Abstract
Objectives
To date, experiences of leaders in the implementation of Lean after a Lean Training Programme have not been systematically investigated within teaching hospitals. Existing studies have identified barriers and facilitators only from an improvement programme perspective and have not considered the experiences of leaders themselves. This study aims to bridge this gap.
Design
Semistructured, indepth interviews.
Setting
One of largest teaching hospitals in the Netherlands.
Participants
31 medical, surgical and nursing professionals with an average of 19.2 years of supervisory experience. All professionals were appointed to a Lean Training Programme and were directly involved in the implementation of Lean.
Results
The evidence obtained in this study shows that, from the perspectives of participants, leadership management support, a continuous learning environment and cross-departmental cooperation play a significant role in successful Lean implementation. The results suggest that a Lean Training Programme contributed to positive outcomes in personal and professional skills that were evident during the first 4 months after programme completion.
Conclusions
Implementing Lean in a teaching hospital setting is a challenge because of the ambiguous and complex environment of a highly professionalised organisation. The study found that leadership management support and a continuous learning environment are important facilitators of Lean implementation. To increase the successful outcomes of leadership actions, training should be supplemented with actions to remove perceived barriers. This requires the involvement of all professionals, the crossing of departmental boundaries and a focus on meaning-making processes rather than simply ‘implementing’ facts. Therefore, this research suggests that programme participants, such as staff members and leaders, can mutually explore the meanings of Lean thinking and working for their own contexts. By entering this shared learning process (eg, learning on the job) the ownership of Lean implementation could also increase.
Keywords: Medical Education & Training
Article summary.
Strengths and limitations of this study
We acquired detailed records of leader experiences in clinical practices.
This was a qualitative study whose purpose was to explore experiences of leaders in the implementation of lean in a teaching hospital; further multiple centre studies are necessary to show causal links.
Most outcome measures of this study are self-reported and may be influenced by information or recall bias.
Introduction
Lean improvements have been initiated in hospitals throughout the world for the benefit of patients, employees and hospital organisations. In the Netherlands, budget constraints and the growing patient population have urged healthcare organisations to improve efficiency and reduce costs while maintaining quality.1 2 In addition, the focus on the quality of patient care has been increased by health inspectorate accreditation organisations. As a result of this focus, healthcare leaders need to focus on efficient, patient-centred operations and continuous quality improvements.3 One possible way to achieve this is by implementing Lean; however, an organisation cannot become Lean overnight. Lean projects in other industries have shown that the application of Lean practices requires perseverance and top-down commitment combined with bottom-up implementation.4–6 These requirements imply the crossing of departmental boundaries, collaboration and a high-quality training programme.7–9
A recent study of McConnell et al10 shows that patient outcomes can be improved by a Lean management system. Yet, little is known about the barriers and facilitators—defined as factors that influence Lean implementation—that are encountered during the implementation of Lean within hospital settings.11–13 Various psychology studies and studies of patient safety education have shown that 40–50% of the intended actions after training are never executed or are only partially implemented.14 15 This finding may also apply to the outcomes of a Lean Training Programme (LTP). However, few studies have discussed the barriers and facilitators that may be encountered in follow-up actions after an LTP in a hospital setting.
The aim of this paper is to provide insight into the barriers and facilitators that are encountered in implementing Lean within clinical practices. This paper explores the experiences of team leaders after they attended an LTP to improve their management skills and behaviour to aid in the implementation of Lean practices.
Methods
Setting
The study was conducted at the VU University Medical Center (VUmc), a 733-bed academic hospital located in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. The VUmc employs 5610 full-time staff operating within a current budget of €301 million. In 2010, the VUmc had 27 096 admissions performed 24 729 outpatient treatments and received 322 696 visits to its outpatient units, of which 122 120 were first contacts. The Dutch Institute for Accreditation in Healthcare (NIAZ) accredited the VUmc by an external audit in the fall of 2010. Subsequently, the VUmc adopted Lean as a philosophy for continuous improvement. Roth16 describes Lean as: “lean is not a program or an outcome, nor does it reside at an executive level or within the workforce. Lean is a way of operating that spans from executive strategy setting for developing people and managing business growth to the commitment of the workforce to continuous improvement.”
During the first wave of Lean implementation, after careful debate and commitment from hospital leadership, the selected pilot departments included two surgery wards, the operating theatre of the VUmc and an affiliated outpatient psychiatry clinic. Subsequently, each of the 35 team leaders of these departments, who were targeted as key players, participated in a 4 day LTP. In this study, we understood leaders to be those people who were team leader by occupation with a minimum of 3 years of experience. The total programme consisted of 16 h of plenary and group sessions that were led by various Lean experts. The aim of the LTP was to increase the team leaders’ knowledge and skills concerning Lean management, with the central goal of transforming these skills and knowledge into leadership behaviours in day-to-day practice. The key themes included: (1) an introduction to Lean thinking and working; (2) management by standards; (3) solving problems and (4) Lean leadership. The learning goals of each theme are displayed in table 1.
Table 1.
The key themes and the content of the 4 day LTP
| Key themes | Content of LTP |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction to lean thinking and working |
|
| 2. Management by standards |
|
| 3. Solving problems |
|
| 4. Lean leadership |
|
At the end of the LTP, all participants were asked to formulate at least one action point for improving their work using lean as an improvement philosophy.
Qualitative study approach
A qualitative study approach was chosen to elicit in-depth insight into the perspectives of the participants concerning the barriers and facilitators that they encountered after the LTP, as qualitative research methods are helpful in addressing matters that concern organisational behaviour.17 Moreover, a study concerning employee perspectives requires a qualitative approach to enhance understanding of the context, personal experiences and interpretations of participants.
Participants
The participants were selected for an interview if they formulated at least one action point for improvement after completing the LTP. Eventually, 31 healthcare professionals, who were all the head of their team, with an average of 19.2 years of leadership experience, were selected. More than half (18) of the respondents were part of the operating theatre, one-third (9) belonged to the surgery ward and the remainder (4) were part of the mental hospital.
Data collection
The participants were invited to a semistructured, in-depth interview 3 months after the LTP. The semistructured interviews allowed for new issues to be mentioned during the interview by the respondents.18 Prior to conducting the interviews, we created an interview guide that contained open questions (box 1).
Box 1. Interview guide.
What is your opinion of the Lean Training Programme in which you have participated in terms of its content and organisation?
What action did you envisage to execute as a result of the Lean training?
Have you succeeded in executing the envisaged action?
To what extent has the execution of the action been successful?
Which factors facilitated the execution of your action?
To what extent have these facilitating factors contributed to the execution of your action?
Which factors obstructed the execution of your action?
To what extent have these various factors obstructed the execution of your action?
Have you already envisaged new actions that should be addressed by means of Lean (whether or not they emerged from previously mentioned actions)? If yes, what actions are you considering?
This guide provided consistency in the interviews, ensuring that the same general topics were addressed by each of the respondents. The respondents chose a favourable date, place and time for the interviews, which were conducted by the first author. Prior to the interview, the interviewees were informed about the anonymity and confidentiality of the information. The length of the interviews ranged from 23 to 84 min, and the interviews were audio recorded with permission from the interviewees. All recordings were transcribed literally (ad verbatim) prior to the data analysis.
Data analysis
First, we investigated the extent to which actions were executed. The following categories were used: (1) fully executed; (2) partially executed; and (3) not executed. An action was classified as partially executed if a leader had taken action but had not yet reached the goal or if some of the required actions had not yet been taken thus far. Second, we investigated how the team leaders had experienced the Lean programme. Experiences, barriers and facilitators were analysed with an inductive thematic analysis approach.19 The first four interviews were used to capture key patterns, which were used to assign labels (codes) to text fragments (open coding). The data that were extracted from the text fragments were subsequently analysed using a constant comparison method.20 21 Subsequently, axial coding was used to develop a framework of categories that focused on the barriers and facilitators that summarised the raw data and conveyed the key themes and processes (table 2). Axial coding assigns codes to categories. To ensure the reliability and accuracy of the data analysis, consistency checks were performed by two different researchers (KHA and FES). In addition, member checks of the results of the analysis with the respondents were performed to enhance the credibility of the findings.
Table 2.
Barriers to and facilitators of lean implementation
| Barrier/facilitator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Senior management support and commitment | Leaders are important in acting as role models to exemplify the desired behaviours for Lean implementation. As with all change and improvement programmes, support and commitment from senior management is critical to a Lean initiative. The ‘management commitment’ barrier referred to whether top management was involved in Lean implementation, spent time in the workplace to supervise the process as part of their support and provided the necessary resources to implement lean in the workplace |
| Resources | Because the availability of resources is a primary concern in healthcare organisations, it must be properly considered when implementing lean. The ‘resources’ barrier has two meanings. The majority of the respondents mentioned that implementation was hindered because of insufficient available time. Others mentioned that a lack of personnel resources hindered the implementation |
| Strategy and purpose | One of the drivers for the success of Lean is to have a clear, well-communicated strategy. Constant changes in an improvement strategy inhibit the continuity of potentially successful programmes |
| Resistance to change | Resistance to change is a significant problem in any improvement programme in any organisation. Resistance deserves special attention from those attempting to implement Lean because staff empowerment, which is a key issue in Lean theory, is needed for engaging healthcare professionals |
| Multidisciplinary collaboration | Collaboration (or the lack thereof) within a multidisciplinary team was experienced as a barrier in most cases |
| Functional and professional silos | The fragmentation of healthcare organisations into silos (professional or functional) imposes a major barrier to the flow of patients, goods and information and consequently to the implementation of Lean techniques in an organisation |
| Training and education | The successful implementation of Lean requires employees to be effective problem solvers and learners, thereby eliminating errors and making operating improvements. The knowledge that is acquired in the LTP and the transfer of this knowledge into practice were perceived as constituting a barrier. Moreover, this barrier referred to the lack of experience in the principles, methods and tools of Lean thinking and working |
LTP, Lean Training Programme; VUmc, VU University medical center.
Results
Action points
A total of 31 respondents indicated that they had taken action on 159 formulated action points (mean per respondent: 5.5), with 117 (74%) action points executed and 65 of those 117 (56% of all executed action points) fully executed. The executed action points included expanding Lean knowledge, using Lean tools (eg, 5S, stand-ups, value stream mapping (VSM)), measuring key performance indicators, adjusting one’s own work structure, learning to recognise waste, asking ‘Why’ five times, improving care processes/eliminating waste, giving coworkers time for improvement, involving senior management, improving the culture and educating colleagues about Lean. Some respondents (n=6) reported their future intended action points as a follow-up to the original executed action points that resulted from the LTP. Figure 1 provides an overview of the envisaged action points and the degree to which the actions were implemented.
Figure 1.
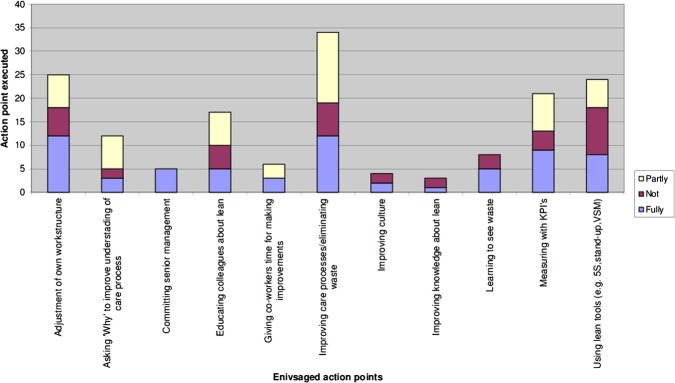
Overview of the envisaged and executed action points.
Experiences with the LTP
In general, the majority of the participants experienced the LTP as helpful; they indicated that they had acquired new skills that were necessary for Lean thinking and working. These skills had been taught during LTP training exercises, which were rated as valuable by the majority of the respondents. However, although this ‘learning by doing’ during the training sessions was beneficial, some respondents noted that ‘training on the job’ might result in better outcomes: this could be linked to the finding that most participants found it difficult to apply the acquired skills and knowledge in their jobs. Some participants stated that the workplace environment was a significant factor that influenced the extent of this training transfer to the workplace.
The majority of the respondents suggested that Lean coach interventions (eg, consultation, observation and coaching) between the four half-day training sessions may be helpful to transfer the acquired skills and knowledge to their actual work practices. The respondents also suggested a precourse briefing with each participant's manager as a means of initiating a discussion on how to apply the principles, techniques and skills that were learned after they returned from training. One participant stated that “a pre-course briefing sends a powerful message that the organization is serious about seeing the benefits of training.” Another suggestion was to introduce the programme or deliver one or more components of the programme to the participants’ supervisors or managers. These suggestions were motivated by the difficulty of executing the intended actions after the LTP, as reported by the respondents. One respondent stated that “if the training programme does not ultimately change workplace behaviour, then the money and time spent on training is simply wasted.”
Most participants actively engaged in the subject matter because they recognised the purpose of learning Lean. The organisational objectives of the programme were clearly described to the participants at the beginning of the programme. This information was experienced as helpful in showing how the programme related directly to the day-to-day work of the participants. Nevertheless, one participant stated that her new role expectations after the training programme were not clearly communicated to her: “I was left wondering why my superior nominated me for the programme.”
The participants also appreciated the interpersonal interaction in the training, in which goals and aspirations were shared, experiences were discussed and work practices were demonstrated. The participants explained that these interactions resulted in shared learning between the LTP participants in their workplace.
Despite the positive evaluation, some respondents experienced challenges concerning the timing of the LTP. These respondents would have preferred to attend the LTP in the morning or afternoon rather than in the early evening, given the low level of alertness after a day of work. Furthermore, some respondents proposed reading and exercises between meetings to prepare for the training programme.
Perceived barriers and facilitators
Barriers and facilitators were defined as factors that influence the implementation of Lean from the perspectives of participants. The participants addressed issues that were primarily related to internal organisation and leadership. Occasionally, the participants cited environmental factors; however, these factors were not considered in the analysis because organisations and leaders have little control over them when implementing Lean.
Senior management support and commitment
The participants noted that it is important for Lean implementation that team leaders, supervisors and management exemplify the desired behaviour. Participants characterised this behaviour as ‘the support and commitment of senior management’. The barrier ‘lack of management commitment’ refers to whether top management was involved in Lean implementation, spent time in the workplace to supervise the process as part of their support and provided the necessary resources to implement Lean in the workplace. One participant offered the following explanation: “The problem is that top management sits in their ivory towers. They trust that everything will work out fine on the work floor. I think there is too much distance between management and their teams because they are always busy, busy, busy.” Another respondent stated the following: “I think that motivation is very important because if management stops giving support, lean will fall apart.” In contrast, the respondents who noted that leaders served as role models for the desired behaviour considered management support to be a facilitator of Lean implementation.
Resources
The respondents considered sufficient resources, such as time to make improvements, sufficient staff resources and financial support for employee training, to be critical to a successful Lean implementation. The majority of the respondents noted that the implementation was hindered by insufficient available time. One respondent stated that “one of the main barriers is time. That is the main hindrance. I find it very disappointing that after the training, you have a positive attitude towards change, but in your daily routine, you become rapidly consumed by day-to-day things, and then the intentions and training will fade away very easily.” Another respondent noted that getting staff released from workloads and other work pressures with dedication of time to make the necessary improvements, as well as the availability of an effective facilitator on the work floor are important success factors.
Strategy and purpose
Important facilitators of Lean implementation include a compelling vision and a clear and well-planned strategy. According to the participants of our study, objectives, purposes and goals must be evident for everyone involved. One participant stated that “senior management must know for sure what they want to achieve [with lean], how to achieve it, and know which aspects [for implementing change] must be taken into account.” The participants also agreed that a lack of integration of a Lean strategy with the overall hospital strategy and other organisation-wide programmes is a major barrier.
Resistance to change
Several participants perceived their own staff's lack of motivation to change as a barrier to Lean implementation. Resistance to change is a significant problem in any improvement programme in any organisation; however, the participants of this study stated that resistance deserves special attention in Lean implementation because staff empowerment is perceived as essential for engaging healthcare professionals. One respondent explained that “by empowering employees, team leaders can build on a nurturing environment in which employees can learn, improve and effectively implement goals.”
Multidisciplinary collaboration
A lack of multidisciplinary collaboration within a team was experienced as a barrier. Multidisciplinary collaboration requires teamwork. To function well, team members must work towards a common goal, communicate clearly with other team members and understand one another's roles. Communication breakdowns appeared to increase because of cultural and organisational differences between professionals. Several participants noted that not all team members shared a common language for making sense of each other's actions. One participant stated the following: “The problems that demand a multidisciplinary approach are very frustrating problems. You are confronted with difficult collaboration [not the same understanding of each other's roles and communication problems] between physicians and operating staff.”
Functional and professional silos
Some participants indicated that the fragmentation of the care process into different professional and functional departments—silos—imposes a major barrier to the flow of patients, goods and information and consequently to the implementation of Lean techniques in the organisation. Silos can be important for accomplishing specific, focused tasks; however, although fragmentation in silos undoubtedly improves specific skills, some participants argued that this fragmentation presents a challenge in determining how to be effective while still maintaining professional competencies. One leader stated that “sometimes you experience problems outside your circle of influence, and then you are stuck with a problem because you have not established an infrastructure that reflects collaborative work with other departments.” According to our respondents, the optimal means of interacting effectively across silos is to build personal connections and establish common goals as well as to support those people who are willing to reach across boundaries and celebrate successes.
Training and education
The transfer of knowledge acquired from the LTP into practice was also perceived as a barrier. The participants cited the lack of knowing how to use Lean tools in daily practices as a barrier. One participant said that “not knowing how to use lean tools, such as “5 Whys”, is a barrier. You may try using the “5 Whys” tool to determine which area you can improve.” Furthermore, the respondents pointed to their lack of experience in the principles, methods and tools of Lean thinking. Many respondents suggested that coaching during implementation and site visits to other Lean organisations (eg, Scania, Toyota) would be helpful.
Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate the experiences of hospital leaders (middle management) in implementing Lean after attending an LTP. This study also aimed to provide further insight into the barriers and facilitators that may be encountered when implementing Lean within a clinical practice. The results indicate that the involvement of top management and the creation of a shared learning environment are important factors in the successful implementation of Lean; in addition, we observed a need for a holistic Lean philosophy.
In general, the findings suggest that the daily presence of top management on the work floor is a key factor in the success of Lean implementation. Most participants of our study experienced a lack of involvement of top management, and many wanted leaders to be present in daily settings more frequently and to function as role models. We feel that by doing so, leaders could increase ownership of the processes and encourage and empower employees to participate in Lean. Previous studies of Lean implementation have also reported a relationship between the success of Lean implementation and management leadership behaviour.21–26 Top management should be more involved and must take ownership of Lean programmes.27
According to our study, a lack of vision and strategy regarding how to integrate Lean with the overall hospital strategy is a major barrier to Lean implementation. Lean implementation in the Dutch context began with techniques: leaders attempted to implement isolated parts of the Lean system without understanding the entire philosophy. However, the literature has shown that Lean philosophy and techniques require the adoption of the entire system in a holistic manner, rather than applying techniques in a piecemeal fashion.28 The comments of our participants also indicate that LTPs might be more effective if they are established as a multidimensional activity: not merely creating a list of Lean tools and methodologies and learning how to use them, but also applying a certain hierarchy. This means that to learn advanced tools or methodologies, people must first learn the basics and then build from there. We believe that achieving this hierarchical approach requires an understanding of all aspects of implementing Lean. While some tools and methodologies can be presented in a classroom, others must include exercises or a practical portion of training to show the relation with other aspects of Lean.
The findings of this study demonstrate that the participants experience challenges in applying the acquired knowledge in practice, and they articulated a need for training on the job. This is in keeping with the well-supported idea that some Lean tools can, arguably, only be learned by applying them in real work situations, so-called ‘learning by doing’.23 29–36 It may be hypothesised that the added value of “learning by doing” may lie in the dialogical process of sharing insights, knowledge and challenges, which gives context to Lean procedures. This importance of dialogical learning in Lean has also been addressed in other studies.37 We suggest that mixing training on the job with a continuous learning environment—as suggested by our participants—may facilitate dialogical learning, encourage collaboration between colleagues and thus facilitate the transfer of learning goals to daily practices. The findings of our study show that sole attention for assigning ‘appropriate’ roles and rules, strategies and training programme, does not lead to improvement in the implementation of Lean. According to the study participants, physicians and operating staff are highly trained individuals who act with autonomy, whereas Lean culture requires teamwork and collaboration.38 39 Therefore, solely establishing an ‘appropriate’ hierarchy and a set of roles does not appear to be sufficient. In addition, acknowledgement of the complexity and ambiguities of daily practices in organisations, could enhance Lean implementation.40 41 This implies leaders to focus more on the Lean meaning-making process through several participants involved rather than on implementing Lean solely as a fact.
Conclusion
Implementing Lean in a hospital setting is a challenge because of the ambiguous and complex environment of a highly professionalised organisation. This study investigated a wide range of barriers to and facilitators of Lean implementation in a clinical setting. The study found that involvement of top management (eg, consolidation of Lean with the overall hospital strategy), the daily presence of leaders on the work floor and their function as a role model are important facilitators of Lean implementation. To increase the successful outcomes of leadership intentions and actions, training should be supplemented with actions to remove perceived barriers, most of which are related to sufficient resources, such as time to make improvements. The successful implementation of Lean actions by leaders requires the involvement of all professionals, the crossing of departmental boundaries and a focus on meaning-making processes rather than simply ‘implementing’ facts. Therefore, this research suggests that programme participants, such as staff members and leaders, can mutually explore the meanings of Lean thinking and working for their own contexts. By entering this shared learning process (eg, learning on the job) the ownership of Lean implementation could also increase.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Contributors: KA was responsible for the design of the study. KA and FS conducted the data collection and were responsible for the data analysis. MV and GW supervised the study. All authors contributed to the writing of this paper and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: KA has received a research grant from LIDZ: a Dutch network for lean healthcare for the submitted work.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1.Slobbe LCJ, Smit JM, Groen J, et al. Cost of Illness in the Netherlands 2007: trends in healthcare expenditure 1999–2010. Retrieved from The National Institute for Public Health and the Environment website: http://www.rivm.nl/dsresource?objectid=rivmp:61294&type=org&disposition=inline&ns_nc=1 (accessed 28 Nov 2011). [Google Scholar]
- 2.Al MJ, Feenstra T, Brouwer WBF. Corrigendum to ‘Decision makers views on health care objectives and budget constraints: results from a pilot study’. Health Policy 2005;74:109–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Øvretveit J. Leading improvement. J Health Organ Manag 2005;19:413–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Womack JP, Jones DT. Lean thinking: banish waste and create wealth in your corporation. (First Free Press 2003 edn.) New York: Free Press, 2003 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ben-Tovim DI. Seeing the picture through ‘lean thinking’. BMJ 2007;334:169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Radnor Z, Walley P, Stephens A, et al. Evaluation of the lean approach to business management and its use in the public sector. Edinburgh: The Scottish Government, 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ballé M, Régnier A. Lean as a learning system in a hospital ward. Leadersh Health Serv 2007;20:33–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.de Souza LB, Pidd M. Exploring the barriers to lean health care implementation. Public Money Manag 2011;31:59–66 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mazur L, McCreery J, Rothenberg L. Facilitating lean learning and behaviors in hospitals during the early stages of lean implementation. Eng Manag J 2010;24:11–22 [Google Scholar]
- 10.McConnell KJ, Lindrooth RC, Wholey DR, et al. Management practices and the quality of care in cardiac units management practices in cardiac units. JAMA Intern Med 2013; 173:684–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.De Souza LB. Trends and approaches in lean healthcare. Leadersh Health Serv 2009;22:121–39 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robinson S, Radnor ZJ, Burgess N, et al. SimLean: utilising simulation in the implementation of lean in healthcare. Eur J Oper Res 2012;219:188–97 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Burgess N, Radnor Z. Evaluating Lean in healthcare. Int J Health Care Qual Assur 2013;26:220–35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holland R, Meyers D. Creating champions for health care quality and safety. Am J Med Qual 2010;25:102–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Salanova M, Schaufeli W, Martinez I, et al. How obstacles and facilitators predict academic performance: the mediating role of study burnout and engagement. Anxiety Stress Coping 2010; 23:53–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roth G. Distributing leadership practices for lean transformation. Reflections 2006;7:15–29 [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ehigie BO, Ehigie RI. Applying qualitative methods in organizations: a note for industrial/organizational psychologists. Qual Rep 2005;10:621–38 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lindlof TR, Taylor BC. Qualitative communication research methods, 3rd edn Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2011 [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saldana J. The coding manual for qualitative researchers. Sage, Londen, 2013:218 [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Qualitative research in health care. Analysing qualitative data. BMJ 2000;320:114–16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boeije HR. Analysis in qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications Ltd, 2010 [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bahensky JA, Roe J, Bolton R. Lean sigma—will it work for healthcare? J Healthc Inf Manag 2005;19:39–44 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fillingham D. Can lean save lives? Leadersh Health Serv 2007;20:231–41 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Aherne J. Think lean. J NursManag 2007;13:13–15 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Massey L, Williams S. CANDO: implementing change in an NHS Trust. Int J Public Sect Manag 2005;18:330–49 [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nelson-Peterson D, Leppa C. Creating an environment for caring using lean principles of the Virginia Mason Production System. J Nurs Adm 2007;37:287–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kotter JR. Leading change: why transformation efforts fail. Harv Bus Rev 2007;85:96–103 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Womack JP, Jones DT. Beyond Toyota: how to root out waste and pursue perfection. Harv Bus Rev 1996;74:140–58 [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dickson EW, Singh S, Cheung DS, et al. Application of lean manufacturing techniques in the emergency department. J Emerg Med 2008;37:177–82 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kaplan G, Patterson S. Seeking perfection in healthcare. A case study in adopting Toyota Production System methods. Healthc Exec 2008;23:16–21 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jimmerson C, Weber D, Sobek D. Reducing waste and errors: piloting lean principles at IHC. J Qual Saf 2005;31:249–57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Manos A, Sattler M, Alukal G. Make healthcare lean. Qual Prog 2006;39:24 [Google Scholar]
- 33.Esain A, Williams S, Massey L. Combining planned and emergent change in a healthcare lean transformation. Public Money Manage 2008;28:21–6 [Google Scholar]
- 34.Panchak P. Lean health care? It works! Ind Week 2003; 252:34–40 [Google Scholar]
- 35.Persoon T, Zaleski S, Frerichs J. Improving preanalytic processes using the principles of lean production (Toyota Production System). Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:16–25 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Achanga P, Shehab E, Roy R, et al. Critical success factors for lean implementation within SMEs. J Manu Technol Manag 2006;17:460–71 [Google Scholar]
- 37.Martinez Leon HC, Temblador Perez MDC, Farris JA, et al. Integrating Six Sigma tools using team-learning processes. Int J Lean Six Sigma 2010;3:133–56 [Google Scholar]
- 38.Endsley S, Magill MK, Godfrey MM. Creating a lean practice. Fam Pract Manag 2006;13:34–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Spear SJ. Fixing health care from the inside: teaching residents to heal broken delivery processes as they heal sick patients. Acad Med 2006;81:144–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Weick KE. Sensemaking in organizations. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications Inc, 1995 [Google Scholar]
- 41.Czarniawska B. Emerging institutions: pyramids or anthills? Organ Stu 2009;30:423–41 [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


