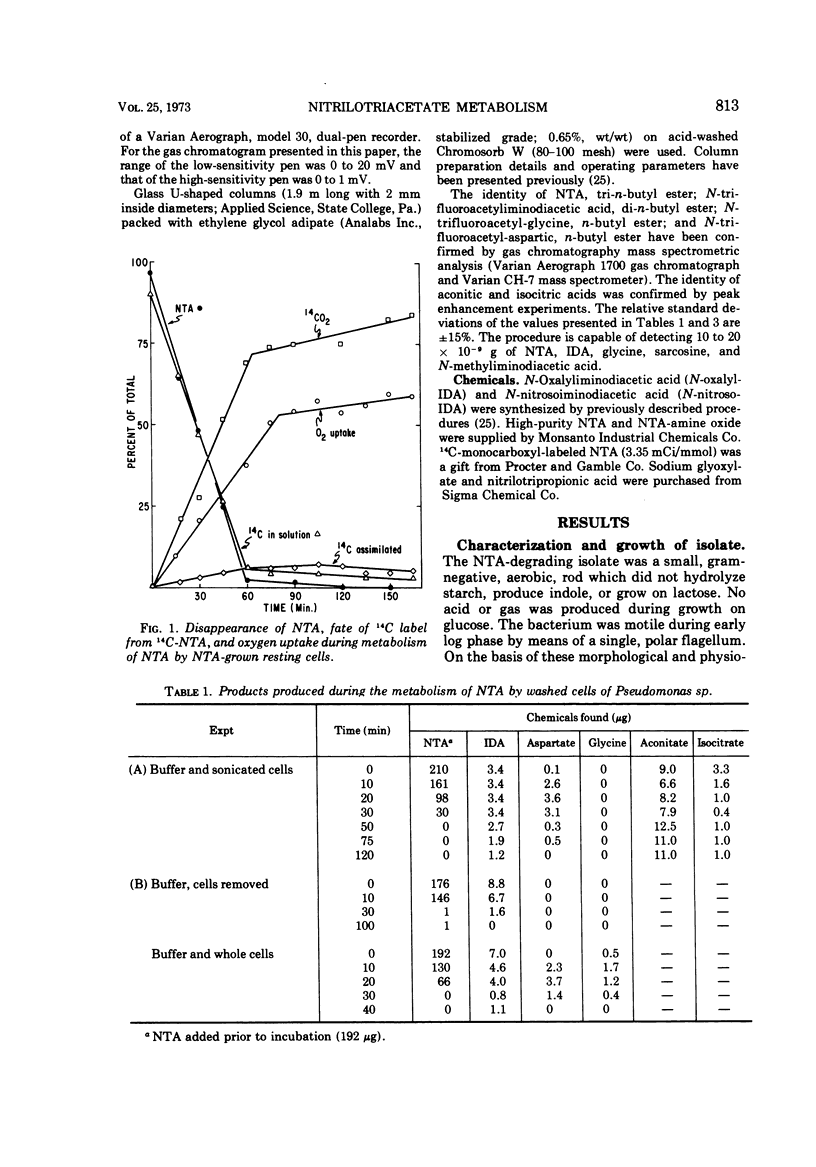
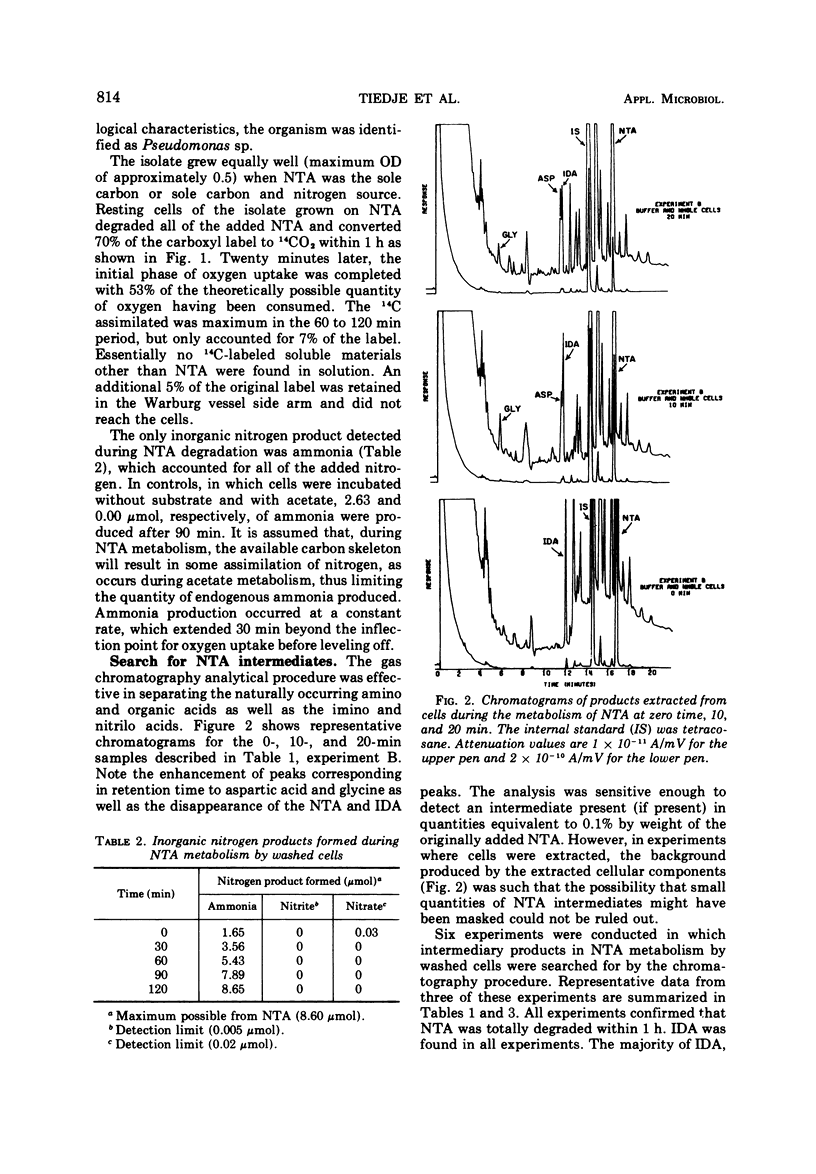
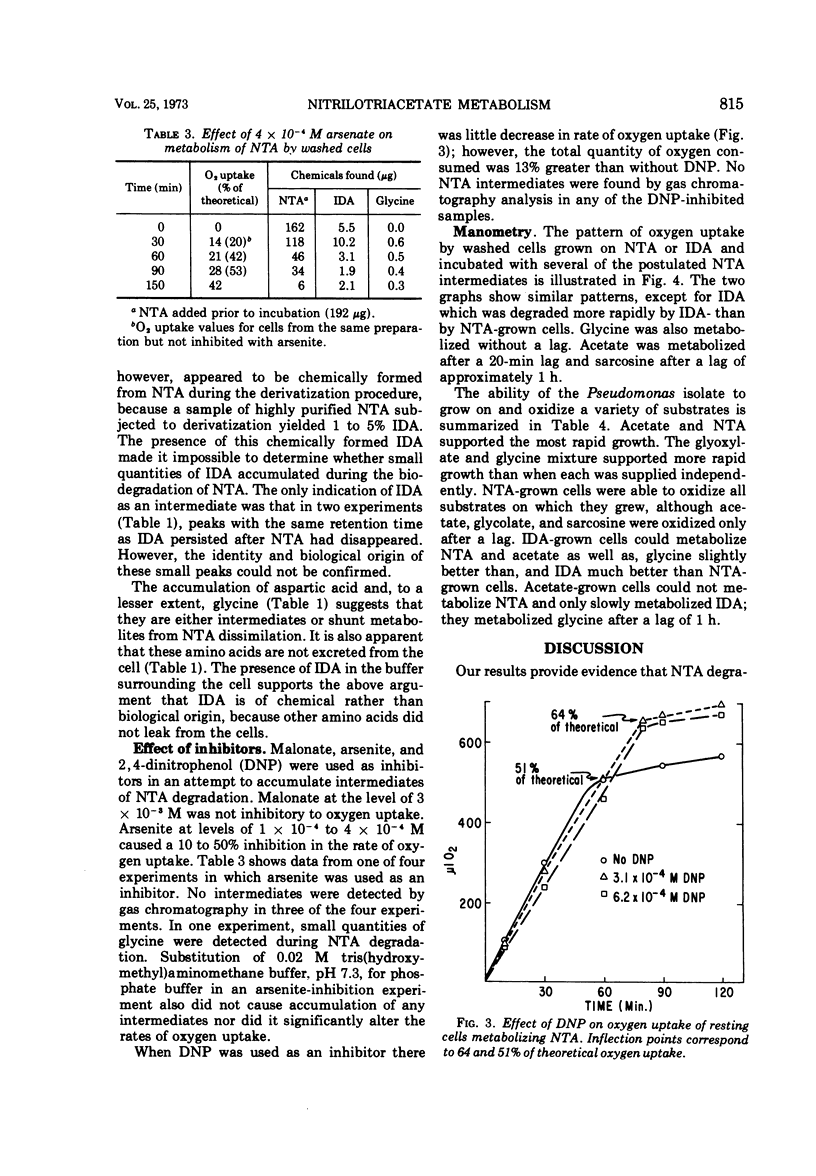
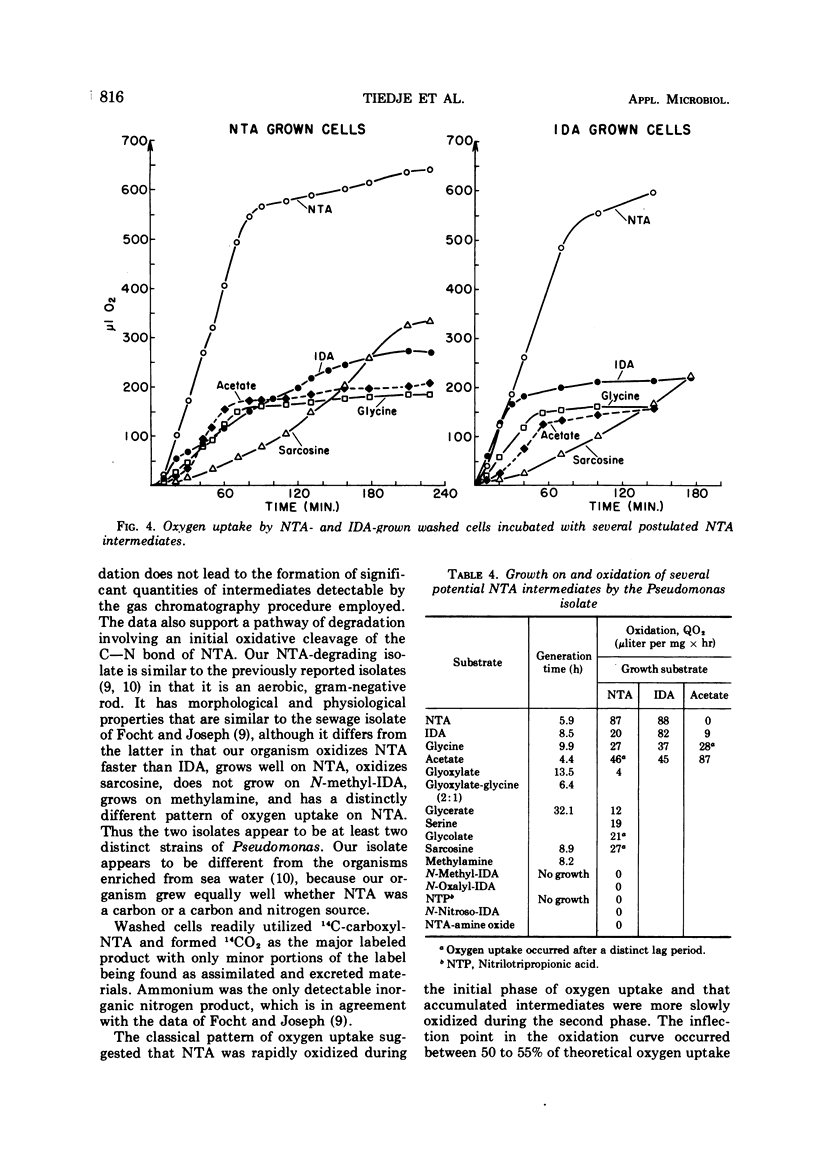
Abstract
A Pseudomonas species was isolated from soil which could degrade nitrilotriacetate (NTA) to CO2, H2O, NH3, and cellular constituents without the accumulation of significant quantities of intermediates either in the presence or absence of several inhibitors. After extensive gas chromatography analysis, small quantities of aspartate, glycine, and aconitate were the only detectable compounds to accumulate during NTA degradation, and these compounds were not excreted from the cells. Manometric studies indicated that iminodiacetate, glycine, and glyoxylate are possible intermediates, whereas N-methyliminodiacetate, sarcosine, and acetate are not. The data are consistent with an oxidative cleavage of the C—N bond of NTA as the initial degradation step.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clifton C. E., Logan W. A. On the Relation between Assimilation and Respiration in Suspensions and in Cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1939 May;37(5):523–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.37.5.523-540.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. The purification and properties of a bacterial trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):9P–10P. doi: 10.1042/bj1210009p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Jarman T. R., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Partial purification of a mixed-function secondary-amine oxidase system from Pseudomonas aminovorans that contains an enzymically active cytochrome-P-420-type haemoprotein. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):449–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1250449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Joseph H. A. Bacterial degradation of nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA). Can J Microbiol. 1971 Dec;17(12):1553–1556. doi: 10.1139/m71-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., GOTTO A. M. The metabolism of C2 compounds in micro-organisms. 6. Synthesis of cell constituents from glycollate by Pseudomonas sp. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:69–82. doi: 10.1042/bj0780069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., MORRIS J. G. THE UTILIZATION OF GLYCOLLATE BY MICROCOCCUS DENITRIFICANS: THE BETA-HYDROXYASPARTATE PATHWAY. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:577–586. doi: 10.1042/bj0950577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large P. J., Boulton C. A., Crabbe M. J. The reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate- and oxygen-dependent N-oxygenation of trimethylamine by Pseudomonas aminovorans. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):137P–138P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280137pb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGERS R. D., GUNSALUS I. C. Intermediatry metabolism of Diplococcus glycinophilus. I. Glycine cleavage and one-carbon interconversions. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:541–549. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.541-549.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharpf L. G., Jr, Hill I. D., Wright P. L., Plank J. B., Keplinger M. L., Calandra J. C. Effect of sodium nitrilotriacetate on toxicity, teratogenecity, and tissue distribution of cadmium. Nature. 1972 Sep 22;239(5369):231–234. doi: 10.1038/239231b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. E., Duthie J. R. The biodegradability and treatability of NTA. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1968 Feb;40(2):306–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. B., Malec E. J. Biodegradation of nitrilotriacetic acid and related imino aand amino acids in river water. Science. 1972 Apr 21;176(4032):277–279. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4032.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren C. B., Malec E. J. Quantitative determination of nitrilotriacetic acid and related aminopolycarboxylic acids in inland waters. Analysis by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1972 Feb 2;64(2):219–237. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)85400-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


