Abstract
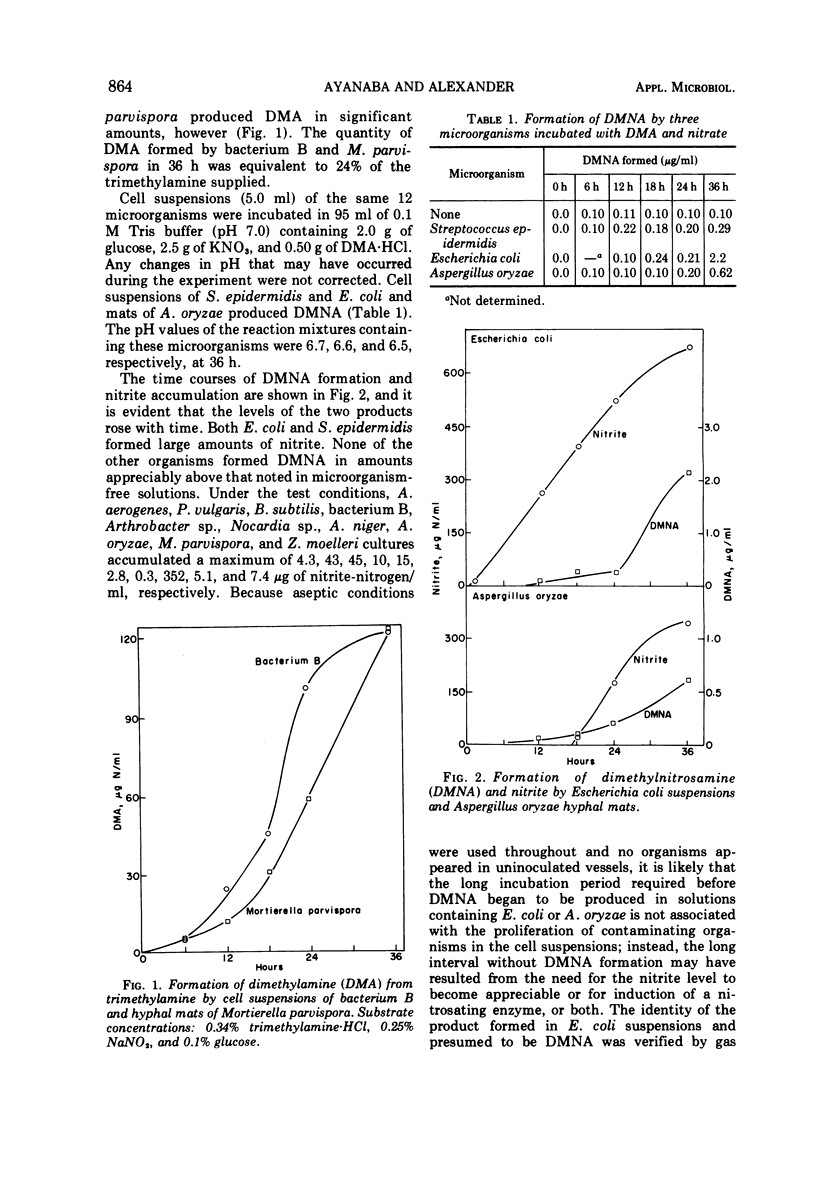
Mortierella parvispora and an unidentified bacterium converted trimethylamine to dimethylamine, and the bacterium (but not the fungus) formed dimethylnitrosamine in the presence of nitrite. Dimethylnitrosamine also appeared in cell suspensions of Escherichia coli and Streptococcus epidermidis and in hyphal mats of Aspergillus oryzae incubated with dimethylamine and nitrate. Suspensions of a number of microorganisms produced N-nitrosodiphenylamine from diphenylamine and nitrite at pH 7.5, and soluble enzymes catalyzing the N-nitrosation of diphenylamine were obtained from two of these organisms. In the presence of these enzymes, several dialkylamines were converted to the corresponding N-nitroso compounds.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam B. S., Saporoschetz I. B., Epstein S. S. Formation of N-nitrosopiperidine from piperidine and sodium nitrite in the stomach and the isolated intestinal loop of the rat. Nature. 1971 Jul 9;232(5306):116–118. doi: 10.1038/232116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam B. S., Saporoschetz I. B., Epstein S. S. Synthesis of nitrosopiperidine from nitrate and piperidine in the gastro-intestinal tract of the rat. Nature. 1971 Jul 16;232(5307):199–200. doi: 10.1038/232199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asatoor A. M., Simenhoff M. L. The origin of urinary dimethylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 16;111(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Cherry W. B., Thacker L., Alley C. C. Analysis by gas chromatography of amines and nitrosamines produced in vivo and in vitro by Proteus mirabilis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Aug;126(2):143–153. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Plessis L. S., Nunn J. R., Roach W. A. Carcinogen in a Transkeian Bantu food additive. Nature. 1969 Jun 21;222(5199):1198–1199. doi: 10.1038/2221198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawksworth G. M., Hill M. J. Bacteria and the N-nitrosation of secondary amines. Br J Cancer. 1971 Sep;25(3):520–526. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1971.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijinsky W., Epstein S. S. Nitrosamines as environmental carcinogens. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):21–23. doi: 10.1038/225021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlashan N. D., Walters C. L., McLean A. E. Nitrosamines in African alcoholic spirits and oesophageal cancer. Lancet. 1968 Nov 9;2(7576):1017–1017. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL E. O., ERRINGTON F. P. Generation times of individual bacteria: some corroborative measurements. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 May;31:315–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREUSSMANN R., DAIBER D., HENGY H. A SENSITIVE COLOUR REACTION FOR NITROSAMINES ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. Nature. 1964 Feb 1;201:502–503. doi: 10.1038/201502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pengra R. M., Cole M. A., Alexander M. Cell walls and lysis of Mortierella parvispora hyphae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1056–1061. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1056-1061.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander J. Nitrosaminsynthese durch Bakterien. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Apr;349(4):429–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraete W., Alexander M. Mechanism of nitrification by Arthrobacter sp. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):962–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.962-967.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


