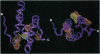Abstract
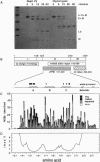
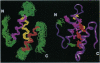
Transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II is regulated by the general elongation factor TFIIS. This factor stimulates RNA polymerase II to transcribe through regions of DNA that promote the formation of stalled ternary complexes. Limited proteolytic digestion showed that yeast TFIIS is composed of three structural domains, termed I, II, and III. The two C-terminal domains (II and III) are required for transcription activity. The structure of domain III has been solved previously by using NMR spectroscopy. Here, we report the NMR-derived structure of domain II: a three-helix bundle built around a hydrophobic core composed largely of three tyrosines protruding from one face of the C-terminal helix. The arrangement of known inactivating mutations of TFIIS suggests that two surfaces of domain II are critical for transcription activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aso T., Lane W. S., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. Elongin (SIII): a multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1439–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.7660129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby S., Harvey T. S., Eagle S. G., Inouye S., Ikura M. NMR-derived three-dimensional solution structure of protein S complexed with calcium. Structure. 1994 Feb 15;2(2):107–122. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Polyakov A., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. GreA protein: a transcription elongation factor from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8899–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Goldfarb A. Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradsher J. N., Jackson K. W., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII. I. Identification, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25587–25593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Zhou H. Functional domains of transcription factor TFIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5633–5637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie K. R., Awrey D. E., Edwards A. M., Kane C. M. Purified yeast RNA polymerase II reads through intrinsic blocks to elongation in response to the yeast TFIIS analogue, P37. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):936–943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cipres-Palacin G., Kane C. M. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis of human transcript elongation factor TFIIS. Biochemistry. 1995 Nov 21;34(46):15375–15380. doi: 10.1021/bi00046a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cipres-Palacin G., Kane C. M. Cleavage of the nascent transcript induced by TFIIS is insufficient to promote read-through of intrinsic blocks to elongation by RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8087–8091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Nilges M., Sukumaran D. K., Brünger A. T., Karplus M., Gronenborn A. M. The three-dimensional structure of alpha1-purothionin in solution: combined use of nuclear magnetic resonance, distance geometry and restrained molecular dynamics. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2729–2735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaglio F., Grzesiek S., Vuister G. W., Zhu G., Pfeifer J., Bax A. NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR. 1995 Nov;6(3):277–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00197809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Driscoll P. C., Kay L. E., Wingfield P. T., Bax A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Overcoming the overlap problem in the assignment of 1H NMR spectra of larger proteins by use of three-dimensional heteronuclear 1H-15N Hartmann-Hahn-multiple quantum coherence and nuclear Overhauser-multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy: application to interleukin 1 beta. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6150–6156. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi T., Nakano A., Nomura K., Sekimizu K., Natori S. Purification, gene cloning, and gene disruption of the transcription elongation factor S-II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13200–13204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi T., Shimoaraiso M., Kubo T., Natori S. Structure-function relationship of yeast S-II in terms of stimulation of RNA polymerase II, arrest relief, and suppression of 6-azauracil sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 14;270(15):8991–8995. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Gronenborn A. M., Brünger A. T., Clore G. M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins by simulated annealing with interproton distance restraints. Application to crambin, potato carboxypeptidase inhibitor and barley serine proteinase inhibitor 2. Protein Eng. 1988 Apr;2(1):27–38. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Calibration of the angular dependence of the amide proton-C alpha proton coupling constants, 3JHN alpha, in a globular protein. Use of 3JHN alpha for identification of helical secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Gozani S. N., Yoon H., Jeon C. J., Agarwal K., Weiss M. A. Novel zinc finger motif in the basal transcriptional machinery: three-dimensional NMR studies of the nucleic acid binding domain of transcriptional elongation factor TFIIS. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):9944–9959. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Jeon C., Yoon H., Agarwal K., Weiss M. A. Structure of a new nucleic-acid-binding motif in eukaryotic transcriptional elongation factor TFIIS. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):277–279. doi: 10.1038/365277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield C., Dobson C. M. 1H NMR studies of human lysozyme: spectral assignment and comparison with hen lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7201–7214. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Chamberlin M. J., Kane C. M. Transcription elongation factor SII (TFIIS) enables RNA polymerase II to elongate through a block to transcription in a human gene in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10799–10809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Mote J., Jr Elongation factor SII-dependent transcription by RNA polymerase II through a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1917–1921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. J., Sutcliffe M. J., Redfield C., Dobson C. M. Analysis of phi and chi 1 torsion angles for hen lysozyme in solution from 1H NMR spin-spin coupling constants. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):986–996. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Braun W., Havel T. F., Schaumann T., Go N., Wüthrich K. Protein structures in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. The polypeptide fold of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor determined using two different algorithms, DISGEO and DISMAN. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):611–639. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Lane W. S., Young R. A. Yeast RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9 is essential for growth at temperature extremes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19053–19055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Pseudo-structures for the 20 common amino acids for use in studies of protein conformations by measurements of intramolecular proton-proton distance constraints with nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 5;169(4):949–961. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Zeng Q., Colangelo C. M., Lewis M., Summers M. F., Scott R. A. The N-terminal domain of TFIIB from Pyrococcus furiosus forms a zinc ribbon. Nat Struct Biol. 1996 Feb;3(2):122–124. doi: 10.1038/nsb0296-122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]