Proteins containing carboxylate-bridged binuclear iron centers are members of a class of enzymes that activate dioxygen for subsequent oxidation and oxygenation chemistry.1 Well-studied members of this superfamily are soluble methane monooxygenase (sMMO) that oxidizes methane to methanol,2 the ribonucleotide reductase R2 subunit (R2) that generates a tyrosyl radical essential for the reduction of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides in DNA biosynthesis,3 and stearoyl-ACP Δ9 desaturase (Δ9D)4 that introduces a double bond into saturated fatty acids.5 Despite differences in their overall structures and chemistry, dioxygen activation by these enzymes occurs at a nonheme diiron site that is supported by 2 histidines and 4 carboxylate ligands where, typically, a kinetically labile biferric-peroxo intermediate forms when O2 reacts with the biferrous cofactor, followed by O–O bond cleavage and formation of high valent intermediates believed to be the reactive oxidants in at least MMO and R2. Despite these similarities, there are remarkable chemical differences among these enzymes. Understanding how these differences emerge and providing the basis for diverse catalytic pathways while preserving commonalities remains to be achieved. Furthermore the structures and the energetics of many of the intermediates and transition states within the catalytic cycles are controversial.6-8
To simplify and understand the mechanisms of enzymatic reactions at the diiron centers in a protein environment we have taken the approach of examining oxygen-activating reactions at the diiron center in our designed model system, the due ferri (DF) scaffold.9-16 The DF scaffold is a simplified model of the natural enzymes, where the diiron site is housed within a four-helix bundle consisting of four carboxylate and two His ligands. Although our DF scaffold does not contain enzyme specific cofactor-tuning components, it has commonalities with the natural systems. Therefore, the reaction with ferrous ions and oxygen is expected to have functionally simplified properties that are common to the nonheme diiron carboxylate enzymes and can be used to identify properties that differentiate the members of this superfamily of enzymes from one another. The DF scaffold has the advantage over small molecule model complexes of reproducing the actual ligand set and sterically eliminating disproportination of intermediates.
To explore O2 reactivity with our de novo designed DF proteins, we start with the simplest reaction common with other diiron proteins, the ferroxidase reaction. In these substrate-independent reactions, the biferrous form of the enzymes react with O2 to generate putative biferric μ-hydroxo/oxo adducts. Herein we present the reactivity of the single chain DF protein (DFsc) and the coordinating amino acid variant DFscE11D. In previous studies of dimeric and tetrameric DF proteins we observed rapid formation of a biferric-oxo species that displays LMCT bands at 300 and 325 nm with extinction coefficients of 3240 and 2400 M−1 cm−1, >respectively.10,14,15,17 These values are in agreement with the ferroxidase sites of ferritin and other diiron proteins.18-21 In the DFsc monomeric analogues the reaction of O2 with either the FeII preloaded or aerobically added produces a distinct species with a λmax of 520 nm (19230 cm−1) (insets of Figure 1). Similarly species have occasionally been observed in some variants of previous designs in DF2 and DFtet.22
Figure 1.
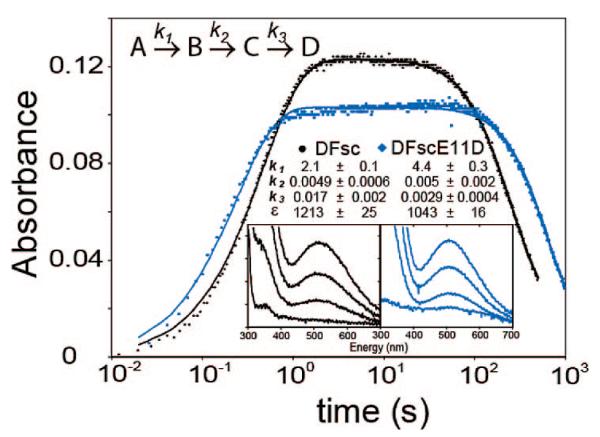
Log of kinetics of O2 reaction of biferrous loaded peptides. Reaction was monitored at 520 nm for DFsc (black) and DFscE11D (blue). Solid lines are three phase fits with parameters given in the text. Inserts show full spectrum development of the 520 nm band. Experimental details are given in the Supporting Information.
Kinetic studies showed that starting the reaction by addition of ferrous iron aerobically results in differences in the rate of formation of the 520 nm species between DFsc (t1/2 ≈ 200 s) and DFscE11D (t1/2 ≈ 2200 s); this reflects differences in iron loading kinetics between the variants (Figure S1). When FeII is anaerobically preloaded into the peptides, rates of formation of the 520 nm species upon O2 exposure are increased and within a factor of 2 of each other (vide infra). These differences in iron loading mask the actual reactivity of the cofactor site. Thus, the Fe preloaded complexes were chosen for further kinetic study.
The protein–iron complex was prepared anaerobically, and O2-saturated buffer was added to the biferrous complex, in a double-mixing stopped-flow reaction (Figure 1). A two phase model could not accurately reproduce the data (Figure S2). The observed kinetic behavior requires three phases (model shown in Figure 1) consisting of a formation phase and two subsequent phases. This model, where only B and C absorb at 520 nm (with the same extinction coefficient since full specta taken near the beginning and end of the k2 phase overlay, Figure S3), well reproduces the observed kinetics. Parameters from this model that give realistic estimates for ε520nm are: k1 = 2.1 ± 0.1, k2 = 0.0049 ± 0.0006 and k3 = 0.017 ± 0.002 s−1 with ε520nm = 1213 ± 25 M−1 cm−1 (for both B and C) for DFsc, and k1 = 4.4 ± 0.3, k2 = 0.005 ± 0.002 and k3 = 0.0029 ± 0.0004 s−1 with ε520nm = 1043 ± 16 M−1 cm−1 (both B and C) for DFscE11D. The rate of formation is linearly dependent on O2 concentration (up to saturation at 25 °C) and reflects O2 reacting with the biferrous site which is directly comparable to the O2 reactions of the binuclear nonheme iron enzymes. The k3 phase represents loss of the biferric cluster (produced in the O2 reaction) from the peptide resulting in precipitated iron products. While the k2 phase may reflect relaxation of the DFsc scaffold subsequent to the formation of an Fe–O(phenolate) bond (vide infra), as this phase is lacking in a Y51 variant.23
The rates for the formation of the 520 nm species (k1) are 3 orders of magnitude faster then the rates of formation for the biferric-oxo bridge species in the A2B2 DF systems24 but similar to E. coli R2 (~1 s−1),25 suggesting that the diiron site in DFsc is quite accessible to dioxygen and ready for rapid reaction. The 520 nm species formed in DFscE11D is more stable with respect to loss of FeIII (vide supra) and displayed more intense resonance Raman (rR) features enabling the absorption band to be profiled.
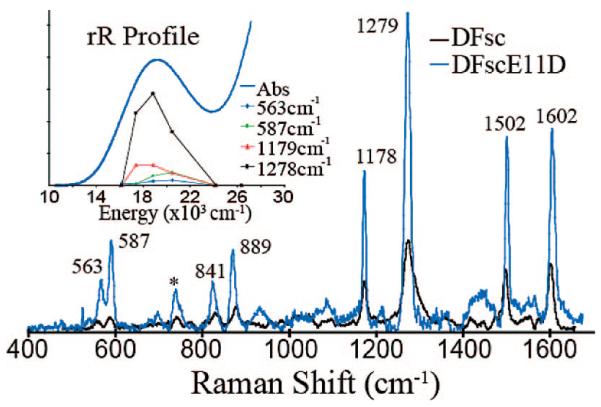
rR spectroscopy was used to characterize the 520 nm species in DFsc and DFscE11D (Figure 2). Both spectra, taken with 530 nm laser excitation, exhibit highly similar resonance enhanced vibrations (based on loss of these features in spectra taken off-resonance at 752 nm excitation). The intensity pattern and energy of the bands at 1178, 1279, 1502, and 1602 cm−1 (labeled for DFscE11D in Figure 2) correlate well with δC–H, νC–O, νC–C, and νC–C modes, respectively, of a phenolate bound to FeIII, and the features at 841 and 889 cm−1 are assigned as a metal-coordinated tyrosyl Fermi doublet, frequently observed in the rR spectra from tyr→FeIII charge transfer transitions in enzymes such as purple acid phosphatase and catechol 1,2-dioxygenase.26-28 No isotope shift was observed for these features using either 18O2 or H218O (data not shown) thus confirming that these vibrations are associated with coordination of a tyr residue producing a tyr→FeIII CT. Since at low temperature the 520 nm species does not show a MCD signal (Figure S4) the oxidized site must be diamagnetic and consist of two antiferromagnetically coupled ferric ions. Thus oxidation of the biferrous DFsc cofactor site produces a tyrosine-bound biferric site.
Figure 2.
Resonance Raman spectra of O2 reacted DFsc (black) and DFsc-E11D (blue). Spectra were obtained with 530 nm laser excitation and the specifics of experiment are in Supporting Information. Inset shows enhancement profiles for DFscE11D of the labeled features as a function of excitation energy.
In the diZn-DFsc NMR29 structure two tyrosine residues (Y18 and Y51) are present in close proximity to the cofactor site. Therefore, in principle, either or both could coordinate terminally to a ferric center. Coordination of two to one iron or bridging would require extensive changes in the secondary structure of the peptide. Two resonance enhanced vibrations are observed at 563 and 587 cm−1 (in the O–FeIII stretch region) and one could derive from each Fe–O(phenolate) mode or both could be due to one Fe–O(phenolate) vibration split by Fermi resonance. To determine if one or two tyr residues are bound to the ferric centers in the oxidized species, the excitation profile of the 520nm band in DFscE11D was determined (inset Figure 2). The 563, 587, 1179 and 1278 cm−1 modes all profile together across the absorption band in a manner consistent with only one phenolate to ferric CT. Therefore, upon exposure to dioxygen either Y18 or Y51, but not both, binds terminally to a ferric center at a biferric oxidized site. Preliminary results on DFsc variants show that Y51 is bound in the biferric state.23
These de novo designed preloaded cofactor sites react with O2 at a rate similar to that of the biferrous site of R2. However, the species formed is not an oxygen intermediate but an oxidized biferric site with one nearby tyr of the protein coordinated terminally. This indicates that while the initial reaction reduces O2 to a putative peroxide level intermediate, this is rapidly lost leaving a tyr coordinated, oxidized biferric site. Spectroscopic evidence shows that no tyr residue is coordinated in the biferrous state.23 Thus phenol coordination to the oxidized site would provide a H+ to promote loss of H2O2, similar to the ferroxidase reaction observed in the early stage of the biferrous M-ferritin reaction with O2. Studies are underway to further understand this reaction and to eliminate the appropriate tyr from the scaffold.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment
We are grateful for financial support by NSF-Biophysics Program Grant MCB-0342807 (E.I.S.) and NIH Grant GM54616 (W.F.D). We also thank Dr. Grit Straganz and Dr. James Lear for insightful discussions regarding these data and conclusions.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Experimental methods, aerobic kinetics, 2-phase simulations to the anerobic kinetic data and a low temperature CD/MCD spectrum of the DFscE11D oxidized species. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- (1).Solomon EI, Brunold TC, Davis MI, Kemsley JN, Lee SK, Lehnert N, Neese F, Skulan AJ, Yang YS, Zhou J. Chem. Rev. 2000;100:235–350. doi: 10.1021/cr9900275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).Merkx M, Kopp DA, Sazinsky MH, Blazyk JL, Muller J, Lippard SJ. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:2782–807. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20010803)40:15<2782::AID-ANIE2782>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Strand KR, Karlsen S, Kolberg M, Rohr AK, Gorbitz CH, Andersson KK. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:46794–801. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407346200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).Lindqvist Y, Huang W, Schneider G, Shanklin J. EMBO J. 1996;15:4081–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (5).Fox BG, Lyle KS, Rogge CE. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:421–9. doi: 10.1021/ar030186h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (6).Rinaldo D, Philipp DM, Lippard SJ, Friesner RA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:3135–47. doi: 10.1021/ja0654074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (7).Murray LJ, Garcia-Serres R, Naik S, Huynh BH, Lippard SJ. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:7458–9. doi: 10.1021/ja062762l. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8).Krebs C, Galonic Fujimori D, Walsh CT, Bollinger JM., Jr Acc. Chem. Res. 2007;40:484–92. doi: 10.1021/ar700066p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).Lear JD, DeGrado WF, Calhoun JR. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003;100:14772–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2536751100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Pasternak A, Kaplan J, Lear JD, Degrado WF. Protein Sci. 2001;10:958–69. doi: 10.1110/ps.52101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Di Costanzo L, Wade H, Geremia S, Randaccio L, Pavone V, DeGrado WF, Lombardi A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:12749–57. doi: 10.1021/ja010506x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12).Calhoun JR, Kono H, Lahr S, Wang W, DeGrado WF, Saven JG. J. Mol. Biol. 2003;334:1101–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (13).Cochran FV, Wu SP, Wang W, Nanda V, Saven JG, Therien MJ, Degrado WF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:1346–7. doi: 10.1021/ja044129a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).Calhoun JR, Nastri F, Maglio O, Pavone V, Lombardi A, Degrado WF. Biopolymers. 2005:264–78. doi: 10.1002/bip.20230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15).Wei PP, Skulan AJ, Wade H, DeGrado WF, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:16098–106. doi: 10.1021/ja053661a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (16).Wade H, Stayrook SE, Degrado WF. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2006;45:4951–4. doi: 10.1002/anie.200600042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (17).Kaplan J, DeGrado WF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2004;101:11566–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404387101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).Yang YS, Baldwin J, Ley BA, Bollinger JM, Jr., Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000;122:8495–510. [Google Scholar]
- (19).Yang Y-S, Broadwater JA, Pulver SC, Fox BG, Solomon EI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:2770–83. [Google Scholar]
- (20).Bollinger JM, Jr., Tong WH, Ravi N, Huynh BH, Edmondson DE, Stubbe JA. Methods Enzymol. 1995;258:278–303. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)58052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).Fox BG, Shanklin J, Ai J, Loehr TM, Sanders-Loehr J. Biochemistry. 1994;33:12776–86. doi: 10.1021/bi00209a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Marsh EN, DeGrado WF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002;99:5150–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052023199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (23).Bell CB, 3rd, Calhoun JR, Slonkina E, Wei PP, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, DeGrado WF, Solomon EI. Unpublished results [Google Scholar]
- (24).Summa CM, Rosenblatt MM, Hong JK, Lear JD, DeGrado WF. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;321:923–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00589-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).Tong WH, Chen S, Lloyd SG, Edmondson DE, Huynh BH, Stubbe J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996;118:2107–8. [Google Scholar]
- (26).Waldo GS, Theil EC. Biochemistry. 1993;32:13262–9. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).Antanaitis BC, Strekas T, Aisen P. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:3766–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (28).Gaber BP, Sheridan JP, Bazer FW, Roberts RM. J. Biol. Chem. 1979;254:8340–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).Calhoun JR, Liu W, Spiegel K, Dal Peraro M, Klein ML, Valentine KG, Wand AJ, DeGrado WF. Structure. 2008;16:210–5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2007.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.