Abstract
Two classes of RNA ligands that bound to separate, high affinity nucleic acid binding sites on Q beta replicase were previously identified. RNA ligands to the two sites, referred to as site I and site II, were used to investigate the molecular mechanism of RNA replication employed by the four-subunit replicase. Replication inhibition by site I- and site II-specific ligands defined two subsets of replicatable RNAs. When provided with appropriate 3' ends, ligands to either site served as replication templates. UV crosslinking experiments revealed that site I is associated with the S1 subunit, site II with elongation factor Tu, and polymerization with the viral subunit of the holoenzyme. These results provide the framework for a three site model describing template recognition and product strand initiation by Q beta replicase.
Full text
PDF
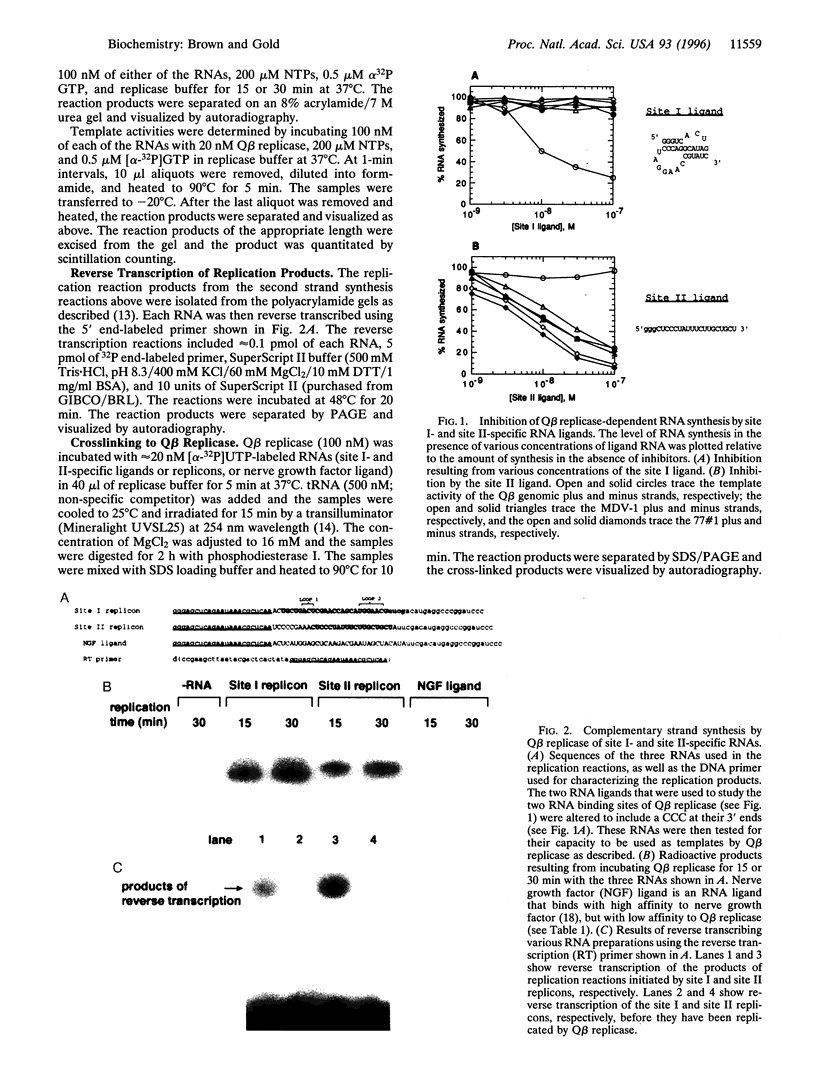


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrera I., Schuppli D., Sogo J. M., Weber H. Different mechanisms of recognition of bacteriophage Q beta plus and minus strand RNAs by Q beta replicase. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):512–521. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biebricher C. K. Replication and evolution of short-chained RNA species replicated by Q beta replicase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:299–306. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binkley J., Allen P., Brown D. M., Green L., Tuerk C., Gold L. RNA ligands to human nerve growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Aug 25;23(16):3198–3205. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.16.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A., Weber K. Bacteriophage Q replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF Tu and EF Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Gold L. Selection and characterization of RNAs replicated by Q beta replicase. Biochemistry. 1995 Nov 14;34(45):14775–14782. doi: 10.1021/bi00045a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Gold L. Template recognition by an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: identification and characterization of two RNA binding sites on Q beta replicase. Biochemistry. 1995 Nov 14;34(45):14765–14774. doi: 10.1021/bi00045a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobkin C., Mills D. R., Kramer F. R., Spiegelman S. RNA replication: required intermediates and the dissociation of template, product, and Q beta replicase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):2038–2044. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
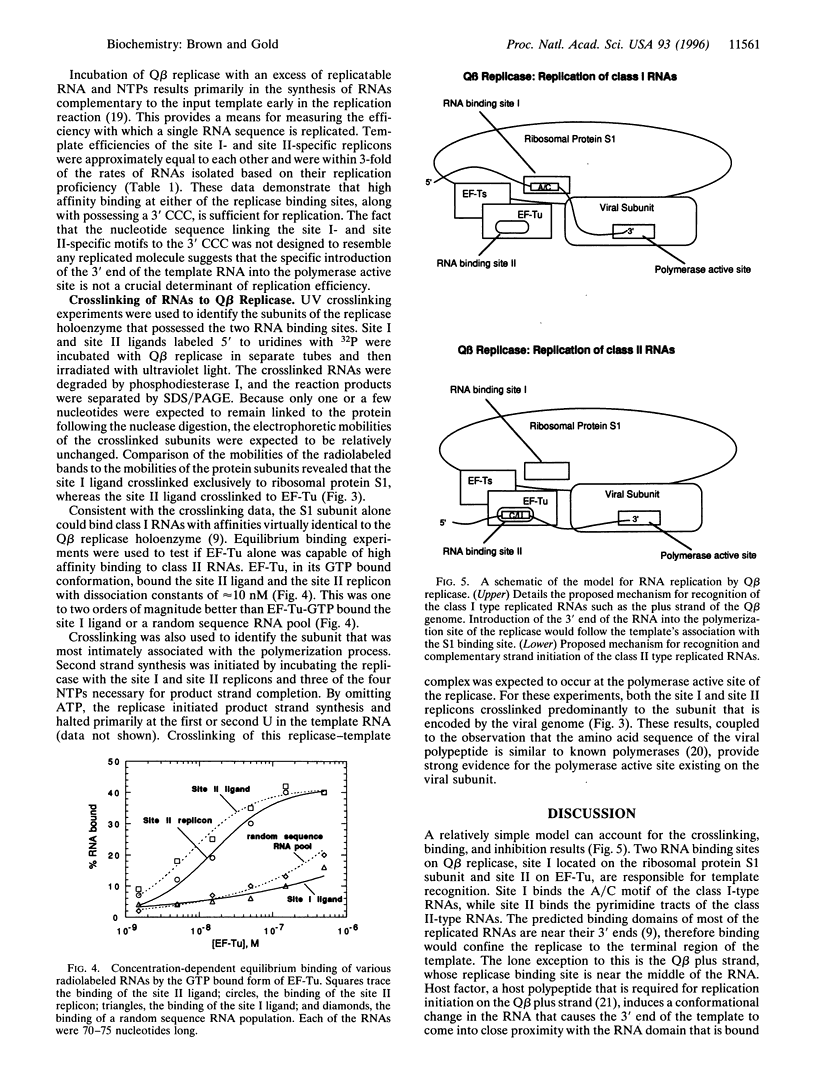
- Franze de Fernandez M. T., Hayward W. S., August J. T. Bacterial proteins required for replication of phage Q ribonucleic acid. Pruification and properties of host factor I, a ribonucleic acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):824–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Ultraviolet light-induced crosslinking of mRNA to proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):715–732. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haruna I., Spiegelman S. Autocatalytic synthesis of a viral RNA in vitro. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):884–886. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Pollack Y., Petre J. Physical and functional homology between ribosomal protein S1 and interference factor i. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):109–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Mills D. R., Kramer F. R., Spiegelman S. A replicating RNA molecule suitable for a detailed analysis of extracellular evolution and replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3038–3042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. Characterization of the subunits of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):527–533. doi: 10.1038/228527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo M., Gallerani R., Weissmann C. Subunit structure of Q-beta replicase. Nature. 1970 Nov 7;228(5271):525–527. doi: 10.1038/228525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Weber H., Weissmann C. Interactions of Q beta replicase with Q beta RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):631–660. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90411-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Priano C., DiMauro P., Binderow B. D. Q beta replicase: mapping the functional domains of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):751–764. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. D., Burg J. L., DiFrancesco R., Lovern D., Stanick W., Lin-Goerke J., Mahdavi K., Wu Y., Farrell M. P. Evolution of host cell RNA into efficient template RNA by Q beta replicase: the origin of RNA in untemplated reactions. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 22;33(46):13836–13847. doi: 10.1021/bi00250a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko I. A., Uhlenbeck O. C. Defining a smaller RNA substrate for elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 28;34(8):2545–2552. doi: 10.1021/bi00008a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Miller M. J., Niveleau A., Landers T. A., Carmichael G. G., Weber K., Hawley D. A., Slobin L. I. Subunit I of G beta replicase and 30 S ribosomal protein S1 of Escherichia coli. Evidence for the identity of the two proteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3314–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C. The making of a phage. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 23;40(0):suppl–suppl:S18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80684-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]