Abstract
Purpose
To overcome the potential disadvantages of the use of foreign materials and autologous fat or collagen, we introduce here an autologous plasma gel for injection laryngoplasty. The purpose of this study was to present a new injection material, a plasma gel, and to discuss its clinical effectiveness.
Materials and Methods
From 2 mL of blood, the platelet poor serum layer was collected and heated at 100℃ for 12 min to form a plasma gel. The plasma gel was then injected into a targeted site; the safety and efficacy thereof were evaluated in 30 rats. We also conducted a phase I/II clinical study of plasma gel injection laryngoplasty in 11 unilateral vocal fold paralysis patients.
Results
The plasma gel was semi-solid and an easily injectable material. Of note, plasma gel maintains the same consistency for up to 1 year in a sealed bottle. However, exposure to room air causes the plasma gel to disappear within 1 month. In our animal study, the autologous plasma gel remained in situ for 6 months in animals with minimal inflammation. Clinical study showed that vocal cord palsy was well compensated for with the plasma gel in all patients at two months after injection with no significant complications. Jitter, shimmer, maximum, maximum phonation time (MPT) and mean voice handicap index (VHI) also improved significantly after plasma gel injection. However, because the injected plasma gel was gradually absorbed, 6 patients needed another injection, while the gel remained in place in 2 patients.
Conclusion
Injection laryngoplasty with autologous plasma gel may be a useful and safe treatment option for temporary vocal cord palsy.
Keywords: Plasma gel, injection, vocal cord palsy, laryngoplasty, acoustical analysis
INTRODUCTION
Since Brunnings1 first injected paraffin into unilateral vocal fold palsy patients, several injection materials have been developed for vocal fold injection in glottal insufficiency. Duration of injection vocal cord augmentation is one of the most important factors in selection of an injection material. The main purpose of temporary vocal fold injection is to close the laryngeal gap during recovery from unilateral vocal fold paralysis.2,3
Over the past 10 years, advances in materials science have led to the development of a number of injectables with excellent safety and biomechanical profiles, making it possible to avoid deleterious foreign body and inflammatory reactions caused by paraffin, silicone, and Teflon™.4,5 Popular materials for injection laryngoplasty include hyaluronic acid and artificial bovine collagen. Despite several advantages with these materials, their high cost and the injection of foreign materials which may induce inflammation must be addressed.
With increasing interest in autologous bio-implants in recent years, several materials including fat,6 collagen,7 and fascia8 have been introduced for augmentative injection treatment.9 However, the available autologous materials possess some inherent problems: requirement of anesthesia, donor site morbidity, variable reabsorption time, and difficulty with volume control of acquired tissue.10 Therefore, there is a need for a new autologous material which can be easily acquired, results in low donor morbidity, and exists in a liquid or semi-solid state to allow for easy and accurate injection.
Recently, the use of autologous materials from the blood of individual patients has been discussed at length.11-15 Autologous materials from a patient's blood have been used widely for adhesion prevention, hemostasis, and enhancement of wound healing processes in surgery.16,17 In particular, platelet-poor plasma (plasma gel), also known as fibrin glue, has gained popularity in plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery, oral surgery, and various other fields.18-21 Despite its popularity, however, injection laryngoplasty using autologous serum or platelet poor plasma had not been reported, prior to the current study.
Therefore, we investigated and report here on the use of autologous plasma gel for injection laryngoplasty to overcome the potential disadvantages of the use of foreign materials and autologous fat or collagen. We standardized the preparation and manufacturing of plasma gel and characterized its physical properties. In addition, the safety and efficacy thereof were evaluated in an animal model and as a phase I/II clinical study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Preparation of plasma gel
An 8.7 mL venous blood sample was drawn under aseptic conditions. The blood was aspirated with a 21 G needle into a 10 mL syringe preloaded with 1.3 mL of anticoagulant citrate dextrose (ACD) solution (in rats: 2 mL venous blood sample mixed with 0.3 mL of ACD). Each blood sample was centrifuged for 15 minutes at 3000 RPM, 72 g, at 4℃, resulting in the following three layers: an inferior layer composed of red cells, an intermediate layer composed of white cells, and a superior layer made up of plasma. The 6 mL plasma layer was centrifuged for another 5 minutes at 1000 g in order to obtain a two-part plasma sample: the upper part consisting of 5.5 mL of platelet-poor plasma (PPP) and the lower part consisting of 0.5 mL of platelet-rich plasma (PRP).22 The PPP was then gently aspirated with a pipette and placed in a sterile injection bottle, being careful not to mix the PPP with PRP.
The injection bottle was attached to a dental syringe and heated at 100℃ for 12 minutes in a heating machine (ALSA S-1, Genexel-Seine, Seoul, Korea). The injectable plasma gel was then ready for use (Fig. 1). An injection needle was attached to the dental syringe, and the plasma gel was injected into the target site.
Fig. 1.
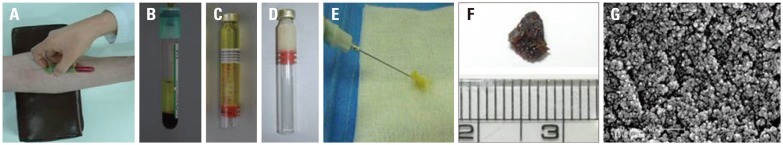
(A) Taking a whole blood sample and centrifuging at 3000 RPM for 15 min. (B) The blood was separated into three layers. (C) The platelet-poor serum layer was collected and pipette into sterilized injection bottles. (D) The injection bottle was attached to a dental syringe and heated at 100℃ for 12 minutes. The collected serum finally turned to plasma gel. (E) The plasma gel was a semi-solid and easily injectable material that was stable at the injection site. (F) The plasma gel was maintained over 1 year in the sterilized injection bottle, but exposed to room air, the plasma gel disappeared within 1 month. (G) Electron microscope findings of plasma gel: the plasma gel showed the typical shape of protein structures on an electron microscope.
In vivo animal experiment
The present animal study was performed after obtaining approval from the Animal Research Committee, Gyeongsang National University. Thirty Sprague-Dawley rats (Samtako, Osan, Korea) with body weights of over 200 grams were used in the study.
For preparation of the plasma gel, blood was withdrawn from the tail vein after the rats were anesthetized with i.p. injections of xylazine hydrochloride (10 mg/kg) (Rompun, Bayer, Germany) and Zoletile 50 (10 mg/kg) (Virbac Laboratories, Carros, France). The acquired blood was processed to produce plasma gel following the above protocol. Two 0.2 mL subcutaneous injections of plasma gel were given to each animal at intervals of 5 mm along the dorsal area. Animals were examined at weekly to monthly intervals for signs of irritation, ulceration, or inflammation, and the amount of plasma gel remaining in situ was measured by electric measurement.
The skin and underlying tissue at the injection sites were removed for analysis at 24 hours (n=3), 30 days (n=3), 90 days (n=3), and 180 days (n=21) post injection. The tissues were dehydrated and processed according to standard paraffin-embedding procedures. Five-micrometer sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for evaluation of histological changes after injection of plasma gel.
The H&E stained sections were examined for inflammatory cell infiltration according to time of absorption. Inflammatory cells in the subcutaneous space were counted at ×100 magnification from two representative areas (superior and inferior injection sites) for each of the animals. The counts were averaged and used for comparisons.
Phase I/II clinical study
The present clinical study was conducted in patients diagnosed with unilateral vocal cord palsy in the Department of Otolaryngology at Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Korea, between January 2010 and March 2011. Eleven patients (8 males and 3 females) who wished to relieve their voice and aspiration symptoms were enrolled. The mean age of the patients was 53 years (range, 25-80 years). The inclusion criteria were as follows: patients having dysphonia associated with idiopathic unilateral vocal fold palsy (VFS), 4 cases; and patients having mobile vocal folds with glottal insufficiency due to either chest surgery or thyroid surgery, 7 cases. This study was performed after obtaining approval from the Institutional Review Board of Gyeongsang National University Hospital, and all patients provided signed written consent.
Percutaneous injection of plasma gel was performed under local anesthesia by one author (SHW) using the thyrohyoid membrane approach. Through the midline area of the thyroid notch, by penetrating the thyrohyoid membrane, the tip of the needle was exposed at the upper vocal cord. While observing the vocal cord of the patient using a flexible laryngoscope, the prepared plasma gel was injected to the muscle layer of the vocal cord. The injection volume was approximately 1.0 mL. After the procedure, the patient rested in a ward for 2-3 hours, and was discharged on the same day.
Subjective and objective measurement of clinical efficacy
The standardized voice handicap index (VHI) before and at the fourth week after injection was used. Three domains (functional, physical, and emotional) are included in the index, and each contains 10 questions requiring patients to indicate how frequently they experienced each situation. Responses to each question were graded from 0 to 4, depending on the perceived degree of handicap.
In addition, a transoral video-stroboscopic examination was performed in all patients before and at 1, 2, and 3 months after injection for structural evaluation. The findings were analyzed and sorted into three categories (disappeared, improved, or no change) by comparing the size of the vocal gap at the follow-up visit with that before the procedure. Acoustic recordings and phonatory function studies were also performed on patients. A voice sample of the patients uttering a sustained vowel sound ("aaa") for 3 seconds at a conversational pitch and loudness was acquired. All voice inputs were recorded and sampled with a multidimensional voice program (MDVP) (Model 4500; Kay Elemetrics Corp., Lincoin Park, NJ, USA) for voice analysis. Four MDVP parameters were used in this study: average fundamental frequency (F0), jitter (jitt %), shimmer (shim %), and noise to harmony ratio. The aerodynamic study was conducted with a computerized system (Phonatory Aerodynamic System, Model 6600; Kay Elemetrics Corp.). The maximum phonation time (MPT) during vowel emission was expressed in seconds.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS software, version 15.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The acoustic analysis data before and after injection were compared using a paired Student's t-test. Statistically significant differences in VHI before and after injection were determined with the Wilcoxon signed rank test. Null hypotheses of no difference were rejected for p-values less than 0.05.
RESULTS
Plasma gel is a homogenous, stable, and easily injectable material
The plasma gel was a semi-solid and easily injectable material which was stable at the injection site (Fig. 1E). The plasma gel was maintained well at the same consistency for over 1 year in a sealed injection bottle; however, when exposed to room air (opened bottle), the plasma gel disappeared within one month (Fig. 1D and F). Under an electron microscope, plasma gel was seen to consist of many same-sized round particles, which represented a consistent and homogenous protein feature (Fig. 1G).
Plasma gel in rats induced minor inflammation and completely dissolved by 6 months
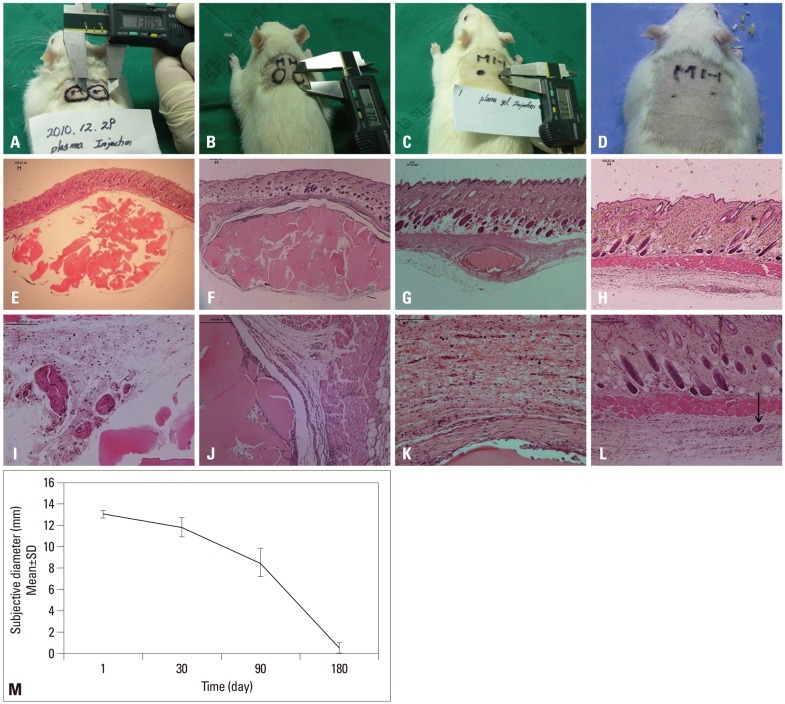
Injection sites in the animals were first graded at 24 hours after injection, and the mean diameter was 13.07±0.4 mm (Fig. 2). The mean diameter was 11.8±0.9 mm at day 30, 8.5±1.35 mm at day 90, and 0.5±0.48 mm at day 180. We found that two (3.3%) injection sites eventually exhibited ulceration and scarring. These rare adverse events, typically occurring 1 month post injection, may be attributed to animal behavior (scratching and biting).
Fig. 2.
The findings of injected plasma gel in rats: (A) 24 hours after plasma gel injection. (B) At 1 month. (C) At 3 months. (D) Six months later the injected material nearly disappeared. (E and I) Histological findings of the plasma gel at the subcutaneous layer of rats, 1 day after injection, there was a slight marked cellular infiltration of inflammation cells. (F and J) 1 month later, there was no evidence of infiltration of acute inflammation cells. (G and K) 3 months later, a mature fibrous capsule surrounded the plasma gel deposit. (H and L) There was no visible fibrous capsule or inflammation cell infiltration. Arrow: remnant of the plasma gel (hematoxylin and eosin stain, E-H ×40, I-L ×100). (M) Serial changes of the injected autologous plasma gel at the subcutaneous layer of rats.
At 1 day post injection, there was no evidence of infiltration of acute inflammatory cells (Fig. 2). At day 30, slight inflammatory cellular infiltration was noted, and a mature fibrous capsule surrounded the plasma gel depot at day 90. Deep dermal cysts, which were lined by flattened epithelial cells, were prominent by 3 months at injection sites in the animals. However, chronic inflammation and foreign body giant cells around the plasma gel depot were absent. At day 180, there was no visible fibrous capsule or cell infiltration.
Plasma gel laryngoplasty effectively enhanced vocal acoustics without any significant complications in patients with unilateral vocal cord paralysis
Eleven patients were enrolled in this study; all received a percutaneous plasma gel injection at a site of vocal cord palsy via the thyrohyoid membrane under topical anesthesia. The average volume of injection material was 1.2 mL per vocal fold.
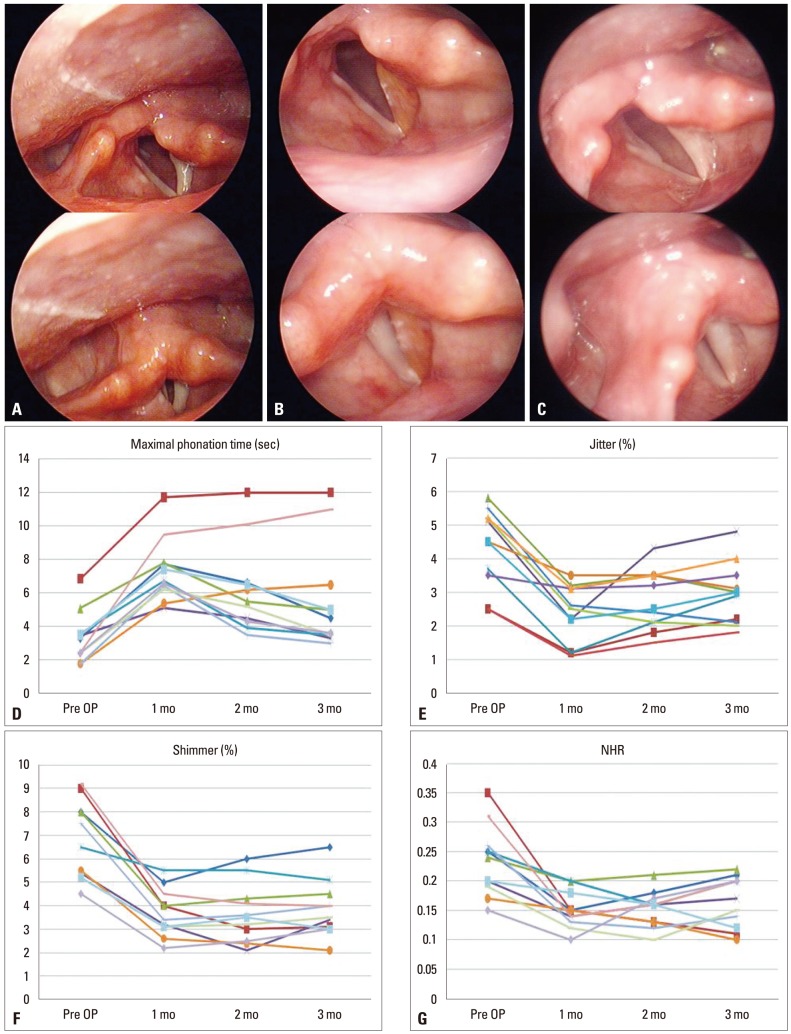
The stroboscopic findings showed that the vocal gap disappeared and the grade of hoarseness improved in all patients (Table 1). The preoperative and postoperative acoustic and aerodynamic parameters also improved significantly. A clear and significant improvement was visible for the mean values of jitter % (p<0.001), shimmer % (p<0.001), and MPT (p<0.05). Mean VHI score also showed significant improvement for all domains after injection (p<0.001) (Fig. 3).
Table 1.
Serial Changes in Video Stroboscopic Findings, Phonatory Results, and Perceptual Scores
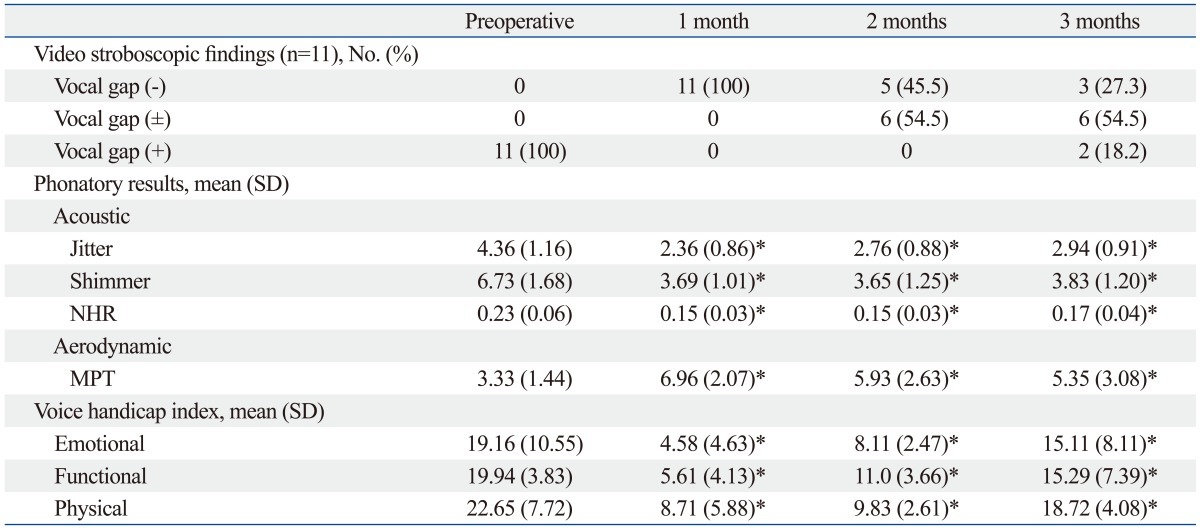
MPT, maximum phonation time; NHR, noise to harmony ratio.
*p<0.05.
Fig. 3.
Serial changes in injected plasma gel in patients with unilateral vocal palsy. This patient was treated for left vocal cord palsy. (A) Left vocal cord palsy. The vocal cord did not move symmetrically. The vocal cord did not close and the voice was husky. (B) One month after injection, the left vocal cord became straightened, the color was slightly yellow, and the vocal cord closed completely. (C) Three months after injection, the glottis gap was re-developed, but was not wider than pre-injection status. (D-G) Changes in maximum phonation time and vocal acoustics after injection laryngoplasty with plasma gel. NHR, noise to harmony ratio; OP, operation.
Among the video stroboscope findings, vocal cord volume began to decrease gradually after 2 months in most patients. In 3 out of 11 patients, at 2 months after injection, voluntary mobility of the vocal cord was observed (Table 2). Meanwhile, in 6 of the 11 patients, hoarseness redeveloped gradually, and voluntary mobility of the vocal cord was absent, thus after 3 months, other artificial materials were re-injected. In the other 2 cases (cases 1 and 9), although vocal fold palsy did not recover, the patients' symptoms were not severe, and thus the patients were maintained under follow-up observation without undergoing additional treatments. The only complication in this study was a hematoma in the area injected with plasma gel in one patient who was taking anticoagulant agents. However, the hematoma was small and there was no symptom of respiration, so we continued to observe the hematoma in the outpatient department. One month later the hematoma disappeared. In the other patients, no complications related to plasma gel injection were observed.
Table 2.
Profiles and Outcomes of Patients Who Underwent Plasma Gel Injection Laryngoplasty
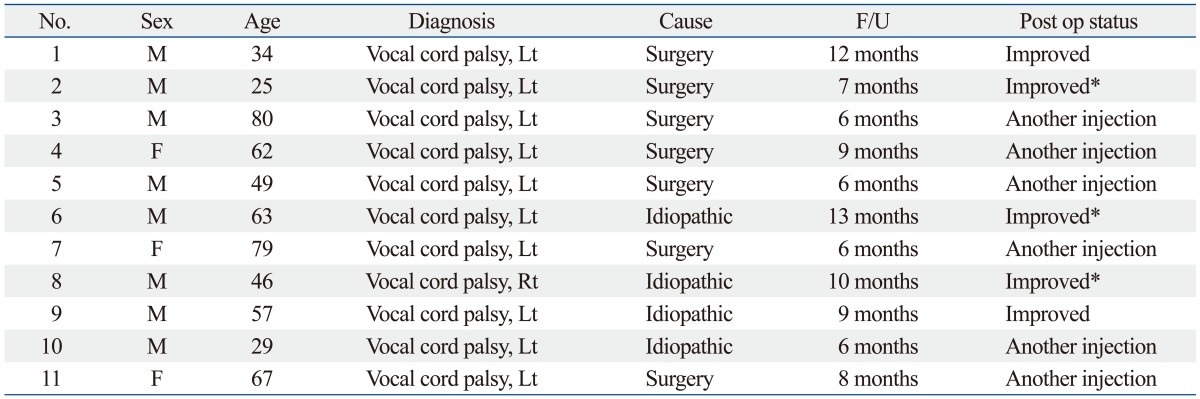
F/U, follow up.
*Spontaneous recovery of vocal fold paralysis.
DISCUSSION
Vocal fold injection for treating glottal insufficiency has gained popularity because of its noninvasiveness, its convenience, and the availability of variety injection materials.1,3,23-27 However, previously used graft materials were known to result in complications such as foreign body reactions or the formation of granulomas. In addition, although various forms of bovine collagen-based materials have been utilized in temporary vocal fold augmentation, they have not been formally studied or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Thus more convenient, safe, and inexpensive autologous materials are required. If materials from a patient's own blood could maintain the vocal cord volume for a certain period, it could be very useful for vocal cord palsy. These clinical needs prompted us to try plasma gel for use in injection laryngoplasty.
Plasma gel was thought to suitable for injection laryngoplasty for several reasons. First, it is prepared from plasma separated from autologous blood, and undesirable immune reactions could therefore be avoided. In addition, after the collection of venous blood, without any pretreatments such as anesthesia or other procedures, the plasma can be processed only by centrifugation and heating. Thus plasma gel could be considered superior to other materials for injection laryngoplasty from the aspect of lessening patient discomfort. Furthermore, plasma gel maintains its gel form through the heat-induced denaturation process, which enables the injection of an accurate amount to a desired site. Although its maintenance period is not sufficiently long in patients with temporary vocal cord palsy, plasma gel could be an effective, safe alternative material for injection laryngoplasty, improving patient quality of life.
In our animal study, we injected plasma gel into the dorsal side of rats, not the vocal cords. The vocal cord of the rat is very small, and thus it would be difficult to observe any foreign body reactions therein. On the dorsal side of the rats, however, we were easily able to observe that the plasma gel did not cause any foreign body reactions after injection.
In our clinical study, 9 out of 11 patients demonstrated very good voice quality after the injection. Two patients were not satisfied with their voice quality (one of the patients was over-injected, and the other was under-injected). Laryngeal stroboscope revealed "normal" mucosal vibration at each follow-up visit of the patients with a good voice outcome. Based on the results from 11 patients who completed the follow-up, the augmentation effect lasted 2 to 3 months. Particularly in patients with temporary vocal fold palsy, the injected plasma gel was gradually absorbed, and thus did not hinder the spontaneous natural recovery of vocal cord mobility. However, our study analyzed voice quality for only a short period after injection laryngoplasty and in only a small number of patients, and thus additional studies, involving greater numbers of patients, will be required to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of plasma gel, as well as to compare it to other currently available materials and perform cost analysis.
In conclusion, plasma gel is easily prepared from host blood with low donor morbidity. It is also safe, not inducing unfavorable immune reactions, as well as accurately injectable. Thus injection laryngoplasty with autologous plasma gel may be a useful and safe treatment option for temporary vocal cord palsy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (2013R1A1A1012542).
This research was supported by Leading Foreign Research Institute Recruitment Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) (2012K 1A4A3053142).
Footnotes
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Brunnings W. Uber eine neue Behandlungsmethode der Rekurrenslahmung. Verhandl Ver Dtsch Laryngol. 1911;18:93–151. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lewy RB. Tracheotomy avoidance. Glycerine vocal cord injection. Arch Otolaryngol. 1970;92:502–504. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1970.04310050084013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kwon TK, Rosen CA, Gartner-Schmidt J. Preliminary results of a new temporary vocal fold injection material. J Voice. 2005;19:668–673. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2005.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mallur PS, Rosen CA. Vocal fold injection: review of indications, techniques, and materials for augmentation. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;3:177–182. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.4.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sulica L, Rosen CA, Postma GN, Simpson B, Amin M, Courey M, et al. Current practice in injection augmentation of the vocal folds: indications, treatment principles, techniques, and complications. Laryngoscope. 2010;120:319–325. doi: 10.1002/lary.20737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hill DP, Meyers AD, Harris J. Autologous fat injection for vocal cord medialization in the canine larynx. Laryngoscope. 1991;101(4 Pt 1):344–348. doi: 10.1002/lary.1991.101.4.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ford CN, Staskowski PA, Bless DM. Autologous collagen vocal fold injection: a preliminary clinical study. Laryngoscope. 1995;105(9 Pt 1):944–948. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199509000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rihkanen H. Vocal fold augmentation by injection of autologous fascia. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(1 Pt 1):51–54. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199801000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee BJ, Wang SG, Goh EK, Chon KM, Lee CH. Intracordal injection of autologous auricular cartilage in the paralyzed canine vocal fold. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;131:34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shindo ML, Zaretsky LS, Rice DH. Autologous fat injection for unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996;105:602–606. doi: 10.1177/000348949610500803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee SW, Kim JW, Koh YW, Shim SS, Son YI. Comparative Analysis of Efficiency of Injection Laryngoplasty Technique for with or without Neck Treatment Patients: A Transcartilaginous Approach Versus the Cricothyroid Approach. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;3:37–41. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goodman GJ. Blood transfer: the use of autologous blood as a chromophore and tissue augmentation agent. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:857–862. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Margolis DJ, Kantor J, Santanna J, Strom BL, Berlin JA. Effectiveness of platelet releasate for the treatment of diabetic neuropathic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:483–488. doi: 10.2337/diacare.24.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McAleer JP, Sharma S, Kaplan EM, Persich G. Use of autologous platelet concentrate in a nonhealing lower extremity wound. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2006;19:354–363. doi: 10.1097/00129334-200609000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zavadil DP, Satterlee CC, Costigan JM, Holt DW, Shostrom VK. Autologous platelet gel and platelet-poor plasma reduce pain with total shoulder arthroplasty. J Extra Corpor Technol. 2007;39:177–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Eppley BL, Pietrzak WS, Blanton M. Platelet-rich plasma: a review of biology and applications in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;118:147e–159e. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000239606.92676.cf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pietrzak WS, Eppley BL. Platelet rich plasma: biology and new technology. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16:1043–1054. doi: 10.1097/01.scs.0000186454.07097.bf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cillo JE, Jr, Marx RE, Stevens MR. Evaluation of autologous platelet-poor plasma gel as a hemostatic adjunct after posterior iliac crest bone harvest. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65:1734–1738. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2006.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Floryan KM, Berghoff WJ. Intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet-poor plasma for orthopedic surgery patients. AORN J. 2004;80:668–674. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)61320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Man D, Plosker H, Winland-Brown JE. The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (platelet gel) and autologous platelet-poor plasma (fibrin glue) in cosmetic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107:229–237. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200101000-00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shim HS, Woo SH. Vocal fold hemorrhage in a CML patient after Glivec treatment. Acta Oncol. 2013;52:866–868. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2012.728715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Luengo Gimeno F, Gatto S, Ferro J, Croxatto JO, Gallo JE. Preparation of platelet-rich plasma as a tissue adhesive for experimental transplantation in rabbits. Thromb J. 2006;4:18. doi: 10.1186/1477-9560-4-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Courey MS. Injection laryngoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2004;37:121–138. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2003.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Homicz MR, Watson D. Review of injectable materials for soft tissue augmentation. Facial Plast Surg. 2004;20:21–29. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-822955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Woo SH, Son YI, Lee SH, Park JJ, Kim JP. Comparative analysis on the efficiency of the injection laryngoplasty technique using calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA): the thyrohyoid approach versus the cricothyroid approach. J Voice. 2013;27:236–241. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2012.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim JP, Cho SJ, Son HY, Park JJ, Woo SH. Analysis of clinical feature and management of laryngeal fracture: recent 22 case review. Yonsei Med J. 2012;53:992–998. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.5.992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee EJ, Yang YS, Kim JS, Hong KH. A "boxer glove" contoured laryngeal amyloidosis. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;5:240–242. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.4.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]