Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
To test the hypothesis that systemic administration of vitamin C, through its action of stimulating collagen synthesis and cross-linking, would decrease the recurrence and improve the occlusion experimental aneurysms treated with platinum coil embolization.
METHODS
Nineteen experimental aneurysms in female rabbits were embolized with platinum coils (>30% packing density). The animals were divided into three groups: Group 1 (n=6) rabbits served as controls, Group 2 (n=5) rabbits were fed with a vitamin C-supplemented feed and Group 3 (n=8) rabbits were medicated with vitamin C pills. Digital subtraction angiography was used to evaluate stability after embolization. Subjects were euthanized at 12 weeks after coil implantation, and serum vitamin C levels were then measured. Histological samples were examined with a grading system (range, 0-12) based on the neck and dome features. Masson Trichrome staining was employed to evaluate collagen deposition. Parametric data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance and non-parametric data were examined using a Kruskal-Wallis test.
RESULTS
There were no significant differences between groups in mean aneurysm size. Mean serum vitamin C concentration was significantly higher in Group 3 and Group 2 compared to Group 1, while vitamin C levels between Group 2 and Group 3 were statistically comparable. Coil compaction was noted in one of six subjects in Group 1 and three of eight subjects in Group 3. All the remaining aneurysms in the test and control groups showed stable occlusion. There were no significant differences in histological scores or collagen deposition among groups.
CONCLUSION
Vitamin C supplementation following platinum coil embolization does not demonstrate improvement of long-term occlusion rates of aneurysms.
INTRODUCTION
Coil embolization of saccular, intracranial aneurysms has been widely accepted as a safe alternative therapy to open surgery. However, treatment of large and giant aneurysms remains problematic given ongoing low rates of initial complete aneurysm obliteration as well as high rates of late aneurysm recanalization (1, 2). The exact mechanisms responsible for aneurysm recanalization remain unclear. Ideally, the aneurysm becomes covered by a robust, endothelialized neointima and the dome is replaced by dense connective tissue. Numerous agents have been delivered or proposed for delivery in the aneurysm cavity to improve healing and some have reached clinical application, but none has shown definite efficacy to date (3-9).
Collagen synthesis is a central process in wound healing, providing both increased strength for the healing wound’s structural matrix as well as a surface or substrate for adhesion and attraction of cells involved in inflammation, angiogenesis and connective tissue construction to the injured area (10, 11). Previous histologic studies of both experimental and human aneurysms treated with platinum coils show a dearth of collagen synthesis within the aneurysm cavity and along the neck/parent artery interface (12, 13). Local delivery of collagen or collagen formation factors into aneurysm cavities has been proposed as means for improved aneurysm healing, but this approach has not been tested clinically (14-19).
We hypothesized that systemic delivery of agents that may promote collagen synthesis or cross-linking might improve healing within and around the embolized aneurysm cavity. Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, plays an important role in collagen synthesis and cross-linking (20, 21). Pathways affected by vitamin C include stimulation of collagen biosynthesis by promoting the activity of hydroxylases as well as increasing the steady-state level of the procollagen mRNA without changing the synthesis of non-collagen proteins (22-24). If vitamin C is active in the treated aneurysm’s healing response, it might improve long-term occlusion rates by stimulating collagen synthesis. This collagen along the aneurysm neck may improve cell adherence with subsequent neointimal formation.
The purpose of the current study was to test the hypothesis that vitamin C supplementation following platinum coil embolization would improve histologic healing as compared to subjects treated with platinum coils without subsequent vitamin C supplementation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
ANEURYSM CREATION AND COIL EMBOLIZATION
Elastase-induced saccular aneurysms were created in female, New Zealand white rabbits (2.5–4 kg). The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all procedures prior to study initiation. Some of the rabbits employed in this study were originally used as part of another investigation, which was entirely unrelated to the current project(25). Detailed procedures for aneurysm creation have been described in depth elsewhere (26). Aneurysms were permitted to mature for at least 21 days after creation. Animals were anesthetized and a cutdown was performed to gain access to the right common femoral artery (CFA). A microcatheter was inserted coaxially through the guiding catheter into the aortic arch. Heparin (100 U/kg) was administered intravenously. Aneurysms were embolized with platinum coils as via the microcatheter.
The size of the aneurysm cavity was assessed by direct comparison with radiopaque sizing devices during digital subtraction angiography (DSA). The volumetric occlusion rate was calculated as follows: Volume = π (dome)2 (length)/6. In this study, we assumed the value of the aneurysm dome in this formula was equal to that of aneurysm width. The volumetric occlusion was calculated in real time, during aneurysm embolization, using AngioCalc tool (http://www.angiocalc.com/index.aspx). Appropriate-sized platinum coils (Heraeus Precious Metals GmbH & Co, Germany; diameter 0.0008’’) were placed into the aneurysm as in typical practice. Before and after each successive coil was placed, volumetric occlusion was calculated. Aneurysm cavities were packed as tightly as possible (>30% packing density) in all cases. Final DSAs were performed immediately following embolization.
VITAMIN C MEDICATION
Rabbits were divided into three groups. Group 1 (n=6) rabbits served as controls, while Group 2 (n=5) and Group 3 (n=8) animals, respectively, were fed a diet containing vitamin C (1732ppm) or were medicated with vitamin C pill (80mg/kg, QD) for 12 weeks following embolization. Vitamin C content (1732ppm) in the diet is equal to 80 mg vitamin C per kg body weight per day in rabbits.
VITAMIN C MEASUREMENT
Arterial blood was collected from the rabbits just prior to aneurysm embolization and at the time of sacrifice. Vitamin C level in blood was measured calorimetrically by using a commercial ascorbic acid assay kit (AbCam, Cambridge, MA)
TISSUE HARVEST AND PROCESSING
At the time of sacrifice, the subjects were deeply anesthetized, blood was obtained, and DSA was performed. Animals were then euthanized with a lethal injection of pentobarbital. Harvested aneurysms were immediately fixed in 10 % neutral buffered formalin. The degree of aneurysm neck tissue coverage was evaluated as previously described (27). Using a modified histology technique (28), samples were embedded in paraffin and sectioned at 1000-μm intervals in a coronal orientation. Coil fragments were then carefully removed. Sections were re-embedded in paraffin and partitioned at 5-μm intervals. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for conventional histologic evaluation and Masson Trichrome for collagen deposition.
ANGIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION
All sacrifice angiograms were compared to post-embolization angiograms and assessed for changes in coil configuration or aneurysm filling. Sacrifice angiograms were then categorized as stable, progressive occlusion, or coil compaction/recanalization as compared to the post-embolization angiograms. Stable and progressive occlusions were categorized as positive outcomes while compaction was deemed a negative result.
HISTOLOGIC EVALUATION
Sections were viewed by a single experienced reviewer paying particular attention to the thickness of the cellular layer across the neck of aneurysms and the collagen matrix deposition within the aneurysm dome. An ordinal grading system was used to evaluate histologic healing (27). This scale was devised based on findings at the neck and in the dome. Neck coverage was included both on gross and microscopic inspection. Tissue coverage across the neck was graded, on gross inspection as well as microscopic findings, which included tissue thickness and tissue type. The scores from the gross and microscopic neck inspections were averaged to yield a single neck score. Micro-compaction assessment was based on the shape of the coil mass across the neck, from convex to concave. Histologic characteristics in the dome were categorized on the density of cellular infiltration and presence of organized tissue. These scores (the neck, microcompaction, and dome) were summed to obtain a total score representative of the aneurysm’s pathology.
COLLAGEN DEPOSITION ANALYSIS
We quantitatively analyzed collagen deposition or fibrosis identified with Masson Trichrome staining using a recently described and experimentally verified image analysis technique based on Photoshop software (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA) (14). A fibrosis ratio, the total area of fibrosis within the aneurysmal cavity and neck divided by the total area of the aneurysmal cavity and neck, was calculated for each aneurysm.
COLLAGEN GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS
Collagen-I gene expression level was measured by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Briefly, total RNA was isolated from the formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections using RNeasy FFPE kit (Qiagen, CA). First-strand cDNAs were synthesized from 500 ng of total RNA using Superscript III First Strand Synthesis (Invitrogen, CA). The quantitative real-time RT–PCR was performed for collagen-I and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) using IQ SYBR Green Supermix in an iCycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA). The primer sequences for collagen-1 and GAPDH were constructed as described previously (29). Thermal cycling parameters were 90°C for 8 min and 30 sec (DNA polymerase activation), followed by 40 cycles of amplifications at 95°C for 30 s and 60°C for 1 min. Relative levels of mRNA expression were normalized in all of the samples analyzed, with respect to the levels of GAPDH amplification.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Parametric data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). If there was a main effect then post hoc analysis would be conducted with a Tukey post hoc test. Non-parametric data were examined using a Kruskal-Wallis test; a non-parametric test of independent samples, similar to ANOVA.
RESULTS
ANGIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
Aneurysm sizes and coil packing densities are summarized in Table 1. There were no significant differences in aneurysm size or packing density among groups (ANOVA, p>0.05). Coil compaction was noted in one of six subjects in Group 1 and three of eight subjects in Group 3. All the remaining aneurysms in the test and control groups showed stable occlusion. There were no differences in coil compaction between groups (Kruskal-Wallis test, p>0.05).
Table 1.
Summary of aneurysm sizes, volume and coil packing density by group
| Neck (mm) |
Width (mm) |
Height (mm) |
Packing density (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1, n=6 | 3.22 ± 0.58 | 3.36 ± 0.34 | 7.43 ± 1.01 | 35.02 ± 4.84 |
| Group 2, n=5 | 3.98 ± 0.81 | 3.24 ± 0.69 | 7.15 ± 2.68 | 32.08 ± 2.11 |
| Group 3, n=8 | 3.98 ± 0.95 | 3.73 ± 0.74 | 9.32 ± 2.33 | 39.95 ± 9.87 |
VITAMIN C LEVELS
The blood vitamin C levels were significantly higher in Group 3 (45.4±9.0 mM, p<0.001) and Group 2 (38.6±8.9 mM, p=0.005) compared to Group 1 (21.1±3.6 mM). There was an increase in the vitamin C level in Group 3 compared to Group 2, but this difference did not reach statistical significance (ANOVA, p>0.05).
QUALITATIVE HISTOLOGY
Group 1 (Control)
There was a thin membranous tissue covering the neck orifice in the aneurysms (four of six subjects). Microscopy demonstrated that poorly organized thrombus filled the majority of the aneurysm cavity in four of six aneurysms. Collagen deposition was minimal and scant in these subjects. Loose connective tissue, associated with a thin collagen matrix, filled the aneurysmal cavity in three of six subjects (Figure 1). An endothelial lined, thin neointimal layer that bridged the aneurysm neck was noted in three of six aneurysms. Unorganized fibrin was noticed across the neck in the remaining three subjects. There was mild, scattered chronic inflammation infiltrating the organized loose connective in all the aneurysm samples.
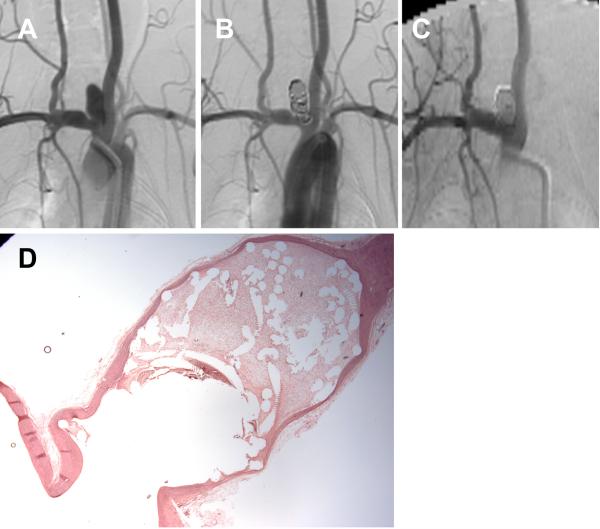
Figure 1.
A set of representative images of a single aneurysm packed with platinum coils (control group). (A) Angiogram of the aneurysm cavity pre-embolization. (B) Aneurysm cavity is completely occluded immediately after coil embolization. (C) Aneurysm is stable 12 weeks post-embolization. (D) Loose connective tissue filled in the aneurysm cavity (H&E; magnification=12.5×).
Group 2 (Vitamin C received via feed)
Three of five aneurysms had organized loose connective tissue, which completely filled the aneurysm cavity. These same three subjects also had endothelial-lined, thin layer of neointima which completely crossed the neck/parent artery interface. In the other two subjects, loose connective tissue completely filled the aneurysm cavity; thin layers of both neointima and unorganized fibrin were present at the neck interface in these latter two subjects (Figure 2). Collagen deposition was minimal in all subjects. Microscopic coil compaction at the neck interface was present in all 5 subjects.
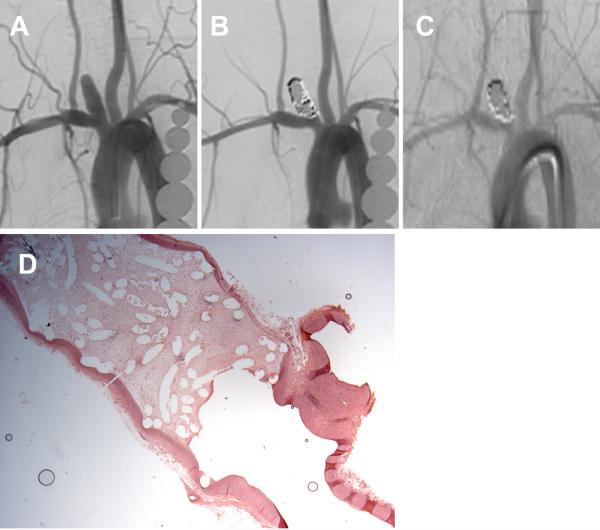
Figure 2.
A set of representative images of a single aneurysm packed with platinum coils (vitamin C fed group). (A) Angiogram of the aneurysm cavity pre-embolization. (B) Aneurysm cavity is completely occluded immediately after coil embolization. (C) Aneurysm is stable 12 weeks post-embolization. (D) Aneurysm cavity is completely filled with loose connective tissue and unorganized fibrin is covering part of the neck interface (H&E; magnification=12.5×).
Group 3 (Vitamin C received via pill)
Gross examination showed that three of eight subjects had a thin, membranous tissue partially covering the neck orifice. These three subjects had organized loose connective tissue which filled the aneurysm cavity completely, and had an endothelial-lined, thin layer of neointima and unorganized fibrin at the parent artery/neck interface. A separate three subjects had an endothelial-lined, thin layer of neointima completely crossing the neck interface. One of these latter three subjects had organized, loose, connective tissue filling the cavity while the other two had large areas of unorganized thrombus within the cavity. One of eight subjects had unorganized fibrin crossing the neck; loose connective tissue and unorganized thrombus were noted within aneurysmal cavity in this subject (Figure 3). The remaining subject had poorly organized thrombus filling respective dome and covering the parent artery/neck interface. Microcompaction of coils and minimal collagen deposition was noted in all subjects.
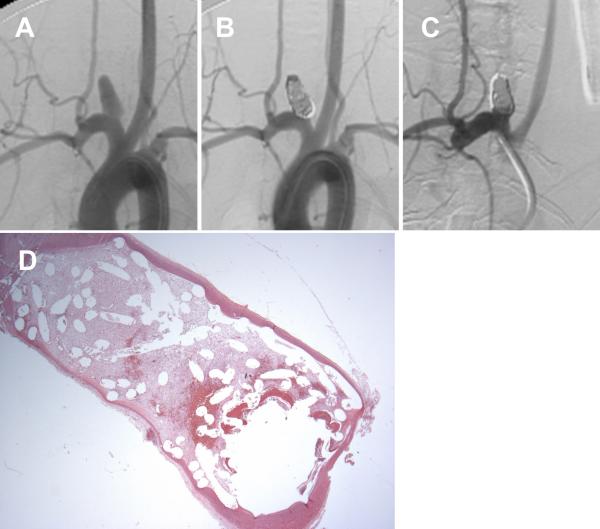
Figure 3.
A set of representative images of a single aneurysm packed with platinum coils (vitamin C pilled group). (A) Angiogram of the aneurysm cavity pre-embolization. (B) Aneurysm cavity is completely occluded immediately after coil embolization. (C) Aneurysm recanalization 12 weeks post-embolization; note that part of the aneurysm cavity has refilled with contrast, indicating recanalization. (D) Remnant neck and unorganized thrombus crossing the neck interface (H&E; magnification=12.5×).
QUANTITATIVE HISTOLOGY
The histological scoring data for control and vitamin C administered groups are shown in Table 2. There were no significant differences in the mean gross neck score, micro-compaction, dome score and total score among three groups studied. There was no difference in the fibrosis ratio between test and control groups.
Table 2.
Summary of histologic scores by group
| Gross neck | Micro-neck | Micro- compaction |
Dome | Total score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1, n=6 | 0.67±0.52 | 2.42±0.49 | 0.17±0.41 | 3.67±0.98 | 5.38±1.08 |
| Group 2, n=5 | 0.40±0.55 | 2.6±0.55 | 0±0 | 3.80±0.45 | 5.30±0.84 |
| Group 3, n=8 | 1.50±1.31 | 1.94±1.15 | 0.38±0.74 | 3.13±1.13 | 5.22±1.84 |
COLLAGEN-I GENE EXPRESSION
To determine the effect of vitamin C on the gene expression level of collagen-I, we performed real time RT-PCR experiments. There was no significant difference in the collagen-I gene expression in vitamin C medicated rabbits and control rabbits (Fold change 1.08 ± 0.96, n=5 for both control and vitamin C pilled groups).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we evaluated the effect of systemic administration of vitamin C on the healing of aneurysms embolized with platinum coils. Our results suggest that systemic vitamin C supplementation does not improve the long term histological healing of rabbit aneurysms following platinum coil embolization as evidenced by lack of cellularity and fibrosis in the aneurysm cavity as well as dearth of neointimal coverage at the neck of the aneurysm. These negative results were found even though adequate levels of vitamin C were achieved in both test groups. Thus, clinical trials of vitamin C to improve coil stability likely are not warranted.
The dose of vitamin C was selected based on our preliminary dose escalation study, where four groups of aneurysms were purposely loosely packed with coils (packing density <25%) and animals in each group, respectively, were fed a diet containing 0, 866, 1,732 and 4,330 ppm vitamin C for 12 weeks. These parts per million correspond to 0, 40, 80 and 200 mg vitamin C per kg body weight based on the daily food intake of rabbits. At the end of 12 weeks, serum vitamin C levels were measured at sacrifice. Our analysis showed that there were no significant differences in histological scores among control and vitamin C fed groups, but mean total histologic score and serum vitamin C levels were higher in Group 3 compared to other groups. Since we did not observe significant changes in histological healing after aneurysms loosely embolized with coils in the dose study, we embolized aneurysms with coils packed as tightly as possible, the goal was to achieve 30% packing density by volume, in the present study. The selected vitamin C dose in the present study (1,732 ppm; equivalent to 80 mg/kg body weight) was the dose that produced the highest serum vitamin C concentrations and histological healing among the groups in the dose study.
Local delivery of collagen fibers into the aneurysm cavity has shown to improve the healing of aneurysms (17). Instead of employing local delivery to the aneurysm cavity, we hypothesized that systemic delivery of vitamin C might improve collagen deposition in the coil-embolized aneurysms. We have previously reported a relatively small study in rabbit aneurysms suggesting efficacy of vitamin C supplementation (30). In the current study we substantially enhanced the methodology as compared to the prior study. First, we controlled packing density across groups, since previous reports have shown improved healing with higher packing density and poorer healing in the aneurysms with reduced packing densities (31). Second, we compared two methods of vitamin C medication delivery and confirmed adequate levels were achieved. In this large and well-controlled study, we failed to demonstrate improved aneurysmal healing as evidenced by lack of positive influence of vitamin C on the gene expression and deposition of collagen. Even though vitamin C has been shown to increase collagen synthesis and to decrease inflammatory responses in the wound healing process, vitamin C supplementation has not been demonstrated to increase wound closure rate in otherwise healthy individuals(32-34). These findings suggest that vitamin C may only affect specific facets of the wound healing response.
The present study had several limitations. We used an elastase-induced rabbit aneurysm model. This rabbit aneurysm is similar to human aneurysm histologically, morphologically and hemodynamically (12, 35); aneurysms created using elastase share some molecular features with human intracranial aneurysms (15, 36) and they mimic the healing seen in human aneurysms after embolization with platinum coils (12). However, rabbits can synthesize their own vitamin C while humans cannot. Employing animals that cannot synthesize their own vitamin C would be more controlled model to address the effects of vitamin C supplementation. We acknowledge that the ordinal scale for grading the histological findings has not been validated. Nevertheless, this method has been widely used by several investigators (37-39).
CONCLUSION
Vitamin C supplementation following platinum coil embolization may not improve long-term occlusion of aneurysms.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported in part by the American Heart Association Scientist Development grant (AHA 09SDG2160146–01) and the National Institutes of Health grant (R01NS076491)We express our gratitude to Dr Arash Ehteshami Rad and Dr Soon Chan Kwon for their generous help with the study. .
REFERENCES
- 1.Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1398–403. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000073841.88563.E9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferns SP, Sprengers ME, van Rooij WJ, Rinkel GJ, van Rijn JC, Bipat S, et al. Coiling of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review on initial occlusion and reopening and retreatment rates. Stroke. 2009 Aug;40(8):e523–9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.553099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG. Durability of aneurysm embolization with matrix detachable coils. Neurosurgery. 2006 Jan;58(1):51–9. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000194190.45595.9e. discussion -9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gaba RC, Ansari SA, Roy SS, Marden FA, Viana MA, Malisch TW. Embolization of intracranial aneurysms with hydrogel-coated coils versus inert platinum coils: effects on packing density, coil length and quantity, procedure performance, cost, length of hospital stay, and durability of therapy. Stroke. 2006 Jun;37(6):1443–50. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000221314.55144.0b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gunnarsson T, Tong FC, Klurfan P, Cawley CM, Dion JE. Angiographic and clinical outcomes in 200 consecutive patients with cerebral aneurysm treated with hydrogel-coated coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Oct;30(9):1657–64. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ishii A, Murayama Y, Nien YL, Yuki I, Adapon PH, Kim R, et al. Immediate and midterm outcomes of patients with cerebral aneurysms treated with Matrix1 and Matrix2 coils: a comparative analysis based on a single-center experience in 250 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery. 2008 Dec;63(6):1071–7. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000334047.30589.13. discussion 7-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Piotin M, Spelle L, Mounayer C, Loureiros C, Ghorbani A, Moret J. Intracranial aneurysms coiling with matrix: immediate results in 152 patients and midterm anatomic follow-up from 115 patients. Stroke. 2009 Jan;40(1):321–3. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.520866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Linfante I, DeLeo MJ, 3rd, Gounis MJ, Brooks CS, Wakhloo AK. Cerecyte versus platinum coils in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: packing attenuation and clinical and angiographic midterm results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Sep;30(8):1496–501. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O’Hare AM, Fanning NF, Ti JP, Dunne R, Brennan PR, Thornton JM. HydroCoils, occlusion rates, and outcomes: a large single-center study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010 Nov;31(10):1917–22. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Klebe RJ, Rosenberger PG, Naylor SL, Burns RL, Novak R, Kleinman H. Cell attachment to collagen. Isolation of a cell attachment mutant. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jan;104(1):119–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McCarthy JB, Vachhani B, Iida J. Cell adhesion to collagenous matrices. Biopolymers. 1996;40(4):371–81. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1996)40:4%3C371::AID-BIP3%3E3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, et al. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical comparison of human, rabbit, and swine aneurysms embolized with platinum coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Nov-Dec;26(10):2560–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Szikora I, Seifert P, Hanzely Z, Kulcsar Z, Berentei Z, Marosfoi M, et al. Histopathologic evaluation of aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils or matrix detachable microcoils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006 Feb;27(2):283–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA, Kadirvel R, Helm GA, Lewis DA, et al. Endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms with use of fibroblast transfected with replication-deficient adenovirus containing bone morphogenetic protein-13 gene. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Apr;29(4):739–44. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA, Kadirvel R, Hunter LW, Zhan WZ, et al. Endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms by use of fibroblast-coated platinum coils: an angiographic and histopathologic study. Stroke. 2007 Jan;38(1):170–6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000252128.83405.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dawson RC, Krisht AF, Barrow DL, Joseph GJ, Shengelaia GG, Bonner G. Treatment of experimental aneurysms using collagen-coated microcoils. Neurosurgery. 1995 Jan;36(1):133–9. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199501000-00017. discussion 9-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kallmes DF, Fujiwara NH, Yuen D, Dai D, Li ST. A collagen-based coil for embolization of saccular aneurysms in a New Zealand White rabbit model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003 Apr;24(4):591–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Raymond J, Metcalfe A, Desfaits AC, Ribourtout E, Salazkin I, Gilmartin K, et al. Alginate for endovascular treatment of aneurysms and local growth factor delivery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003 Jun-Jul;24(6):1214–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Szikora I, Wakhloo AK, Guterman LR, Chavis TD, Dawson RC, 3rd, Hergenrother RW, et al. Initial experience with collagen-filled Guglielmi detachable coils for endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997 Apr;18(4):667–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Quaglino D, Fornieri C, Botti B, Davidson JM, Pasquali-Ronchetti I. Opposing effects of ascorbate on collagen and elastin deposition in the neonatal rat aorta. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;54(1):18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dunn DM, Franzblau C. Effects of ascorbate on insoluble elastin accumulation and cross-link formation in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle cultures. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4195–202. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lyons BL, Schwarz RI. Ascorbate stimulation of PAT cells causes an increase in transcription rates and a decrease in degradation rates of procollagen mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2569–79. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pinnel SR, Murad S, Darr D. Induction of collagen synthesis by ascorbic acid. A possible mechanism. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Dec;123(12):1684–6. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.12.1684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schwarz RI. Procollagen secretion meets the minimum requirements for the rate-controlling step in the ascorbate induction of procollagen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3045–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lewis DA, Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Danielson MA, Cloft HJ, et al. Morbidity and mortality associated with creation of elastase-induced saccular aneurysms in a rabbit model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Jan;30(1):91–4. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Altes TA, Cloft HJ, Short JG, DeGast A, Do HM, Helm GA, et al. 1999 ARRS Executive Council Award Creation of saccular aneurysms in the rabbit: a model suitable for testing endovascular devices. American Roentgen Ray Society. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Feb;174(2):349–54. doi: 10.2214/ajr.174.2.1740349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dai D, Ding YH, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF. A proposed ordinal scale for grading histology in elastase-induced, saccular aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006 Jan;27(1):132–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dai D, Ding YH, Danielson MA, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, et al. Modified histologic technique for processing metallic coil-bearing tissue. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005 Sep;26(8):1932–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Monjo M, Lamolle SF, Lyngstadaas SP, Ronold HJ, Ellingsen JE. In vivo expression of osteogenic markers and bone mineral density at the surface of fluoride-modified titanium implants. Biomaterials. 2008 Oct;29(28):3771–80. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dai D, Ding YH, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF. Can vitamin c supplement improve histologic healing of aneurysm following platinum coil embolization? A prospective study. Proceedings of the 9th Congress of World Federation of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology.2007. p. 13.p. M44. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Relationship between aneurysm volume and histologic healing after coil embolization in elastase-induced aneurysms: a retrospective study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Jan;29(1):98–101. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Silverstein RJ, Landsman AS. The effects of a moderate and high dose of vitamin C on wound healing in a controlled guinea pig model. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1999 Sep-Oct;38(5):8333–8. doi: 10.1016/s1067-2516(99)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Thompson C, Fuhrman MP. Nutrients and wound healing: still searching for the magic bullet. Nutr Clin Pract. 2005 Jun;20(3):331–47. doi: 10.1177/0115426505020003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Vaxman F, Olender S, Lambert A, Nisand G, Aprahamian M, Bruch JF, et al. Effect of pantothenic acid and ascorbic acid supplementation on human skin wound healing process. A double-blind, prospective and randomized trial. Eur Surg Res. 1995;27(3):158–66. doi: 10.1159/000129395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Short JG, Fujiwara NH, Marx WF, Helm GA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Elastase-induced saccular aneurysms in rabbits: comparison of geometric features with those of human aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Nov-Dec;22(10):1833–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mangrum WI, Farassati F, Kadirvel R, Kolbert CP, Raghavakaimal S, Dai D, et al. mRNA expression in rabbit experimental aneurysms: a study using gene chip microarrays. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 May;28(5):864–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ionita CN, Natarajan SK, Wang W, Hopkins LN, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, et al. Evaluation of a second-generation self-expanding variable-porosity flow diverter in a rabbit elastase aneurysm model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Sep;32(8):1399–407. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Killer M, Hauser T, Wenger A, Richling B, Ladurner G. Comparison of experimental aneurysms embolized with second-generation embolic devices and platinum coils. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2009 May;151(5):497–505. doi: 10.1007/s00701-009-0237-1. discussion. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tsumoto T, Matsumoto H, Terada T, Tsuura M, Itakura T, Hamamoto T. A polyvinyl alcohol core coil containing basic fibroblast growth factor evaluated in rabbits with aneurysms induced by elastase. Neurosurgery. 2007 Jul;61(1):160–6. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000279737.07683.57. discussion 6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]