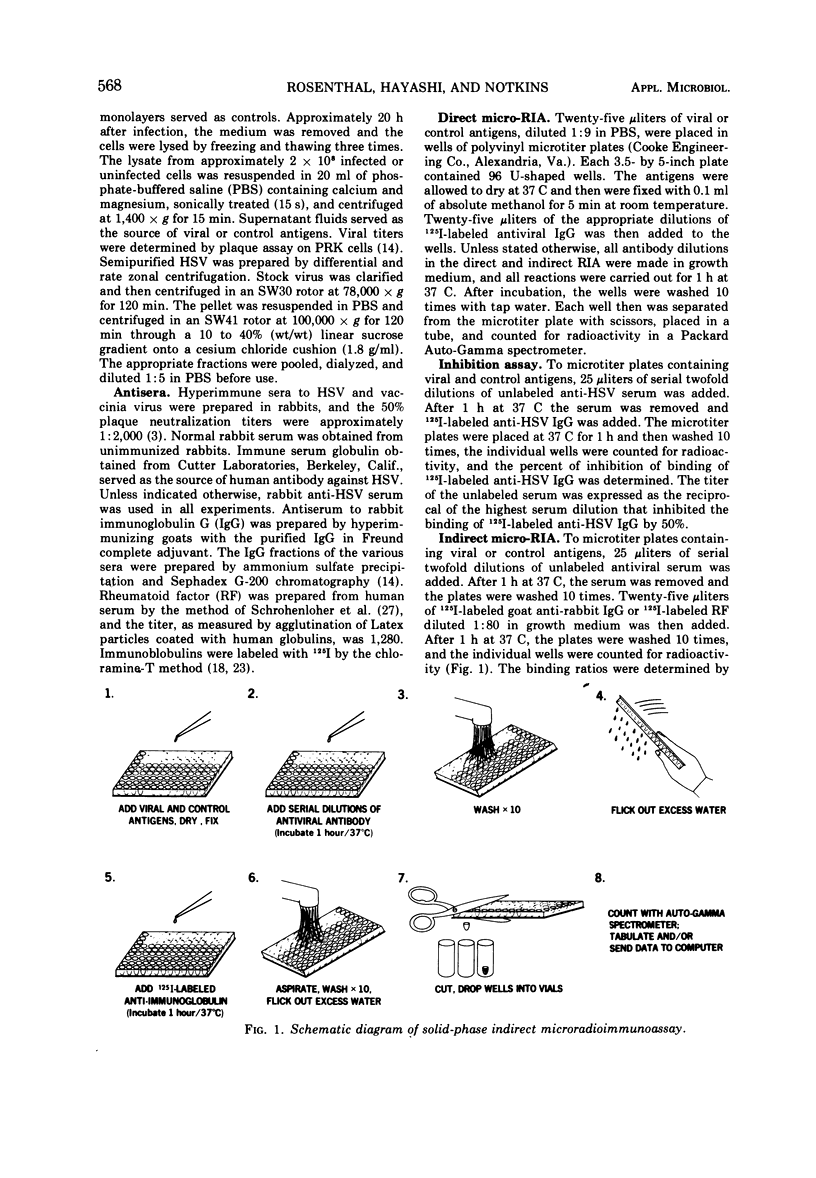
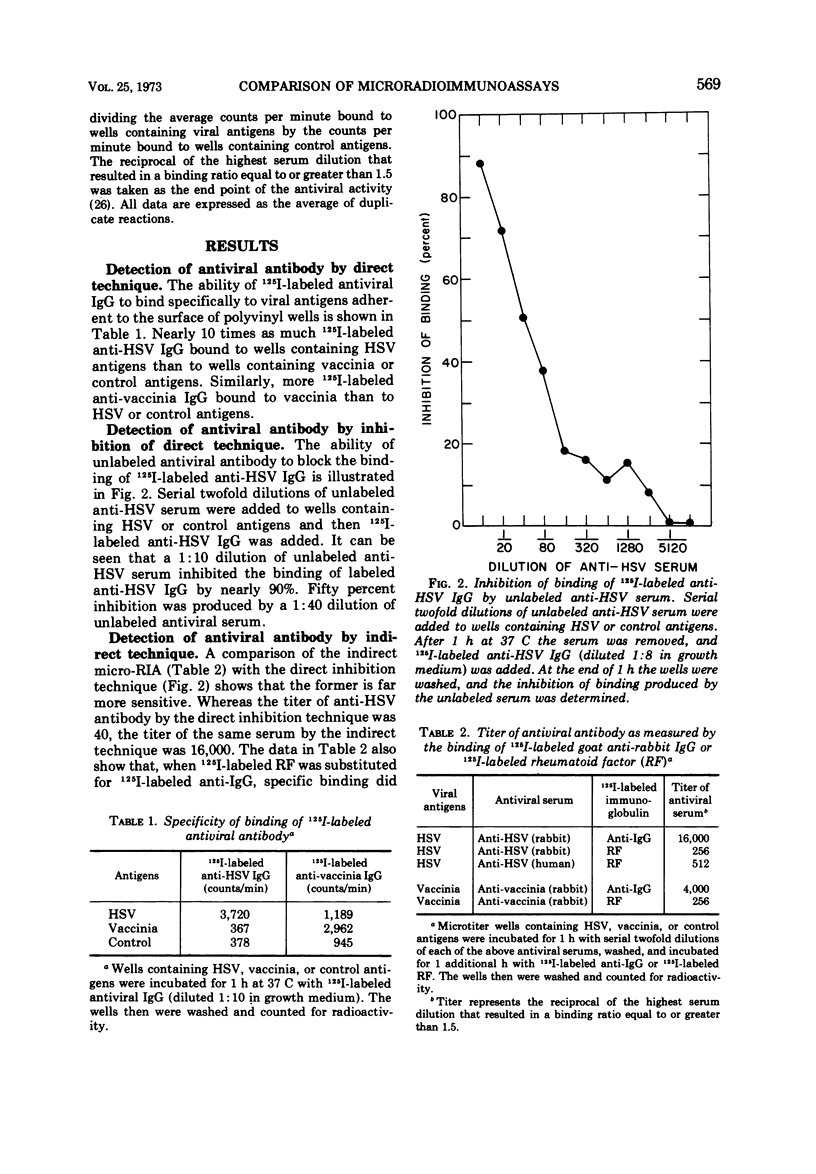
Viral antigens were fixed to the surface of microtiter wells, and serial dilutions of antiviral antibody were added. The amount of antiviral antibody bound to viral antigens was determined by measuring the extent to which the antiviral antibody either inhibited the specific binding of 125I-labeled antiviral immunoglobulin G (IgG) (direct technique) or enhanced the specific binding of 125I-labeled anti-IgG (indirect technique). Immune complexes composed of viral antigens and antiviral antibody (human) could be detected by the binding of 125I-labeled rheumatoid factor. Specific binding was influenced by the concentration of protein in the diluents used during the different steps of the procedure. A high concentration of protein in the diluent used with the viral antigens decreased specific binding, whereas a high concentration of protein in the diluent used with 125I-labeled anti-IgG increased specific binding by decreasing nonspecific attachment of the labeled anti-IgG. Under the conditions employed, the titer of a given antiviral serum was several hundredfold greater by the indirect than by the direct technique.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aach R. D., Grisham J. W., Parker C. W. Detection of Australia antigen by radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1056–1060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashe W. K., Daniels C. A., Scott G. S., Notkins A. L. Interaction of rheumatoid factor with infectious herpes simplex virus-antibody complexes. Science. 1971 Apr 9;172(3979):176–177. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3979.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brier A. M., Wohlenberg C., Rosenthal J., Mage M., Notkins A. L. Inhibition or enhancement of immunological injury of virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardiff R. D., Blair P. B., Nakayama P. In vitro cultivation of mouse mammary tumor virus: detection of MTV production by radioisotope labeling and identification by immune precipitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):895–902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K., Tregear G. W. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay in antibody-coated tubes. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller J. A., Millman I., Halbherr T. C., Blumberg B. S. Radioimmunoprecipitation assay for Australia antigen, antibody, and antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):249–257. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple J. M., Teramoto A. Y., Cardiff R. D., Russell P. K. Radioimmune precipitation of group A arboviruses. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):426–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. A., Mergenhagen S. E., Notkins A. L. Measurement of antibody against human IgG by the neutralization of IgG-sensitized herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):470–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Davis M. L., Kaye H. S. Immunoglobulin class of influenza antibodies investigated by radioimmunoassay (RIA). J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):849–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H. Immunoprecipitin reaction of influenza virus-antibody complex with anti-IgG. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):802–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Warfield D. T., Davis M. L. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of total and influenza-specific immunoglobulin G. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):360–367. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.360-367.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld O., Dutta N. K., Felsenfeld A. D., Brannon R. B. Radioisotope precipitation tests with 14 C and 51 Cr labeled vaccinia antigens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERLOFF R. K., HOYER B. H., McLAREN L. C. Precipitation of radiolabeled poliovirus with specific antibody and antiglobulin. J Immunol. 1962 Oct;89:559–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Notkins A. L., Mage M., Keehn M. A. Heterogeneity in the properties of 7 S and 19S rabbit-neutralizing antibodies to herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):586–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Rosenthal J., Notkins A. L. Iodine-125-labeled antibody to viral antigens: binding to the surface of virus-infected cells. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):516–518. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Vorndam V., Dreesman G. R. Assay of Australia antigen and antibody employing double-antibody and solid-phase radioimmunoassay techniques and comparison with the passive hemagglutination methods. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1099–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempe C. H., Fulginiti V., Minamitani M., Shinefield H. Smallpox vaccination of eczema patients with a strain of attenuated live vaccinia (CVI-78). Pediatrics. 1968 Dec;42(6):980–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling C. M., Overby L. R. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus antigen as revealed by direct radioimmune assay with 125 I-antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Rosenthal J., Johnson B. Rate-zonal centrifugation of herpes simplex virus-antibody complexes. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer H. L., Takemoto K. K., Kirschstein R. L., Axelrod D. Immunochemical characterization of plaque mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):17–24. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.17-24.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHROHENLOHER R. E., KUNKEL H. G., TOMASI T. B. ACTIVITY OF DISSOCIATED AND REASSOCIATED 19S ANTI-GAMMA-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1215–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. H., Yalow R., Berson S. A. Detection of Australia antigen and antibody by means of radioimmunoassay techniques. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):550–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H., Dixon F. Radioimmunoassay procedure for rabies binding antibodies. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):464–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


