Abstract
Cox14p and Coa3p have been shown to regulate translation of the mitochondrial COX1 mRNA and to be required for assembly of cytochrome oxidase. We present evidence that Cox14p and Coa3p stabilize previously identified Cox1p intermediates and that in the absence of either protein, Cox1p aggregates with itself and other mitochondrial gene products, including cytochrome b, Var1p and Cox2p. Our evidence suggests that Cox1p assembly intermediates are in close proximity to other mitochondrially translated proteins and that an important function of Cox14p and Coa3p is to prevent Cox1 from entering into unproductive aggregation pathways.
Keywords: Mitochondria, cytochrome oxidase, biogenesis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Cox14p, Coa1p, Coa3p, Cox1p stability
1. Introduction
Yeast cytochrome oxidase (COX)2 is composed of 11 distinct subunits three of which make up the catalytic core of the enzyme, are encoded in mitochondrial DNA. Cox1p, an important catalytic subunit containing the cytochrome a and a3 centers, is translationally regulated by at least four accessory proteins, Mss51p [1], Cox14p [2], Coa1p [3] and Coa3p [4, 5]3. Newly translated Cox1p interacts with Mss51p, its specific translational activator, and with Cox14p, Coa3p and Coa1p [2, 3, 6–8]. Current models envision translation of Cox1p to be down-regulated until Mss51p, sequestered by its interaction with newly translated Cox1p, is released by a downstream event during COX assembly. The complexity of this regulatory pathway and more generally of COX assembly, is underscored by recent evidence indicating the existence of at least five different Cox1p assembly intermediates [9].
The involvement of Cox14p and Coa3p in regulating Cox1p expression is supported by their physical association with Mss51p and Cox1p and more importantly by the observation that cox14 and coa3 mutants, on their own or in combination with other mutations that arrest COX assembly, display normal translation of Cox1p [2, 4, 5]. Cox14p and Coa3p, in addition to their function in regulating Cox1p translation have also been inferred to play a role in COX assembly as mutations in either protein produce a COX deficient phenotype [4, 5, 10].
In this communication we report a new function of Cox14p and Coa3p in Cox1p biogenesis, deduced from the radiolabeled products detected following in organello labeling of mitochondria from different mutants. Our evidence indicates that one, if not the main, function of both proteins is to prevent Cox1p from forming assembly-incompetent aggregates. The aggregation of Cox1p with itself and with cytochrome b, Var1p and Cox2p in cox14 and coa3 mutants suggests that newly translated mitochondrial gene products may be in close proximity to one another in the inner membrane.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Strains and growth media
The genotypes and sources of the strains of S. cerevisiae used in this study are listed in Table 1. The compositions of liquid and rich glucose (YPD), galactose (YPGal) and glycerol/ethanol (YEPG) media used to grow wild type and mutant yeast have been described [10].
Table 1.
Genotypes and Sources of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strains
| Strain | Genotype | mtDNA | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| W303-1A | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 | ρ+ | A |
| W303-1B | MATα ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 | ρ+ | A |
| MRS-3B | MATα ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 arg8::HIS3 | ρ+ (S288C) | [9] |
| aW303ΔCOA3 | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coa3::HIS3 | ρ+ | This study |
| aW303ΔCOX4 | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 cox4::URA3 | ρ+ | This study |
| aW303ΔCOX4/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 cox4::URA3 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| aW303ΔCOX14/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 cox14::TRP1 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| aW303ΔCOA3/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coa3::HIS3 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| aW303ΔCOA1/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coa1:HIS3 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| DFK/COX1-HACρ− | MATα kar1-1 ade2-10 arg8::URA3 leu2Δura3-52 lys2 | ρ−(pCOX1/ST12) | [9] |
| MRS/COX1-HAC | MATα ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 arg8::HIS3 | COX1-HAC allele | [9] |
| aW303ΔCOX4/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 cox4::URA3 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| aW303ΔCOX14/COX1-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 cox14::TRP1 | COX1-HAC allele | This study |
| aW303/COA3-HAC | MATa ade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coa3::HIS3 leu2::COA3- HAC | ρ+ | This study |
| aW303/COA1-HAC | MATαade2-1 his3-1,15 leu2-3,112 trp1-1 ura3-1 coa1::HIS3 URA3::COA1-HAC | ρ+ | [9] |
R. Rothstein, Department of Human Genetics and Development, Columbia University
2.2 Labeling of mitochondrial gene products in isolated mitochondria and purification of Cox1p-HAC on protein C antibody beads
Mitochondria were prepared by the method of Herrmann et al [11] from yeast grown to early stationary phase in YPGal. In some experiments cells were transferred to fresh YPGal containing 2 mg/ml chloramphenicol for 2 hours of additional growth. Mitochondria (500 μg protein) were labeled at 24°C for 30 min with a mixture of 35S-methionine plus cysteine (3,000 Ci/mmol, MP Biochemicals, Solon, OH) in a total volume of 170 μl [12]. Translation was terminated by addition of puromycin to a final concentration of 100 μM. After an additional 10 min of incubation at 24°C, 1.2 volumes of 4% digitonin in extraction buffer was added and the mixture was centrifuged at 100,000 × gav for 10 min. Alternatively, mitochondria were pelleted by centrifugation at 10,000 gav for 10 min and extracted with 3% digitonin as above. The supernatant obtained after the high speed centrifugation was collected and mixed with 50 μl of packed protein C antibody beads (Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN). The beads were rotated at 4°C for 90 min and unadsorbed proteins were removed by centrifugation at 500 × gav for 30 seconds. The beads were then washed 3 times with 10 volumes of a buffer containing 0.5% digitonin, 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 2 mM CaCl2 and 200 mM NaCl (wash buffer) and eluted with 100 μl a buffer containing 0.5% digitonin, 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 7 mM EDTA and 200 mM NaCl (elution buffer). The beads in elution buffer were rotated at 4°C for 30 min proteins eluted with the EDTA were collected by centrifugation of the beads at 500 × gav for 30 seconds.
2.3 Construction of the plasmid expressing Coa3p with a C-terminal double HA plus protein C tag
Approximately 500 bp of 5′ UTR plus the COA3 coding sequence minus the termination codon was amplified from yeast nuclear DNA with primers coa3–5′ GCGAGATCTCTGTTGTCTCCTGCTAAAAAC and coa3-HA GGCGTCGACTCAA-GCGTAGTCTGGGACGTCGTATGGTGCCTTCTTCTTGGCTTCGTA. The PCR product was used as a template to amplify the HA tagged gene with primers coa3–5′ and Coa3-C GGCCTGCAGTCATTTACCATCGATTAATCTTGGATCTACTTGATCTT-CTCCTCCAGCGTAGTCTGGGACGTCGTATGG. The resultant product consisted of 500 bp of 5′-UTR followed by the coding sequence, the HA tag, 3 glycine codons and ending with the protein C epitope. The fusion gene was digested with XbaI and PstI and cloned into YIp351 [13] to yield pG127/ST3, which was linearized at the LEU2 gene for homologous recombination [14] in a coa3 null mutant.
2.4 Miscellaneous Procedures
Preparation and ligation of DNA and transformation of E. coli were done by standard methods [15]. Yeast was transformed by the lithium acetate method of Schiestl and Gietz [16]. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE on different concentrations of polyacrylamide gels in the buffer system of Laemmli [17] and by BN-PAGE on 4–13% polyacrylamide gels as described [18]. Second dimensions SDS-PAGE were run on 12% polyacrylamide gels. Western blots were treated with a monoclonal antibody against the HA tag followed by a second reaction with anti-mouse IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Proteins were detected with SuperSignal chemiluminescent substrate kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Protein concentrations were estimated by the Lowry procedure [19].
3. Results
3.1 Association of Coa3p with Cox1 assembly intermediates
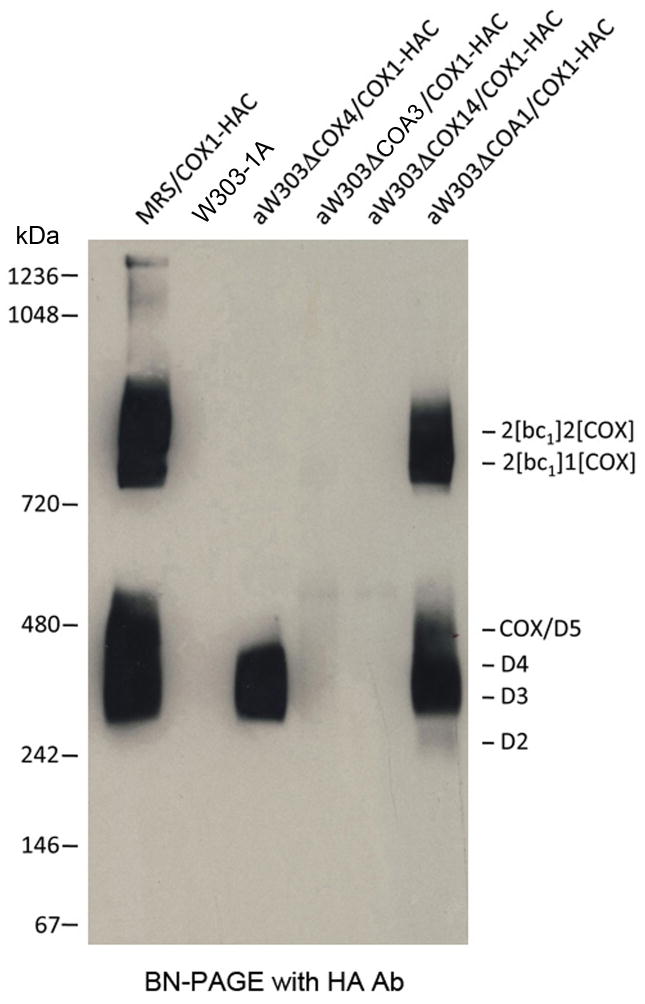
Newly translated Cox1p was previously shown to be present in five different high molecular weight complexes (D1–D5), which were inferred from pulse-chase experiments to be precursors of COX [9]. The intermediates were characterized with respect to their content of all currently known COX chaperones except Coa3p. Cox14p interacts physically with Coa3p and shares many of its properties [4, 5]. Cox14p is associated with newly translated Cox1p in four of the precursors (complexes D2–D5) [9]. To ascertain if Coa3p is present in the same intermediates as Cox14p, pull-down assays were performed on pulse-labeled mitochondria from a strain expressing Coa3p with a C-terminal HAC double tag consisting of HA followed by a protein C epitope (W303/COA3-HAC). The presence of this tag did not compromise the ability of yeast to grow on respiratory substrates (Fig. S1A). As controls we used mitochondria of the parental W303-1B strain lacking tagged Coa3p and of MRS/COX1-HAC, which expresses Cox1p with the double HAC tag [9]. Digitonin extracts of mitochondria from strains with tagged Coa3p or Cox1p, when purified on the protein C antibody beads, showed the same enrichment of radiolabeled Cox1p (Cox1p-HAC), Cox2p and Cox3p (Fig. S1B). Only background levels of the radiolabeled products were detected in the eluates of the control W303-1B parental strain. Separation of the eluates on blue native gels disclosed radiolabeled D2–D5 (Fig. S1C), as had previously been observed in the strain expressing tagged Cox14p [9]. The presence or absence of Coa3p in D1 could not be determined because of the very low level of labeling of this intermediate in this experiment.
3.2 Cox1 intermediates in cox14, coa3 and coa1 mutants
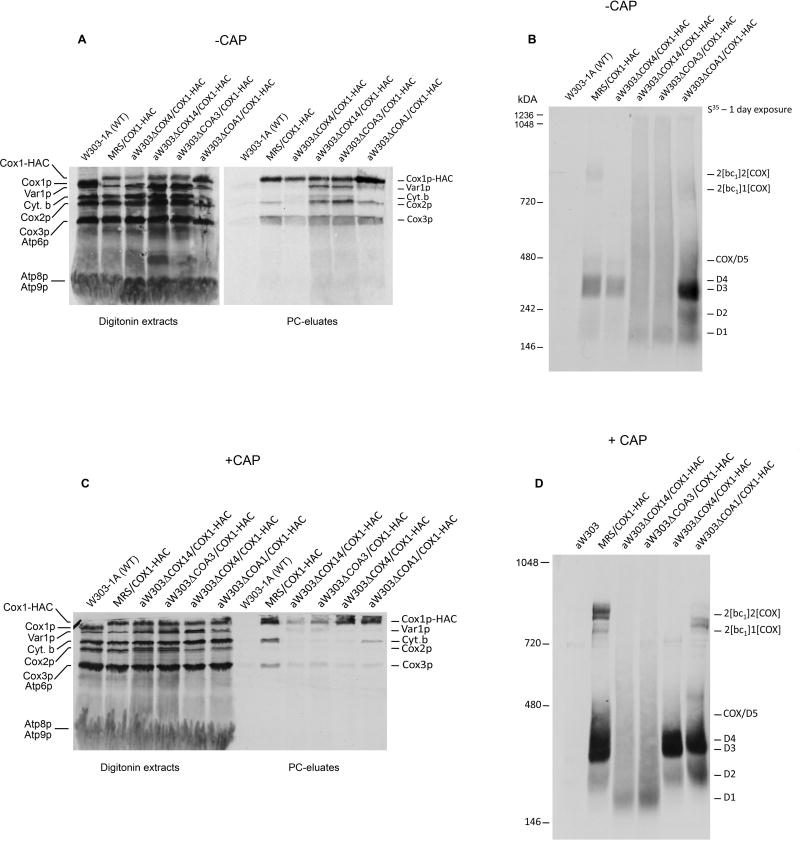
Both Cox14p and Coa3p have been shown to stabilize the Cox1p-Mss51p complex of D3 [2, 4, 5]. To ascertain if the stability of the other Cox1p intermediates also depends on these proteins, a mitochondrial genome containing the COX1-HAC fusion gene was introduced into cox14, coa3 and coa1 null mutants. Coa1p was of interest as it has been proposed to alter the interaction of Mss51p with Cox1p [4]. Cox1p intermediates were analyzed in the three mutants and in control cells that included respiratory competent strains with and without Cox1p-HAC and a cox4 mutant blocked in assembly of COX [20]. The steady-state concentrations of Cox1p intermediates were assessed by western analysis of Cox1p-HAC in digitonin extracts of mitochondria following purification on protein C antibody beads and separation on a blue native gel. In agreement with earlier results the antibody against the HA tag detected principally the more abundant intermediates D3 and D4 and the two supercomplexes of the respiratory competent and the coa1 mutant, which has a leaky growth phenotype on non-fermentable carbon sources. Over-exposure of the blot, however, also showed the presence of D5/COX and of a weaker D2 signal in the coa1 mutants (Fig. 1). While D3 and D4 were also present in the eluates of the cox4 mutant, the other intermediates were either absent or their concentrations were below the sensitivity of the assay. None of the Cox1p intermediates were detected in the cox14 and coa3 mutants (Fig. 1). A long exposure of the Western blot, however, revealed a diffuse background in the D3–D5 region of the coa3 mutant and to a lesser degree also in the cox14 mutant. Both mutants had a weak discrete signal above the 480 kDa marker and in the region corresponding to the smaller of the two supercomplexes (Fig 1).
Figure 1.
Supercomplexes, COX and Cox1p intermediates in different COX mutants. Mitochondria of the parental strain W303-1A expressing untagged Cox1p, of MRS/COX1-HAC and of cox4, cox14, coa3 and coa1 mutants, each harbouring the COX1-HAC fusion gene were extracted with digitonin and fractionated as described in Materials and Methods. The fraction eluted from the protein C antibody beads with EDTA was separated by BN-PAGE on 4–13% polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane and probed with a monoclonal antibody against the HA tag followed with peroxidase coupled anti-mouse antibody. Cox1p-HAC was detected with the Super Signal chemiluminescent substrate kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Mitochondria of the same strains, grown to early stationary phase with and without an additional 2 hours growth in the presence of chloramphenicol, were labeled in organello, extracted with digitonin and Cox1p-HAC purified on protein C antibody beads. All the eluates from the antibody beads except that of control mitochondria with untagged Cox1p, when separated by SDS-PAGE, showed the expected enrichment of Cox1p-HAC, Cox2p and Cox3p (Fig. 2A, 2C). Interestingly, there was also an enrichment of Var1p, cytochrome b and Cox2p in the cox14 and coa3 mutants. To a lesser extent this was also true of the coa1 mutant. The blue native gel of the eluates revealed radiolabeled Cox1p intermediates D1–D5 in mitochondria of all the strains grown in the absence of chloramphenicol except the control respiratory competent W303- 1A (with untagged Cox1p) and the cox14 and coa3 mutants (Fig. 2B). The latter two mutants had a band at the position of the smallest intermediate D1 but lacked any discernable bands corresponding to D2–D5. Instead the cox14 and coa3 mutants showed diffuse radioactivity extending from the D1 intermediate to the very top of the gel (Fig. 2B). Very similar results were obtained when mitochondria were isolated from cells that had been grown for 2 hours in the presence of chloramphenicol, except that D1 was reduced to undetectable levels (Fig. 2D). The additional growth in chloramphenicol was included to permit mitochondria to accumulate nuclear gene products that might be limiting and hence cause Cox1p to aggregate. The size heterogeneity of Cox1p-HAC appears to be specific to cox14, coa3 and partially to the coa1 mutant, as the cox4 (Figs. 2) and other mutants blocked in COX assembly fail to show this phenotype [9]. Aggregation of Cox1p-HAC was also seen when the fraction purified on protein C antibody beads from the cox14 mutant, was size-fractionated by sedimentation in a sucrose gradient (Fig. S2).
Figure 2.
Aggregates of Cox1p in cox14, coa3 and coa1 mutants. (A), (C). Mitochondria of the indicated strains grown in YPGal, with and without a final 2 hour incubation in fresh medium containing 2 mg/ml chloramphenicol, were labeled for 30 min and chased for 10 min after addition of puromycin. The mitochondria were extracted with 3% digitonin and purified on protein C antibody beads as described in Materials and Methods. The digitonin extracts (10%) and the EDTA eluates (45%) were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 17% polyacrylamide gel, transferred to nitrocellulose and exposed to X-ray film. The radiolabeled proteins are identified in the margins. (B), (D). The remainder of the eluates from the antibody beads was separated by BN-PAGE on a 4–13% polyacrylamide gel. The radiolabeled bands are marked in the margin.
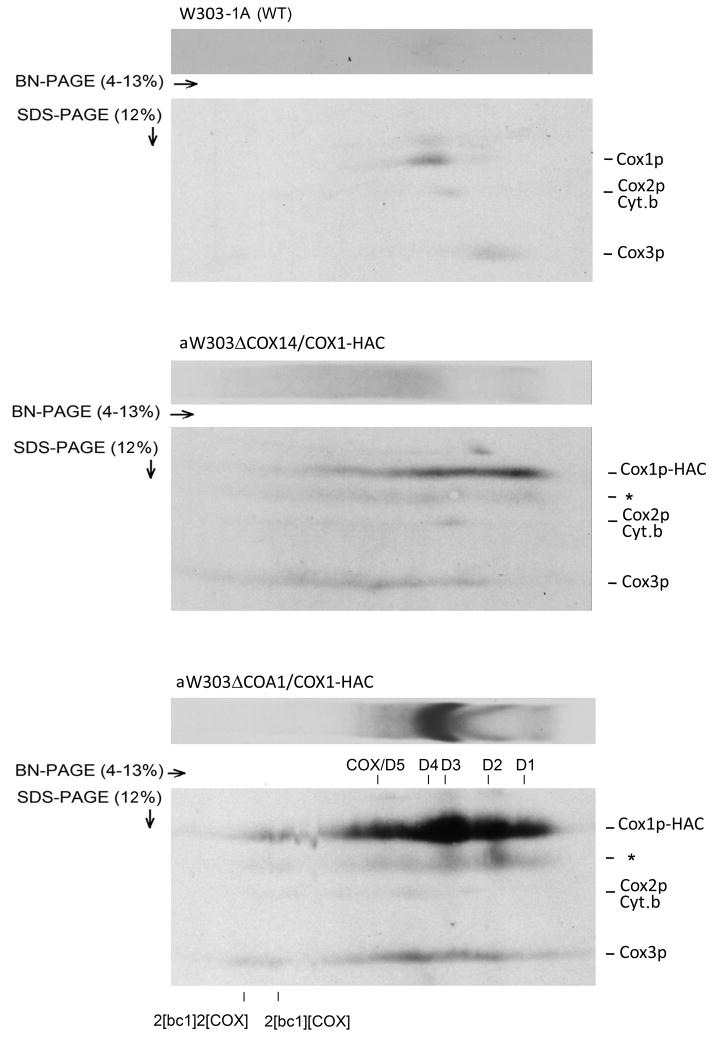
The enrichment of Var1p and cytochrome b in the antibody eluates of the cox14, coa3 and coa1 mutants suggested that Cox1p also aggregates with COX-unrelated proteins. To ascertain if Cox1p aggregates with the other mitochondrial gene products randomly, the eluates from the control strain (expressing untagged Cox1p) and from the cox14 and coa1 mutants were separated in the first dimension by BN-PAGE and in the second dimension by SDS-PAGE. The 2-D gel of the eluate from the cox14 mutant revealed that the radiolabeled bands corresponding to Cox1p, cytochrome b, Cox2p, and Cox3p were similarly distributed across the length of the first dimension (Fig. 3). The sucrose gradient analysis of the cox14 mutant confirmed aggregation of cytochrome b, Cox2p and Cox3p. This is consistent with random aggregation of Cox1p with itself and other newly translated mitochondrial gene products. Identical results were obtained with the coa3 mutant (not shown). The 2-D gel of the eluate from the coa1 mutant showed that most of Cox1p migrated as discrete bands corresponding to the supecomplexes and the different Cox1p intermediates. With the exception of a small fraction of radiolabeled Cox3p present in the supercomplexes, most of Cox3p migrated as a streak in the region between COX/D5 and D1 of the coa1 mutant (Fig. 3, lower panel). This is consistent with some aggregation of Cox1p with Cox3p, which normally is present only in the supercomplexes and COX/D5 (Fig. S1C, middle panel).
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional BN- and SDS-PAGE analysis of newly translated mitochondrial gene products associated with the Cox1p aggregates in cox14 and coa1 mutants. Mitochondria of the control strain with wild type mtDNA and of mutants expressing Cox1p-HAC were labeled and fractionated as in Fig. 2. The fractions purified on the protein C antibody beads were separated in two dimensions, transferred to a PVDF membrane and exposed to X-ray film. The band marked with an asterisk is probably a degradation product of Cox1p-HAC.
3.3 Evidence that the Cox1p aggregates of cox14 and coa1/coa3 mutants are formed in mitochondria
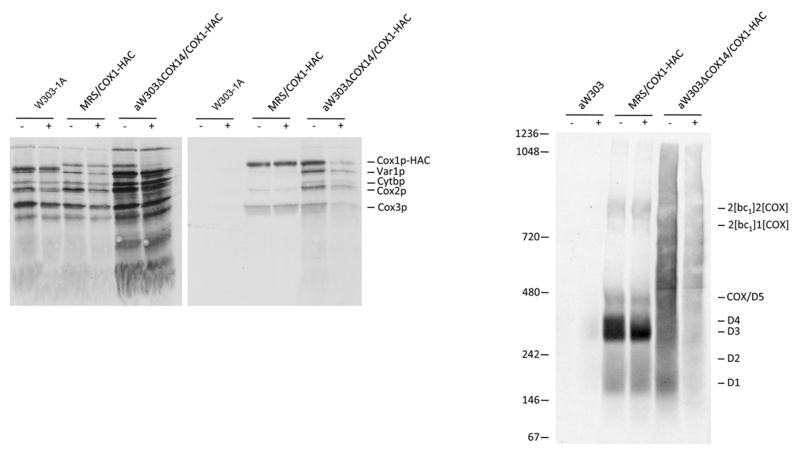
The Cox1p aggregates observed in cox14 and coa3 mutants may have originated in mitochondria or could have been formed after extraction with digitonin. Since non-specific interaction of hydrophobic proteins is a time dependent process, we reasoned that if the aggregates are formed after extraction, their sizes should increase upon incubation of the extracts prior to purification on protein C antibody beads. Mitochondria from the respiratory competent control strain and from cox14 and coa3 mutants were labeled and fractionated under the same conditions except that in one case the extracts were incubated 20 hours at 4°C before purification on antibody beads. The labeled products of the respiratory control strain MRS/COX1-HAC were nearly identical in the two samples (Fig. 4A, B), indicating the Cox1p intermediates are very stable and are neither degraded nor do they aggregate anew or further in the digitonin extract. In the cox14 mutant, however, the overnight incubation of the extract led to a substantial reduction in the amount of radiolabeled Cox1p-HAC. This was evident from the level of Cox1p-HAC detected following separation of the extracts by SDS-PAGE as well as the radioactivity seen in the radioautogram of the blue native gel (Figs. 4A, B). Even though this experiment indicated an increased susceptibility of the aggregates to proteolytic degradation, the relative size distribution of the Cox1p aggregates was not noticeably affected by the overnight incubation of the digitonin extract.
Figure 4.
Effect of incubation of a digitonin extract on the state of aggregation of Cox1p in a respiratory competent strain and in a cox14 mutant. Mitochondria labeled for 30 min and chased with puromycin were extracted with digitonin and the extracts purified on protein C antibody beads with (+) and without (−) a prior 20 hours incubation at 4°C. (A) Samples of the digitonin extracts (10% of total) and eluates from the beads (45% of total) were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 17% polyacrylamide gel by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and exposed to X-ray film. (B) The rest of each sample was applied to a 4–13% blue native gel and after electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane and exposed to X-ray film. The identity of the different radiolabeled products and of molecular weight standards is indicated in the margin.
4. DISCUSSION
Newly synthesized Cox1p interacts with its translational activator Mss51p [1, 6] to form an assembly intermediates that have been proposed to be stabilized by Cox14p and Coa3p [2, 4, 5]. At least 4 different Cox1p intermediates have been identified that contain Mss51p, Cox14p and, as shown in the present study, also Coa3p. Some Cox1p intermediates also contain Coa1p and the nuclear encoded subunits Cox5ap and Cox6p [4, 9]. The sequestration of Mss51p prevents it from exercising its role in Cox1p translation until it is disengaged from the complex at a later assembly step [2, 6, 11]. This regulatory loop is currently believed to be the mechanism by which mitochondrial translation of Cox1p is coupled to it subsequent utilization for COX assembly, much in the same way as translation of certain proteins on chloroplast ribosomes depends on their assembly into photosynthetic complexes [21].
Cox14p and Coa3p have also been implicated in COX biogenesis as mutations in the respective genes elicit a severe COX deficiency. The relationship between the functions of Cox14p and Coa3p in regulating translation of Cox1p and COX assembly has not been delineated. The studies described in this communication help to account for the COX assembly defect of cox14 and coa3 mutants. The observed polymerization of Cox1p into a heterogeneous collection of different sized aggregates indicates that Cox14p, Coa3p and to a lesser degree Coa1p play an important role in stabilizing Cox1p intermediates. A reasonable interpretation, and one consistent with all the data, is that in the absence of either Cox14p or Coa3p, the Cox1p-Mss51p complex is either prevented from forming, or is readily dissociated and as a result Cox1p is free to be channeled into irreversible and unproductive aggregation pathways.
Our evidence indicates that the Cox1p aggregates present in the antibody purified fractions of cox14 and coa3 mutants are most likely formed in situ following their translation in mitochondria rather than after solubilization of Cox1p with digitonin. This is supported by the similarity in the size-distribution of the Cox1p aggregates in the eluates obtained from the digitonin extract that had been purified on the antibody beads immediately after extraction or after an added period of incubation at 4°C. Most of the aggregates migrate below the 720 kDa maker. If the aggregation had occurred after solubilization, the overnight incubation would have been expected to cause further polymerization of Cox1p into larger aggregates.
It is significant that the Cox1p aggregates include mitochondrial gene products unrelated to COX. This would suggest that Cox1 and some of the other mitochondrially translated proteins detected in the aggregates are in close proximity to one another in the mitochondrial inner membrane. The presence in the Cox1p aggregates of Var1p, the only endogenously expressed protein component of mitochondrial ribosomes, is not altogether surprising as this water soluble protein has been shown to be translated also at the inner membrane [22]. One possibility is that the mitochondrial gene products of COX and the bc1 complex are inserted into a physically identical or distinct but proximal compartment of the inner membrane where the partner subunits are matured and assembled. Biogenesis of the two complexes may, therefore, be not only temporally but also physically coordinated to yield a supercomplex of bc1 and COX. According to this model, the absence of ATP synthase subunits in the Cox1p aggregates suggests that assembly of this complex occurs in a separate compartment. This is consistent with the absence of evidence for an association of the ATP synthase with the bc1/COX supercomplexes (Heinemeyer et al, 2007: Mileykovskaya et al, 2012).
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Coa3p is associated with the same four Cox1p assembly intermediates as Cox14p.
Cox14p and Coa3p stabilize four Cox1p assembly intermediates.
Cox1p aggregates with other mitochondrial gene products in cox14 or coa3 mutants.
Aggregated Cox1p is incompetent in assembling into cytochrome oxidase.
Some newly translated mitochondrial gene products are proximate in the membrane.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health Research grant GM50187.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used: COX, cytochrome oxidase; BN, blue native; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; SDS, sodium dodecyl sulfate; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA.
Coa3p, also called Cox25p, was identified as a component of the Cox1p-Mss51p complex independently in two different laboratories (see references 4 and 5). The standard name Coa3p is used in this communication.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Perez-Martinez X, Broadley SA, Fox TD. Mss51p promotes mitochondrial Cox1p synthesis and interacts with newly synthesized Cox1p. EMBO J. 2003;22:5951–5961. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barrientos A, Zambrano A, Tzagoloff A. Mss51p and Cox14p jointly regulate mitochondrial Cox1p expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 2004;23:3472–3482. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pierrel F, Bestwick ML, Cobine PA, Khalimonchuk O, Cricco JA, Winge DR. Coa1 links the Mss51 post-translational function to Cox1 cofactor insertion in cytochrosme c oxidase assembly. EMBO J. 2007;26:4335–4346. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mick DU, Vukotic M, Piechura H, Meyer HE, Warscheid B, Deckers M, Rehling P. Coa3 and Cox14 are essential for negative feedback regulation of COX1 translation in mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 2010;191:141–154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fontanesi F, Clemente P, Barrientos A. Coa3 teams up with Mss51, Ssc1, and Cox14 to regulate mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 expression and assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:555–566. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Perez-Martinez X, Butler CA, Shingu-Vazquez M, Fox TD. Dual functions of Mss51 couple synthesis of Cox1 to assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20:4371–4380. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-06-0522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fontanesi F, Soto IC, Horn D, Barrientos A. Mss51 and Ssc1 facilitate translational regulation of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:245–259. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00983-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mick DU, Fox TD, Rehling P. Inventory control: cytochrome c oxidase assembly regulates mitochondrial translation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:14–20. doi: 10.1038/nrm3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McStay GP, Su CH, Tzagoloff A. Modular assembly of yeast cytochrome oxidase. Mol Biol Cell. 2013 doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-10-0749. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Glerum DM, Koerner TJ, Tzagoloff A. Cloning and characterization of COX14, whose product is required for assembly of yeast cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:15585–15590. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.26.15585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Herrmann JM, Foelsch H, Neupert W, Stuart RA. Isolation of yeast mitochondria and study of mitochondrial protein translation. In: Celis JE, editor. Cell Biology: A Laboratory Handbook. I. San Diego: Academic Press; 1994. pp. 538–544. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rak M, Gokova S, Tzagoloff A. Modular assembly of yeast mitochondrial ATP synthase. EMBO J. 2011;30:920–930. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hill JE, Myers AM, Koerner TJ, Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986;2:163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rothstein RJ. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory. Manual. NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schiestl RH, Gietz RD. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989;16:339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wittig I, Braun HP, Schagger H. Blue native PAGE. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:418–428. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dowhan W, Bibtus CR, Schatz G. The cytoplasmically-made subunit IV is necessary for assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in yeast. EMBO J. 1985;4:179–184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Choquet Y, Wostrikoff K, Rimbault B, Zito F, Girard-Bascou J, Drapier D, Wollman FA. Assembly-controlled regulation of chloroplast gene translation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29:421–426. doi: 10.1042/bst0290421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fiori A, Mason TL, Fox TD. Evidence that synthesis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondrially encoded ribosomal protein Var1p may be membrane localized. Eucaryot Cell. 2003;2:651–653. doi: 10.1128/EC.2.3.651-653.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heinemeyer J, Braun HP, Boekema EJ, Kouril R. A structural model of the cytochrome c reductase/oxidase supercomplex from yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:12240–12248. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610545200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mileykovskaya E, Penczek PA, Fang J, Mallampalli VK, Sparagna GC, Dowhan W. Arrangement of the respiratory chain complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae supercomplex III2IV2 revealed by single particle cryo-electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:23095–23103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.367888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.