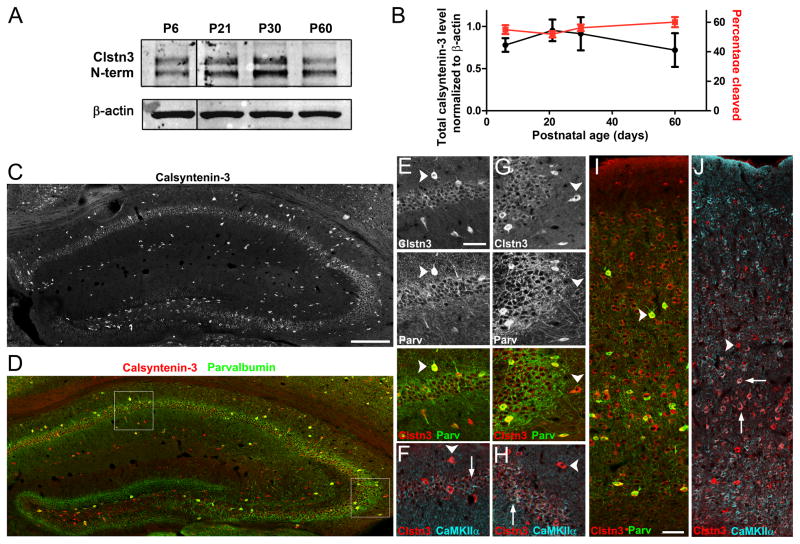
Figure 6. Calsyntenin-3 is Expressed by Neuron Subsets in Hippocampus and Cortex.
(A, B) Western blot and quantification of the expression level and fraction of total calsyntenin-3 present as the cleaved form during development (P, postnatal day).
(C–J) Distribution of calsyntenin-3 (Clstn3, with C-terminal antibody) in adult mouse hippocampus (C-H) and cortex (I,J). Co-labeling was performed for parvalbumin (D, E, G, I) and CaMKIIα (F, H, J).
(C–H) In hippocampus, calsyntenin-3 immunoreactivity was detected most strongly in interneurons, both parvalbumin-positive and parvalbumin-negative (arrowheads in E and G, respectively). Parvalbumin-negative interneurons were identified by their position outside the pyramidal cell layer and by the absence of immunoreactivity for CaMKIIα (arrowheads in F and H). By comparison with Clstn3 −/− tissue (see Figure 7), wild-type pyramidal neurons (arrows) in CA1 (E, F) and in CA3 (G, H) were also immunopositive for calsyntenin-3 whereas no immunoreactivity was detectable in dentate granule cells. (I, J) In neocortex, calsyntenin-3 was widely expressed, at highest levels by interneurons (arrowheads) including parvalbumin-positive interneurons (I) but also by some pyramidal neurons particularly in layer V (arrows in J).
Scale bars: 200 μm in C and D, 50 μm in E–J. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S5.