Abstract
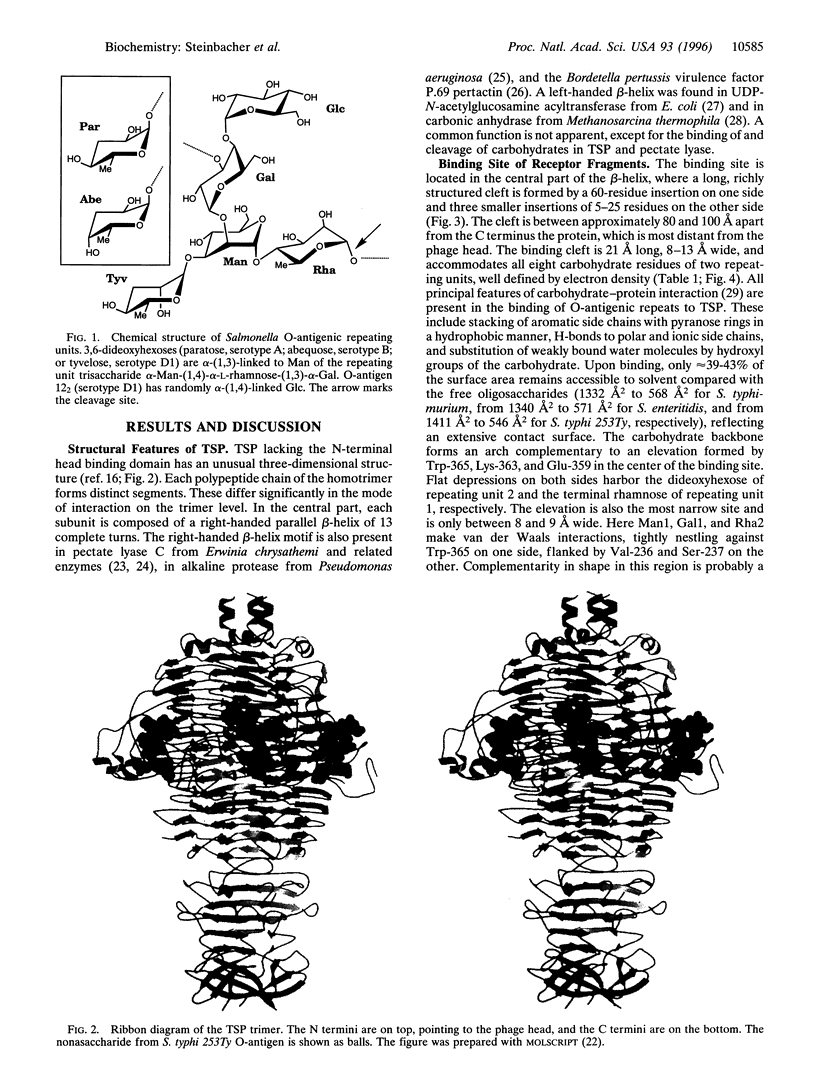
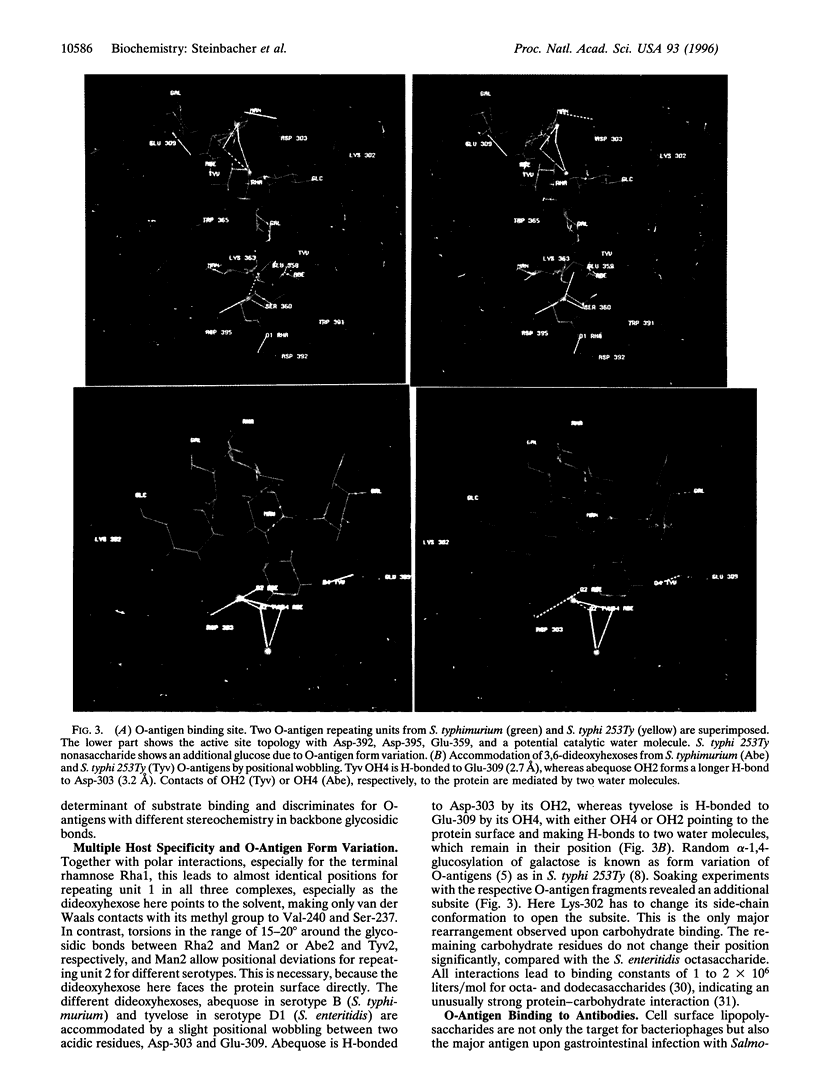
The O-antigenic repeating units of lipopolysaccharides from Salmonella serogroups A, B, and D1 serve as receptors for the phage P22 tailspike protein, which also has receptor destroying endoglycosidase (endorhamnosidase) activity, integrating the functions of both hemagglutinin and neuraminidase in influenza virus. Crystal structures of the tailspike protein in complex with oligosaccharides, comprising two O-antigenic repeating units from Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella enteritidis, and Salmonella typhi 253Ty were determined at 1.8 A resolution. The active-site topology with Asp-392, Asp-395, and Glu-359 as catalytic residues was identified. Kinetics of binding and cleavage suggest a role of the receptor destroying endorhamnosidase activity primarily for detachment of newly assembled phages.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Air G. M., Laver W. G. The neuraminidase of influenza virus. Proteins. 1989;6(4):341–356. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann U., Wu S., Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B. Three-dimensional structure of the alkaline protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a two-domain protein with a calcium binding parallel beta roll motif. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3357–3364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Eichler E., Gidney M. A., Meldal M., Ragauskas A., Sigurskjold B. W., Sinnott B., Watson D. C., Yaguchi M., Young N. M. Molecular recognition of a Salmonella trisaccharide epitope by monoclonal antibody Se155-4. Biochemistry. 1994 May 3;33(17):5172–5182. doi: 10.1021/bi00183a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M. Influenza virus neuraminidase: structure, antibodies, and inhibitors. Protein Sci. 1994 Oct;3(10):1687–1696. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Rose D. R., Bundle D. R. Recognition of a cell-surface oligosaccharide of pathogenic Salmonella by an antibody Fab fragment. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.1713710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Wu S., Zdanov A., Bundle D. R., Rose D. R. Recognition of a carbohydrate antigenic determinant of Salmonella by an antibody. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 May;21(2):437–441. doi: 10.1042/bst0210437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G., Henrissat B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995 Sep 15;3(9):853–859. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley P., Charles I. G., Fairweather N. F., Isaacs N. W. Structure of Bordetella pertussis virulence factor P.69 pertactin. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):90–92. doi: 10.1038/381090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U., Lindberg A. A. Adsorption of phage P22 to Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):207–221. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U., Svenson S. B., Lönngren J., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella phage glycanases: substrate specificity of the phage P22 endo-rhamnosidase. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):503–511. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. P., Berget P. B., King J. Maturation of the tail spike endorhamnosidase of Salmonella phage P22. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7864–7871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. C., Leive L. Heterogeneity of antigenic-side-chain length in lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli 0111 and Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrler G., Rott R., Klenk H. D., Müller H. P., Shukla A. K., Schauer R. The receptor-destroying enzyme of influenza C virus is neuraminate-O-acetylesterase. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1503–1506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman K., Peluso R. W., Moscona A. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of human parainfluenza 3: role of the neuraminidase in the viral life cycle. Virology. 1995 Dec 1;214(1):294–300. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.9925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel J. V., Anderson T. F., Levine M. in vitro MORPHOGENESIS OF PHAGE P22 FROM HEADS AND BASE-PLATE PARTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):284–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Kanegasaki S. Enzymic and molecular properties of base-plate parts of bacteriophage P22. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):87–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann F. A Typhoid Variant and a New Serological Variation in the Salmonella Group. J Bacteriol. 1941 Feb;41(2):127–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.41.2.127-140.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisker C., Schindelin H., Alber B. E., Ferry J. G., Rees D. C. A left-hand beta-helix revealed by the crystal structure of a carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2323–2330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Eichelberger M. C., Compans R. W., Air G. M. Influenza type A virus neuraminidase does not play a role in viral entry, replication, assembly, or budding. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):1099–1106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.1099-1106.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter J. D., Withers S. G. Mechanisms of enzymatic glycoside hydrolysis. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;4(6):885–892. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Biswas B., Carlton R., Jensen N. C., Creed G. J., Zullo S., Adhya S. Long-circulating bacteriophage as antibacterial agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 16;93(8):3188–3192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.8.3188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Salmonella typhimurium analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Roderick S. L. A left-handed parallel beta helix in the structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Science. 1995 Nov 10;270(5238):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5238.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbacher S., Seckler R., Miller S., Steipe B., Huber R., Reinemer P. Crystal structure of P22 tailspike protein: interdigitated subunits in a thermostable trimer. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):383–386. doi: 10.1126/science.8023158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Colman P. M. Structure of the influenza virus glycoprotein antigen neuraminidase at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):35–40. doi: 10.1038/303035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasak R., Luytjes W., Spaan W., Palese P. Human and bovine coronaviruses recognize sialic acid-containing receptors similar to those of influenza C viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4526–4529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder M. D., Jurnak F. Protein motifs. 3. The parallel beta helix and other coiled folds. FASEB J. 1995 Mar;9(5):335–342. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.5.7896002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder M. D., Keen N. T., Jurnak F. New domain motif: the structure of pectate lyase C, a secreted plant virulence factor. Science. 1993 Jun 4;260(5113):1503–1507. doi: 10.1126/science.8502994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]