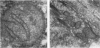
Abstract
Sequences of nuclear-encoded small-subunit rRNA genes have been determined for representatives of the enigmatic genera Dermocystidium, Ichthyophonus, and Psorospermium, protistan parasites of fish and crustaceans. The small-subunit rRNA genes from these parasites and from the "rosette agent" (also a parasite of fish) together form a novel, statistically supported clade. Phylogenetic analyses demonstrate this clade to diverge near the animal-fungal dichotomy, although more precise resolution is problematic. In the most parsimonious and maximally likely phylogenetic frameworks inferred from the most stably aligned sequence regions, the clade constitutes the most basal branch of the metazoa; but within a limited range of model parameters, and in some analyses that incorporate less well-aligned sequence regions, an alternative topology in which it diverges immediately before the animal-fungal dichotomy was recovered. Mitochondrial cristae of Dermocystidium spp. are flat, whereas those of Ichthyophonus hoferi appear tubulovesiculate. These results extend our understanding of the types of organisms from which metazoa and fungi may have evolved.
Full text
PDF
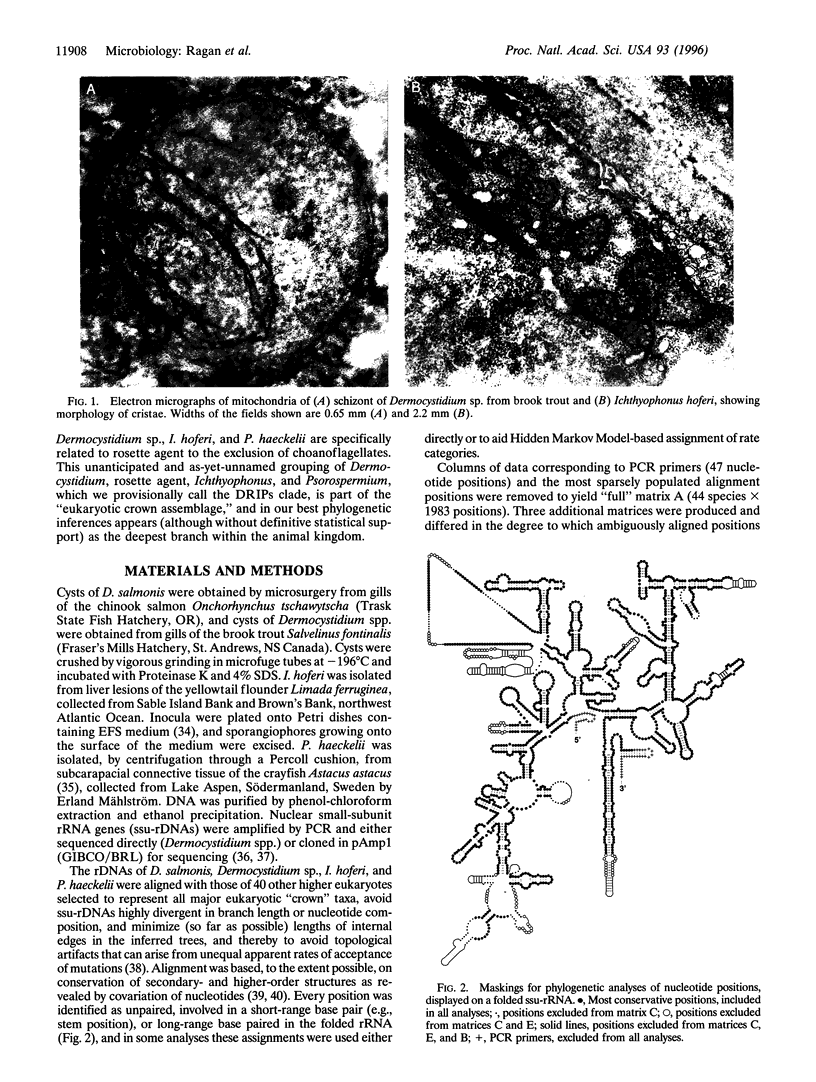

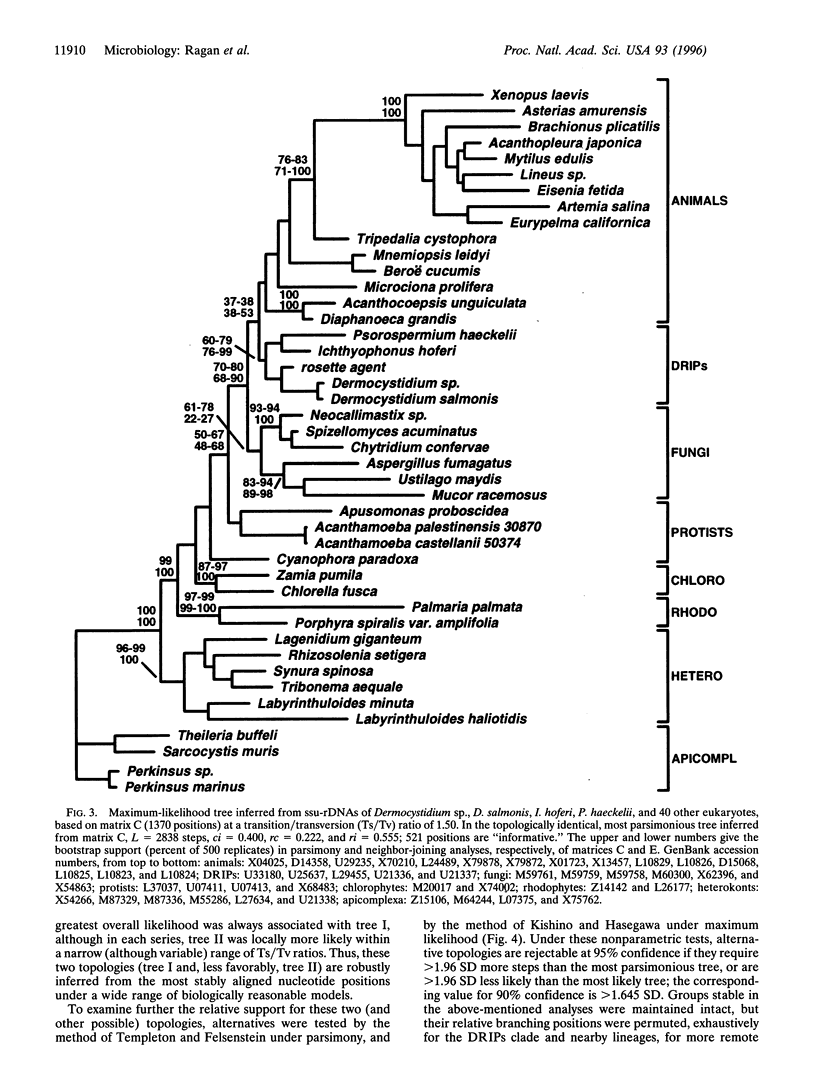
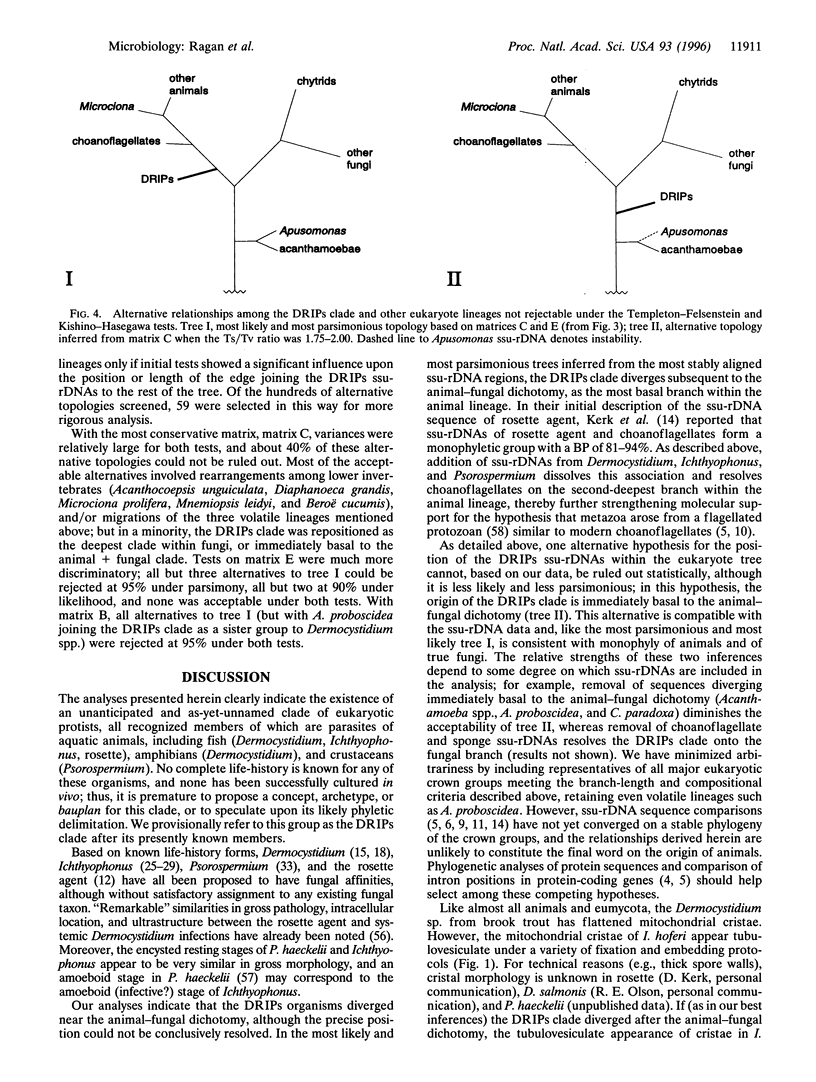

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker F. T., Olsen J. L., Stam W. T., van den Hoek C. The Cladophora complex (Chlorophyta): new views based on 18S rRNA gene sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1994 Dec;3(4):365–382. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1994.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldauf S. L., Palmer J. D. Animals and fungi are each other's closest relatives: congruent evidence from multiple proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11558–11562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Kingdom protozoa and its 18 phyla. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Dec;57(4):953–994. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.953-994.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauvier G. Mycose viscérale de poissons dulçaquicoles tropicaux. Note préliminaire. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1979 Jan-Feb;54(1):105–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. T., Hillis D. M. Ribosomal RNA secondary structure: compensatory mutations and implications for phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):256–267. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J., Churchill G. A. A Hidden Markov Model approach to variation among sites in rate of evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1996 Jan;13(1):93–104. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Larsen N., Woese C. R. Lessons from an evolving rRNA: 16S and 23S rRNA structures from a comparative perspective. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):10–26. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.10-26.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino H., Hasegawa M. Evaluation of the maximum likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J Mol Evol. 1989 Aug;29(2):170–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02100115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll A. H. The early evolution of eukaryotes: a geological perspective. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):622–627. doi: 10.1126/science.1585174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Matsuda H., Hagstrom R., Overbeek R. fastDNAmL: a tool for construction of phylogenetic trees of DNA sequences using maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci. 1994 Feb;10(1):41–48. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/10.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand T. G., Cone D. K. Effects of Ichthyophonus hoferi on condition indices and blood chemistry of experimentally infected rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Wildl Dis. 1990 Jul;26(3):323–328. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-26.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitnikova T., Rzhetsky A., Nei M. Interior-branch and bootstrap tests of phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1995 Mar;12(2):319–333. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smothers J. F., von Dohlen C. D., Smith L. H., Jr, Spall R. D. Molecular evidence that the myxozoan protists are metazoans. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1719–1721. doi: 10.1126/science.8085160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainright P. O., Hinkle G., Sogin M. L., Stickel S. K. Monophyletic origins of the metazoa: an evolutionary link with fungi. Science. 1993 Apr 16;260(5106):340–342. doi: 10.1126/science.8469985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler W. C., Honeycutt R. L. Paired sequence difference in ribosomal RNAs: evolutionary and phylogenetic implications. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Jan;5(1):90–96. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]