Abstract
Hippocampal pyramidal cells, receiving domain specific GABAergic inputs, express up to 10 different subunits of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor, but only 3 different subunits are needed to form a functional pentameric channel. We have tested the hypothesis that some subunits are selectively located at subsets of GABAergic synapses. The alpha 1 subunit has been found in most GABAergic synapses on all postsynaptic domains of pyramidal cells. In contrast, the alpha 2 subunit was located only in a subset of synapses on the somata and dendrites, but in most synapses on axon initial segments innervated by axo-axonic cells. The results demonstrate that molecular specialization in the composition of postsynaptic GABAA receptor subunits parallels GABAergic cell specialization in targeting synapses to a specific domain of postsynaptic cortical neurons.
Full text
PDF

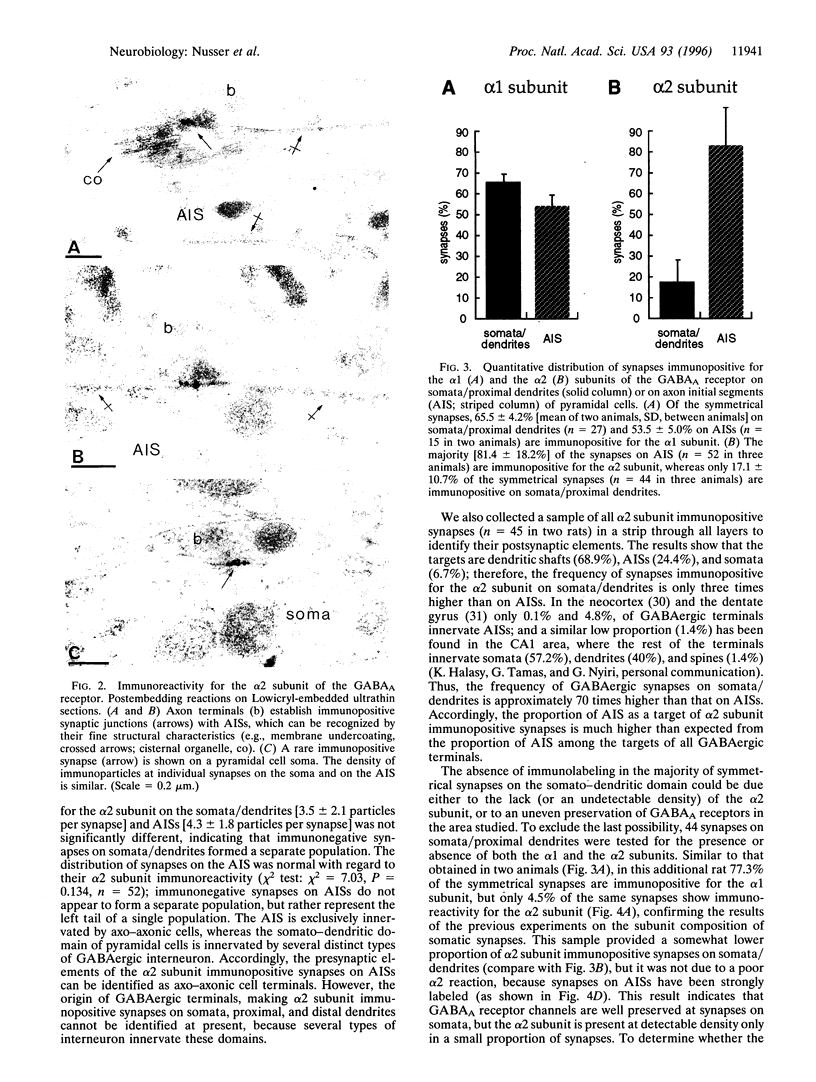



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. PATHWAY OF POSTSYNAPTIC INHIBITION IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 Jul;27:608–619. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.4.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN P., ECCLES J. C., LOYNING Y. Recurrent inhibition in the hippocampus with identification of the inhibitory cell and its synapses. Nature. 1963 May 11;198:540–542. doi: 10.1038/198540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baude A., Nusser Z., Roberts J. D., Mulvihill E., McIlhinney R. A., Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):771–787. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu C., Kisvarday Z., Somogyi P., Cynader M., Cowey A. Quantitative distribution of GABA-immunopositive and -immunonegative neurons and synapses in the monkey striate cortex (area 17). Cereb Cortex. 1992 Jul-Aug;2(4):295–309. doi: 10.1093/cercor/2.4.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedeczky I., Molnár E., Somogyi P. The cisternal organelle as a Ca(2+)-storing compartment associated with GABAergic synapses in the axon initial segment of hippocampal pyramidal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1994;101(2):216–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00228742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benke D., Fritschy J. M., Trzeciak A., Bannwarth W., Mohler H. Distribution, prevalence, and drug binding profile of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subtypes differing in the beta-subunit variant. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):27100–27107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bragin A., Jandó G., Nádasdy Z., Hetke J., Wise K., Buzsáki G. Gamma (40-100 Hz) oscillation in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. J Neurosci. 1995 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):47–60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00047.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Cobb S. R., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Properties of unitary IPSPs evoked by anatomically identified basket cells in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Sep 1;7(9):1989–2004. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Somogyi P. Diverse sources of hippocampal unitary inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and the number of synaptic release sites. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):823–828. doi: 10.1038/368823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. R., Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Paulsen O., Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):75–78. doi: 10.1038/378075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Starkey S. J., Pozza M. F., Collingridge G. L. GABA autoreceptors regulate the induction of LTP. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):609–611. doi: 10.1038/349609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritschy J. M., Mohler H. GABAA-receptor heterogeneity in the adult rat brain: differential regional and cellular distribution of seven major subunits. J Comp Neurol. 1995 Aug 14;359(1):154–194. doi: 10.1002/cne.903590111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyás A. I., Miles R., Hájos N., Freund T. F. Precision and variability in postsynaptic target selection of inhibitory cells in the hippocampal CA3 region. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Dec 1;5(12):1729–1751. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halasy K., Somogyi P. Distribution of GABAergic synapses and their targets in the dentate gyrus of rat: a quantitative immunoelectron microscopic analysis. J Hirnforsch. 1993;34(3):299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDEL E. R., SPENCER W. A., BRINLEY F. J., Jr Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. I. Sequential invasion and synaptic organization. J Neurophysiol. 1961 May;24:225–242. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Hama K. Physiological heterogeneity of nonpyramidal cells in rat hippocampal CA1 region. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(3):494–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00250594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch J., Wolters I., Triller A., Betz H. Gephyrin antisense oligonucleotides prevent glycine receptor clustering in spinal neurons. Nature. 1993 Dec 23;366(6457):745–748. doi: 10.1038/366745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Katsumaru H., Hama K., Wu J. Y., Heizmann C. W. GABAergic neurons containing the Ca2+-binding protein parvalbumin in the rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90575-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T. The axon initial segment as a synaptic site: ultrastructure and synaptology of the initial segment of the pyramidal cell in the rat hippocampus (CA3 region). J Neurocytol. 1980 Dec;9(6):861–882. doi: 10.1007/BF01205024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulen P., Sassoè-Pognetto M., Grünert U., Wässle H. Selective clustering of GABA(A) and glycine receptors in the mammalian retina. J Neurosci. 1996 Mar 15;16(6):2127–2140. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-02127.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. I. Intracellular response characteristics, synaptic responses, and morphology. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1400–1410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01400.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüddens H., Korpi E. R., Seeburg P. H. GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor heterogeneity: neurophysiological implications. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Mar;34(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00158-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Olsen R. W. GABAA receptor channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:569–602. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marksitzer R., Benke D., Fritschy J. M., Trzeciak A., Bannwarth W., Mohler H. GABAA-receptors: drug binding profile and distribution of receptors containing the alpha 2-subunit in situ. J Recept Res. 1993;13(1-4):467–477. doi: 10.3109/10799899309073673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C. J., DiChiara T. J., Kauer J. A. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors differentially affects two classes of hippocampal interneurons and potentiates excitatory synaptic transmission. J Neurosci. 1994 Jul;14(7):4433–4445. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-07-04433.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Inhibitory control of local excitatory circuits in the guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:611–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Unitary inhibitory synaptic potentials in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:97–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Ueda T. Affinity-purified anti-protein I antibody. Specific inhibitor of phosphorylation of protein I, a synaptic protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10657–10663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Milan F., Freund T. F., Somogyi P., Smith A. D. Cholecystokinin-immunoreactive cells form symmetrical synaptic contacts with pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons in the hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jul 22;237(4):485–505. doi: 10.1002/cne.902370406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusser Z., Roberts J. D., Baude A., Richards J. G., Sieghart W., Somogyi P. Immunocytochemical localization of the alpha 1 and beta 2/3 subunits of the GABAA receptor in relation to specific GABAergic synapses in the dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Apr 1;7(4):630–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusser Z., Sieghart W., Stephenson F. A., Somogyi P. The alpha 6 subunit of the GABAA receptor is concentrated in both inhibitory and excitatory synapses on cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan;16(1):103–114. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-01-00103.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Velazquez J. L., Angelides K. J. Assembly of GABAA receptor subunits determines sorting and localization in polarized cells. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):457–460. doi: 10.1038/361457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persohn E., Malherbe P., Richards J. G. Comparative molecular neuroanatomy of cloned GABAA receptor subunits in the rat CNS. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Dec 8;326(2):193–216. doi: 10.1002/cne.903260204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Lüddens H., Seeburg P. H. Type I and type II GABAA-benzodiazepine receptors produced in transfected cells. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1389–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2551039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E., Nitsch R., Seress L. Proportion of parvalbumin-positive basket cells in the GABAergic innervation of pyramidal and granule cells of the rat hippocampal formation. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Oct 22;300(4):449–461. doi: 10.1002/cne.903000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W. Structure and pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1995 Jun;47(2):181–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sik A., Penttonen M., Ylinen A., Buzsáki G. Hippocampal CA1 interneurons: an in vivo intracellular labeling study. J Neurosci. 1995 Oct;15(10):6651–6665. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06651.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Smith A. D. A new type of specific interneuron in the monkey hippocampus forming synapses exclusively with the axon initial segments of pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 17;259(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A. The GABAA receptors. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 15;310(Pt 1):1–9. doi: 10.1042/bj3100001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. J., Sakmann B. Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):69–72. doi: 10.1038/367069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triller A., Cluzeaud F., Pfeiffer F., Betz H., Korn H. Distribution of glycine receptors at central synapses: an immunoelectron microscopy study. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):683–688. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Laurie D. J., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H. The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1040–1062. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01040.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylinen A., Soltész I., Bragin A., Penttonen M., Sik A., Buzsáki G. Intracellular correlates of hippocampal theta rhythm in identified pyramidal cells, granule cells, and basket cells. Hippocampus. 1995;5(1):78–90. doi: 10.1002/hipo.450050110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezula J., Fuchs K., Sieghart W. Separation of alpha 1, alpha 2 and alpha 3 subunits of the GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor complex by immunoaffinity chromatography. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 1;563(1-2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91556-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






