Abstract
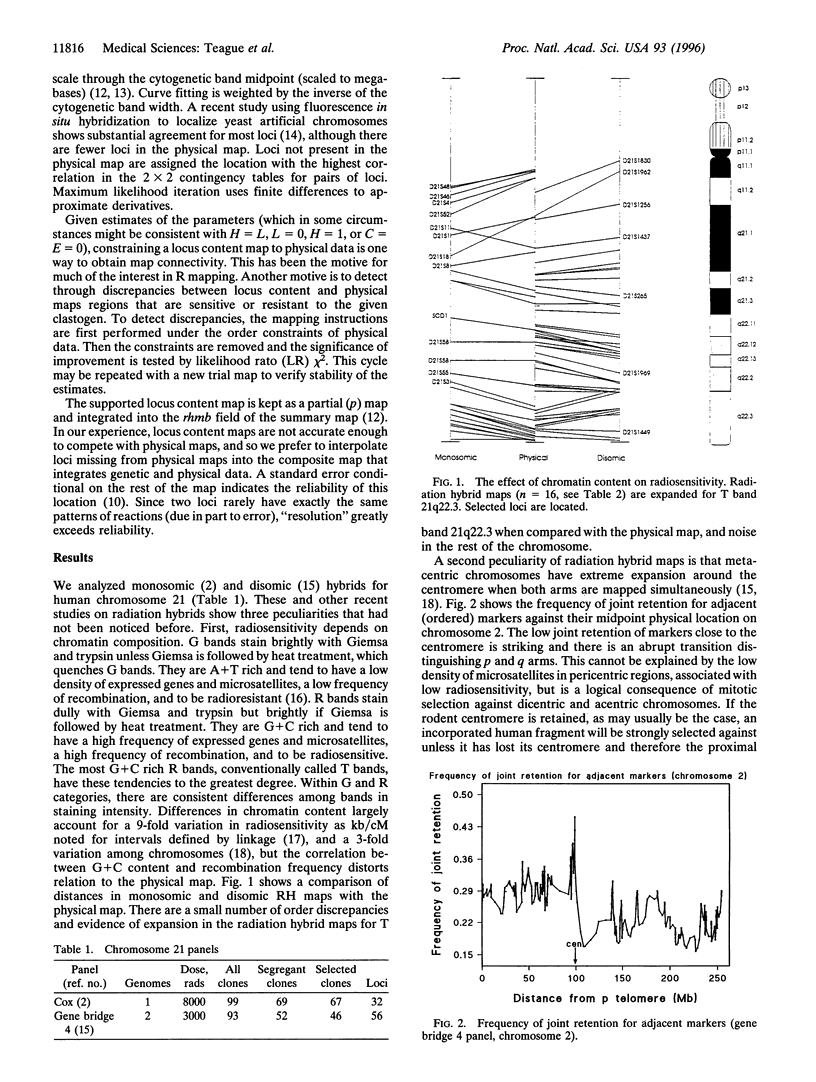
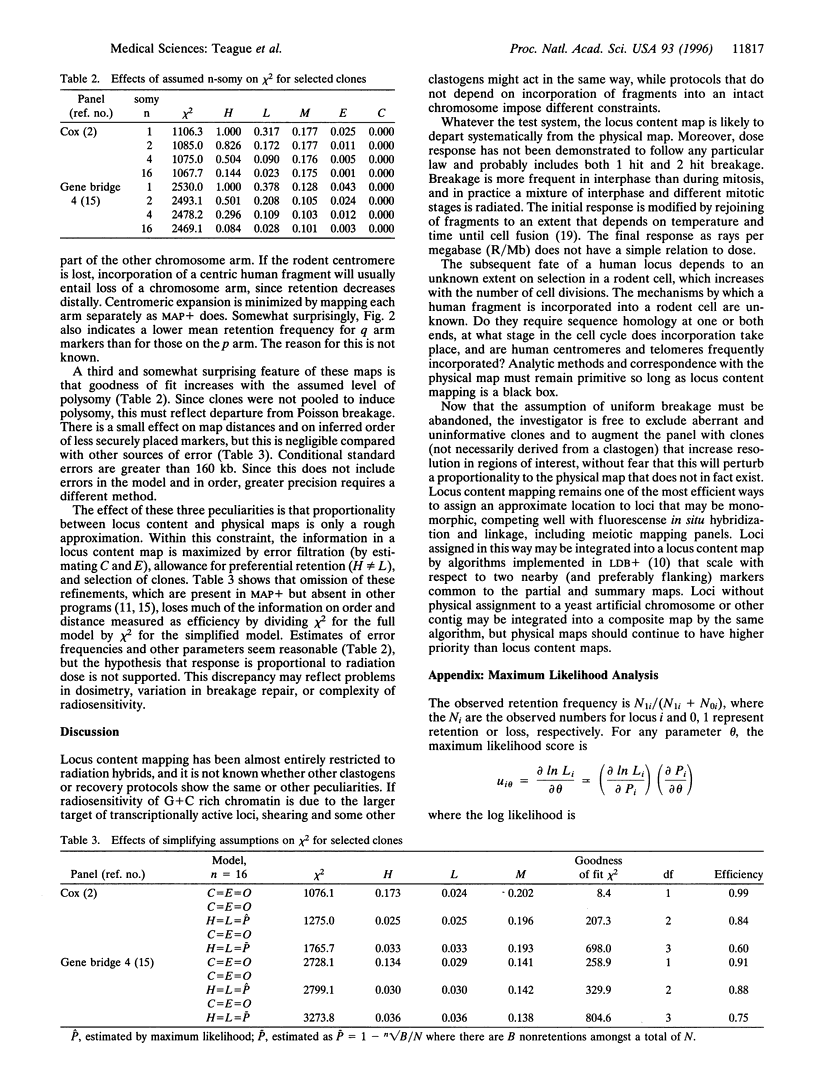
Locus content maps are derived from monosomic or disomic chromosomes broken by radiation, shearing, or other clastogen, the fragments being distributed among clones by dilution or incorporation into the cells of another species and scored for segregation of markers. Locus content maps provide evidence about radiosensitivity of chromosome regions, support for order, and approximate location. Omission of the most aberrant and least informative clones increases efficiency of localization. Correct analysis must allow for preferential retention of certain sequences, monosomy or polysomy of donor chromosomes, and error filtration. Combination of these refinements extracts substantially more information from fewer clones. Because of unmodeled peculiarities in the data, the best analysis does not recover the physical map but roughly localizes markers that may be monomorphic and therefore unsuitable for linkage mapping. As with linkage for polymorphic loci, distance in the composite map should be confirmed by physical methods.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E. Third International Workshop on Human Chromosome 21. Genomics. 1992 Dec;14(4):1126–1132. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray-Ward P., Menninger J., Lieman J., Desai T., Mokady N., Banks A., Ward D. C. Integration of the cytogenetic, genetic, and physical maps of the human genome by FISH mapping of CEPH YAC clones. Genomics. 1996 Feb 15;32(1):1–14. doi: 10.1006/geno.1996.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov I., Rigault P., Guillou S., Ougen P., Billaut A., Guasconi G., Gervy P., LeGall I., Soularue P., Grinas L. Continuum of overlapping clones spanning the entire human chromosome 21q. Nature. 1992 Oct 1;359(6394):380–387. doi: 10.1038/359380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear P. H., Cook P. R. Happy mapping: linkage mapping using a physical analogue of meiosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):13–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Digitized and differentially shaded human chromosome ideograms for genomic applications. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;65(3):206–218. doi: 10.1159/000133633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Chromosomal region of the cystic fibrosis gene in yeast artificial chromosomes: a model for human genome mapping. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):94–98. doi: 10.1126/science.2218515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyapay G., Schmitt K., Fizames C., Jones H., Vega-Czarny N., Spillett D., Muselet D., Prud'homme J. F., Dib C., Auffray C. A radiation hybrid map of the human genome. Hum Mol Genet. 1996 Mar;5(3):339–346. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Chromosome bands, their chromatin flavors, and their functional features. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):17–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. J., Stein L. D., Gerety S. S., Ma J., Castle A. B., Silva J., Slonim D. K., Baptista R., Kruglyak L., Xu S. H. An STS-based map of the human genome. Science. 1995 Dec 22;270(5244):1945–1954. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5244.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence S., Morton N. E., Cox D. R. Radiation hybrid mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7477–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach R. J., O'Connell P. Mapping of mammalian genomes with radiation (Goss and Harris) hybrids. Adv Genet. 1995;33:63–99. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunetta K. L., Boehnke M., Lange K., Cox D. R. Experimental design and error detection for polyploid radiation hybrid mapping. Genome Res. 1995 Sep;5(2):151–163. doi: 10.1101/gr.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matise T. C., Perlin M., Chakravarti A. Automated construction of genetic linkage maps using an expert system (MultiMap): a human genome linkage map. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):384–390. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Collins A., Lawrence S., Shields D. C. Algorithms for a location database. Ann Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;56(Pt 3):223–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1992.tb01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E. Disomic locus content mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1421–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. C., Collins A., Buetow K. H., Morton N. E. Error filtration, interference, and the human linkage map. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6501–6505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



