Abstract
The role of β-catenin in skeletal development and osteogenic cell differentiation is well established, but the molecular mechanisms attending these effects remain largely unknown. We conducted a structure/function analysis of β-catenin to gain further insights on these mechanisms. Retroviral transduction of a full-length, constitutively active β-catenin mutant inhibited adipogenesis and stimulated osteoblast differentiation from multipotent embryonic fibroblasts (C3H10T1/2). However, N-terminal truncated β-catenin mutants with weak Tcf/Lef activity retained their pro-osteogenic action, as did a constitutively stabilized mutant lacking the C-terminal Tcf/Lef transactivation domain. Importantly, this Tcf/Lef-defective β-catenin did not suppress adipogenesis, and even elicited spontaneous adipogenesis when expressed in cells cultured in osteogenic conditions. Thus, Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity of β-catenin is critical for inhibition of adipogenesis, while it is dispensable for its pro-osteogenic effect. BMP-2 greatly enhanced both osteogenesis and adipogenesis in the presence of the C-terminally truncated mutant, though it selectively enhanced only osteoblast differentiation in cells transduced with the full-length, Tcf/Lef active β-catenin mutant. C3H10T1/2 cells produce BMP-4, and inhibition of endogenous BMP signaling by Noggin curtailed osteogenic differentiation by constitutively active β-catenin. Therefore, BMP signaling must be active for full induction by β-catenin of osteogenic differentiation from multipotent precursors. These data suggest that cooperative interactions between β-catenin and BMP signaling systems drive osteoblast cell fate specification and differentiation.
Introduction
β-catenin orchestrates cell fate decisions in diverse tissues and organisms. In vertebrates, β-catenin directs lineage allocation of intestinal stem cells, favoring proliferation of crypt cells over villous differentiation (Batlle et al., 2002). In the epidermis, it determines the differentiation of follicular keratinocytes while inhibiting epidermal lineages (Huelsken et al., 2001). During skeletal development, β-catenin favors osteoblast over chondrocyte fate in mesodermal and neural crest progenitors, thereby bearing an essential role in both endochondral and intramembranous ossification (Hu et al., 2005a; Day et al., 2005; Hill et al., 2005). In the adult skeleton, new osteoblasts are recruited from bone marrow stromal cells, which also give rise to adipocytes. In vitro studies demonstrate that canonical Wnts, via β-catenin and Tcf/Lef transcription factors, effectively block adipogenesis (Ross et al., 2000); and we previously showed a postnatal osteogenic to adipogenic shift in bone marrow stromal cells derived from transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative N-cadherin, which sequesters β-catenin on the cell surface (Castro et al., 2004). This differentiation defect was rescued by expression of activated β-catenin, suggesting β-catenin favors osteoblast over adipocyte commitment from undifferentiated precursors in the adult bone marrow microenvironment.
As an integral component of adherens junctions, β-catenin stabilizes cell-cell adhesion by binding to cadherins (Nelson et al., 2004). β-catenin is also part of canonical Wnt signaling, a cascade initiated by binding of Wnt(s) to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5 or 6 (LRP-5/6) and Frizzled co-receptors, resulting in inhibition of GSK-3β–mediated degradation of β-catenin. Stabilized β-catenin accumulates in the nucleus, stimulating transcription via the Tcf/Lef family of DNA-binding proteins (Cadigan et al., 1997; van Es et al., 2003). Abundant genetic and epidemiological data support a role for canonical Wnt signaling in skeletal development (Hartmann, 2006) and post-natal bone mass acquisition (Gong et al., 2001; Little et al., 2002; Boyden et al., 2002). However, ablation or activation of the β-catenin gene in the mouse does not phenocopy genetic ablation or constitutive activation of lrp5 (Kato et al., 2002; Babij et al., 2003), resulting in severe skeletal malformations (Hu et al., 2005a; Hill et al., 2005; Day et al., 2005). Furthermore, many components of the canonical Wnt pathway are involved in Wnt-independent signal transduction pathways (Xu et al., 2004; Nam et al., 2006; Fujino et al., 2003; Jia et al., 2005); and Wnt-independent transactivation of Tcf/Lefs by β-catenin can be stimulated by lysophosphatidic acid (Yang et al., 2005) or by prostaglandin E2 (Castellone et al., 2005). Therefore, while Wnts can certainly provide osteogenic signals, it is possible that the osteogenic role of β-catenin may not derive exclusively from generation of canonical Wnt (Tcf/Lef-dependent) signals.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are important in osteoblast specification, bone formation and maintenance (Zhao et al., 2002; Wan et al., 2005; Mishina et al., 2004; Mishina et al., 2004), but can elicit the development of multiple mesenchymal skeletal lineages (Ahrens et al., 1993). Interactions between BMPs and Wnt signaling have been studied by others in a variety of mesenchymal cell lines, suggesting that such interactions are essential for osteoblast differentiation (Rawadi et al., 2003). We previously demonstrated that β-catenin synergizes with BMP-2 to stimulate osteoblast differentiation in the mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line C3H10T1/2, and to induce new bone formation in mouse calvaria (Mbalaviele et al., 2005). More recently, β-catenin signaling has been shown to be critical for BMP-2 stimulation of ectopic bone formation in vivo (Chen et al., 2007). We hypothesized that interaction with BMP signaling offers one potential mechanism by which β-catenin, a ubiquitous signaling system, provides osteogenic cues to undifferentiated multipotent cells.
To test this hypothesis, we performed a structure/function analysis of β-catenin in C3H10T1/2 cells, which differentiate into osteoblasts or adipocytes in response to BMP treatment (Ahrens et al., 1993). Our results indicate that Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional activity of β-catenin is not required for its pro-osteogenic action, despite that it is necessary for inhibition of adipogenesis. Furthermore, we show that BMP signaling is required for full osteogenic stimulation by β-catenin, as well as adipogenesis.
Material and Methods
Reagents
β-catenin antibody was purchased from BD Transduction Laboratories (San Diego, CA); KT3-tag antibody from Covance (Princeton, NJ); TCF4 antibody from Upstate (Charlottesville, VA); BMP-2/4 antibody from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Purified recombinant human BMP-2 and murine Noggin were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO) and R&D systems, respectively. pTopFlash (Tcf/Lef-luc) was purchased from Promega (Madison, WI) and consists of the luciferase open reading frame preceded by 6 tandemly-arranged Tcf/Lef binding elements. p12X-SBE-Luc (SBE-luc) was a kind gift from Dr. Di Chen (University of Rochester, NY) and consists of 12 tandem Smad binding elements upstream of an osteocalcin minimal promoter and the luciferase open reading frame (Zhao et al., 2002). Primers were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Unless otherwise indicated, all other chemicals and reagents were purchased from Sigma.
Cell Culture and Differentiation
C3H10T1/2 murine embryonic fibroblast cells, obtained from ATCC (Manassas, VA) were maintained in basal medium of Eagle (BME; Gibco; Carlsbad, CA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Atlas Biologicals; Fort Collins, CO), 40 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin-G, and 100 mg/ml streptomycin, and incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2. To stimulate differentiation, we applied well-established methods, already described for the C3H10T1/2 cell line (Mbalaviele et al., 2005; Shin et al., 2000). Briefly, for osteogenic differentiation cells were seeded in 24-well dishes (105 cells per well) and cultured in osteogenic medium (10 mM β-glycerophosphate and 50 μg/ml ascorbic acid). As a marker of osteoblast lineage, ALP activity was assessed after 6–7 days in culture using a biochemical assay and normalized to protein content. In some experiments, enzyme activity was detected by direct staining in fixed cells (Mbalaviele et al., 2005). For adipogenic differentiation, C3H10T1/2 cells were cultured in adipogenic medium (5 μg/ml insulin, 50 μM indomethacin, and 0.1 μM dexamethasone) for 10 days, and adipocytes were identified after fixation by the presence of lipid droplets stained using Oil Red O (Mbalaviele et al., 2005; Shin et al., 2000).
Expression of β-catenin mutants in C3H10T1/2
β-catenin cDNAs for wild type, mutGSK, ΔN90, and ΔN151 were kind gifts from Dr. James Nelson (Stanford University, Stanford, CA). mutGSK is full length β-catenin containing four point mutations in the CK1 (S45A) and GSK3β (S33/37T41A) phosphorylation domain. ΔN90, and ΔN151 are N-terminal truncation mutants that include the phosphorylation domain (Barth et al., 1997). The cDNAs encoding β-catenin mutants were subcloned into the polylinker site of pIRES2-EGFP (BDBiosciences; San Diego, CA) using SacII and BamHI. IRES-EGFP or bicistronic β-catenin-IRES-EGFP constructs were subcloned into pLNCX2 retroviral vector (BD Biosciences; San Diego, CA) using XhoI and NotI. We also generated a C-terminally truncated β-catenin, mutGSKΔC, using a modified PCR strategy (Byrappa et al., 1995) and the pLNCX2-mutGSK-IRES-EGFP plasmid as a template. Briefly, amino acids 675–781 of mutGSK β-catenin were deleted in frame from the pLNCX2-mutGSK-IRES-EGFP plasmid by amplifying the plasmid template using a high fidelity polymerase (Pfu-Turbo; Stratagene; La Jolla, CA), a forward primer complementary to the C-terminal KT3 tag of mutGSK, and a reverse primer complementary to coding sequence for β-catenin amino acids 674–668. The purified PCR product was circularized with T4 DNA ligase and cloned. Retroviral particles were generated by using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen; Carlsbad, CA) to transfect pLNCX2 retroviral vectors into 293GPG packaging cells, which express MuLV gag-pol and vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein (VSV-G) under tetracycline regulation (Ory et al., 1996). Following removal of tetracycline repression, 293GPG conditioned media were collected daily and tested for ability to transduce C3H10T1/2 cells. Infectious fractions were pooled and supplemented with 6 μg/ml anionic polybrene. Subconfluent C3H10T1/2 cells were incubated in viral-conditioned media for 48 hr and selected for 7 d with 1 mg/ml G418 antibiotic. Transgene expression was assessed by both fluorescence microscopy (detection of EGFP) and SDS-PAGE/immunoblot (detection of transgenic β-catenin or C-terminal KT3 tag).
Luciferase Assay
Following a previously described method (Stains et al., 2003), cells were seeded in 24-well plates (4×104 cells per well), and the following day plasmids (0.4 μg/well of TopFlash or SBE-luc) were transfected using Lipofectamine2000 (Invitrogen; Carlsbad, CA) per manufacturer’s instructions. Transfection medium was replaced with complete medium containing additional treatments as indicated. Tcf/Lef-luc and SBE-luc were harvest after 24 hr of treatment. Luciferase activity was assessed in an Optocomp luminometer using a Luciferase kit (Promega; Madison, WI) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Since the Renilla reporters commonly used for normalization of transfection efficiency were modulated by some treatments used in this study, Firefly activity is shown as a ratio over the average of the control group. Assays were repeated >3 times.
Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
Whole cell protein extracts were prepared as previously described (Mbalaviele et al., 2005). Protein content was determined Pierce BCA kit, separated by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to PDVF membranes (Millipore; Billerica, MA). Membranes were blocked and probed in PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 and 5% non-fat dry milk. Antigen-antibody complexes were visualized by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:5000) and West-Pico detection (Pierce; Rockford, IL).
RNA Isolation and PCR
Briefly, 1 μg total RNA was isolated using RNeasy kit (Qiagen; Valencia, CA) and was reverse transcribed using Superscript II reverse transcriptase and oligo(dT)15 primers (Stains et al., 2003; Stains et al., 2005). Quantitative real time PCR was performed using SYBR green (Applied Biosystems; Foster City; CA) and an ABI Prism 7300 detector using these conditions: 40 cycles (95°C/10 min, 95°C/15 sec, 60°C/30 sec). Data were normalized to gapdh expression. For semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis, the following conditions were used: 95°C/5 min; 30 cycles (95°C for 30 sec, 55°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 30 sec); 72°C for 5 min. Primers: bmp-2 (RT-PCR) sense 5′-cggagactctctcaatggac-3′ and antisense 5′-gttcctccacggcttctagt-3′; bmp-4 (RT-PCR) sense 5′-ctcccaagaatcatggactg-3′ and antisense 5′-aaagcagagctctcactggt-3′; bmp-4 (QPCR) sense 5′-ttcctggtaaccgaatgctga-3′ and antisense 5′-cctgaatctcggcgacttttt-3′.
Statistical Analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Group means were compared by unpaired t-test.
Results
We first functionally characterized the transcriptional and osteogenic activities of 3 constitutively stabilized β-catenin mutants, mutGSK, ΔN90, and ΔN151 (Figure 1A) in C3H10T1/2 cells. Effective expression of these mutants, achieved by retroviral transduction using bicistronic constructs that also express EGFP, was verified by both EGFP fluorescence and Western blotting using antibody to β-catenin C-terminus. G418-resistant cells exhibited fluorescence in the green spectrum (Figure 1B), and the level of protein expression of each mutant was similar to endogenous β-catenin (Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
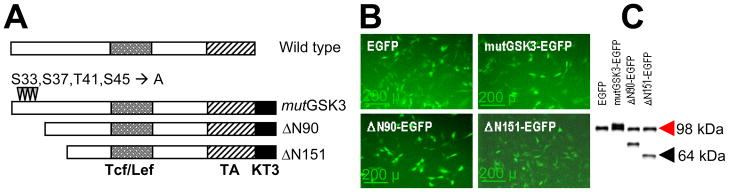
Structure and expression of β-catenin mutants. (A) Three different β-catenin mutants (mutGSK, ΔN90 and ΔN151) are shown below the basic structure of the wild type protein. The 4 phosphorylation sites (mutated to alanine in mutGSK3) at the N-terminus are shown, as well as the Tcf/Lef-binding domain (shaded), the transactivation domain (TA, hatched), and the KT3 epitope (solid). (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were transduced with VSV-G retroviruses encoding EGFP only, or a bicistronic construct comprised of one β-catenin mutant and IRES-EGFP. Fluorescence microscopy shows G418-resistant cells expressing EGFP. (C) Western analysis detects expression of the β-catenin mutant proteins in similar abundance to endogenous β-catenin (red arrowhead).
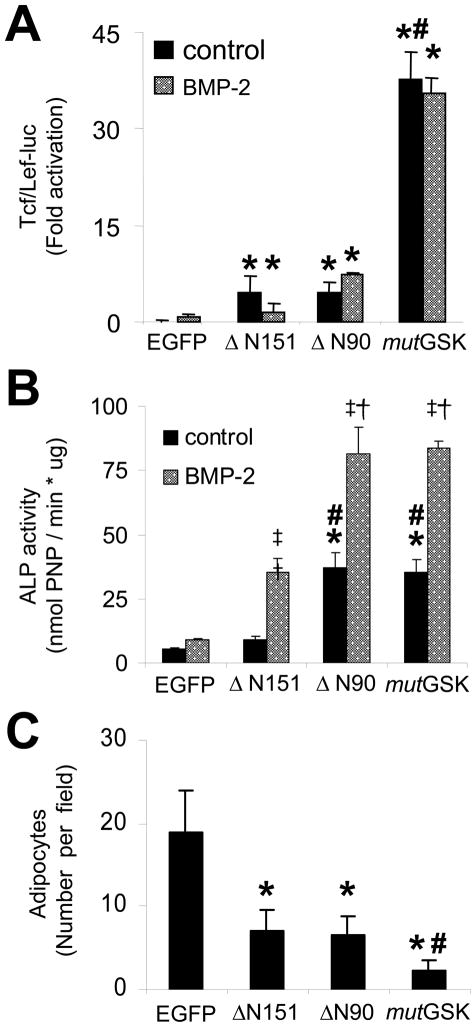
Each β-catenin mutant stimulated the activity of a Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional reporter (Tcf/Lef-luc). However, despite the similar abundance of protein expression (Figure 1C), mutGSK was a far more potent transcriptional co-activator than was ΔN90 or ΔN151 (Figure 2A, black bars). Consistent with our previous findings (Mbalaviele et al., 2005), BMP-2 treatment for 24 h did not activate Tcf/Lef-luc alone and did not enhance the effect of any β-catenin mutant (Figure 2A, gray bars). As we previously reported (Mbalaviele et al., 2005), ΔN151 was at best a weak stimulator of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, an early marker of osteoblast differentiation. By contrast, mutGSK or ΔN90 stimulated substantially higher levels of ALP activity after 7 days of culture (Figure 2B, black bars). Importantly, BMP-2 (100ng/ml) synergistically enhanced ALP stimulation by each β-catenin mutant (Figure 2B, gray bars). However, ΔN90 was stronger in stimulating ALP activity than was ΔN151 (Figure 2B), despite that ΔN90 and ΔN151 were equivalent activators of Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription (Figure 2A). Also, ΔN90 and mutGSK stimulated similar levels of ALP activity (Figure 2B) despite that ΔN90 was a weaker activator of Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription (Figure 2A). By contrast, after 10 days in culture with an adipogenic medium, transduction with either of the N-terminally truncated mutants, ΔN90 or ΔN151, resulted in about 70% fewer adipocytes compared to EGFP, while mutGSK nearly abrogated adipogenesis (Figure 2C). Thus, inhibition of adipogenesis by β-catenin directly correlates with its Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity, whereas stimulation of ALP activity by β-catenin does not.
Figure 2.
Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional activity of β-catenin mutants and C3H10T1/2 differentiation. (A) After retroviral transduction, G418-resistant C3H10T1/2 cells were monitored for Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity in the absence or presence of 100 ng/ml BMP-2 for 24 hr after transfection with Tcf/Lef-luc. (B) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was quantified from cells grown in the absence or presence of 100 ng/ml BMP-2. (C) C3H10T1/2 cells transduced with EGFP or β-catenin mutants were grown in adipogenic medium for 10 d, and the number of adipocytes, defined by presence of Oil Red O positive lipid droplets, was determined in 6 random 40X microscopic fields per genotype; p<0.05 versus EGFP (*), versus ΔN151 (#), versus BMP-2 (‡), or versus ΔN151 plus BMP-2 (†), two-tailed Student’s t-test.
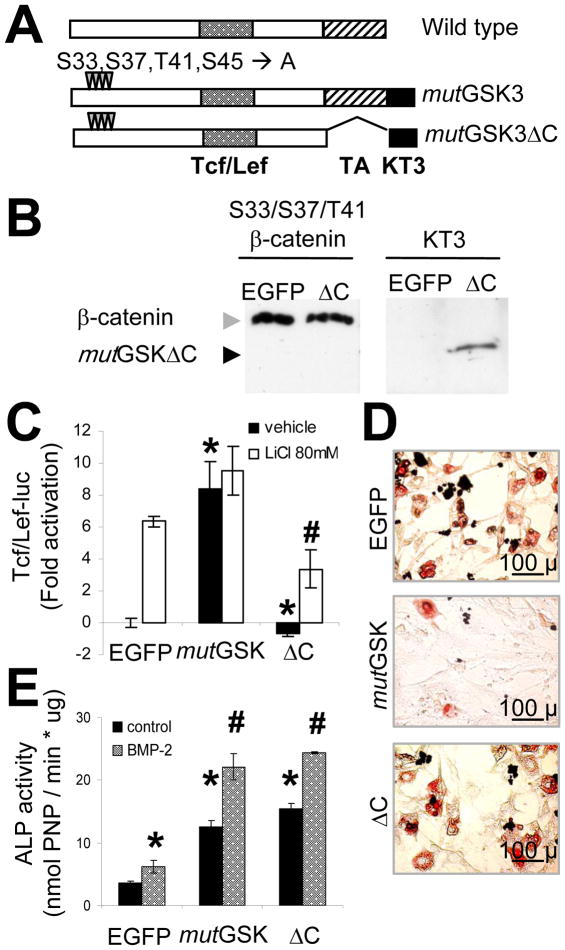
To better test whether induction of ALP activity can be dissociated from β-catenin transactivation of Tcf/Lef, a stabilized but transcriptionally-defective β-catenin mutant lacking the C-terminal transactivation domain was generated from the mutGSK retrovirus vector backbone (mutGSKΔC; Figure 3A). It was successfully expressed in C3H10T1/2 cells, as shown by immunoblots of lysates from mutGSKΔC transduced cells (Figure 3B). To test the biologic activity of mutGSKΔC, we first compared its ability to stimulate Tcf/Lef transcription against 80mM LiCl, a pharmacological inhibitor of GSK3 or the Tcf/Lef-active mutant, mutGSK. Exposure to 80 mM LiCl and expression of mutGSK resulted in a similar degree of Tcf/Lef-dependent promoter activity, and no further stimulation was obtained by treating mutGSK-transduced cells with LiCl. Conversely, mutGSKΔC did not autonomously transactivate Tcf/Lef-luc, and in fact, it significantly inhibited endogenous and LiCl-stimulated Tcf/Lef activity (Figure 3C). These results confirm that the C-terminal domain is required for canonical β-catenin transcriptional activity (Cong et al., 2003), and demonstrate that this construct functions as a dominant-negative on Tcf/Lef dependent transactivation. To determine whether loss of β-catenin’s Tcf/Lef activity correlates with a loss of biological function, we monitored adipogenesis in cells transduced with either mutGSK or mutGSKΔC. As noted earlier, transduction with mutGSK prevented formation of Oil Red O positive cells in adipogenic medium, however transduction with mutGSKΔC was ineffective in this regard, yielding an abundance of adipocytes similar to those observed in EGFP control cultures (Figure 3D). Importantly, despite the loss of both Tcf/Lef-activity and its anti-adipogenic effect, mutGSKΔC stimulated a comparable level of ALP activity as mutGSK, an effect which was enhanced by exogenous BMP-2 (Figure 3E).
Figure 3.
The C-terminal transactivation domain of β-catenin is necessary for Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity and for suppression of adipogenesis, but is dispensable for osteogenic stimulation. (A) Schematic diagram of wild type and mutant (mutGSK, or mutGSKΔC) β-catenin constructs, with their functional domains illustrated as in Fig 1A. (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were transduced with either EGFP or mutant β-catenin (mutGSK, or mutGSKΔC) VSV-G retroviruses. Whole cell lysates were immunoblotted using either an anti-β-catenin or anti-KT3 antibody, as indicated. (C) Cells transduced with the different mutants were monitored for Tcf/Lef transcriptional activity in the absence or presence of 80 mM LiCl after transfection with Tcf/Lef-luc; p<0.05 versus EGFP (*) or versus EGFP plus LiCl (#), two-tailed Student t-test. (D) Adipogenic differentiation was determined in transduced C3H10T1/2 cells by Oil Red O staining after 10 d incubation in adipogenic medium. (E) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was quantified in cell lysates in the absence or presence of 100 ng/ml BMP-2 after 7 d; p<0.05 versus EGFP (*) or versus EGFP plus BMP-2 (#), two-tailed Student t-test. Results are representative of 3 separate experiments. Bar, 100 μm.
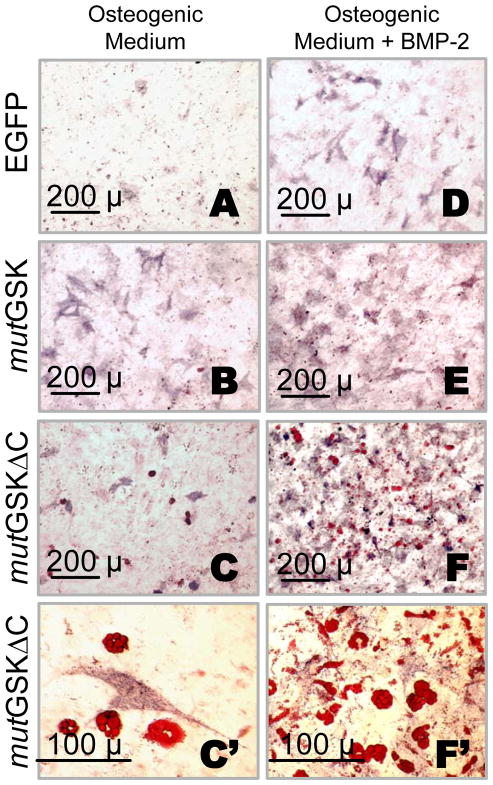
Consistent with quantitative biochemical results, the number of ALP positive cells in 10-day mutGSK or mutGSKΔC osteogenic cultures was much higher than in EGFP cultures, although the number in mutGSKΔC cultures was slightly less than in mutGSK cultures (Figure 4A, B, and C). BMP-2 (200 ng/ml) greatly enhanced the ability of mutGSK to stimulate ALP staining (Figures 4A, B, D, and E). The number of ALP positive cells in mutGSKΔC plus BMP-2 cultures equaled or exceeded that of mutGSK plus BMP-2 (Figures 4F and 4E). Remarkably, adipocytes appeared among ALP-positive cells in mutGSKΔC cultures but not in mutGSK cultures (Figures 4B–C′ and 4E–F′). Adipogenesis in mutGSKΔC cells ensued spontaneously, in the absence of adipogenic stimuli and the presence of osteogenic supplements (Fig. 4C, C′); and it became vigorous with BMP-2 treatment (Fig. F, F′).
Figure 4.
A Tcf/Lef-defective β-catenin mutant stimulates both osteoblasts and adipocytes under osteogenic conditions and enhances BMP-2 effects. C3H10T1/2 cells transduced with either EGFP or mutant β-catenin (mutGSK, or mutGSKΔC) VSV-G retroviruses and selected with G418 were cultured in osteogenic medium for 10 d, stained with Oil Red O and subsequently counterstained for ALP activity (A-F′). Stained monolayers were microphotographed at 10X or 40X magnification. Adipocytes contain red-colored lipid droplets and osteoblasts are stained purple.
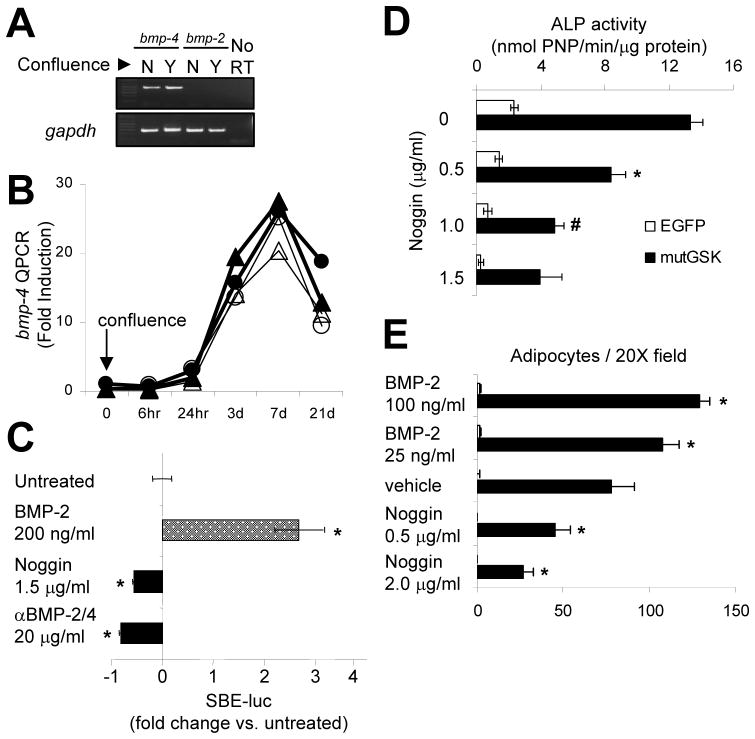
These results indicate that mutGSK, ΔN90, and mutGSKΔC, but not ΔN151, stimulate osteoblast differentiation in the absence of exogenous BMP-2. However, C3H10T1/2 cells have been reported to produce BMPs (Shea et al., 2003). To determine if endogenously produced BMPs are required for the “intrinsic” osteogenic activity of these β-catenin mutants, we first assessed BMP expression by RT-PCR in 20% and 100% confluent C3H10T1/2 cells. C3H10T1/2 cells express abundant bmp-4 mRNA, perhaps more abundantly in confluent than non-confluent cells, whereas bmp-2 mRNA is undetectable (Figure 5A). Temporal expression profiling revealed that bmp-4 expression sharply increased >25-fold after the first 7 days post-confluence in osteogenic medium, receding by 21 d (Figure 5B). Neither exposure to exogenous BMP-2, nor transduction of mutGSK altered expression of bmp-4 (Figure 5B) or bmp-2 (data not shown). To ascertain the signaling activity of endogenous BMPs, a BMP-responsive transcriptional luciferase reporter (SBE-luc) was transfected into C3H10T1/2 cells. Addition of recombinant Noggin (a BMP-2/4/7 antagonist) or a BMP-2/4 neutralizing antibody significantly inhibited basal SBE-luc activity while exogenous BMP-2, used as positive control, stimulated SBE-luc activity 3-fold (Figure 5C).
Figure 5.
C3H10T1/2 cells express endogenous BMP-4 and it accounts for most of the “intrinsic” pro-osteogenic β-catenin activity. (A) Expression of bmp-2 and bmp-4 mRNA by RT-PCR in confluent and sub-confluent cultures of C3H10T1/2 cells grown in osteogenic medium. As a control for mRNA stability and abundance, gapdh mRNA was determined. (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were transduced with either EGFP (circles) or mutGSK (triangles) and incubated in the presence (open) or in the absence (solid) of BMP-2 for up to 21 d. Total mRNA, extracted at indicated time points, was used for determination of bmp-4 mRNA abundance by quantitative real time PCR, relative to gapdh. (C) C3H10T1/2 cells were transiently transfected with a BMP-specific luciferase reporter containing 12 tandem Smad-binding elements (SBE-luc), and then treated with Noggin (1.5 μg/ml), a BMP-2/4 neutralizing antibody (20 μg/ml), or BMP-2 (200 ng/ml) for 24 h; p<0.05 versus untreated (*), two-tailed Student’s t-test. (D) Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was quantified in C3H10T1/2 cells transduced with mutGSK and treated with Noggin; p<0.05 versus mutGSK (*) or versus mutGSK plus 0.5 μg/ml Noggin (#), two-tailed Student t-test. (E) C3H10T1/2 cells were grown in adipogenic medium containing either BMP-2 or Noggin for 10 d and the number of adipocytes, defined by presence of Oil Red O positive lipid droplets, was determined in 6 random 20X microscopic fields; p<0.05 versus vehicle (*), two-tailed Student’s t-test.
More to the point, when mutGSK-transduced cells were cultured in osteogenic media in the presence of different concentrations of Noggin for 7 days, induction of ALP activity by mutGSK was dose-dependently attenuated by BMP blockade (Figure 5D). Notably, at a concentration of 1.5 μg/ml, Noggin inhibited BMP-dependent SBE-luc activity by 50% (Figure 5C) and mutGSK-dependent ALP activity by 70% (Figure 5D), indicating that endogenous BMPs, probably BMP-4, contribute in great part, if not entirely, to osteoblast differentiation induced by activated β-catenin in C3H10T1/2 cells. Since adipogenesis was enhanced by BMP-2 in cells transduced with the transcriptionally inactive mutGSKΔC, we tested the sensitivity of induced adipogenesis to BMP signaling blockade. The formation of Oil Red O positive cells in cells grown in adipogenic medium for 9 days was dose-dependently stimulated by exogenous BMP-2, and dose-dependently inhibited by Noggin (Figure 5E). Thus, endogenous BMPs drive both adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation in C3H10T1/2 cells.
Discussion
We previously reported that stabilized β-catenin synergizes with BMP-2 to stimulate in vitro osteoblast differentiation and in vivo new bone formation (Mbalaviele et al., 2005). That study evaluated the effects of a single mutant, ΔN151, which displayed little osteogenic action by itself and required exogenous BMP-2 treatment to generate an osteogenic stimulus. Here, we utilize a more comprehensive structure-function analysis to demonstrate that the ability of β-catenin to stimulate Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional activity is neither necessary nor sufficient to induce osteoblast differentiation, but rather requires active BMP signaling.
Previous studies reported that β-catenin contributes to formation of new ectopic bone in response to BMPs (Chen et al., 2007); that genetic ablation of β-catenin blocks the osteogenic effect of BMP-2 in ex vivo mouse calvaria cultures (Hill et al., 2005); and that canonical Wnt signaling is induced by BMPs via an autocrine loop (Rawadi et al., 2003; Bain et al., 2003). These data suggested a model whereby canonical Wnt signaling, via β-catenin, is part of the downstream events activated by BMPs to induce osteogenesis. However, others found that blockade of BMP signaling impedes Wnt-induced osteoblast differentiation (Winkler et al., 2005); and the present work demonstrates that blockade of BMP signaling impedes the stimulatory effect of constitutively activated β-catenin, which does not require expression of canonical Wnts to stimulate Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription. Thus, while others had reported “intrinsic” osteogenic activity in various β-catenin mutants, (Rawadi et al., 2003; Bain et al., 2003), we here clarify that even a full-length β-catenin mutant with potent Tcf/Lef activity is still largely dependent on endogenously produced BMPs for its pro-osteogenic activity. Furthermore, since we find that up-regulation of endogenous BMP-4 requires at least 3 days of culture in differentiation medium, the assessment of effects by β-catenin/Wnt and BMP signaling interactions is heavily dependent on timing of experimental endpoints. This factor may in part explain some of the discrepant results from independent groups. Nonetheless, collective findings do not support a simple epistatic model of osteogenesis where Wnts are downstream mediators of BMPs. Instead, emerging data suggest that canonical Wnt signaling through β-catenin is necessary, though not sufficient in the absence of BMPs, to stimulate osteoblast differentiation (Chen et al., 2007). Although it is possible that canonical Wnts may induce expression of BMPs in a β-catenin-dependent manner to stimulate osteoblast differentiation (Winkler et al., 2005), the present results together with others’ findings (Hill et al., 2005), strongly suggest that β-catenin activation and BMP signaling are required simultaneously to deliver an osteogenic cue.
Our structure-function analysis of β-catenin establishes that its anti-adipogenic and pro-osteogenic actions are separable. We find that the anti-adipogenic action of β-catenin directly correlates with Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional activity and requires the C-terminal transactivation domain. By contrast, the transactivation domain is dispensable for the pro-osteogenic function of β-catenin, which is not accurately predicted by Tcf/Lef activity. Although the molecular nature of this β-catenin-dependent but non-canonical pro-osteogenic mechanism remains to be determined, Tcf/Lef-independent functions of β-catenin in cell fate specification have been proposed in other cell types. For example, ablation of β-catenin in skin stem cells induces epidermal differentiation at the expense of follicular keratinocyte differentiation (Huelsken et al., 2001) while expression of a Tcf/Lef-defective β-catenin mutant instead had both dominant-positive and dominant-negative actions, depending upon the cell context in which it was expressed (DasGupta et al., 2002). It is also worth considering why constitutive activation or ablation of β-catenin leads to severe skeletal malformations in mice (Hu et al., 2005a; Day et al., 2005; Hill et al., 2005), while ablation of lrp5 results only in low bone mass and an osteoblast defect but no skeletal malformations (Kato et al., 2002). Thus, previous findings support the notion that the pro-osteogenic action of β-catenin can operate in a non-canonical (Tcf/Lef-independent) manner. And furthermore, mechanistically separable cell fate cues may be operative in other tissues as well.
A non-canonical mechanism could be related to cross-talk between components of the Wnt and BMP signaling systems. For example, direct interaction between Smad1 and Dvl-1 in undifferentiated mesenchymal cells decreases cell proliferation (Chen et al., 2007). Alternatively, β-catenin itself and Tcf/Lef proteins may interact with Smad-containing transcription complexes on promoters containing both Tcf/Lef and Smad-binding elements (Hussein et al., 2003; Lei et al., 2004; Hu et al., 2005b). Or, β-catenin may even directly interact with BMP-2 signaling independently of Tcf/Lef proteins. Intriguingly, canonical Wnt signals are reported to regulate gene expression in osteoblasts which are involved in osteoclast function, such as opg (Glass et al., 2005); but to date there is no strong evidence that osteoblastic genes, such as runx2 or osterix, are directly activated by Tcf/Lef-dependent mechanisms (Glass et al., 2005; Kato et al., 2002). Determining if non-canonical β-catenin signaling regulates osteoblast gene expression and differentiation therefore represents an attractive hypothesis to test.
Our data support a model where β-catenin refines a BMP-2 signal into either an adipocyte or osteoblast cue, depending upon its transcriptional activity. When β-catenin is fully active, adipogenesis is inhibited and BMP signaling is fully osteogenic. When transcriptional activity is inhibited, BMP signals become ambiguous, inducing both osteogenesis and adipogenesis. Thus, both Tcf/Lef-dependent and Tcf/Lef-independent actions of β-catenin are necessary to make a BMP signal strictly osteogenic. While the anti-adipogenic function is linked to the C-terminal transactivation domain, the topology of β-catenin pro-osteogenic activity is less clear. The differences in ALP stimulatory activities between the ΔN90 and ΔN151 mutants point to a region between residues 90 and 151 that might be critically important for β-catenin pro-osteogenic action. However, the ΔN151 mutant was still able to enhance BMP-2 induced osteoblast differentiation, implying that additional domains are involved. These do not include the transactivation domain, since C-terminal deletion of β-catenin has no detrimental effect on its pro-osteogenic function. Finer resolution of the structure-function correlates of β-catenin should be useful for understanding its pro-osteogenic action, and the mode of interaction with the BMP signaling system.
In summary, we demonstrate that β-catenin employs at least two mechanistically distinct actions that control differentiation of mesenchymal lineages: a Tcf/Lef-dependent function of β-catenin operates to suppress the adipocyte lineage; and, a Tcf/Lef-independent function integrates with a BMP signal to induce osteogenesis. Our results support a model whereby β-catenin and BMP effectors act cooperatively, so full induction of an osteoblastogenesis program occurs when they signal in tandem. This cooperative interaction of two osteogenic signaling systems will now be tested in vivo.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by National Institutes of Health grants AR43470 and AR41255 (RC). The authors wish to express their gratitude to Drs. Adriana Di Benedetto, Joseph Stains, and previous members of the Civitelli laboratory for help with some technical aspects of the work and for critical discussion of the results. Parts of this work have been presented in abstract form at the 27th annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, Nashville, TN, September 23–27, 2005.
Abbreviations
- BMP
bone morphogenetic protein
- luc
luciferase
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- SBE
Smad-binding element
- RT
reverse transcription
References
- 1.Ahrens M, Ankenbauer T, Schroder D, Hollnagel A, Mayer H, Gross G. Expression of human bone morphogenetic proteins-2 or -4 in murine mesenchymal progenitor C3H10T1/2 cells induces differentiation into distinct mesenchymal cell lineages. DNA Cell Biol. 1993;12:871–880. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Babij P, Zhao W, Small C, Kharode Y, Yaworsky PJ, Bouxsein ML, Reddy PS, Bodine PV, Robinson JA, Bhat B, Marzolf J, Moran RA, Bex F. High bone mass in mice expressing a mutant LRP5 gene. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:960–974. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.6.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bain G, Muller T, Wang X, Papkoff J. Activated β-catenin induces osteoblast differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells and participates in BMP2 mediated signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;301:84–91. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02951-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barth AI, Pollack AL, Altschuler Y, Mostov KE, Nelson WJ. NH2-terminal deletion of β-catenin results in stable colocalization of mutant β-catenin with adenomatous polyposis coli protein and altered MDCK cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1997;136:693–706. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Batlle E, Henderson JT, Beghtel H, van den Born MM, Sancho E, Huls G, Meeldijk J, Robertson J, van de WM, Pawson T, Clevers H. Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell. 2002;111:251–263. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)01015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L, Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K, Lifton RP. High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein 5. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1513–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa013444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Byrappa S, Gavin DK, Gupta KC. A highly efficient procedure for site-specific mutagenesis of full-length plasmids using Vent DNA polymerase. Genome Res. 1995;5:404–407. doi: 10.1101/gr.5.4.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cadigan KM, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 1997;11:3286–3305. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO, Druey KM, Gutkind JS. Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science. 2005;310:1504–1510. doi: 10.1126/science.1116221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Castro CH, Shin CS, Stains JP, Cheng SL, Sheikh S, Mbalaviele G, Szejnfeld VL, Civitelli R. Targeted expression of a dominant-negative N-cadherin in vivo delays peak bone mass and increases adipogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2853–2864. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen Y, Whetstone HC, Youn A, Nadesan P, Chow EC, Lin AC, Alman BA. Beta-catenin signaling pathway is crucial for bone morphogenetic protein 2 to induce new bone formation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:526–533. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602700200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cong F, Schweizer L, Chamorro M, Varmus H. Requirement for a nuclear function of beta-catenin in Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8462–8470. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8462-8470.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.DasGupta R, Rhee H, Fuchs E. A developmental conundrum: a stabilized form of β-catenin lacking the transcriptional activation domain triggers features of hair cell fate in epidermal cells and epidermal cell fate in hair follicle cells. J Cell Biol. 2002;158:331–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200204134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell. 2005;8:739–750. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fujino T, Asaba H, Kang MJ, Ikeda Y, Sone H, Takada S, Kim DH, Ioka RX, Ono M, Tomoyori H, Okubo M, Murase T, Kamataki A, Yamamoto J, Magoori K, Takahashi S, Miyamoto Y, Oishi H, Nose M, Okazaki M, Usui S, Imaizumi K, Yanagisawa M, Sakai J, Yamamoto TT. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) is essential for normal cholesterol metabolism and glucose-induced insulin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:229–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0133792100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Glass DA, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G. Canonical wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 2005;8:751–764. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gong Y, Slee RB, Fukai N, Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S, Reginato AM, Wang H, Cundy T, Glorieux FH, Lev D, Zacharin M, Oexle K, Marcelino J, Suwairi W, Heeger S, Sabatakos G, Apte S, Adkins WN, Allgrove J, Arslan-Kirchner M, Batch JA, Beighton P, Black GC, Boles RG, Boon LM, Borrone C, Brunner HG, Carle GF, Dallapiccola B, De Paepe A, Floege B, Halfhide ML, Hall B, Hennekam RC, Hirose T, Jans A, Juppner H, Kim CA, Keppler-Noreuil K, Kohlschuetter A, LaCombe D, Lambert M, Lemyre E, Letteboer T, Peltonen L, Ramesar RS, Romanengo M, Somer H, Steichen-Gersdorf E, Steinmann B, Sullivan B, Superti-Furga A, Swoboda W, van den Boogaard MJ, Van Hul W, Vikkula M, Votruba M, Zabel B, Garcia T, Baron R, Olsen BR, Warman ML. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development. Cell. 2001;107:513–523. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00571-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hartmann C. A Wnt canon orchestrating osteoblastogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:151–158. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hill TP, Spater D, Taketo MM, Birchmeier W, Hartmann C. Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Dev Cell. 2005;8:727–738. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hu H, Hilton MJ, Tu X, Yu K, Ornitz DM, Long F. Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development. Development. 2005a;132:49–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.01564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hu MC, Rosenblum ND. Smad1, beta-catenin and Tcf4 associate in a molecular complex with the Myc promoter in dysplastic renal tissue and cooperate to control Myc transcription. Development. 2005b;132:215–225. doi: 10.1242/dev.01573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B, Cotsarelis G, Birchmeier W. β-Catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell. 2001;105:533–545. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hussein SM, Duff EK, Sirard C. Smad4 and β-catenin coactivators functionally interact with LEF1 to regulate graded expression of Msx2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:48805–48814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305472200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jia J, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Tong C, Wang B, Hou F, Amanai K, Jiang J. Phosphorylation by double-time/CKIepsilon and CKIalpha targets cubitus interruptus for Slimb/beta-TRCP-mediated proteolytic processing. Dev Cell. 2005;9:819–830. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kato M, Patel MS, Levasseur R, Lobov I, Chang BH, Glass DA, Hartmann C, Li L, Hwang TH, Brayton CF, Lang RA, Karsenty G, Chan L. Cbfa1-independent decrease in osteoblast proliferation, osteopenia, and persistent embryonic eye vascularization in mice deficient in Lrp5, a Wnt coreceptor. J Cell Biol. 2002;157:303–314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200201089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lei S, Dubeykovskiy A, Chakladar A, Wojtukiewicz L, Wang TC. The murine gastrin promoter is synergistically activated by transforming growth factor-beta/Smad and Wnt signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:42492–42502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404025200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Little RD, Carulli JP, Del Mastro RG, Dupuis J, Osborne M, Folz C, Manning SP, Swain PM, Zhao SC, Eustace B, Lappe MM, Spitzer L, Zweier S, Braunschweiger K, Benchekroun Y, Hu X, Adair R, Chee L, FitzGerald MG, Tulig C, Caruso A, Tzellas N, Bawa A, Franklin B, McGuire S, Nogues X, Gong G, Allen KM, Anisowicz A, Morales AJ, Lomedico PT, Recker SM, Van Eerdewegh P, Recker RR, Johnson ML. A mutation in the LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene results in the autosomal dominant high-bone-mass trait. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70:11–19. doi: 10.1086/338450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mbalaviele G, Sheikh S, Stains JP, Salazar VS, Cheng SL, Chen D, Civitelli R. β-catenin and BMP-2 synergize to promote osteoblast differentiation and new bone formation. J Cell Biochem. 2005;94:403–418. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mishina Y, Starbuck MW, Gentile MA, Fukuda T, Kasparcova V, Seedor JG, Hanks MC, Amling M, Pinero GJ, Harada S, Behringer RR. Bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor signaling regulates postnatal osteoblast function and bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:27560–27566. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404222200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nam JS, Turcotte TJ, Smith PF, Choi S, Yoon JK. Mouse cristin/R-spondin family proteins are novel ligands for the Frizzled8 and LRP6 receptors and activate beta -catenin-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2006 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508324200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004;303:1483–1487. doi: 10.1126/science.1094291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ory DS, Neugeboren BA, Mulligan RC. A stable human-derived packaging cell line for production of high titer retrovirus/vesicular stomatitis virus G pseudotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:11400–11406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rawadi G, Vayssiere B, Dunn F, Baron R, Roman-Roman S. BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:1842–1853. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.10.1842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ross SE, Hemati N, Longo KA, Bennett CN, Lucas PC, Erickson RL, MacDougald OA. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Wnt signaling. Science. 2000;289:950–953. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5481.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shea CM, Edgar CM, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC. BMP treatment of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells induces both chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90:1112–1127. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shin CS, Lecanda F, Sheikh S, Weitzmann L, Cheng SL, Civitelli R. Relative abundance of different cadherins defines differentiation of mesenchymal precursors into osteogenic, myogenic, or adipogenic pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2000;78:566–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Stains JP, Civitelli R. Gap junctions regulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling to affect gene transcription. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:64–72. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-04-0339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stains JP, Lecanda F, Screen J, Towler DA, Civitelli R. Gap junctional communication modulates gene transcription by altering the recruitment of Sp1 and Sp3 to connexin-response elements in osteoblast promoters. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:24377–24387. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212554200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.van Es JH, Barker N, Clevers H. You Wnt some, you lose some: oncogenes in the Wnt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003;13:28–33. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wan M, Cao X. BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328:651–657. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Winkler DG, Sutherland MS, Ojala E, Turcott E, Geoghegan JC, Shpektor D, Skonier JE, Yu C, Latham JA. Sclerostin inhibition of Wnt-3a-induced C3H10T1/2 cell differentiation is indirect and mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:2498–2502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400524200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Xu Q, Wang Y, Dabdoub A, Smallwood PM, Williams J, Woods C, Kelley MW, Jiang L, Tasman W, Zhang K, Nathans J. Vascular development in the retina and inner ear: control by Norrin and Frizzled-4, a high-affinity ligand-receptor pair. Cell. 2004;116:883–895. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yang M, Zhong WW, Srivastava N, Slavin A, Yang J, Hoey T, An S. G protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors stimulate proliferation of colon cancer cells through the {beta}-catenin pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:6027–6032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501535102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhao M, Harris SE, Horn D, Geng Z, Nishimura R, Mundy GR, Chen D. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signaling is necessary for normal murine postnatal bone formation. J Cell Biol. 2002;157:1049–1060. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]