Abstract
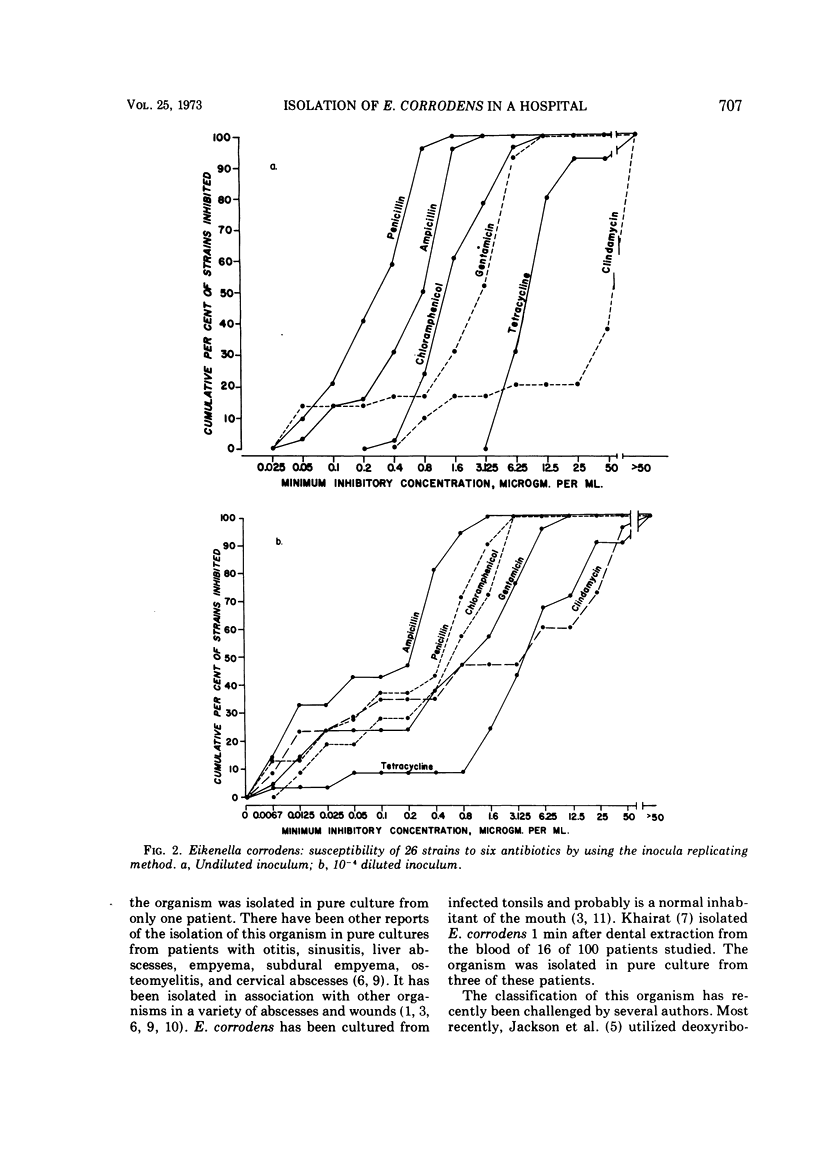
Eikenella corrodens is a small pleomorphic gram-negative bacillus which produces pitting on agar. From December 19, 1970, to December 2, 1971, E. corrodens (also known as HBI) was isolated from material submitted to the Diagnostic Bacteriology Laboratory of the Boston City Hospital from 72 patients (48 males, 24 females) ranging in age from 8 months to 92 years. The organism was recovered from sputum or bronchial washings in 46 instances, from throat or nasopharyngeal swabs in 11, from wounds in 8, from 2 human bites, and from 3 abscesses. It was isolated in pure culture from one of the human bites. Antibiotic susceptibility was measured for 26 strains against six antibiotics by using the inocula replicating method on heart infusion blood agar. E. corrodens was most susceptible to penicillin and ampicillin with 100% and 96% of strains inhibited by 1.65 μg of these antibiotics per ml, respectively. Eighty percent of the strains were inhibited by 3.125 μg of chloramphenicol per ml and 52% were inhibited by this amount of gentamicin. Resistance was greater for tetracycline and clindamycin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EIKEN M. Studies on an anaerobic, rodshaped, gram-negative microorganism: Bacteroides corrodens n. sp. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;43(4):404–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen S. D. Corroding bacteria from the respiratory tract. 2. Bacteroides corrodens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1969;75(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. L., Goodman Y. E., Bel F. R., Wong P. C., Whitehouse R. L. Taxonomic status of facultative and strictly anaerobic "corroding bacilli" that have been classified as Bacteroides corrodens. J Med Microbiol. 1971 May;4(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khairat O. Bacteroides corrodens isolated from bacteriaemias. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. B., Hyde W. A. Isolation of Bacteroides corrodens from infections in children. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;24(2):117–119. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.2.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold L. Untersuchungen an Bacteroides corrodens (Eiken 1958) Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1966 Sep;201(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter G., Stawru J. Die Bedeutung von Bacgeroides corrodens Eiken 1958 im Rahmen der Tonsillenflora. Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1970;155(3):241–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


