Abstract
α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (nagalase) accumulates in the serum of cancer patients and its activity correlates with tumor burden, aggressiveness and clinical disease progression. The administration of GC protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) to cancer patients with elevated levels of nagalase has been associated with a decrease of serum nagalase activity and with significant clinical benefits. Here, we report the results of the administration of GcMAF to a heterogeneous cohort of patients with histologically diverse, advanced neoplasms, generally considered as “incurable” diseases. In most cases, GcMAF therapy was initiated at late stages of tumor progression. As this is an open-label, non-controlled, retrospective analysis, caution must be employed when establishing cause-effect relationships between the administration GcMAF and disease outcome. However, the response to GcMAF was generally robust and some trends emerged. All patients (n = 20) presented with elevated serum nagalase activity, well above normal values. All patients but one showed a significant decrease of serum nagalase activity upon weekly GcMAF injections. Decreased nagalase activity was associated with improved clinical conditions and no adverse side effects were reported. The observations reported here confirm and extend previous results and pave the way to further studies aimed at assessing the precise role and indications for GcMAF-based anticancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: cancer, complementary medicine, immunotherapy, macrophages, Vitamin D
Introduction
α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (nagalase) is known to accumulate in the serum of cancer patients, where it mediates the deglycosylation of group-specific component (GC), best known as vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP), which is the precursor of GC protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF). Deglycosylated VDBP cannot be converted into GcMAF1 and decreased GcMAF levels reportedly promote immunodeficiency in individuals bearing advanced neoplasms.2 The increase in nagalase activity observed in cancer patients is mostly due to the fact that malignant cells release enzymatically active nagalase.3 Thus, serum nagalase activity reflects not only tumor burden and aggressiveness, but also the clinical progression of the disease.4-7 Nowadays, the assessment of serum nagalase activity is proposed as a reliable means to determine the clinical severity of multiple neoplasms.3
In serum, nagalase acts as an endo- (but not as an exo-) enzyme, being unable to deglycosylate an N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) residue of GcMAF.5 Thus, circulating nagalase cannot degrade exogenous GcMAF.5-7 This observation suggested that patients with elevated nagalase activity may benefit from the exogenous provision of GcMAF. Alongside, GcMAF was observed to exert multiple anticancer effects in vivo and in vitro, both in experimental and in spontaneous tumor models. Given the impact of GcMAF on macrophages and their central role anticancer immune responses, GcMAF is widely considered as an immunotherapeutic agent.7
However, in addition to stimulating tumor-infiltrating macrophages,8 GcMAF not only directly inhibits the proliferation of various human cancer cells in vitro,9,10 but also reverts the malignant phenotype of human breast cancer cells.10 Moreover, GcMAF reportedly inhibits angiogenesis, thus depriving neoplastic lesions of the oxygen and nutrient supplies that are needed for tumor progression and metastasis.10-13 Recently, it has been proposed that the antineoplastic effects of GcMAF are mediated by the vitamin D receptor (VDR), and it was demonstrated that GcMAF stimulates an intracellular signaling pathway impinging on cyclic AMP. This signal transduction cascade could actually be responsible for death of malignant cells exposed to GcMAF.12 Taken together, these in vitro and in vivo findings lend a rationale to the observation that GcMAF exert dramatic anticancer effects in (at least a fraction of) patients with advanced cancer.5-7 Of note, in the aforementioned studies, the anticancer effects of GcMAF were evaluated by measuring serum nagalase activity as a marker of tumor burden and progression.2,3,14
The biological effects of GcMAF have been documented in a variety of experimental systems and make the subject of more than 50 peer-reviewed papers published during the past 20 y.15 Because of the solid scientific rationale underlying the compassionate use of GcMAF in advanced cancer patients, hundreds of physicians in all parts of the world have adopted this approach for a variety of indications in which it could prove useful. Here, we present a series of clinical cases exemplifying the results that have been obtained with the administration of GcMAF to patients with diverse types of advanced cancers, with a particular focus on the effects of GcMAF on serum nagalase activity. We are well aware that these cases, because of their heterogeneity and reduced number, can be considered anecdotal. However, a very recent study on the evaluation of clinical practice strongly encourages the re-evaluation of individual cases such as those presented here.16 Thus, while some studies present large and impressive statistics obtained from large clinical cohorts, others may report a limited number of noteworthy cases, as we do here. According to this novel, authoritative, epistemological approach, “all of these stories become evidence of what works in medicine.”16 Therefore, we believe that the clinical cases reported below point to beneficial effects for the administration of GcMAF to advanced cancer patients, prompting further studies to formally address this possibility.
Results
The mean pre-GcMAF treatment serum nagalase activity documented in our patient cohort was 2.84 ± 0.26 nM/min/mg, with a range of 1.00–5.60 nM/min/mg (Table 1). At the time of second testing (average interval = 112 d), the mean serum nagalase activity in the course of GcMAF treatment was 2.01 ± 0.22 nM/min/mg, with a range of 1.00–3.20 nM/min/mg. The difference between these values was statistically significant (p < 0.05). Of note, no patient of this cohort was initially observed to be within the laboratory reference range for serum nagalase activity (0.90–0.92 nM/min/mg). At the time of final testing (average interval = 263 d), the mean serum nagalase activity of the patient cohort was 1.59 ± 0.17 nM/min/mg, with a range of 0.60–2.80 nM/min/mg. The difference between this value and the serum nagalase activity recorded before the initiation of GcMAF treatment was also statistically significant (p < 0.01).
Table 1. Nagalase levels before and after GcMAF therapy*.
| N° | Gender | Age | Tumor type | Serum nagalase activity |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre draw date | Pre result | First-post draw date | First-post result | Days between pre and first post draw | Last draw date | Last result | Days between pre and last draw | Pre-last difference | |||||
|
1) |
M |
64 |
Bladder CA |
October, 2012 |
2.90 |
|
|
|
January, 2013 |
2.60 |
92 |
-0.30 |
|
|
2) |
M |
63 |
Bladder CA |
July, 2011 |
3.10 |
February, 2012 |
2.30 |
215 |
October, 2012 |
1.40 |
458 |
-1.70 |
|
|
3) |
F |
69 |
Bladder CA |
May, 2011 |
4.10 |
October, 2011 |
2.30 |
153 |
December, 2012 |
0.75 |
580 |
-3.35 |
|
|
4) |
F |
60 |
Ovarian CA |
June, 2012 |
3.30 |
June, 2012 |
3.20 |
7 |
November, 2012 |
2.80 |
153 |
-0.50 |
|
|
5) |
F |
62 |
Ovarian CA |
August, 2012 |
2.70 |
- |
- |
- |
February, 2013 |
2.00 |
184 |
-0.70 |
|
|
6) |
F |
61 |
Ovarian CA |
December, 2012 |
2.60 |
- |
- |
- |
February, 2013 |
2.20 |
62 |
-0.40 |
|
|
7) |
M |
67 |
Prostate CA |
August, 2012 |
3.40 |
- |
- |
- |
December, 2012 |
2.80 |
122 |
-0.60 |
|
|
8) |
M |
76 |
Prostate CA |
April, 2011 |
2.00 |
August, 2011 |
1.20 |
122 |
December, 2012 |
0.75 |
610 |
-1.25 |
|
|
9) |
M |
65 |
Prostate CA |
October, 2011 |
1.90 |
February, 2012 |
1.70 |
123 |
October, 2012 |
1.20 |
366 |
-0.70 |
|
|
10) |
F |
66 |
Breast CA |
August, 2011 |
1.70 |
January, 2012 |
1.00 |
153 |
December, 2012 |
0.60 |
487 |
-1.10 |
|
|
11) |
F |
63 |
Breast CA |
May, 2011 |
5.60 |
October, 2011 |
2.90 |
153 |
October, 2012 |
1.10 |
519 |
-4.50 |
|
|
12) |
M |
63 |
Tongue squamous cell CA |
July, 2012 |
3.00 |
September, 2012 |
1.50 |
62 |
December, 2012 |
1.00 |
153 |
-2.00 |
|
|
13) |
F |
55 |
Tongue squamous cell CA |
November, 2012 |
1.20 |
- |
- |
- |
February, 2013 |
0.87 |
92 |
-0.33 |
|
|
14) |
M |
54 |
Colorectal CA |
July, 2012 |
3.90 |
- |
- |
- |
October, 2012 |
2.00 |
92 |
-1.90 |
|
|
15) |
F |
58 |
Head/Neck squamous cell CA |
June, 2012 |
2.90 |
July, 2012 |
2.70 |
30 |
February, 2013 |
2.00 |
245 |
-0.90 |
|
|
16) |
M |
72 |
Larynx CA |
May, 2011 |
4.70 |
October, 2011 |
2.00 |
153 |
December, 2012 |
0.90 |
580 |
-3.80 |
|
|
17) |
F |
35 |
Squamous cell CA |
June, 2012 |
1.50 |
|
|
|
September, 2012 |
1.10 |
92 |
-0.40 |
|
|
18) |
F |
69 |
Follicular lymphoma |
June, 2012 |
1.00 |
August, 2012 |
1.30 |
61 |
January, 2013 |
1.20 |
214 |
0.20 |
|
|
19) |
F |
66 |
Lymphoma |
August, 2012 |
2.20 |
- |
- |
- |
November, 2012 |
1.90 |
92 |
-0.30 |
|
|
20) |
M |
42 |
Grade III anaplastic oligodendroglioma |
November, 2012 |
3.00 |
- |
- |
- |
January, 2013 |
2.60 |
61 |
-0.40 |
|
|
Max |
- |
- |
- |
- |
5.60 |
- |
3.20 |
215 |
- |
2.80 |
610 |
- |
|
|
Min |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.00 |
- |
1.00 |
7 |
- |
0.60 |
61 |
- |
|
|
Mean |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2.84 |
- |
2.01* |
112 |
- |
1.59** |
263 |
- |
|
| SEM | - | - | - | - | 0.26 | - | 0.22 | 19.17 | - | 0.17 | 44.90 | - | |
* Serum nagalase activity values are presented as nM/min/mg. The last column (pre-last nagalase difference) illustrated the decrease in serum nagalase activity between the initiation of GC protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) therapy (pre) and the last time point of testing (last). For patients who had serum nagalase activity tested in more than two instances, the results of the additional determination (first-post) are reported in the column “First-post results.” *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. CA, carcinoma.
Narrative description of some notable clinical cases from The Netherlands
The following reports were collected and communicated by Dr. Steven Hofman (CMC, Capelle aan den Ijssel; The Netherlands) and refer to the years 2011–2012. In addition to GcMAF, most patients were prescribed supplementation of vitamins D and A. Additional supplements are indicated when assumed. Most of the patients did not assume conventional anticancer chemotherapy along with GcMAF. However, several patients had been subjected to conventional anticancer therapies in the previous years, as indicated in individual reports. When patients assumed conventional therapeutics, such as hormones, in the course of GcMAF administration (e.g., patient #8), this is indicated in the individual report. When not indicated otherwise, patients received 100 ng GcMAF weekly, as a single intramuscular injection, in line the commonly accepted recommendations.5-7 Original reports are in italics. Each case is referred to with progressive numbers, as in Table 1.
In Figure 1, the decrease of serum nagalase activity in the patient cohort is plotted in function of the consecutive testing. Of note, since this is a retrospective analysis and not a clinical trial, nagalase determinations were not performed at the same time point in each individual patient. The overall shape of the graph, however, is very similar if not completely superimposable to that of other graphs of the same type that have previously been reported.5-7,17
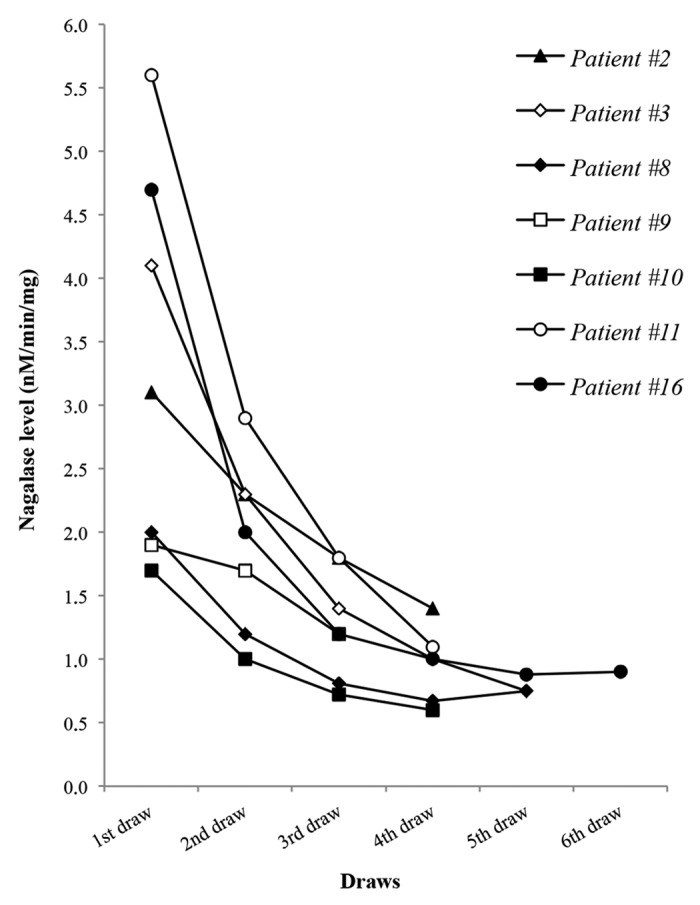
Figure 1. Time course of GcMAF treatment in 7 cancer patients with serum nagalase activity as a prognostic index. Data correspond to the patients described in the section “Narrative description of some notable clinical cases from The Netherlands.” Serum nagalase activity determinations were not performed at the same time point in each individual patient, as detailed in Table 1. Patients are indicated with consecutive numbers as in the Results section and Table 1.
2. Male, born 1950. Carcinoma of the urine-bladder since 2009, previously treated with chemo-solutions locally. Nagalase level at presentation on July 4, 2011: 3.10. February 10, 2012: 2.30. May 25, 2012: 1.80. October 26, 2012: 1.40. Treatment with GcMAF and acupuncture, later GcMAF only (later intravenous route). Bladder considered clean by urologist in summer 2012. GcMAF-treatment continued. In this case, the consistent decrease in serum nagalase activity was associated with a significant clinical improvement. The drop in nagalase activity was evident at the first post-treatment testing, about 7 mo after the initiation of GcMAF treatment, and persisted until the last available determination, i.e., about 15 mo thereafter. The difference in serum nagalase activity as recorded before at last determination and before the initiation of GcMAF therapy was -1.70 nM/min/mg.
3. Female, born 1944. Bladder carcinoma treated since 2011 by urologist with curettage and BCG. Nagalase level at presentation on May 9, 2011: 4.10. October 24, 2011: 2.30. April 3, 2012: 1.40. September 10, 2012: 1.00. December 4, 2012: 0.75. During the nagalase testing period the Patient was advised to inject intramuscular GcMAF weekly, but the Patient was not consistent. The bladder was considered in good condition on several occasions this period by the treating urologist. Also in this case, a consistent decrease in serum nagalase activity was associated with a significant clinical improvement. Such a decrease in nagalase activity was evident at the first post-treatment testing, about 5 mo after the initiation of GcMAF treatment, and persisted until the last available determination, i.e., about 19 mo thereafter. The difference in serum nagalase activity as recorded before at last determination and before the initiation of GcMAF therapy was -3.35 nM/min/mg. The last available value of serum nagalase activity, 0.75 nM/min/mg, was within the normal range.
8. Male, born 1937. Prostate carcinoma found by PSA in 2009, no specific complaints. Treated by hormone-injections, which gave complaints. Before and in the same year colon carcinoma was found, and operated after irradiation and chemotherapy (no untreated tumor/metastases probable). Nagalase level at presentation on April 6, 2011: 2.00. August 29, 2011: 1.20. January 5, 2012: 0.81. July 5, 2012: 0.67. December 6, 2012: 0.75. Treatment with acupuncture and GcMAF; after some time, the hormone treatment was discontinued and complaints, also non-specific, improved a lot. Stays on low-frequency surveillance. Again, serum nagalase activity returned to normal values (0.75 nM/min/mg) after about 20 mo of GcMAF treatment. A decrease in nagalase activity, however, was evident already at the first test, i.e., 4 mo after the initiation of GcMAF treatment. According to the literature,7 the normalization of serum nagalase levels in prostate cancer patients may represent an index of tumor eradication.
9. Male, born 1948. Prostate carcinoma in 2008; prostate extirpated in 2009 with good prognosis. However aspecific reportts fatigue and pain stayed. GcMAF treatment was started, together with a few acupuncture treatments. Nagalase level at presentation on October 21, 2011: 1.90. February 2, 2012: 1.70. October 19, 2012: 1.20. Complaints decreased gradually and the injections were performed intravenously later on. The treatment continues.
10. Female, born 1947. Carcinoma of left breast (found on survey), operated with sentinel nodes in 2010, chemotherapy 4 of 6 series, no specific complaints left. Still some malaise, fatigue and sleep-disorder. Nagalase level at presentation on August 9, 2011: 1.70. January 16, 2012: 1.00. March 12, 2012: 0.72. December 11, 2012: 0.60. GcMAF-treatment (predominantly intravenous route) combined with acupuncture. GcMAF discontinued in April 2012. Aspecific complaints diminished. Patient still seen every few months. A significant decrease in serum nagalase activity could be observed after 5 mo of GcMAF treatment. Such a decrease persisted even after the interruption of GcMAF, and serum nagalase activity was normalized about 16 mo after the initiation of therapy. According to the literature,5 the normalization of serum nagalase activity in breast carcinoma patients may represent an index of tumor eradication.
11. Female, born 1950. Carcinoma of left breast, specific complaints, metastases probable. After local operation, irradiation of thorax, combined with chemotherapy, Herceptin-therapy. Partly complaints in association with treatments. Nagalase level at presentation on May 11, 2011: 5.60. October 6, 2011: 2.90. February 21, 2012: 1.80. October 18, 2012: 1.10. Treated with intramuscular, later intravenous GcMAF, and a few acupuncture-treatments. No further complaints (subsided in 3–6 weeks), still in intravenous GcMAF regimen. A significant decrease in serum nagalase activity could be observed approximately 5 mo after the initiation of therapy. Approximately after 17 mo of GcMAF treatment, serum nagalase levels approached normal values.
16. Male, born 1941. Larynx-carcinoma found and treated with curettage and irradiation in 2010. Hemorrhagic-recto-colitis in anamnesis, few complaints after 2005. Bladder carcinoma found in 2011, treated by local curettage and several cycles of BCG-instillations. Complaints related to tumor growth and treatments, no chemotherapy. Treatment consisted of acupuncture and GcMAF intramuscular, and later intravenous injections on a weekly basis. Nagalase level at presentation on May 16, 2011: 4.70. October 4, 2011: 2.00. February 10, 2012: 1.20. June 15, 2012: 1.00. October 23, 2012: 0.88. December 20, 2012: 0.90. During the immunotherapy with GcMAF there were interesting developments. Insisting on bladder extirpation by the urologists, coped with one change of urologist, two second opinions by a specialized cancer clinic and later by an urologist of the operation team scheduled. From the Patients side there were several favorable adjustments in lifestyle, like discontinuation of smoking and adopting a daily intake of cod-liver-oil and salvia-leaf (his own initiative). In the face of the urologists opinion I decided to give the GcMAF twice weekly over a period of six weeks. The last opinion of the treating urologist was to postpone a more final decision to February, due to a much better impression of the bladder mucosa beginning in January 2013. There is optimism in the three named actors in the current situation. In this case, a significant decrease of in serum nagalase activation following the administration of GcMAF was associated with significant clinical benefits, consistent with previous reports.7
Narrative description of some notable clinical cases from the United States of America
The following reports were communicated by RE and refer to the years 2012–2013. In most patients, the weekly administration of 100 ng GcMAF i.m. was initiated in August 2012, and the first assessment of serum nagalase activity was performed immediately before the initiation of treatment. None of the patients assumed conventional anticancer chemotherapy during along with GcMAF. Here, we report only those cases for which as least two nagalase determinations were available.
1. Male, age 64. Bladder carcinoma. Nagalase level at first testing in October 2012: 2.90. In January 2013: 2.60. Improved. In this case, a decrease in serum nagalase activity could be documented in about 3 mo of GcMAF treatment and was associated with clinical improvement.
4. Female, age 60. Ovarian carcinoma. Nagalase level at first testing in June 2012: 3.30. November 2012: 2.80. CA-125 tumor marker in December 2012: 15.7. In February 2013: 19.1 Improved. The weekly administration of GcMAF resulted in a significant decrease of serum nagalase activity in about 3 mo. Such a decrease was associated with clinical benefits. These changes, however, were not (as yet) associated with a decrease in the circulating levels of cancer antigen 125 (CA-125), another tumor marker.
7. Male, age 67. Prostate carcinoma. Nagalase level at first testing in August 2012: 3.40. In December 2012: 2.80. Improved. In this case, clinical benefits were associated with a significant decrease in serum nagalase activity in about 4 mo from the initiation of GcMAF therapy. These results are consistent with the findings reported above as well as with previously described cases.7
12. Male, age 63. Squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Nagalase level at first testing in July 2012: 3.00. In September 2012: 1.50. In December 2012: 1.00. Improved. Again, clinical improvement was associated with a significant decrease in serum nagalase activity, which approached the normal range in approximately 5 mo. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of a patient affected by squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue receiving GcMAF. Also patient n. Thirteen (Table 1) was treated with GcMAF for a squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and showed a decrease in serum nagalase activity in about 3 mo.
14. Male, age 54. Colorectal cancer. Nagalase level at first testing in July 2012: 3.90. In October 2012: 2.00. Discontinued. In this case, a significant decrease of serum nagalase activity could be documented approximately 3 mo after the initiation of GcMAF therapy. We are not aware of the reasons that led to treatment discontinuation.
15. Female, age 58. Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Nagalase level at first testing in June 2012: 2.90. In July 2012: 2.70. In February 2013: 2.00. Improved. In this case, a minimal decrease in serum nagalase activity as observed after 1 mo of GcMAF administration was associated with clinical benefits.
17. Female, age 35. Squamous cell carcinoma. Nagalase level at first testing in June 2012: 1.50. In September 2012: 1.10. Discontinued. In this case, a decrease of serum nagalase activity was observed after 3 mo of GcMAF therapy. We are not aware of the reasons that led to treatment discontinuation.
18. Female, age 69. Follicular lymphoma. Nagalase level at first testing in June 2012: 1.00. In August 2012: 1.30. In January 2013: 1.20. Improved. In this case, no association between serum nagalase activity, GcMAF treatment and clinical conditions could be revealed.
19. Female, age 66. Lymphoma. Nagalase level at first testing in August 2012: 2.20. In November 2012: 1.90. Improved. In this case, a clinical improvement was associated with a significant decrease in serum nagalase activity in about 3 mo after the initiation of GcMAF treatment.
Discussion
GcMAF has been shown to inhibit multiple aspects of neoplastic transformation in vitro, in a variety of tumor models.5-10 The clinical cases reported here are heterogeneous and refer to patients with different types of neoplasms and at different stages of malignant progression. These cases include cancer patients in whom the effects of GcMAF had not been described before, such as subjects bearing various types of head and neck carcinoma (including tumors of the larynx and tongue), lymphoma, oligodendrocytoma and ovarian carcinoma. In some instances, patients were simultaneously affected by multiple types of tumors, as reported in the narrative description. In many cases, patients received GcMAF along with other complementary treatments, such as acupuncture or administration of nutritional supplements. In all cases, GcMAF therapy was initiated at late stages of tumor progression, as conventional therapies were obviously preferred at less advanced stages. Thus, most of the cases described here fall under the category of compassionate treatment. In fact, most of these patients had undergone conventional anticancer therapy in the previous years and had referred to GcMAF treatment when conventional chemo- or radiotherapy had proven ineffective or intolerable, as described in the individual reports. Since this is an open-label, non-controlled, retrospective analysis, caution must be employed in drawing a cause-effect relationship between treatment and clinical outcome. However, the response to GcMAF was often relatively robust and certain trends stand out.
Trends from Dutch cases
1. All patients presented with serum nagalase activity well above the normal value, that is about 0.95 nM/min/mg.
2. All patients showed a significant decrease in serum nagalase activity following GcMAF injections.
3. In all cases, serum nagalase activity was reduced at the second assessment, and such a decrease persisted in the following determinations.
4. In 4/7 cases, serum nagalase activity returned to normal levels by the last assessment.
Trends from American cases
1. All patients, but one, presented with serum nagalase activity well above the normal value. Patient #18, indeed, presented with a serum nagalase activity that was very close to normal.
2. In most patients, a significant decrease in serum nagalase activity was observed upon the administration of GcMAF. In patient #18, such a decrease was not associated with clinical benefits, even though her serum nagalase activity was always on the low side. This lack of a strict inverse relationship between serum nagalase activity and clinical responses has been recently observed in a study describing the effects of GcMAF in autistic children. Most of these patients showed indeed a decrease in serum nagalase activity as well as a significant improvement of symptoms, but the two phenomena were not strictly correlated with each other.18
A significant point that emerges from the analysis of the cases described above is the apparent absence of GcMAF-related side effects. This point, which has previously been documented in autistic children,18 is of great importance when GcMAF is considered for the compassionate treatment of patients with advanced or incurable diseases. As a matter of fact, in many countries, the complete absence of side effects is a prerequisite for the compassionate administration of substances that have not yet been approved by local sanitary authorities.
Obviously, these preliminary observations require a prolonged follow-up period to determine the best indications for the compassionate administration of GcMAF. As of today, GcMAF has been used (always as a compassionate therapy) with encouraging results in patients affected by virtually all types of cancers and at all stages of disease progression. However, it is tempting to hypothesize that patients bearing specific types and/or stages of malignancy might obtain consistent clinical benefits from the administration of GcMAF. Also the genetic background of patients, in particular in terms of VDR polymorphisms, might influence the individual response to GcMAF. In fact, we have recently demonstrated that the degree of response of human monocytes to GcMAF is associated with individual VDR genotypes.13 It can therefore be hypothesized that the antineoplastic effects of GcMAF may also be influenced by such polymorphisms. Moreover, it should be kept in mind that the prognosis of patients affected by all types of cancers is dependent upon their nutritional and inflammatory status, which can be monitored by the Prognostic Inflammatory and Nutritional Index (PINI).19 The PINI score might therefore become part of the laboratory assessments performed in the course of GcMAF therapy, and - together with the assessment of serum nagalase activity testing and VDR polymorphisms - it may assist physicians in monitoring the response of individual patient to GcMAF and adjusting doses and schedules in the course of treatment, if required. Studies investigating the impact of GC polymorphisms on the response of cancer patients to GcMAF therapy as well as the contribution of distinct GC variants to the relative amounts of “non-inducible,” inactive GcMAF species20 will also be instrumental in determining the most correct approach to GcMAF administration.
The results reported here are consistent with previous results5-7 as well as with a recent publication by Inui et al.,21 who described three clinical cases successfully treated with combinatorial therapeutic regimens including subcutaneous or intramuscular injections of GcMAF-containing human serum. At variance with this latter study, the results presented here were obtained with highly purified GcMAF, ruling out the effects of other serum proteins that might have acted as confounding factors.
In conclusion, the clinical cases presented here reinforce the hypothesis that GcMAF could become part of anticancer immunotherapeutic regimens.
Materials and Methods
GcMAF production
Physicians obtained GcMAF from Immuno Biotech Ltd (Guernsey, UK). GcMAF was highly purified according to previously described procedures.7 Briefly, VDBP was isolated from purified human serum obtained from the American Red Cross, using either 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-sepharose high affinity chromatography or actin-agarose affinity chromatography. Bound material was eluted and further processed by incubation with three immobilized enzymes. The resulting GcMAF was filter sterilized. Protein content and concentration of the GcMAF solution were assayed using standard Bradford protein assay methods.22 At the end of the production process, GcMAF was checked for sterility in-house as well as externally, by independent laboratories. The safety and biological activity of GcMAF were tested on human monocytes,13 human breast cancer cells,10 and chick embryo chorionallantoic membranes.12
Data collection
A retrospective chart review for the analysis of nagalase testing was accomplished on the initial cohort of patients seen by the clinicians (RE and Dr. Steven Hofman, CMC, Capelle aan den Ijssel; The Netherlands). All records were reviewed by physicians for confirmation of serum nagalase activity values, diagnoses, time intervals between testing, GcMAF dosing and clinical responses. The diagnosis of cancer was confirmed by other treating physicians.
GcMAF administration
The administration of GcMAF to individual patients was performed exclusively by their physicians (RE and Dr. Steven Hofman, CMC, Capelle aan den Ijssel; The Netherlands), according to the national rules and regulations. Original clinical records are conserved by the physicians, in their respective locations, as indicated. In the Results section, clinical cases are reported as close as possible to the originals notes of physicians, with minimal grammar and spelling corrections. Since each physicians used described the condition of individual patients in a different fashion, some heterogeneity in these notes has to be expected. The notes are purposely presented as they had been written so that each reader can draw her/his conclusions.
Serum nagalase activity determinations
Serum nagalase testing was performed at ELN Laboratories (Bunnik, The Netherlands) following the procedure published by Yamamoto et al.14 In particular, serum nagalase activity was determined by using an endpoint enzymatic assay based on a chromogenic substrate. ELN Laboratories established a reference range of 0.32–0.95 nM/min/mg of substrate based on serum samples collected from healthy volunteers, a range slightly higher than that previously reported, which was of 0.35–0.65 nM/min/mg.14 Further studies on elevated numbers of subjects will establish the most appropriate reference range. Irrespective of this issue, since all determinations were performed in the same laboratory, a relative decrease of in serum nagalase activity following GcMAF administration was used as an index of therapeutic efficacy.
Statistical methods
Statistical comparisons between the serum nagalase activity observed before and after (at two distinct time points) the administration of GcMAF were performed by Student’s t-tests.
Acknowledgments
The Authors wish to thank Dr. Steven Hofman, CMC, Capelle aan den Ijssel, The Netherlands, for providing the data concerning the patients he treated as well as for critical review of this study.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
DN is the CEO of Immuno Biotech Ltd (the company isolating and purifying the GcMAF protein). However, DN had no knowledge of the therapies being used nor of the names of any patients whose data were being analyzed. Neither he, nor any employee of Immuno Biotech Ltd, had any knowledge of the nagalase or other test results or the patient names used in this study.
Glossary
Abbreviations:
- BCG
bacillus Calmette-Guérin
- CA-125
cancer antigen 125
- GalNAc
N-acetylgalactosamine
- GcMAF
GC protein-derived macrophage-activating factor
- PINI
prognostic inflammatory and nutritional index
- PSA
prostate-specific antigen
- VDBP
vitamin D-binding protein
- VDR
vitamin D receptor
Footnotes
Previously published online: www.landesbioscience.com/journals/oncoimmunology/article/25769
References
- 1.Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Moore M, Brent LH. Deglycosylation of serum vitamin D3-binding protein by alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase detected in the plasma of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997;82:290–8. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.4320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mohamad SB, Nagasawa H, Uto Y, Hori H. Tumor cell alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity and its involvement in GcMAF-related macrophage activation. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002;132:1–8. doi: 10.1016/S1095-6433(01)00522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greco M, Mitri MD, Chiriacò F, Leo G, Brienza E, Maffia M. Serum proteomic profile of cutaneous malignant melanoma and relation to cancer progression: association to tumor derived alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity. Cancer Lett. 2009;283:222–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Reddi AL, Sankaranarayanan K, Arulraj HS, Devaraj N, Devaraj H. Serum alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase is associated with diagnosis/prognosis of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Cancer Lett. 2000;158:61–4. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3835(00)00502-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N, Ushijima N. Immunotherapy of metastatic breast cancer patients with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF) Int J Cancer. 2008;122:461–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Nakazato H, Yamamoto N, Koga Y. Immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal cancer with vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor, GcMAF. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008;57:1007–16. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0431-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 7.Yamamoto N, Suyama H, Yamamoto N. Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer with Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor, GcMAF. Transl Oncol. 2008;1:65–72. doi: 10.1593/tlo.08106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nonaka K, Onizuka S, Ishibashi H, Uto Y, Hori H, Nakayama T, et al. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor inhibits HCC in SCID mice. J Surg Res. 2012;172:116–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.07.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gregory KJ, Zhao B, Bielenberg DR, Dridi S, Wu J, Jiang W, et al. Vitamin D binding protein-macrophage activating factor directly inhibits proliferation, migration, and uPAR expression of prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pacini S, Punzi T, Morucci G, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Effects of vitamin D-binding protein-derived macrophage-activating factor on human breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kalkunte S, Brard L, Granai CO, Swamy N. Inhibition of angiogenesis by vitamin D-binding protein: characterization of anti-endothelial activity of DBP-maf. Angiogenesis. 2005;8:349–60. doi: 10.1007/s10456-005-9024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pacini S, Morucci G, Punzi T, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M. Gc protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) stimulates cAMP formation in human mononuclear cells and inhibits angiogenesis in chick embryo chorionallantoic membrane assay. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60:479–85. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0953-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pacini S, Morucci G, Punzi T, Gulisano M, Ruggiero M, Amato M, et al. Effect of paricalcitol and GcMAF on angiogenesis and human peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation and signaling. J Nephrol. 2012;25:577–81. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yamamoto N, Naraparaju VR, Urade M. Prognostic utility of serum alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase and immunosuppression resulted from deglycosylation of serum Gc protein in oral cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1997;57:295–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yamamoto N, Lindsay DD, Naraparaju VR, Ireland RA, Popoff SN. A defect in the inflammation-primed macrophage-activation cascade in osteopetrotic rats. J Immunol. 1994;152:5100–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nunn R. Mere anecdote: evidence and stories in medicine. J Eval Clin Pract. 2011;17:920–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2011.01727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yamamoto N, Ushijima N, Koga Y. Immunotherapy of HIV-infected patients with Gc protein-derived macrophage activating factor (GcMAF) J Med Virol. 2009;81:16–26. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bradstreet JJ, Vogelaar E, Thyer L. Initial observations of elevated alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity associated with autism and observed reductions from GC protein-macrophage activating factor injections. Autism Insights. 2012;4:31–8. doi: 10.4137/AUI.S10485. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fabris A, Biagioni P, Punzi T, Morucci G, Gulisano M, Pacini S, et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Am J Immunol. 2012;8:65–70. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rehder DS, Nelson RW, Borges CR. Glycosylation status of vitamin D binding protein in cancer patients. Protein Sci. 2009;18:2036–42. doi: 10.1002/pro.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Inui T, Kuchiike D, Kubo K, Mette M, Uto Y, Hori H, et al. Clinical Experience of Integrative Cancer Immunotherapy with GcMAF. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:2917–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


