Abstract
One of the noncellular microenvironmental factors that contribute to malignancy of solid tumors is acidic peritumoral pH. We have previously demonstrated that extracellular acidosis leads to localization of the cysteine pro-tease cathepsin B on the tumor cell membrane and its secretion. The objective of the present study was to determine if an acidic extracellular pH such as that observed in vivo (i.e., pHe 6.8) affects the activity of proteases, e.g., cathepsin B, that contribute to degradation of collagen IV by tumor cells when grown in biologically relevant three-dimensional (3D) cultures. For these studies, we used 1) 3D reconstituted basement membrane overlay cultures of human carcinomas, 2) live cell imaging assays to assess proteolysis, and 3) in vivo imaging of active tumor proteases. At pHe 6.8, there were increases in pericellular active cysteine cathepsins and in degradation of dye-quenched collagen IV, which was partially blocked by a cathepsin B inhibitor. Imaging probes for active cysteine cathepsins localized to tumors in vivo. The amount of bound probe decreased in tumors in bicarbonate-treated mice, a treatment previously shown to increase peritumoral pHe and reduce local invasion of the tumors. Our results are consistent with the acid-mediated invasion hypothesis and with a role for cathepsin B in promoting degradation of a basement membrane protein substrate, i.e., type IV collagen, in an acidic peritumoral environment.
Introduction
Reprogramming of energy metabolism is one of two emerging cancer hallmarks that have been added to the original six hallmarks of cancer [1]. The concept that metabolism is altered in cancer dates back to the observation made by Otto Warburg that tumor cells exhibit increased glucose fermentation despite the presence of oxygen [2]. Byproducts of elevated glycolytic activity result in an acidic extracellular pH (pHe) that is heterogeneous within a tumor and changes during tumor progression [for review, see [3]]. Acidification has been attributed to a combination of factors including chaotic tumor vasculature, increased glycolysis, and diminished buffering capacity of tumor interstitial fluids. These factors lead to high concentrations of extracellular lactic acid, which may be toxic to normal and cancer cells. Many cancer cells acquire acid-resistant phenotypes that allow them to survive and proliferate when the pHe is acidic [4].
Acidification of the tumor microenvironment has been shown to increase invasiveness and metastasis, leading to the mathematically modeled and tested hypothesis that acidification is critical to an invasive phenotype [5,6]. According to this hypothesis, acidification occurs as a result of glycolysis both in the presence of oxygen (Warburg effect) and during intermittent hypoxia, causing toxicity in the surrounding normal stroma and thereby providing empty space for tumor cell proliferation and invasion. Acidosis or elevated glycolysis has been shown to persist in areas of adequate oxygen supply [7–9]. Treatment of mouse models with orally available buffers neutralized intratumoral pH and reduced spontaneous and experimental metastasis [10,11]. The elevation of tumoral pHe was shown to reduce the activity of cathepsin B, a lysosomal cysteine protease that has an acidic pH optimum [11].
Proteases have been implicated in every stage of cancer progression, from initiation and growth to invasion and metastasis [12]. Cysteine cathepsins participate in proteolytic networks that mediate cancer progression [for reviews, see [13,14]]. We now hypothesize that analyzing cells cultured at neutral pH may have overemphasized the role of proteases that have neutral pH optima. As the acidification of the tumor microenvironment could favor the activity of pro-teases such as cysteine cathepsins that normally function at an acidic pH, this led us to reexamine proteolysis and the proteases that are secreted and active at the acidic pHe surrounding solid tumors. For these studies, we used a three-dimensional (3D) reconstituted basement membrane (rBM) overlay model that provides a context for mechanisms critical to both mammary gland development and neoplastic processes, as has been described [for reviews, see [15,16]]. We are building on previous studies that have shown that an acidic pHe leads to lysosomal redistribution and secretion of cathepsin B by malignant cells [17]. Our study confirms that cathepsin B is active pericellularly in 3D cultures of breast and colon carcinoma cells and is one of the proteases that participate in the enhanced degradation of collagen IV observed at an acidic pHe.
Materials and Methods
Materials
DMSO, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), Hepes, NaHCO3, Pipes, and all other chemicals not otherwise noted were obtained from Sigma (St Louis, MO). FBS was purchased from Hyclone (Logan, UT), CA074 and E64 from Peptides International (Louisville, KY), Z-Arg-Arg-NHMec from Bachem (Torrance, CA), pimonidazole HCl from Hypoxyprobe (Burlington, MA), and Ventana OmniMap anti-Rb HRP from Roche (Indianapolis, IN). rBM: in vitro studies used reduced growth factor Cultrex from Trevigen (Gaithersburg, MD); in vivo studies used Matrigel (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Click-iT EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) microplate assays, dye-quenched collagen IV (DQ-collagen IV), CellTracker Orange, Hoechst 33342, live/dead assay kit, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), and trypsin EDTA were purchased from Life Technologies (Grand Island, NY). Pierce Protein A/G Plus Agarose beads (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL) and anti-rabbit cathepsin B, anti-rabbit pre-immune IgG [18], anti-rabbit cathepsin S (a kind gift of Dr Boris Turk, Jozef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia), and anti-rabbit cathepsin L (a kind gift of Dr Ekkehard Weber, Martin Luther University, Halle, Germany) antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. GB123, an activity-based probe (ABP) for cysteine cathepsins [19], was provided by Dr Matthew Bogyo (Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA).
Tissue Culture
Low passages of MDA-MB-231 [American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), Manassas, VA] and MDA-MB-231 stably transfected with red fluorescent protein (RFP) and luciferase [11], and HCT116 (ATCC) and Hs578T (ATCC) cells were maintained in phenol red-free DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and penicillin/streptomycin at pH 7.4 for no more than 4 weeks. Cells were monitored by microscopy to confirm that they maintained their original morphology and were regularly screened for mycoplasma by microscopy (MycoFluor; Life Technologies) and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (LookOut; Sigma). Media for pH experiments were additionally buffered to maintain pH 7.4 or 6.8 with 2 g/l sodium bicarbonate, 25 mM Pipes, and Hepes and then incubated overnight at 37°C in 5% CO2 [11] and adjusted to either pH 7.4 or 6.8. Cultures were maintained in humidified conditions under atmospheric oxygen levels and 5% CO2. For subculturing, cells were detached from uncoated tissue culture flasks with 0.05% trypsin EDTA.
Live Cell Assays for Proteolysis and Active Cysteine Cathepsins
A detailed protocol for the live cell proteolysis assay has been published [20]. Briefly, glass coverslips in 35-mm dishes were coated with 45 µl of Cultrex containing 25 mg/ml DQ-collagen IV and placed in a 37°C incubator for 10 minutes to allow solidification. Approximately 50,000 cells were seeded on top of the Cultrex and incubated at 37°C and pH 7.4 for 30 to 60 minutes until adherent, at which point either pH 7.4 or 6.8 culture media containing 2% rBM were applied. Media were changed the following day. For inhibitor studies, 20 µM CA074/E64 or an equal volume of diluent (DMSO) was added to the Cultrex before solidification as well as to the medium overlay. To visualize active cysteine cathepsins in the 3D cultures, 1 µM GB123, an ABP [19], was added to the media 16 to 18 hours before imaging. Cells were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to remove any unbound probe and returned to probe-free complete growth medium at either pH 7.4 or 6.8 for at least 1 hour before imaging. After nuclei were labeled with Hoechst 33342, imaging was performed with a Zeiss LSM 510 META NLO confocal microscope using a 40x water-dipping objective. Under all conditions, the parameters for acquisition of images were identical (laser power, detector gain and offset, and so on). Quantification by the software is based on true pixel intensities, which are raw data from each confocal slice in a volume and always below saturation. The images represented in the figures are rendered in 3D and thus show an additive effect of pixel intensities that depend on the angle of view, which may result in what appears to the naked eye to be pixel saturation. The intensity of the fluorescent signal per cell was measured using MetaMorph and Volocity software. Localization of active cysteine cathepsins was determined using MetaMorph software [20]. Either RFP expression or CellTracker Orange staining was used to determine the cell boundaries in each confocal slice. Cell boundaries were subtracted from the signal for total bound GB123 in each confocal slice to determine the amount of pericellular signal and quantified in the entire 3D volume.
Fluorometric Activity Assay for Cathepsin B
After growing the cultures at pH 7.4 or 6.8, cathepsin B activity (active and latent) in MDA-MB-231 cell lysates and conditioned media was assessed using Z-Arg-Arg-NHMec, a selective cathepsin B substrate, as previously described [21]. To measure intracellular and membrane-bound cathepsin B activities, 50 µl of sample was treated with 300 µl of activator buffer (5 mM EDTA, 10 mM DTT, pH 5.2) for 15 minutes at 37°C. To measure secretion of procathepsin B, activation was accomplished with dextran sulfate [22]. Briefly, 50 µl of conditioned media was mixed with 300 µl of citrate buffer [20 mM citrate buffer (pH 4.6), 10 mM DTT, and 25 µg/ml dextran sulfate] and incubated for 45 minutes at 37°C, then added in triplicate to a 96-well flat-bottom black microtiter plate. For cell lysates, 100 µl of cell lysate/activator buffer mixture was added to 200 µl of appropriate assay buffer containing 50 µMZ-Arg-Arg-NHMec, and fluorescence wasmeasured at 1-minute intervals for 30 minutes using a TECAN SpectraFluor Plus plate reader (Salzburg, Austria) at an excitation of 360 nm and an emission of 465 nm; activity was reported as picomoles of NHMec formed per minute per microgram of DNA. The highly selective cathepsin B inhibitor CA074 (10 µM) was used to confirm the specificity of the assay [23].
Immunoprecipitation of ABP-Bound Cysteine Cathepsins
MDA-MB-231 cells were grown in 3D rBM overlay cultures, and the day before collection, media were changed to serum-free with the addition of 1 µM GB123. On the next day, after washing with PBS and sitting in complete media for an hour, cell lysates were collected in ice-cold RIPA buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 0.5% deoxycholate, and 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)]. Anti-rabbit cathepsin B (1:500), anti-rabbit pre-immune IgG (1:500), anti-rabbit cathepsin S (1:250), and anti-rabbit cathepsin L (1:250) were individually added and mixed at 4°C overnight. Pierce Protein A/G Plus Agarose beads (30 µl) were then added and mixed overnight at 4°C for an additional 30 minutes at room temperature. Supernatants and beads were collected, and the beads were washed with RIPA buffer and boiled after addition of 2x sample buffer (20% glycerol, 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 6% SDS, and 10% β-mercaptoethanol). Acetone at 0°C was added to the supernatant, and the mixture was kept at -80°C for 2 hours and centrifuged at 14,000g at 4°C for 30 minutes; the pellet was air-dried at room temperature and dissolved by boiling in sample buffer. Immunoprecipitated proteins and supernatants were separated on 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and the gels were visualized using a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera-equipped Bio-Rad VersaDoc 5000MP imager (excitation/emission, 633/680 nm).
Animals
Mice were housed according to Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee protocol at the University of South Florida vivarium located within the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center (Tampa, FL). Four-to 6-week-old female SCID-beige mice (Charles River Laboratories, Wilmington, MA) were used for fluorescent imaging of orthotopic tumors.
In Vivo Imaging of Active Cysteine Cathepsins
SCID mice (n = 7) were separated into two cohorts before cell injection and were provided either tap (n = 3) or 400 mM sodium bicarbonate (n = 4) drinking water. In preparation for injection, the MDA-MB-231 cells were trypsinized and washed once with PBS. Cells were resuspended at a concentration of 1 x 107 cells/100 µl in a 1:1 mixture of PBS and Matrigel and injected into the right, number 4 mammary fat pad of each mouse. Tumors were monitored by caliper measurements, and when tumors reached ?400 mm3, animals were imaged. Eighteen hours before imaging, 25 nmol of GB123 was injected intravenously into mice [19]. In vivo measurements were obtained using an Optix MX3 (Advance Research Technologies, a subsidiary of SoftScan Healthcare Group, Montreal, Canada). Fluorescent images were acquired using a 670-nm pulsed laser diode and a scan resolution of 1.5 mm. Images were analyzed using Optix MX3 OptiView software.
Immunohistochemistry of Orthotopic Tumors
Pimonidazole HCl (60 mg/kg; Hypoxyprobe) was injected into the peritoneal cavity 1 hour before tumor removal. MDA-MB-231-RFP tumors were formalin fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) for immunohistochemical analysis. FFPE cross sections were stained with rabbit anti-sera against pimonidazole HCl followed by Ventana OmniMap anti-rabbit HRP secondary antibody. The detection system used was the Ventana ChromoMap Kit, and slides were then counterstained with hematoxylin. Processed slides were scanned using the Aperio ScanScope XT with a x200/0.8 NA objective lens at a rate of 5 minutes per slide using the Basler trilinear array (Aperio Technologies, Vista, CA).
Pimonidazole HCl was used to identify hypoxic areas. However, it does not stain necrotic tissue because of the lack of viable cells, although likely hypoxic. To segment viable and nonviable tissues, an optimized Aperio Genie v1 customized histology pattern recognition algorithm was developed to distinguish between tissue types based on various morphologies. The algorithm was applied to the entire slide's digital image to determine the percentage of each tissue type (viable or nonviable) by area (µm2). Intensity analysis of pimonidazole HCl in viable tissue was performed using an Aperio Positive Pixel Count v9.0 algorithm with the following optimized thresholds to segment positive pixels of various intensities: HueValue = 0.1, HueWidth = 0.5, Iwp (High) = 220, Iwp (Low)/Ip (High) = 175, Ip (Low)/Isp (High) = 100, Isp (Low) = 0, Inp (High) = -1. The percentage of positivity was quantified by the number of cells exhibiting positive stain as a percentage of total viable tumor cell count. The staining intensity can be thresholded into negative (0), low (1+), moderate (2+), and strong positive (3+) by mean stain density (0–255 dynamic range) for each tumor cross section. Positive pixel analysis was completed using Spectrum (Aperio Technologies).
Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test, unless otherwise noted.
Results
Live Cell Imaging of 3D rBM Overlay Cultures Confirms Presence of Active Proteases and Proteolysis
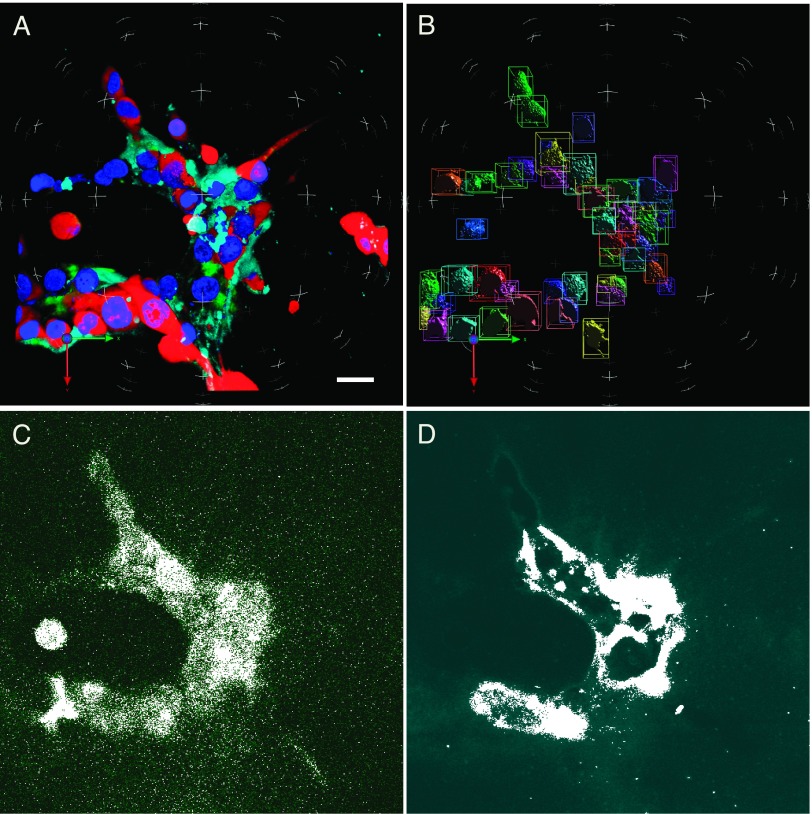
To test our hypothesis that an acidic pHe enhances proteolytic activity and degradation of the basement membrane, we grew MDA-MB-231, a triple negative human breast cancer cell line, in 3D rBM overlay cultures, following our previously described methods [24]. A quenched fluorescent form of the basement membrane protein type IV collagen, i.e., DQ-collagen IV, was used to detect general proteolysis. The ABP GB123, which covalently binds to the active site [19], was used to detect active cysteine cathepsins. We illustrate live cell imaging of degradation products of DQ-collagen IV (Figure 1, A and C) and labeling of active cysteine cathepsins with GB123 (Figure 1, A and D) and nuclei with Hoechst 33342 (Figure 1B) in MDA-MB-231 3D rBM overlay cultures. We use this methodology to examine differences in DQ-collagen IV degradation and in active cysteine cathepsins, including their localization, at an acidic (6.8) compared to a neutral (7.4) pHe.
Figure 1.
Active cysteine cathepsins and degradation fragments of DQ-collagen IV could be detected in breast carcinoma cells grown in 3D rBM overlay cultures. (A) 3D reconstruction of optical sections taken through the entire volume of an MDA-MB-231 3D culture: with red representing RFP in the cytoplasm; blue representing Hoechst 33342-stained nuclei; green representing degradation products of DQ-collagen IV; and cyan representing GB123 bound to active cysteine cathepsins. (B) Illustration of spatial separation in 3D of nuclei for enumeration. (C and D) In single optical sections through the equatorial plane, fluorescence was evenly increased to visually differentiate with mask (white), illustrating measured DQ-collagen IV degradation fragments and ABPs bound to cysteine cathepsins, respectively. Bar, 22.6 µm.
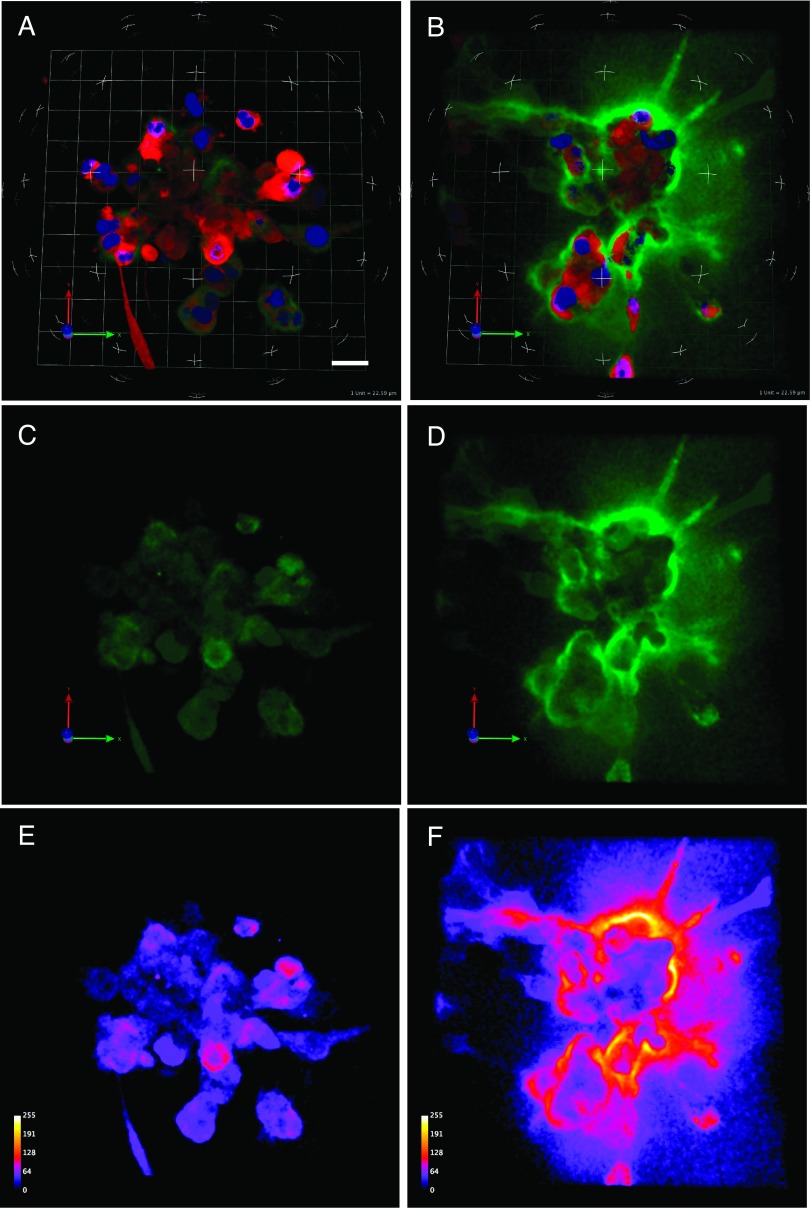
Acidic pHe Enhances Degradation of Collagen IV
A pHe of 6.8 was chosen as our test condition based on literature reports on the acidic pHe present in breast cancers and xenograft models [3]. In MDA-MB-231 3D rBM overlay cultures, we observed accumulation of degradation fragments of the basement membrane protein substrate at both pHe 7.4 (Figure 2, A, C, and E) and 6.8 (Figure 2, B, D, and F) over a period of 3 days. More extensive pericellular degradation products of DQ-collagen IV were observed at pHe 6.8 (Figure 2, B, D, and F). Additional perspectives of the differences in degradation between neutral and acidic pHe (Figure 2, A and B) can be viewed in Movies W1 and W2. This effect was verified in 3D cultures of a second triple-negative breast cancer cell line, Hs578T, and also in HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. HCT116 cells have previously been shown to acidify the tumor microenvironment similarly to MDA-MB-231 cells [25]. The percentage increases in DQ-collagen IV degradation products, normalized to cell number, at pHe 6.8 for MDA-MB-231, HS578T, and HCT116 3D cultures are shown in Figure W1. There was a significant increase in DQ-collagen IV degradation products at the acidic pHe for MDA-MB-231 and HCT116 3D cultures and a trend toward increased DQ-collagen IV degradation products at the acidic pHe for Hs578T 3D cultures (P = .10). To rule out a direct effect of acidic pHe on the stability of DQ-collagen IV, coverslips coated with rBM were incubated as above but without cells; degradation products were not observed at either acidic or neutral pH (Figure W2).
Figure 2.
Degradation of DQ-collagen IV was greater at an acidic pHe. Left (A, C, and E) and right (B, D, and F) panels depict 3-day cultures of MDA-MB-231 cells grown in 3D rBM overlay cultures at pHe 7.4 and 6.8, respectively. A and B represent the entire 3D volume showing cells (red), degradation products of DQ-collagen IV (green), and nuclei (blue). C and D represent degradation products of DQ-collagen IV in the entire 3D volume. E and F represent intensity maps of the degradation products in C and D (white, most intense; violet, least intense). Images depicted represent the average fluorescence intensity of DQ-collagen IV degradation products per cell obtained in 14 to 15 images at the two pHs; bar, 22.6 µm.
Human Carcinoma Cells Exhibit an Acid-Resistant Phenotype in 3D rBM Overlay Culture
To exclude possible effects of acidic pHe on proteolysis due to differences in proliferation and viability, we analyzed 3D rBM overlay cultures of the MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, and HCT116 carcinoma cells for an acid-resistant phenotype. We did not observe any differences in proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells as assessed by Click-iT EdU and MTT assays (Figure W3, A and B) or in cell viability as measured by a live/dead assay (Figure W3C). Similar results were observed using the Click-iT EdU and viability assays for Hs578T and HCT116 cells (data not shown). Thus, under the conditions of our 3D cultures, we established that MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, and HCT116 carcinoma cell lines exhibit an acid-resistant phenotype.
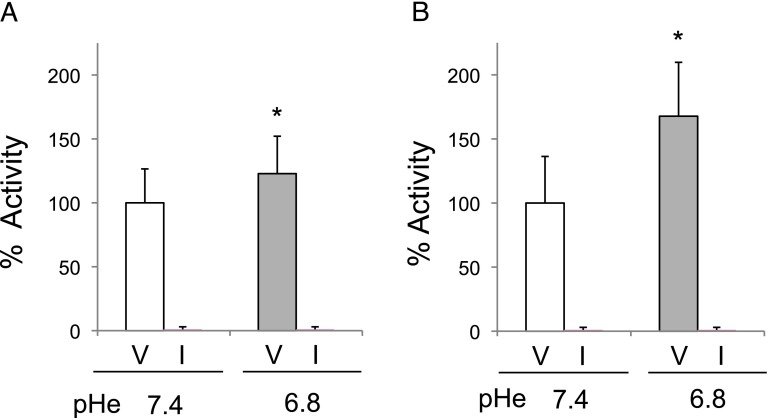
Acidic pHe Increases Procathepsin B and Active Cathepsin B
Previous studies on 2D cultures have demonstrated that an acidic pHe results in a peripheral distribution of cathepsin B intracellularly as well as cathepsin B secretion [17]. In the present study, we found that cathepsin B activity was slightly, yet significantly increased in lysates of MDA-MB-231 cells grown in 3D rBM overlay culture at pHe 6.8 (Figure 3A; P = .046). Secretion of procathepsin B (dextran sulfate activated) was also significantly increased (P = .02), as assessed by assaying cathepsin B activity in the conditioned media (Figure 3B). Activity was eliminated by CA074, a highly selective cathepsin B inhibitor, confirming the specificity of the assay for cathepsin B [23].
Figure 3.
Cathepsin B activity was increased at acidic pHe. MDA-MB-231 cells were grown in 3D rBM overlay cultures at pHe 7.4 or 6.8 and then serum starved (0.2% FBS) for 24 hours in media buffered at either pH 7.4 or 6.8. Cell lysates (A) and conditioned media (B) were analyzed for activity of cathepsin B and dextran sulfate-activated procathepsin B, respectively, using, Z-Arg-Arg-NHMEC. Activity was completely abrogated by 10 µM CA074 (I) versus vehicle control (V), thus confirming the specificity of the assay. Data were normalized to DNA and are scaled to activity at pH 7.4, designated as 100%; *P ≤ .05.
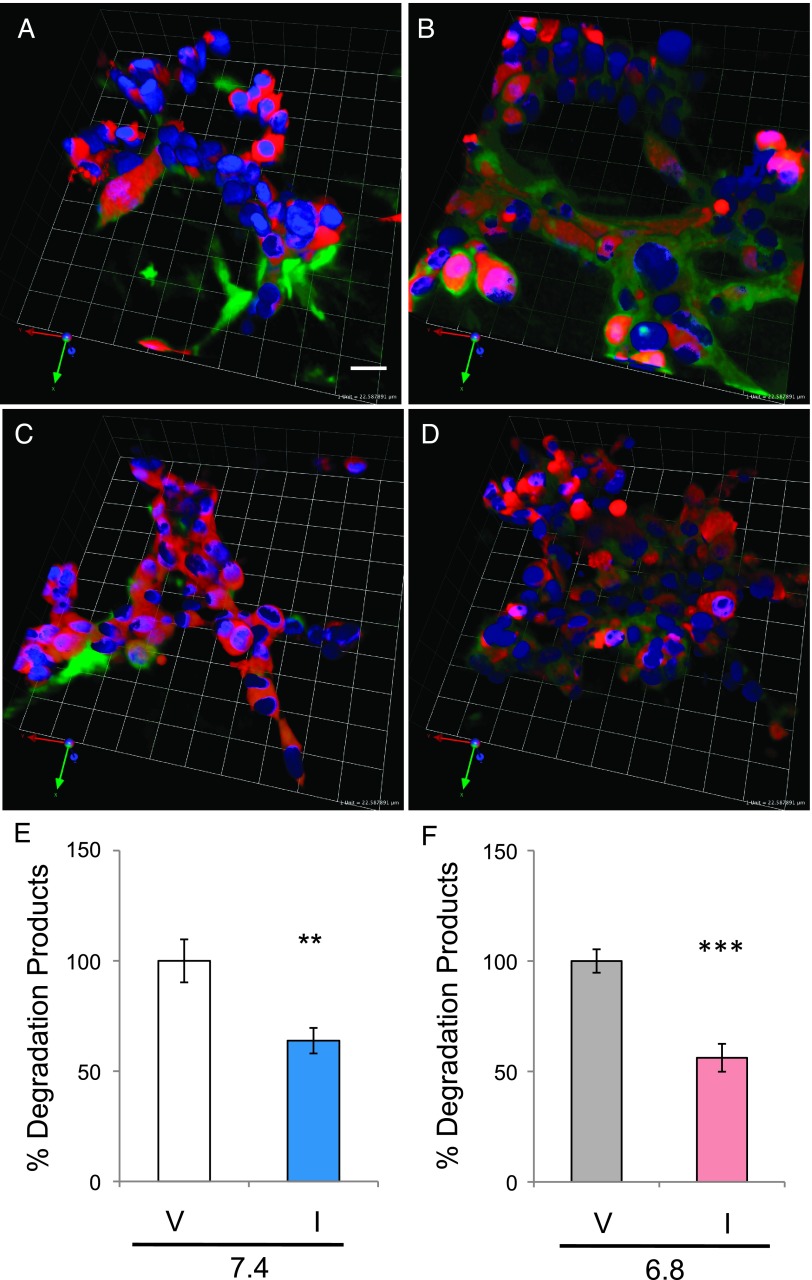
Inhibition of Cathepsin B Decreases Degradation of Collagen IV
To determine whether increased cathepsin B activity at pHe 6.8 contributed to the enhanced degradation of DQ-collagen IV, as shown in Figure 2, we determined the effect of inhibiting cathepsin B activity with CA074, a cell impermeable inhibitor. At both pHe 7.4 (Figure 4, A and C) and 6.8 (Figure 4, B and D), inhibition of cathepsin B reduced the accumulation of degradation fragments of DQ-collagen IV (cf. Figure 4, A and B with C and D; also see Movies W3–W8). Proteolysis was significantly reduced, but not completely abrogated, by CA074 at both pHe 7.4 (Figure 4E; P = .004) and 6.8 (Figure 4F; P = 1E-7). The reduction in proteolysis at pHe 6.8 was 12% greater than at pHe 7.4, consistent with cathepsin B contributing to the enhanced degradation of DQ-collagen IV at pH 6.8. Reduced proteolysis was not due to cell death, as assessed by a live-dead assay (data not shown). Our results suggest that cathepsin B is among the proteases contributing to degradation of the basement membrane protein collagen IV at both neutral and acidic pHe.
Figure 4.
Degradation of DQ-collagen IV was reduced by inhibition of cathepsin B. MDA-MB-231 cells (red) were grown at pHe 7.4 (A, C) or 6.8 (B, D) in 3D rBM overlay cultures in the presence (C, D) or absence (A, B) of CA074. Degradation products of DQ-collagen IV (green) were present in DMSO vehicle controls (A, B) and reduced in the presence of the cathepsin B inhibitor (C, D). Images were chosen as ones representing the average fluorescence intensity of degradation products of DQ-collagen IV per cell (nuclei, blue); bar, 22.6 µm. DQ-collagen IV degradation products were quantified on a per cell basis in the entire 3D volume for pHe 7.4 vehicle (V) and CA074 (I) (E) and 6.8 vehicle (V) and CA074 (I) (F). Values represent percentage of DMSO vehicle controls (100% ± SEM); n ≥ 3 independent experiments with 13 to 19 images analyzed per condition; **P ≤ .01 and ***P ≤ .001.
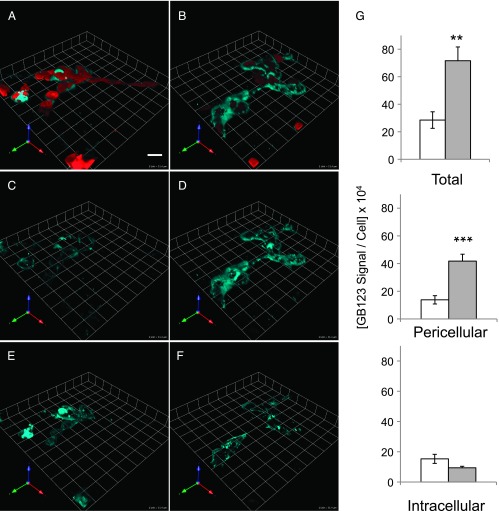
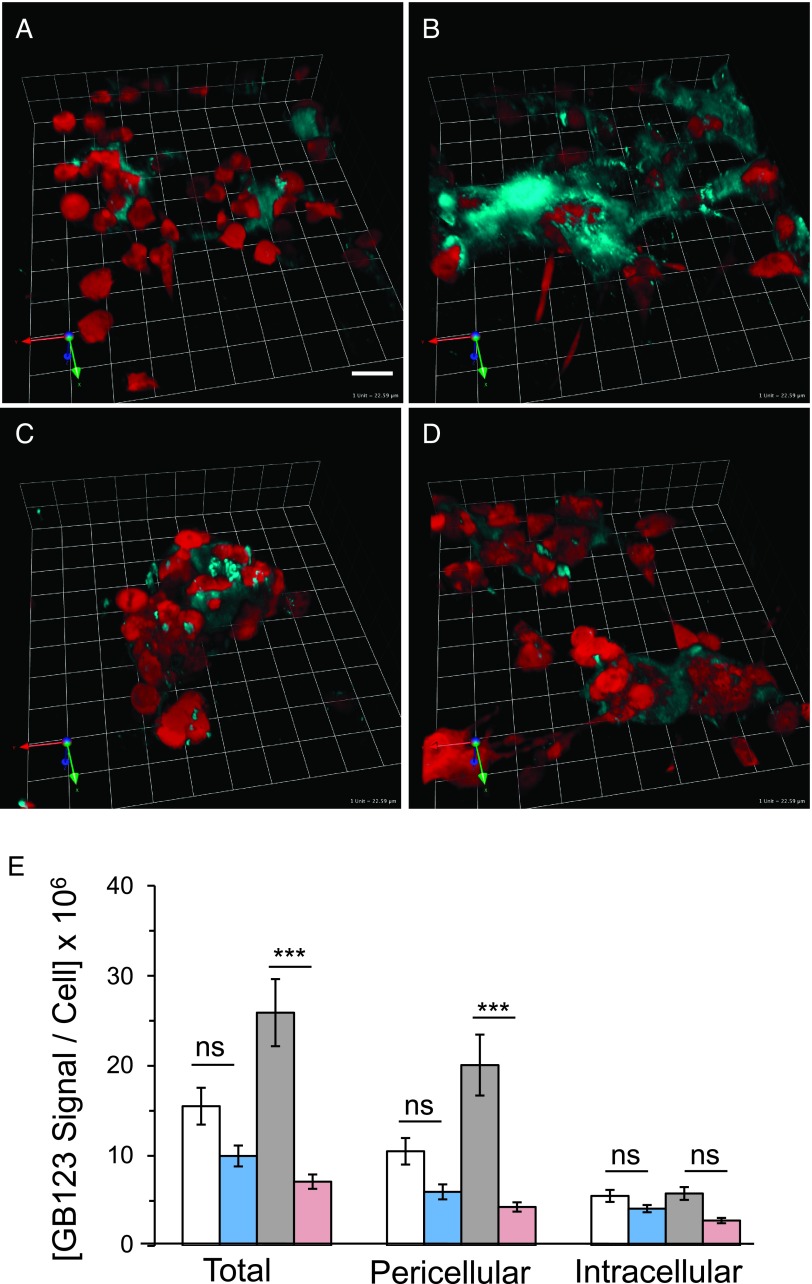
At Acidic pHe, Bound GB123 Is Pericellular
We have shown that we can visualize active cysteine cathepsins in 3D rBM overlay cultures of live breast carcinoma cells using GB123, an ABP that binds covalently to the active site of the cysteine cathepsins B, L, and S (e.g., see Figure 1). Here, we used this same ABP to determine the effect of an acidic pHe on the localization of active cysteine cathepsins. We observed a significant increase in total bound GB123 at pHe 6.8 for MDA-MB-231 cells (cf. Figure 5B with Figure 5A) as well as for Hs578T and HCT116 cells (Figure W4). In normal cells, cysteine cathepsins are localized intracellularly in lysosomes; however, in tumor cells cysteine cathepsins may be found in lysosomes, secreted or bound to the cell surface [14]. We have previously shown that an acidic pHe increases the secretion and cell surface association of cathepsin B in malignant cells grown in monolayer culture [17]. Here, we determined whether pHe 6.8 altered distribution of cysteine cathepsins in our 3D rBM overlay cultures. We used image arithmetic in MetaMorph as described previously [20] to quantify intracellular and extracellular fluorescence of bound GB123. There was a significant increase in GB123 bound (i.e., active cysteine cathepsins) pericellularly in MDA-MB-231 3D cultures at pHe 6.8 (cf. Figure 5D with Figure 5, C and G). Significant increases in pericellular GB123 were also observed in HCT116 and Hs578T cultures (Figure W4). As this is, to our knowledge, the first time that GB123 has been used to detect active cysteine cathepsins pericellularly, we employed the broad-spectrum cysteine protease inhibitor, E64, to confirm that the bound GB123 was detecting active cysteine proteases pericellularly. At pHe 6.8, we again observed significantly greater total and pericellular bound GB123 (cf. Figure 6B with Figure 6A). Pericellular bound GB123 was adjacent to the cells, consistent with the known membrane association of cysteine cathepsins in tumors [14] and with the removal of active non-cell-associated cysteine cathepsins bound to GB123 by washing. The increase in bound GB123 at pHe 6.8 was reduced by E64, confirming that GB123 was detecting active cysteine proteases. To determine which of the cysteine cathepsins known to be detected by GB123 [19] were present in our 3D rBM overlay cultures, we subjected cell lysates to immunoprecipitation using antibodies to cathepsins B, L, and S. We detected binding of GB123 to cathepsin B and cathepsin L but were unable to detect binding of GB123 to cathepsin S (Figure W5). These results would be consistent with active cysteine cathepsins detected by GB123 in the 3D cultures at an acidic pHe, being cathepsins B and L.
Figure 5.
Total and pericellular active cysteine cathepsins were increased at pHe 6.8. Active cysteine cathepsins were labeled, using GB123 (cyan), in the entire volume of 3D rBM overlay cultures of MDA-MB-231 cells (red) grown at pH 7.4 (left panels) and pH 6.8 (right panels). The amount of total bound GB123 is shown in the upper panels (A, B), pericellular bound GB123 in the middle panels (C, D), and intracellular bound GB123 in the bottom panels (E, F). Images depicted represent the average fluorescence intensity of bound GB123 per cell; bar, 22.6 µm. (G) Graphs depict average fluorescence intensity of bound GB123 per cell ± SEM at pHe 7.4  and 6.8
and 6.8 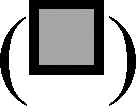 ; n ≥ 3 independent experiments with an average of 26 images analyzed per condition; **P ≤ .01 and ***P ≤ .001.
; n ≥ 3 independent experiments with an average of 26 images analyzed per condition; **P ≤ .01 and ***P ≤ .001.
Figure 6.
Pericellular bound GB123 was reduced by E64, a broad-spectrum inhibitor of cysteine proteases. Active cysteine cathepsins were labeled, using GB123 (cyan), in the entire 3D volumes of 3D rBM overlay cultures of MDA-MB-231 cells (red) grown at pHe 7.4 (A, C) or 6.8 (B, D). Upper (A, B) and lower (C, D) images represent vehicle (DMSO) controls and E64, respectively. Images depicted represent the average intensity of pericellular bound GB123 per cell; bar, 22.6 µm. (E) Graph illustrates average integrated intensity ± SEM of total, pericellular, and intracellular bound GB123 at pHe 7.4 vehicle  and E64
and E64 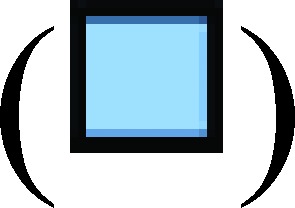 and pHe 6.8 vehicle
and pHe 6.8 vehicle  and E64
and E64 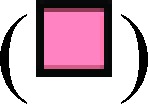 ; n ≥ 3 independent experiments with an average of 19 images analyzed per condition. Analysis of variance with Tukey post-test for multiple comparisons was used to determine significance; ***P ≤ .001.
; n ≥ 3 independent experiments with an average of 19 images analyzed per condition. Analysis of variance with Tukey post-test for multiple comparisons was used to determine significance; ***P ≤ .001.
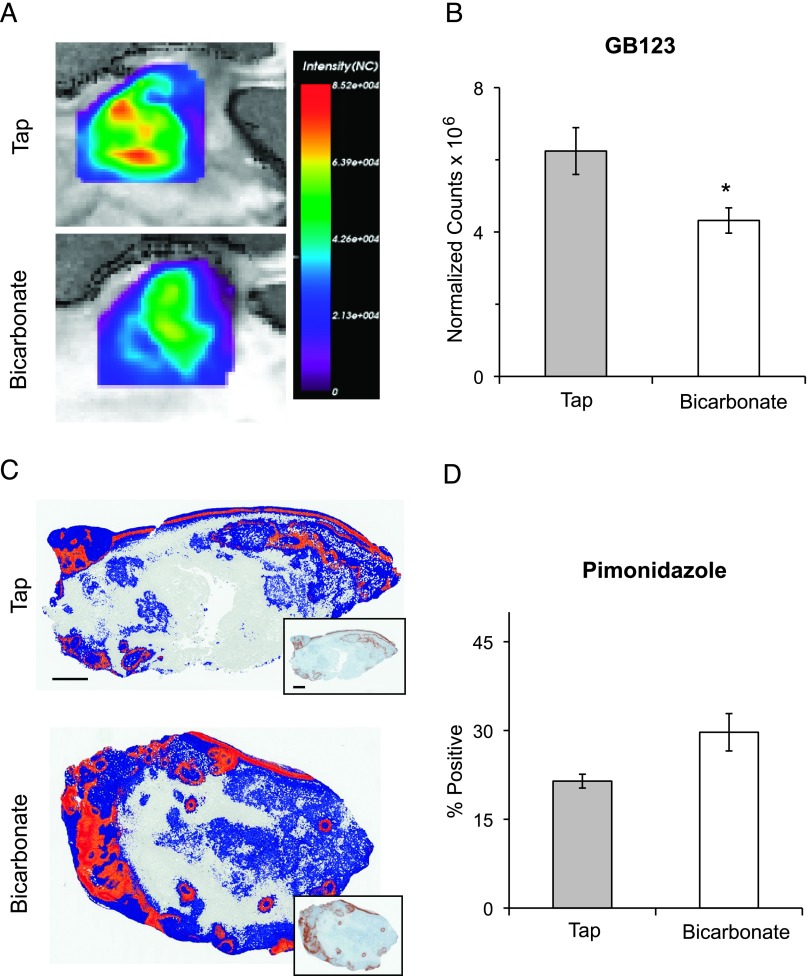
GB123 Is Detected in Tumors In Vivo
Our previous studies have show that, without affecting systemic pH, imbibement of sodium bicarbonate is able to neutralize inter-tumoral pHe and reduce spontaneous metastasis [11]. To test our hypothesis that the acidic tumor microenvironment enhances cysteine cathepsin activity in vivo, we measured GB123 intensity values in acidic or bicarbonate-neutralized orthotopic MDA-MB-231 tumors (Figures 7A and W6). The cohort sample was small, and in addition, one of the tumors in a bicarbonate-treated mouse became severely ulcerated and could not be used for this analysis. Nonetheless, despite the small sample size, there was a significant decrease in bound GB123 with sodium bicarbonate imbibement (Figure 7B). The viable tissue in the control group decreased due to the combination of acidosis and hypoxia (Figure W7) but not the amount of hypoxia (Figure 7, C and D). Our results suggest an increase in active cathepsin B and other cysteine cathepsins in acidic environments in vivo, as detected by the intensity of tumor binding of GB123.
Figure 7.
In vivo buffering of tumor pHe reduced tumor binding of GB123. (A) Enlarged representative fluorescent images, from the six shown in Figure W6, of MDA-MB-231 orthotopic tumors showing retention of GB123 18 hours post-injection. (B) Average normalized counts of GB123 retained in MDA-MB-231 orthotopic tumors ± SEM; a one-tailed unpaired t test was used to determine significance, P = .03. (C) Representative images of positive pixel analysis of viable stained tissue illustrating intensity of pimonidazole staining: blue is negative staining, orange is moderate staining, red is strong positive staining, and gray is nonviable tissue. Inset shows immunohistochemistry of pimonidazole staining used for analysis. Size markers in both are equal to 1 mm. (D) Quantification of pimonidazole staining in FFPE tumors, reported as number of strong positive pixels per number of pixels of viable tissue ± SEM; P = .086.
Discussion
The acid-mediated invasion hypothesis is supported by a large quantity of correlative data, including 1) reaction diffusion modeling [26], 2) increased metastasis formation following acid pretreatment [27–29], 3) peritumoral acidosis measured by intravital microscopy [5,25], and 4) inhibition of spontaneous and experimental metastases following acid neutralization with buffers [10,11,30,31]. Prior experiments have shown that low pH is associated with increased protease activity [32] and increased release of active cysteine cathepsins in 2D culture models [11,17]. This increase in active proteases may enhance invasion because invasion of cancer xenografts has been shown to occur more often in regions in which the pHe is acidic [25]. The possibility that cysteine cathepsins facilitate acid-mediated invasion is supported by prior work demonstrating that an acidic pHe induces redistribution of endosomes and lysosomes to the cell surface and increases release of cysteine cathepsins [17,33,34]. Here, we show by labeling with ABPs and inhibitors that are selective for cysteine cathepsins, notably for cathepsin B, that cysteine cathepsins are involved in acid-mediated degradation of the basement membrane protein type IV collagen. This study shows, for the first time, detection of pericellularly ABP-bound cysteine cathepsins in the 3D cultures of breast and colon carcinoma cells and a significant increase in detection of ABP-bound cysteine cathepsins at pHe 6.8 (Figures 5 and W4). This may reflect 1) the extensive invasive processes on these cells, processes with a large surface area for the binding of membrane-associated cysteine cathepsins such as cathepsin B [14]; 2) the acid resistant-phenotype of these cells; and 3) retention pericellularly of secreted cysteine cathepsins by the matrix used for the 3D rBM overlay cultures. The pattern of pericellular degradation that one can see in Figures 2 and 4 would be consistent with an active role for the cell surface degradation of DQ-collagen IV, including by cathepsin B associated with the light chain of the annexin II heterotetramer in caveolae [21,35] and on invadopodia [35,36].
The exact effects of acidic pHe are still unknown. As the invasive breast cancer cells are acid resistant (Figure W3) and can maintain a neutral intracellular pH even in the face of low pHe [36], we do not suspect that the response to an acidic pHe is transduced through a lowering of cytosolic pH. Rather, we hypothesize that there is an increase in fusion of secretory lysosomes with the plasma membrane and release of their contents. One of the classic examples of cells that contain secretory lysosomes is the osteoclast [37]. At the site of bone degradation, osteoclasts generate resorption lacunae that become highly acidified (pHe ∼ 4.7) through fusion of lysosomes with the plasma membrane. This is a result of insertion of lysosomal vacuolar H+-ATPases into the plasma membrane and is accompanied by release of cathepsin K, a cysteine protease essential for bone degradation [38]. In MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, vacuolar H+-ATPases are highly expressed on the cell surface and are linked to their invasiveness [39], just as observed here for active cysteine cathepsins.
Recently, a number of acid-stimulated ion channels (ASICs) have been identified, which can transduce acidic pHe through inositol trisphosphate/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways and increase calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate signaling [40]. Interestingly, metastatic cancer-associated bone pain, including in breast cancer, has been linked to signaling through ASICs; in this case, the ASICs are on neurons that innervate bone and respond to the acidic pHe produced by osteoclasts involved in bone resorption by the metastatic cancer cells [41]. ASICs are part of the superfamily of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)/degenerin cation channels. ASICs and ENaCs are regulated by proteolysis, including by membrane-anchored serine proteases [42]. ENaCs are also regulated by cysteine cathepsins, specifically by cathepsins B and S [43,44]. Neither regulation of ASICs by cysteine cathepsins nor regulation of both ENaCs and ASICs by cysteine cathepsins has, to our knowledge, been studied in cancer cells. Steffan et al. have shown in prostate cancer cells that an acidic pHe initiates lysosomal trafficking to the plasma membrane, cathepsin B secretion, and increased invasion dependent on micro-tubules, RhoA, and PI3K [34]. Other cell types such as bone marrow-derived macrophages respond to extracellular acidosis by increasing endocytosis through an ASIC-mediated mechanism [45]. Tumor macrophages secrete proteases and cytokines and accumulate in regions of hypoxia and necrosis; whether ASICs are involved and endocytosis altered has not been studied to our knowledge [46]. On the basis of this series of observations and the current work, we propose a model wherein extracellular acidosis is transduced through ASICs into a signal impinging on the PI3K pathway, microtubules, and RhoA to promote the redistribution of a lysosomal population. This, in turn, results in the release of cathepsin B and other lysosomal proteases at the acidic and invasive edges of tumors.
In accordance with the acid-mediated invasion hypothesis, the present study and other studies have shown that an acidic pHe increases expression and activity of matrix-degrading proteases such as the cysteine cathepsins B and L and matrix metalloprotein-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 [35]. Cathepsin B secreted through microvesicles or exosomes has been reported at acidic pHe to induce greater activation of latent MMPs and to potentiate endothelial cell invasion and angiogenesis [47,48]. Here, we have shown a dramatic increase in general proteolysis at an acidic pHe (Figure 2), consistent with participation of multiple proteases in proteolysis at the acidic pHe. Resistance of tumor cells to weakly basic chemotherapeutics is increased in vitro by an acidic pHe [49], and the effectiveness of chemotherapy in mouse models is reduced by the cysteine cathepsins B and S secreted by tumor-associated macrophages [50]. These studies suggest that chemotherapy in combination with an agent that increases pHe (and thereby indirectly reduces cysteine cathepsin activity) or in combination with an agent that directly inhibits cathepsin B activity, such as the insulin-like growth factor binding protein 4 (IGFBP-4) C-terminal protein fragment [51], could be beneficial in the clinic. Indeed, we have shown in mouse models that tap water supplemented with sodium bicarbonate, a systemic alkalizing buffer that increases pHe, decreases metastasis [11] and improves response to chemotherapy [52]. Sodium bicarbonate treatments to neutralize the acidic pHe have been investigated in phase I/IIa trials for bone pain (NCT01350583) and in combination with gemcitabine for unresectable pancreatic cancer (NCT01198821). Both of these trials have closed but are scheduled to reopen as new trials pending reformulation to increase compliance.
Supplementary Methods
Proliferation Assays
Cell proliferation was measured using a Click-iT EdU microplate assay in which incorporation of the nucleoside analog, EdU, into DNA during active DNA synthesis is assessed. For this assay, each well of a 96-well plate was coated with 15 µl of Cultrex before adding ∼1500 cells per well. To each well, 200 µl of either pH 7.4 or 6.8 DMEM containing 2% Cultrex was added. On day 2, EdU was added, and the next day, the assay was performed according to the manufacturer's protocols. Fluorescence values were read at 568/585 nm on a Gemini SpectraMax (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA).
Alternatively, we used MTT assays to assess proliferation. For this assay, each well of a 96-well plate was coated with 15 µl of Cultrex before adding ∼1500 cells per well, followed by 200 µl of either pH 7.4 or 6.8 DMEM containing 2% Cultrex. On the day of the assay, 50 µl of MTT (5 mg/ml) stock solution was added to each well to a final concentration of 1 mg/ml MTT. The plate was incubated at 37°C for 3 hours to allow formation of the formazan crystal product. Media were removed and replaced with 150 µl of DMSO while shaking at room temperature. Absorbance values were read at 485 nm on a TECAN SpectraFluor Plus.
Cell Viability Assay
Glass coverslips were coated with 45 µl of Cultrex and placed in a 35-mm dish. Approximately 5000 cells were seeded on the Cultrex and covered with either pH 7.4 or 6.8 media containing 2% rBM. Media were changed every 3 days. Coverslips were removed, placed in a 24-well plate, and incubated with assay reagents (PBS containing 4 µM EthD-1 and 2 µM calcein AM) for 30 minutes. Six to eight fields of view per coverslip were imaged at 485 and 530 nm. Calcein-positive cells (green) were considered alive, and calcein-negative cells (absence of green) were considered dead.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Boris Turk (Jozef Stefan Institute) for the kind gift of cathepsin S antibody. We also thank Dr Sokol V. Todi (Wayne State University, Detroit, MI) for use of a Bio-Rad Versadoc 5000MP imager. Tissue processing and immunohistochemistry were performed at Moffitt with support of the tissue core and subsequent analyses completed with the support of Agnieszka Kasprzak and the Analytic Microscopy Core Facility.
Abbreviations
- 3D
three-dimensional
- ABP
activity-based probe
- DQ-collagen IV
dye-quenched collagen IV
- pHe
extracellular pH
- rBM
reconstituted basement membrane
- RFP
red fluorescent protein
Footnotes
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institutes of Health under award numbers: R01 CA131990 (B.F.S./R.R.M.) along with a Research Supplement to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research Programs (J.M.R.), R01 CA077575 (R.J.G.), and U54 CA143970 (R.J.G.). Imaging was performed in the Microscopy, Imaging and Cytometry Resources Core that is supported in part by National Institutes of Health Cancer Center Support grant P30 CA22453 and the Perinatology Research Branch of the National Institute of Child Health and Development. Moffitt Core Facilities are supported in part by Cancer Center Support grant P30 CA076292.
his article refers to supplementary materials, which are designated by Figures W1 to W7 and Movies W1 to W8 and are available online at www.neoplasia.com.
References
- 1.Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Warburg O, Wind F, Negelein E. The metabolism of tumors in the body. J Gen Physiol. 1927;8:519–530. doi: 10.1085/jgp.8.6.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gillies RJ, Raghunand N, Karczmar GS, Bhujwalla ZM. MRI of the tumor microenvironment. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;16:430–450. doi: 10.1002/jmri.10181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wojtkowiak JW, Rothberg JM, Kumar V, Schramm KJ, Haller E, Proemsey JB, Lloyd MC, Sloane BF, Gillies RJ. Chronic autophagy is a cellular adaptation to tumor acidic pH microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3938–3947. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gatenby RA, Gawlinski ET, Gmitro AF, Kaylor B, Gillies RJ. Acid-mediated tumor invasion: a multidisciplinary study. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5216–5223. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Martin NK, Gaffney EA, Gatenby RA, Maini PK. Tumour-stromal interactions in acid-mediated invasion: a mathematical model. J Theor Biol. 2010;267:461–470. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.08.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fukumura D, Xu L, Chen Y, Gohongi T, Seed B, Jain RK. Hypoxia and acidosis independently up-regulate vascular endothelial growth factor transcription in brain tumors in vivo. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6020–6024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cherk MH, Foo SS, Poon AM, Knight SR, Murone C, Papenfuss AT, Sachinidis JI, Saunder TH, O'Keefe GJ, Scott AM. Lack of correlation of hypoxic cell fraction and angiogenesis with glucose metabolic rate in non-small cell lung cancer assessed by 18F-Fluoromisonidazole and 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:1921–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hjelmeland AB, Wu Q, Heddleston JM, Choudhary GS, Macswords J, Lathia JD, McLendon R, Lindner D, Sloan A, Rich JN. Acidic stress promotes a glioma stem cell phenotype. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18:829–840. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ibrahim-Hashim A, Cornnell HH, Coelho Ribeiro Mde L, Abrahams D, Cunningham J, Lloyd M, Martinez GV, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Reduction of metastasis using a non-volatile buffer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2011;28:841–849. doi: 10.1007/s10585-011-9415-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Robey IF, Baggett BK, Kirkpatrick ND, Roe DJ, Dosescu J, Sloane BF, Hashim AI, Morse DL, Raghunand N, Gatenby RA, et al. Bicarbonate increases tumor pH and inhibits spontaneous metastases. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2260–2268. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Edwards DR, Hoyer-Hansen G, Blasi F, Sloane BF, editors. The Cancer Degradome-Proteases and Cancer Biology. New York, NY: Springer; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mason SD, Joyce JA. Proteolytic networks in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2011;21:228–237. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.12.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mohamed MM, Sloane BF. Cysteine cathepsins: multifunctional enzymes in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:764–775. doi: 10.1038/nrc1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Debnath J, Brugge JS. Modelling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:675–688. doi: 10.1038/nrc1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Weigelt B, Bissell MJ. Unraveling the microenvironmental influences on the normal mammary gland and breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008;18:311–321. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rozhin J, Sameni M, Ziegler G, Sloane BF. Pericellular pH affects distribution and secretion of cathepsin B in malignant cells. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6517–6525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Moin K, Day NA, Sameni M, Hasnain S, Hirama T, Sloane BF. Human tumour cathepsin B. Comparison with normal liver cathepsin B. Biochem J. 1992;285(pt 2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2850427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Blum G, Mullins SR, Keren K, Fonovic M, Jedeszko C, Rice MJ, Sloane BF, Bogyo M. Dynamic imaging of protease activity with fluorescently quenched activity-based probes. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:203–209. doi: 10.1038/nchembio728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jedeszko C, Sameni M, Olive MB, Moin K, Sloane BF. Visualizing protease activity in living cells: from two dimensions to four dimensions. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2008;39 doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb0420s39. 20.21-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cavallo-Medved D, Rudy D, Blum G, Bogyo M, Caglic D, Sloane BF. Live-cell imaging demonstrates extracellular matrix degradation in association with active cathepsin B in caveolae of endothelial cells during tube formation. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:1234–1246. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caglic D, Pungercar JR, Pejler G, Turk V, Turk B. Glycosaminoglycans facilitate procathepsin B activation through disruption of propeptidemature enzyme interactions. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:33076–33085. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705761200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murata M, Miyashita S, Yokoo C, Tamai M, Hanada K, Hatayama K, Towatari T, Nikawa T, Katunuma N. Novel epoxysuccinyl peptides. Selective inhibitors of cathepsin B, in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1991;280:307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80318-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sameni M, Anbalagan A, Olive MB, Moin K, Mattingly RR, Sloane BF. MAME models for 4D live-cell imaging of tumor: microenvironment interactions that impact malignant progression. J Vis Exp. 2012;60:e3661. doi: 10.3791/3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Estrella V, Chen T, Lloyd M, Wojtkowiak J, Cornnell HH, Ibrahim-Hashim A, Bailey K, Balagurunathan Y, Rothberg JM, Sloane BF, et al. Acidity generated by the tumor microenvironment drives local invasion. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1524–1535. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gatenby RA, Gawlinski ET. A reaction-diffusion model of cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 1996;56:5745–5753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schlappack OK, Zimmermann A, Hill RP. Glucose starvation and acidosis: effect on experimental metastatic potential, DNA content and MTX resistance of murine tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 1991;64:663–670. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rofstad EK, Mathiesen B, Kindem K, Galappathi K. Acidic extra-cellular pH promotes experimental metastasis of human melanoma cells in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6699–6707. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Moellering RE, Black KC, Krishnamurty C, Baggett BK, Stafford P, Rain M, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Acid treatment of melanoma cells selects for invasive phenotypes. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008;25:411–425. doi: 10.1007/s10585-008-9145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ibrahim-Hashim A, Cornnell HH, Abrahams D, Lloyd M, Bui M, Gillies RJ, Gatenby RA. Systemic buffers inhibit carcinogenesis in TRAMP mice. J Urol. 2012;188:624–631. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ibrahim-Hashim A, Wojtkowiak JW, Ribeiro MDLC, Estrella V, Bailey KM, Cornnell HH, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Free base lysine increases survival and reduces metastasis in prostate cancer model. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2011;S1:S1–004. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Martínez-Zaguilán R, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Chu YW, Gillies RJ, Hendrix MJ. Acidic pH enhances the invasive behavior of human melanoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1996;14:176–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00121214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Glunde K, Guggino SE, Solaiyappan M, Pathak AP, Ichikawa Y, Bhujwalla ZM. Extracellular acidification alters lysosomal trafficking in human breast cancer cells. Neoplasia. 2003;5:533–545. doi: 10.1016/s1476-5586(03)80037-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Steffan JJ, Snider JL, Skalli O, Welbourne T, Cardelli JA. Na+/H+ exchangers and RhoA regulate acidic extracellular pH-induced lysosome trafficking in prostate cancer cells. Traffic. 2009;10:737–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rothberg JM, Sameni M, Moin K, Sloane BF. Live-cell imaging of tumor proteolysis: impact of cellular and non-cellular microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1824:123–132. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.07.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gerweck LE, Seetharaman K. Cellular pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. 1996;56:1194–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Andrews NW. Regulated secretion of conventional lysosomes. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:316–321. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)01794-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saftig P, Hunziker E, Wehmeyer O, Jones S, Boyde A, Rommerskirch W, Moritz JD, Schu P, von Figura K. Impaired osteoclastic bone resorption leads to osteopetrosis in cathepsin-K-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:13453–13458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sennoune SR, Bakunts K, Martinez GM, Chua-Tuan JL, Kebir Y, Attaya MN, Martínez-Zaguilán R. Vacuolar H+-ATPase in human breast cancer cells with distinct metastatic potential: distribution and functional activity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C1443–C1452. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00407.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brown D, Wagner CA. Molecular mechanisms of acid-base sensing by the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:774–780. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012010029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yoneda T, Hata K, Nakanishi M, Nagae M, Nagayama T, Wakabayashi H, Nishisho T, Sakurai T, Hiraga T. Involvement of acidic micro-environment in the pathophysiology of cancer-associated bone pain. Bone. 2011;48:100–105. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kota P, García-Caballero A, Dang H, Gentzsch M, Stutts MJ, Dokholyan NV. Energetic and structural basis for activation of the epithelial sodium channel by matriptase. Biochemistry. 2012;51:3460–3469. doi: 10.1021/bi2014773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Haerteis S, Krappitz M, Bertog M, Krappitz A, Baraznenok V, Henderson I, Lindström E, Murphy JE, Bunnett NW, Korbmacher C. Proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by the cysteine protease cathepsin-S. Pflugers Arch. 2012;464:353–365. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1138-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Alli AA, Song JZ, Al-Khalili O, Bao HF, Ma HP, Alli AA, Eaton DC. Cathepsin B is secreted apically from Xenopus 2F3 cells and cleaves the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) to increase its activity. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:30073–30083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.338574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kong X, Tang X, Du W, Tong J, Yan Y, Zheng F, Fang M, Gong F, Tan Z. Extracellular acidosis modulates the endocytosis and maturation of macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2013;281:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lewis CE, Pollard JW. Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2006;66:605–612. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Giusti I, D'Ascenzo S, Millimaggi D, Taraboletti G, Carta G, Franceschini N, Pavan A, Dolo V. Cathepsin B mediates the pH-dependent proinvasive activity of tumor-shed microvesicles. Neoplasia. 2008;10:481–488. doi: 10.1593/neo.08178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Taraboletti G, D'Ascenzo S, Giusti I, Marchetti D, Borsotti P, Millimaggi D, Giavazzi R, Pavan A, Dolo V. Bioavailability of VEGF in tumor-shed vesicles depends on vesicle burst induced by acidic pH. Neoplasia. 2006;8:96–103. doi: 10.1593/neo.05583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jahde E, Glusenkamp KH, Rajewsky MF. Protection of cultured malignant cells from mitoxantrone cytotoxicity by low extracellular pH: a possible mechanism for chemoresistance in vivo. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26:101–106. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90290-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shree T, Olson OC, Elie BT, Kester JC, Garfall AL, Simpson K, Bell-McGuinn KM, Zabor EC, Brogi E, Joyce JA. Macrophages and cathepsin proteases blunt chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2011;25:2465–2479. doi: 10.1101/gad.180331.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moreno MJ, Ball M, Rukhlova M, Slinn J, L'Abbe D, Iqbal U, Monette R, Hagedorn M, O'Connor-McCourt MD, Durocher Y, et al. IGFBP-4 anti-angiogenic and anti-tumorigenic effects are associated with anti-cathepsin B activity. Neoplasia. 2013;15:554–567. doi: 10.1593/neo.13212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Raghunand N, He X, van Sluis R, Mahoney B, Baggett B, Taylor CW, Paine-Murrieta G, Roe D, Bhujwalla ZM, Gillies RJ. Enhancement of chemotherapy by manipulation of tumour pH. Br J Cancer. 1999;80:1005–1011. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6690455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.