Abstract
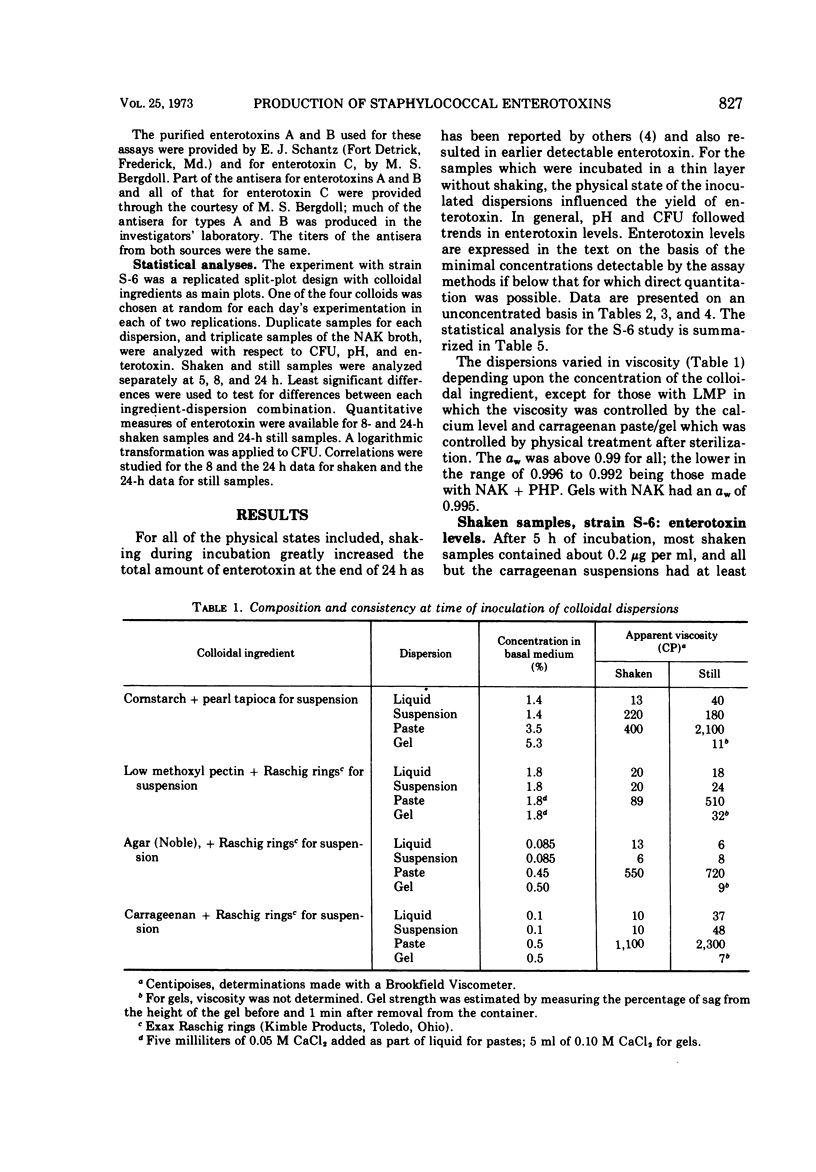
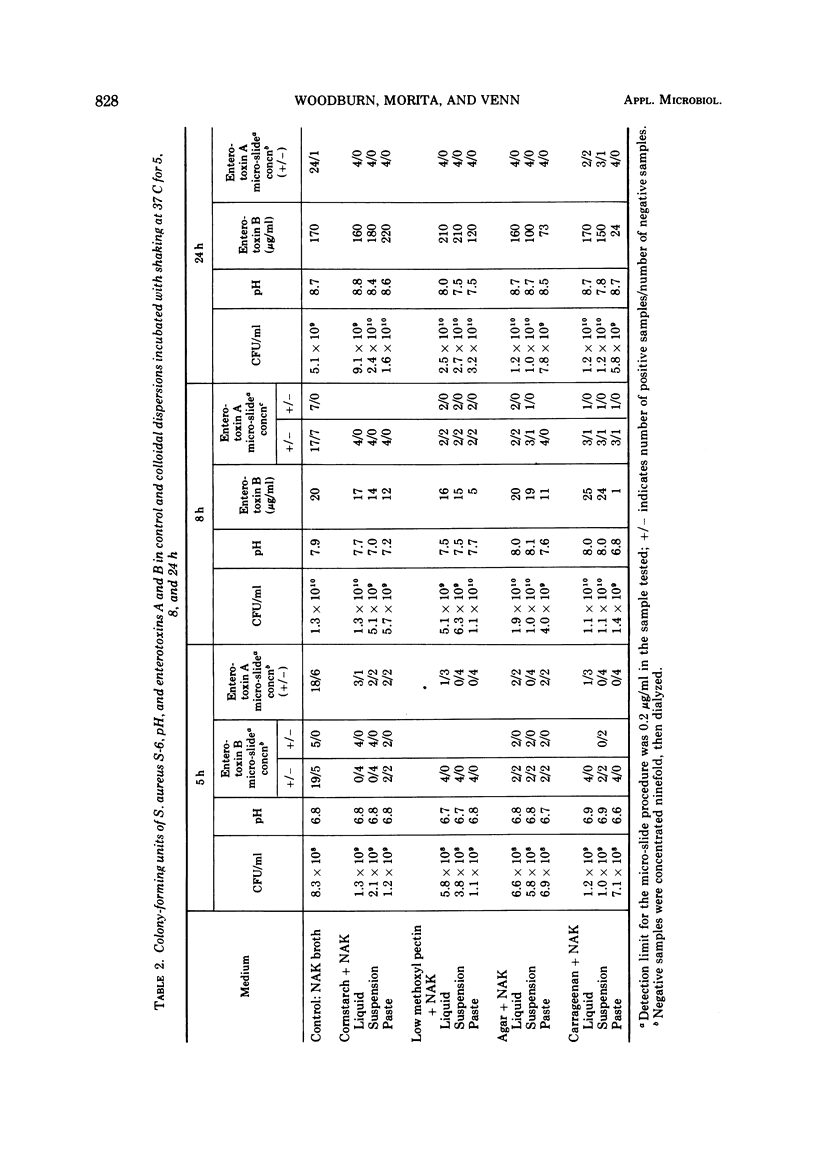
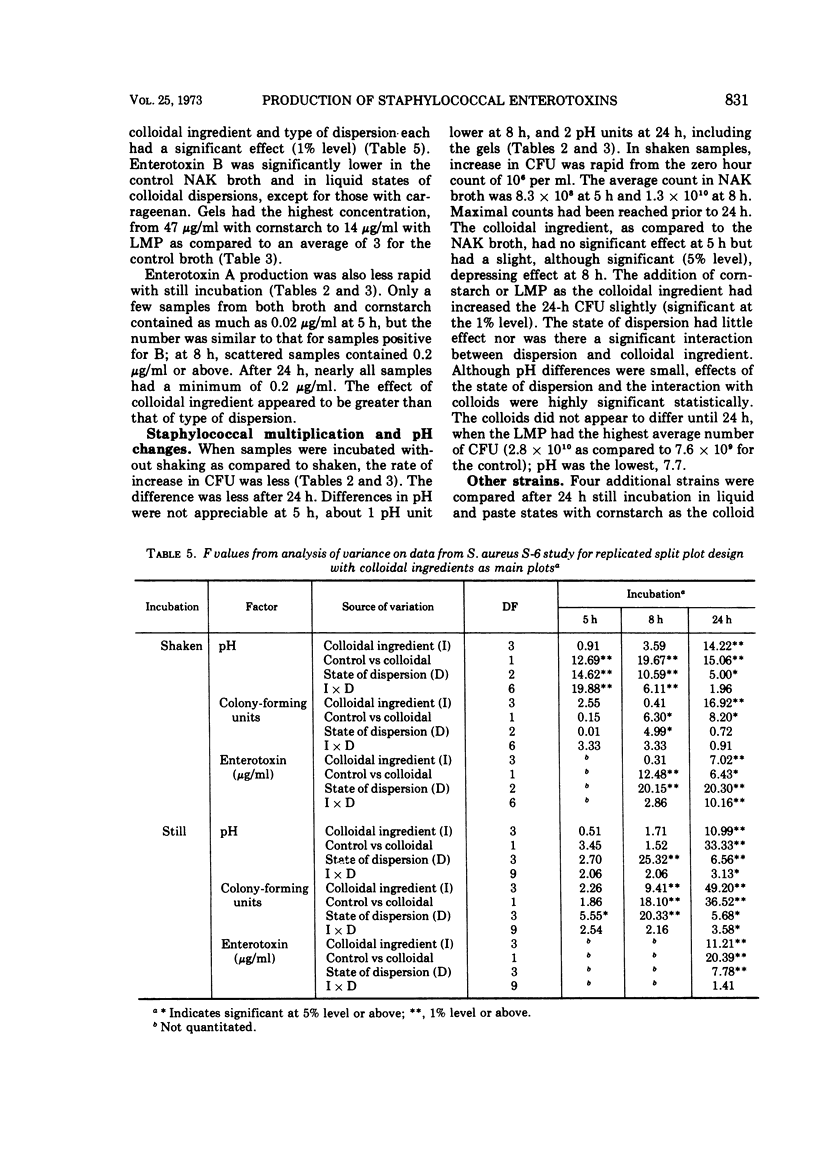
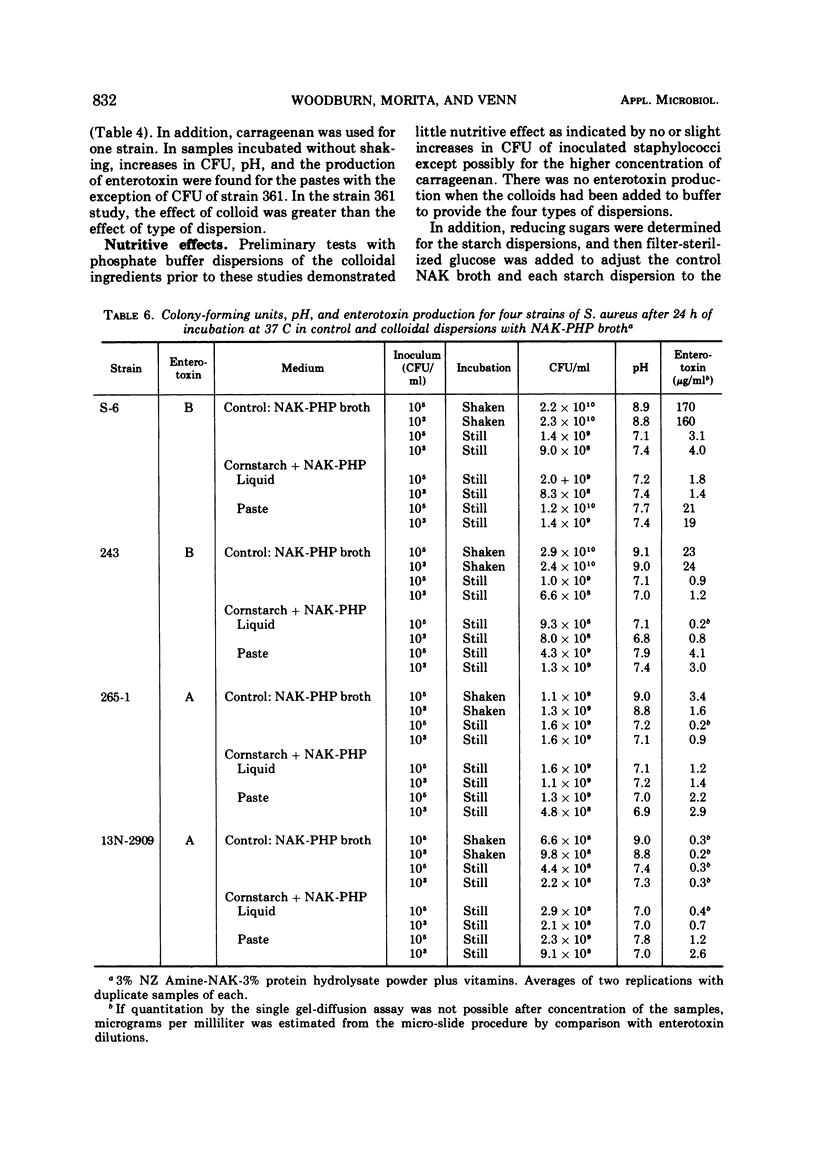
Larger amounts of enterotoxin were produced when Staphylococcus aureus S-6 was grown under still (nonshaken) conditions in a medium that was a paste or gel than were produced in a liquid dispersion with the same colloidal ingredient or in control basal broth (4% NZ Amine-NAK containing 50 μg of thiamine per 100 ml and 1 mg of niacin per 100 ml). Four colloidal ingredients were used which had been previously demonstrated to not support enterotoxin production in buffer. The effect of the type of dispersion occurred earlier than that of the colloidal ingredient, but interactions were found. This effect was not observed when the cells were grown with aeration (shaken). Four other strains of S. aureus followed a similar pattern for enterotoxins A, B, and C, although liquid and paste with cornstarch and carrageenan were the only media compared to the control broth. Enterotoxins A and B were produced earlier by S. aureus S-6, and much greater quantities of enterotoxins were produced for all strains when incubated shaken.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. CULTURE MEDIUM FOR THE PRODUCTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN A. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:18–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.18-23.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich G. G., Watson R. J., Silverman G. J. Effect of shaking speed on the secretion of enterotoxin B by Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):561–566. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.561-566.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLANDER H. O. PRODUCTION OF LARGE QUANTITIES OF ENTEROTOXIN B AND OTHER STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXINS ON SOLID MEDIA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:299–305. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL H. E., ANGELOTTI R., LEWIS K. H. QUANTITATIVE DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN B IN FOOD BY GEL-DIFFUSION METHODS. Public Health Rep. 1963 Dec;78:1089–1098. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT G. A., GOUREVITCH A., LEIN J. Preservation of cultures by drying on porcelain beads. J Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(4):453–454. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.4.453-454.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider K., Filip Z., Martin F. P. Einfluss von Montmorillonit auf die Bildung von Biomasse und Stoffwechselzwischenprodukten durch einige Mikroorganismen. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;73(3):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Lawrence R. C. Production of high titers of enterotoxins for the routine testing of staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):698–699. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.698-699.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi A., Moore G. E. Partial substitution of serum in hematopoietic cell line media by synthetic polymers. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):906–910. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.906-910.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S. J., Knott A. R., Howard M. Rapid, sensitive assay for staphylococcal enterotoxin and a comparison of serological methods. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jul;16(7):1019–1023. doi: 10.21236/ad0838753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simkovicová M., Gilbert R. J. Serological detection of enterotoxin from food-poisoning strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Feb;4(1):19–30. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troller J. A. Effect of water activity on enterotoxin A production and growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):440–443. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.440-443.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


