Abstract
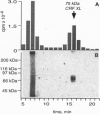
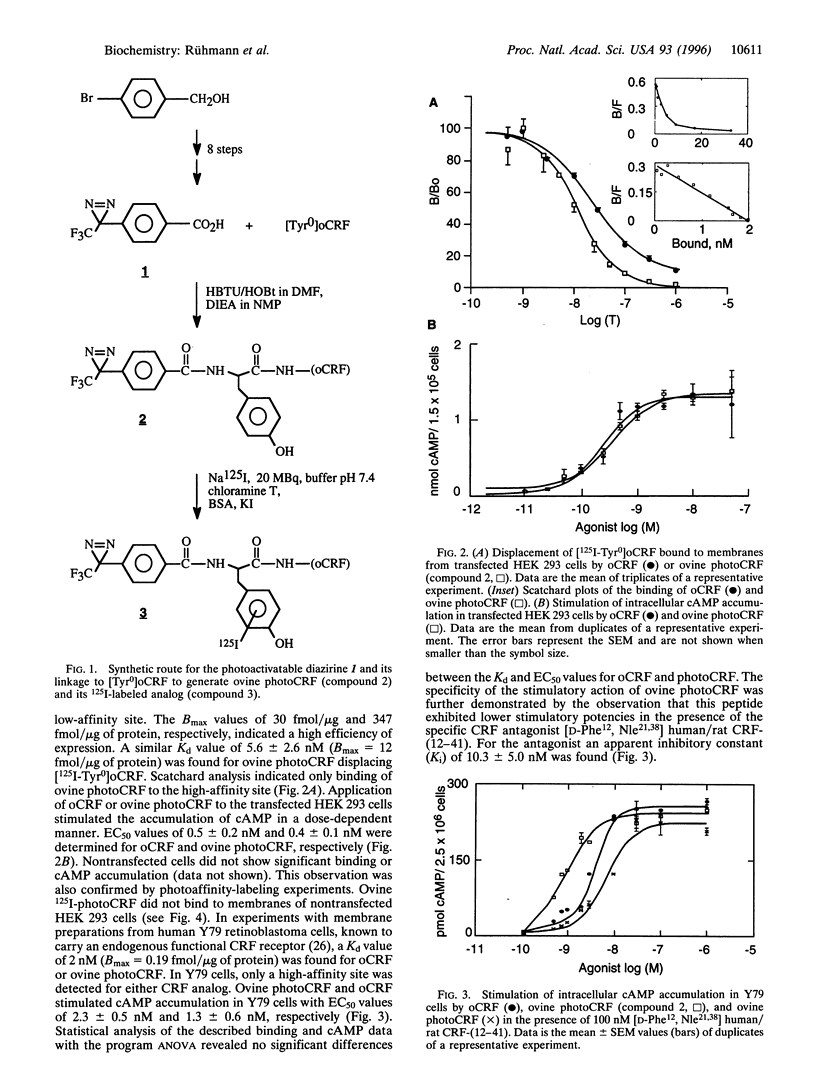
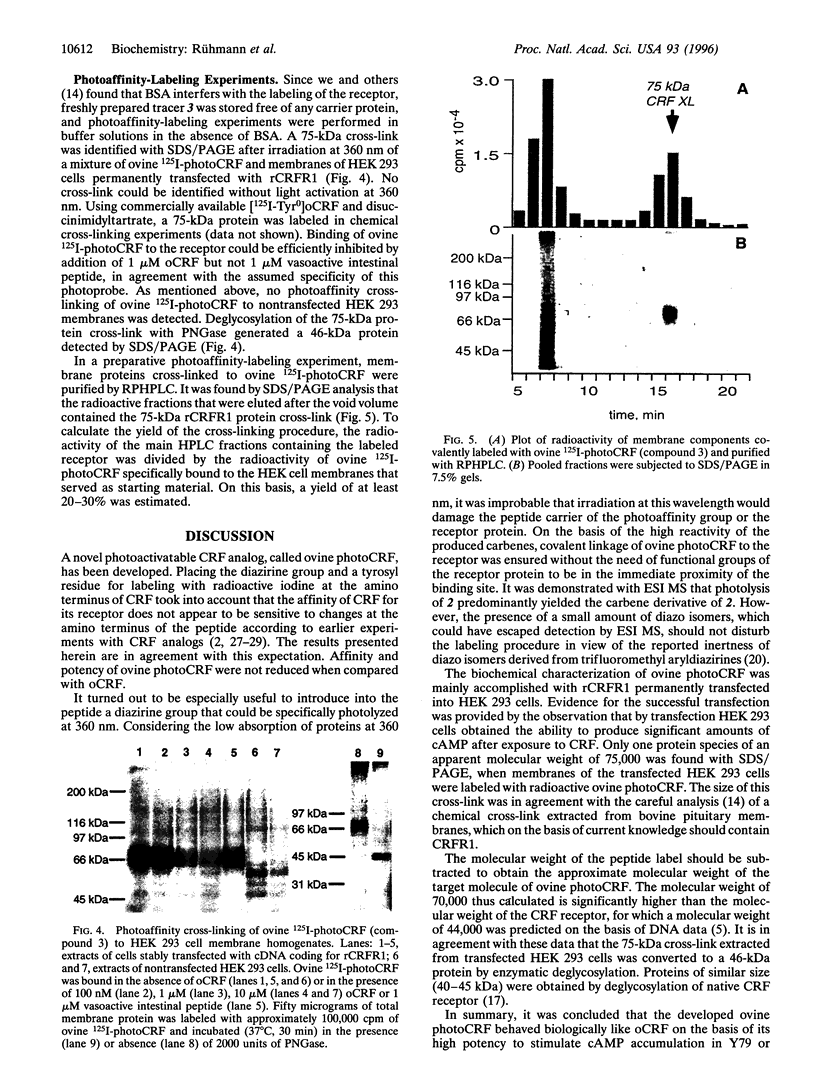
A novel photoactivatable analog of ovine corticotropin-releasing factor (ovine photoCRF) has been synthesized and characterized. A diazirine group, the 4-(1-azi-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)benzoyl residue, was covalently bound to the amino terminus of ovine CRF (oCRF), which was N-terminally extended by a tyrosyl residue for radioactive labeling with 125I. Under mild conditions, photolysis yielded highly reactive carbenes, responsible for the formation of covalent bonds to the CRF receptor. Ovine photoCRF was shown to bind to the high-affinity site of the CRF receptor with a similar Kd value as oCRF. When radioactively iodinated ovine photoCRF (ovine 125I-photoCRF) was covalently linked to rat CRF receptor, type 1 (rCRFR1), permanently transfected into human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells, a highly glycosylated 75-kDa protein was identified with SDS/PAGE. The specificity of ovine 125I-photoCRF was demonstrated by the finding that this analog could be displaced from the receptor by oCRF, but not other unrelated peptides such as vasoactive intestinal peptide. The observed size of the 75-kDa cross-link was in agreement with the molecular weight reported earlier for native CRFR1 from rat brain. Deglycosylation of the 75-kDa cross-link with peptide:N-glycosidase (PNGase) yielded a 46-kDa protein, in agreement with the molecular weight estimated from cDNA coding for rat CRFR1. The developed CRF analog, photoCRF, is expected to facilitate future biochemical and physiological analysis of CRF receptors and--by analogous strategies--of other peptide receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C. P., Pearse R. V., 2nd, O'Connell S., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of a seven transmembrane helix receptor for corticotropin-releasing factor and sauvagine in mammalian brain. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90230-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Lewis K. A., Perrin M. H., Vale W. W. Expression cloning of a human corticotropin-releasing-factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis D. E., De Souza E. B. Heterogeneity between brain and pituitary corticotropin-releasing factor receptors is due to differential glycosylation. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):1877–1888. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis D. E., De Souza E. B. The brain corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) receptor is of lower apparent molecular weight than the CRF receptor in anterior pituitary. Evidence from chemical cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10927–10931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillory R. J. Design, implementation and pitfalls of photoaffinity labelling experiments in in vitro preparations. General principles. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Pearse R. V., 2nd, Lin C. R., Rosenfeld M. G. A sauvagine/corticotropin-releasing factor receptor expressed in heart and skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Liaw C. W., Grigoriadis D. E., Clevenger W., Chalmers D. T., De Souza E. B., Oltersdorf T. Cloning and characterization of a functionally distinct corticotropin-releasing factor receptor subtype from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura E., Billestrup N., Perrin M., Vale W. Identification and characterization of a pituitary corticotropin-releasing factor binding protein by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12893–12896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olianas M. C., Lampis G., Onali P. Human Y-79 retinoblastoma cells exhibit specific corticotropin-releasing hormone binding sites. J Neurochem. 1995 Jan;64(1):402–407. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64010402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin M. H., Donaldson C. J., Chen R., Lewis K. A., Vale W. W. Cloning and functional expression of a rat brain corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor. Endocrinology. 1993 Dec;133(6):3058–3061. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.6.8243338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin M., Donaldson C., Chen R., Blount A., Berggren T., Bilezikjian L., Sawchenko P., Vale W. Identification of a second corticotropin-releasing factor receptor gene and characterization of a cDNA expressed in heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2969–2973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E., Behan D. P., Fischer W. H., Linton E. A., Lowry P. J., Vale W. W. Cloning and characterization of the cDNAs for human and rat corticotropin releasing factor-binding proteins. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):423–426. doi: 10.1038/349423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Rivier C., Vale W. Synthetic competitive antagonists of corticotropin-releasing factor: effect on ACTH secretion in the rat. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):889–891. doi: 10.1126/science.6326264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Spiess J., Vale W. Characterization of rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4851–4855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendale B. E., Jarrett D. B., Robinson A. G. Identification of a corticotropin-releasing factor-binding protein in the plasma membrane of AtT-20 mouse pituitary tumor cells and its regulation by dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2357–2366. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rückert Y., Rohde W., Furkert J. Radioimmunoassay of corticotropin-releasing hormone. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;96(2):129–137. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1211001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Billestrup N., Perrin M., Rivier J., Vale W. Identification of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) target cells and effects of dexamethasone on binding in anterior pituitary using a fluorescent analog of CRF. Endocrinology. 1986 Nov;119(5):2376–2382. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-5-2376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess J., Rivier J., Rivier C., Vale W. Primary structure of corticotropin-releasing factor from ovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6517–6521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel P., Kesterson R., Yeung W., Cone R. D., Rittenberg M. B., Stenzel-Poore M. P. Identification of a novel murine receptor for corticotropin-releasing hormone expressed in the heart. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 May;9(5):637–645. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.5.7565810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton S. W., Behan D. P., Lahrichi S. L., Kaiser R., Corrigan A., Lowry P., Potter E., Perrin M. H., Rivier J., Vale W. W. Ligand requirements of the human corticotropin-releasing factor-binding protein. Endocrinology. 1995 Mar;136(3):1097–1102. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.3.7867564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Spiess J., Rivier C., Rivier J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1394–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.6267699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J., Donaldson C., Bittencourt J., Perrin M. H., Lewis K., Sutton S., Chan R., Turnbull A. V., Lovejoy D., Rivier C. Urocortin, a mammalian neuropeptide related to fish urotensin I and to corticotropin-releasing factor. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):287–292. doi: 10.1038/378287a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Laurent P., Lefort S., Chalon P., Lelias J. M., Kaghad M., Le Fur G., Caput D., Ferrara P. Primary structure and functional expression of mouse pituitary and human brain corticotrophin releasing factor receptors. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 29;335(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80427-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]