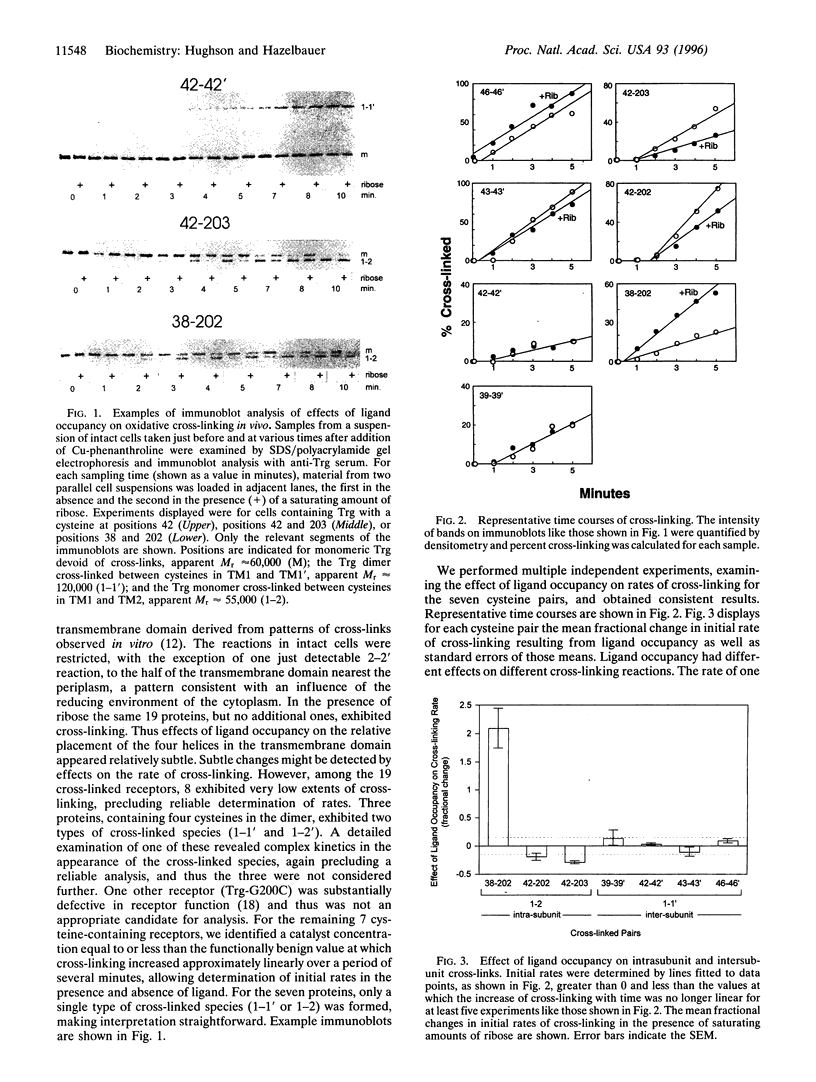
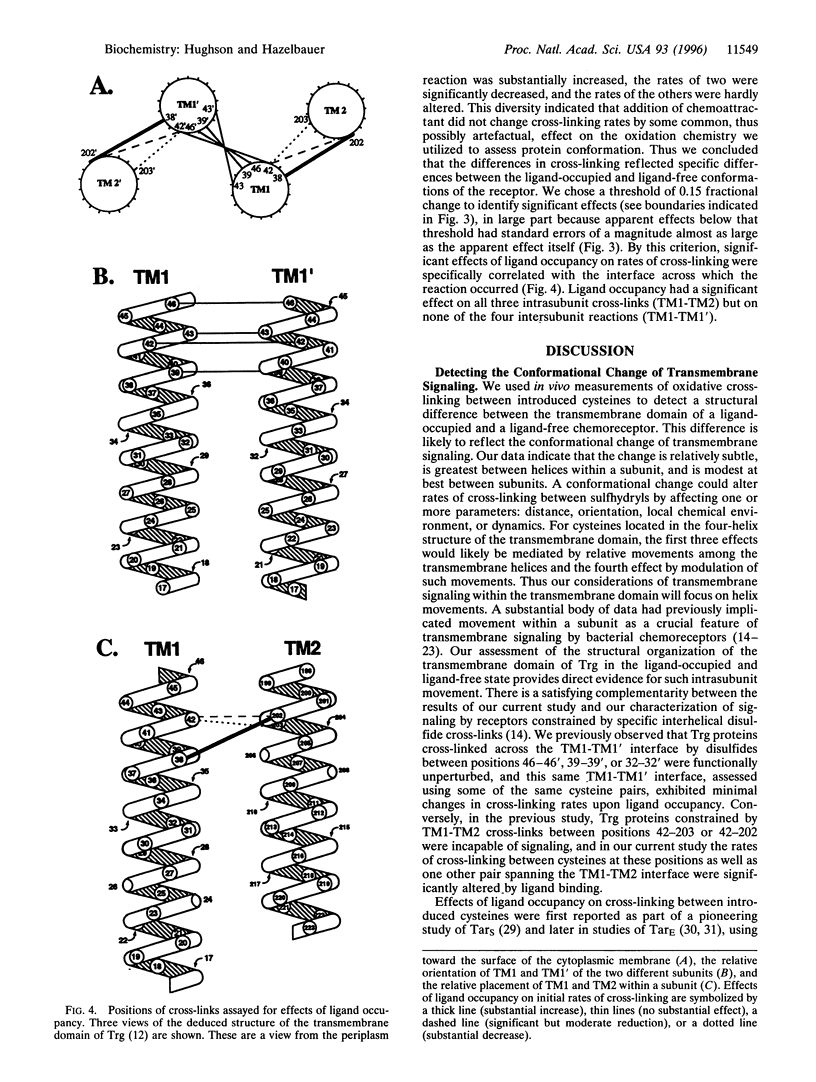
Abstract
Transmembrane signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors is thought to involve relative movement among the four transmembrane helices of the homodimer. We assayed that movement by measuring effects of ligand occupancy on rates of oxidative cross-linking between cysteines introduced into neighboring helices of the transmembrane domain of chemoreceptor Trg from Escherichia coli. Measurements were done on chemoreceptors in their native environment, intact cells that were motile and chemotactically responsive. Receptor occupancy did not appear to cause drastic rearrangement of the four-helix structure since, among 67 cysteine pairs tested, the same 19 exhibited oxidative cross-linking in the presence or absence of saturating chemoattractant. However, occupancy did cause subtle changes that were detected as effects on rates of cross-linking. Among the seven disulfides appropriate for measurements of initial rates of formation, ligand occupancy had significant and different effects on all three cross-links that connected the two helices within a subunit but had minimal effects on the four that spanned the packing interface between subunits. This constitutes direct evidence that the conformational change of transmembrane signaling involves significant movement within a subunit and minimal movement between subunits, a pattern deduced from several previous studies and now documented directly. Among possible modes of movement between the two helices of a subunit, axial sliding of one helix relative to the other was the conformational change that best accounted for the observed effects on cross-linking.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alex L. A., Simon M. I. Protein histidine kinases and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1994 Apr;10(4):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. W., Hazelbauer G. L. Mutational analysis of a transmembrane segment in a bacterial chemoreceptor. J Bacteriol. 1996 Aug;178(15):4651–4660. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.15.4651-4660.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. W., Kim C., Brissette R. E., Inouye M., Park C., Hazelbauer G. L. Transmembrane signalling by a hybrid protein: communication from the domain of chemoreceptor Trg that recognizes sugar-binding proteins to the kinase/phosphatase domain of osmosensor EnvZ. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(4):1157–1163. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.4.1157-1163.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. U., Pakula A. A., Simon M. I. The three-dimensional structure of the aspartate receptor from Escherichia coli. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1995 Mar 1;51(Pt 2):145–154. doi: 10.1107/S0907444994010498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows G. G., Newcomer M. E., Hazelbauer G. L. Purification of receptor protein Trg by exploiting a property common to chemotactic transducers of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17309–17315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervitz S. A., Falke J. J. Lock on/off disulfides identify the transmembrane signaling helix of the aspartate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24043–24053. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.24043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervitz S. A., Falke J. J. Molecular mechanism of transmembrane signaling by the aspartate receptor: a model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Mar 19;93(6):2545–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.6.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervitz S. A., Lin C. M., Falke J. J. Transmembrane signaling by the aspartate receptor: engineered disulfides reveal static regions of the subunit interface. Biochemistry. 1995 Aug 1;34(30):9722–9733. doi: 10.1021/bi00030a010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson M. A., Biemann H. P., Koshland D. E., Jr, Falke J. J. Attractant- and disulfide-induced conformational changes in the ligand binding domain of the chemotaxis aspartate receptor: a 19F NMR study. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6100–6109. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Koshland D. E., Jr Global flexibility in a sensory receptor: a site-directed cross-linking approach. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1596–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.2820061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Park C., Nowlin D. M. Adaptational "crosstalk" and the crucial role of methylation in chemotactic migration by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida A., Harayama S., Iino T., Hazelbauer G. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of genes required for ribose transport and utilization in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.674-682.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. H. "Frozen" dynamic dimer model for transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemotaxis receptors. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):159–165. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. F., Burrows G. G., Lebert M. R., Dutton D. P., Hazelbauer G. L. Deducing the organization of a transmembrane domain by disulfide cross-linking. The bacterial chemoreceptor Trg. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29920–29927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. F., Dutton D. P., Hazelbauer G. L. Identification of functionally important helical faces in transmembrane segments by scanning mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5416–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. F., Lebert M. R., Lilly A. A., Hazelbauer G. L. Transmembrane signaling characterized in bacterial chemoreceptors by using sulfhydryl cross-linking in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch B. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Disulfide cross-linking studies of the transmembrane regions of the aspartate sensory receptor of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10402–10406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I. N., Mikawa Y. G., Maruyama H. I. A model for transmembrane signalling by the aspartate receptor based on random-cassette mutagenesis and site-directed disulfide cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1995 Nov 3;253(4):530–546. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Privé G. G., Milligan D. L., Scott W. G., Yeh J., Jancarik J., Koshland D. E., Jr, Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structures of the ligand-binding domain of the bacterial aspartate receptor with and without a ligand. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1342–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.1660187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Intrasubunit signal transduction by the aspartate chemoreceptor. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1651–1654. doi: 10.1126/science.1661030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Site-directed cross-linking. Establishing the dimeric structure of the aspartate receptor of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6268–6275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. G., Baumgartner J. W., Hazelbauer G. L. Proteins antigenically related to methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Escherichia coli detected in a wide range of bacterial species. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.133-140.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Simon M. I. Determination of transmembrane protein structure by disulfide cross-linking: the Escherichia coli Tar receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4144–4148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. G., Stoddard B. L. Transmembrane signalling and the aspartate receptor. Structure. 1994 Sep 15;2(9):877–887. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard B. L., Bui J. D., Koshland D. E., Jr Structure and dynamics of transmembrane signaling by the Escherichia coli aspartate receptor. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):11978–11983. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi R., Brissette R. E., Rampersaud A., Forst S. A., Oosawa K., Inouye M. Activation of bacterial porin gene expression by a chimeric signal transducer in response to aspartate. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1246–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.2476847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaghmai R., Hazelbauer G. L. Strategies for differential sensory responses mediated through the same transmembrane receptor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1897–1905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh J. I., Biemann H. P., Pandit J., Koshland D. E., Kim S. H. The three-dimensional structure of the ligand-binding domain of a wild-type bacterial chemotaxis receptor. Structural comparison to the cross-linked mutant forms and conformational changes upon ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9787–9792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]