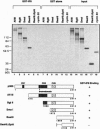
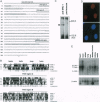
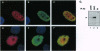
Abstract
p300 and its family member, CREB-binding protein (CBP), function as key transcriptional coactivators by virtue of their interaction with the activated forms of certain transcription factors. In a search for additional cellular targets of p300/CBP, a protein-protein cloning strategy, surprisingly identified SRC-1, a coactivator involved in nuclear hormone receptor transcriptional activity, as a p300/CBP interactive protein. p300 and SRC-1 interact, specifically, in vitro and they also form complexes in vivo. Moreover, we show that SRC-1 encodes a new member of the basic helix-loop-helix-PAS domain family and that it physically interacts with the retinoic acid receptor in response to hormone binding. Together, these results implicate p300 as a component of the retinoic acid signaling pathway, operating, in part, through specific interaction with a nuclear hormone receptor coactivator, SRC-1.
Full text
PDF
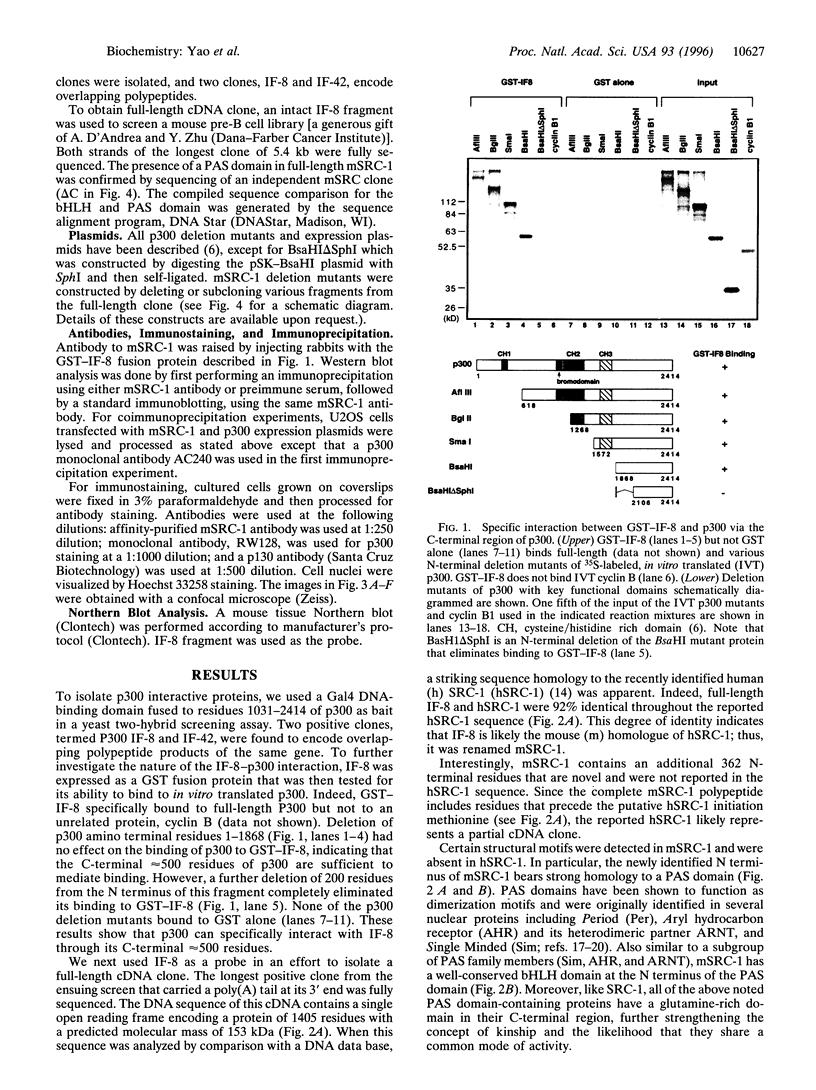



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arany Z., Sellers W. R., Livingston D. M., Eckner R. E1A-associated p300 and CREB-associated CBP belong to a conserved family of coactivators. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias J., Alberts A. S., Brindle P., Claret F. X., Smeal T., Karin M., Feramisco J., Montminy M. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature. 1994 Jul 21;370(6486):226–229. doi: 10.1038/370226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister A. J., Kouzarides T. CBP-induced stimulation of c-Fos activity is abrogated by E1A. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4758–4762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbach K. M., Poland A., Bradfield C. A. Cloning of the Ah-receptor cDNA reveals a distinctive ligand-activated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8185–8189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillès V., Dauvois S., L'Horset F., Lopez G., Hoare S., Kushner P. J., Parker M. G. Nuclear factor RIP140 modulates transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3741–3751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Kwok R. P., Lamb N., Hagiwara M., Montminy M. R., Goodman R. H. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):855–859. doi: 10.1038/365855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S. T., Thomas J. B., Goodman C. S. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a nuclear protein with sequence similarity to the per gene product. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai P., Akimaru H., Tanaka Y., Hou D. X., Yasukawa T., Kanei-Ishii C., Takahashi T., Ishii S. CBP as a transcriptional coactivator of c-Myb. Genes Dev. 1996 Mar 1;10(5):528–540. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.5.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Ewen M. E., Newsome D., Gerdes M., DeCaprio J. A., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the adenovirus E1A-associated 300-kD protein (p300) reveals a protein with properties of a transcriptional adaptor. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 15;8(8):869–884. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.8.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekakis N., Saez L., Delahaye-Brown A. M., Myers M. P., Sehgal A., Young M. W., Weitz C. J. Isolation of timeless by PER protein interaction: defective interaction between timeless protein and long-period mutant PERL. Science. 1995 Nov 3;270(5237):811–815. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5237.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halachmi S., Marden E., Martin G., MacKay H., Abbondanza C., Brown M. Estrogen receptor-associated proteins: possible mediators of hormone-induced transcription. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1455–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.8197458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z. J., Edery I., Rosbash M. PAS is a dimerization domain common to Drosophila period and several transcription factors. Nature. 1993 Jul 15;364(6434):259–262. doi: 10.1038/364259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. R., Bargiello T. A., Yun S. H., Young M. W. Product of per locus of Drosophila shares homology with proteoglycans. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):185–188. doi: 10.1038/320185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei Y., Xu L., Heinzel T., Torchia J., Kurokawa R., Gloss B., Lin S. C., Heyman R. A., Rose D. W., Glass C. K. A CBP integrator complex mediates transcriptional activation and AP-1 inhibition by nuclear receptors. Cell. 1996 May 3;85(3):403–414. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. Nonsteroid nuclear receptors: what are genetic studies telling us about their role in real life? Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):859–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Söderström M., Hörlein A., Halachmi S., Brown M., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Polarity-specific activities of retinoic acid receptors determined by a co-repressor. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):451–454. doi: 10.1038/377451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Thummel C., Beato M., Herrlich P., Schütz G., Umesono K., Blumberg B., Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):835–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90199-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. DNA tumor virus transforming proteins and the cell cycle. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muralidhar M. G., Callahan C. A., Thomas J. B. Single-minded regulation of genes in the embryonic midline of the Drosophila central nervous system. Mech Dev. 1993 May;41(2-3):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90043-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oñate S. A., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1354–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Reisz-Porszasz S., Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson H. I., Chan W. K., Bradfield C. A. DNA binding specificities and pairing rules of the Ah receptor, ARNT, and SIM proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 3;270(44):26292–26302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.44.26292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. B., Crews S. T., Goodman C. S. Molecular genetics of the single-minded locus: a gene involved in the development of the Drosophila nervous system. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. L., Jiang B. H., Rue E. A., Semenza G. L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5510–5514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]