Abstract
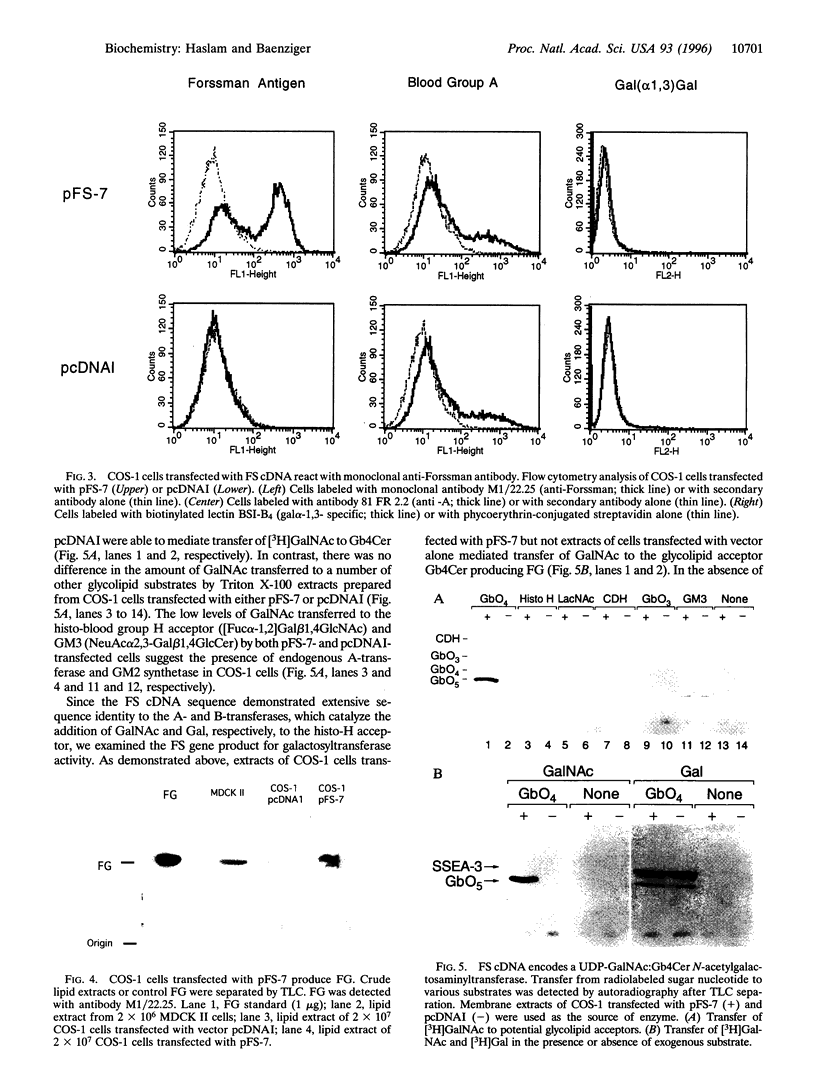
A phenotypic cloning approach was used to isolate a canine cDNA encoding Forssman glycolipid synthetase (FS; UDP-GalNAc:globoside alpha-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; EC 2.4.1.88). The deduced amino acid sequence of FS demonstrates extensive identity to three previously cloned glycosyltransferases, including the enzymes responsible for synthesis of histo-blood group A and B antigens. These three enzymes, like FS, catalyze the addition of either N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) or galactose (Gal) in alpha-1,3-linkage to their respective substrates. Despite the high degree of sequence similarity among the transferases, we demonstrate that the FS cDNA encodes an enzyme capable of synthesizing Forssman glycolipid, and demonstrates no GalNAc or Gal transferase activity when closely related substrates are examined. Thus, the FS cDNA is a novel member of the histo-blood group ABO gene family that encodes glycosyltransferases with related but distinct substrate specificity. Cloning of the FS cDNA will allow a detailed dissection of the roles Forssman glycolipid plays in cellular differentiation, development, and malignant transformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cho S. K., Yeh J., Cho M., Cummings R. D. Transcriptional regulation of alpha1,3-galactosyltransferase in embryonal carcinoma cells by retinoic acid. Masking of Lewis X antigens by alpha-galactosylation. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 9;271(6):3238–3246. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.6.3238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. F., Gorbea C. M., Cummings R. D., Mattox S., Smith D. F. Decreased biosynthesis of Forssman glycolipid after retinoic acid-induced differentiation of mouse F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Lectin-affinity chromatography of the glycolipid-derived oligosaccharide. Carbohydr Res. 1991 Jun 25;213:155–168. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)90606-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Wainwright L. J. Molecular cloning of eukaryotic glycoprotein and glycolipid glycosyltransferases: a survey. Glycobiology. 1995 Jul;5(5):463–472. doi: 10.1093/glycob/5.5.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredman P. Glycosphingolipid tumor antigens. Adv Lipid Res. 1993;25:213–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Bifunctional role of glycosphingolipids. Modulators for transmembrane signaling and mediators for cellular interactions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18713–18716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Structure and function of sphingoglycolipids in transmembrane signalling and cell-cell interactions. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Aug;21(3):583–595. doi: 10.1042/bst0210583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam D. B., Borén T., Falk P., Ilver D., Chou A., Xu Z., Normark S. The amino-terminal domain of the P-pilus adhesin determines receptor specificity. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Nov;14(3):399–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper L. V., Hindsgaul O., Baenziger J. U. Purification and characterization of the GalNAc-4-sulfotransferase responsible for sulfation of GalNAc beta 1,4GlcNAc-bearing oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16327–16332. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Levery S. B., Ishigami F., Hakomori S., Shevinsky L. H., Knowles B. B., Solter D. New globoseries glycosphingolipids in human teratocarcinoma reactive with the monoclonal antibody directed to a developmentally regulated antigen, stage-specific embryonic antigen 3. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8934–8942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominato Y., McNeill P. D., Yamamoto M., Russell M., Hakomori S., Yamamoto F. Animal histo-blood group ABO genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91538-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupnick J. G., Damjanov I., Damjanov A., Zhu Z. M., Fenderson B. A. Globo-series carbohydrate antigens are expressed in different forms on human and murine teratocarcinoma-derived cells. Int J Cancer. 1994 Dec 1;59(5):692–698. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910590518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa N., Hamamoto T., Lee Y. C., Nakaoka T., Kojima N., Tsuji S. Molecular cloning and expression of GalNAc alpha 2,6-sialyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1402–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen R. D., Rajan V. P., Ruff M. M., Kukowska-Latallo J., Cummings R. D., Lowe J. B. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a murine UDPgalactose:beta-D-galactosyl- 1,4-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminide alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase: expression cloning by gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinko J. M., Vincek V., Klein D., Klein J. Primate ABO glycosyltransferases: evidence for trans-species evolution. Immunogenetics. 1993;37(4):274–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00187453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori E., Mori T., Sanai Y., Nagai Y. Radioimmuno-thin-layer chromatographic detection of Forssman antigen in human carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):926–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. A., Goldstein I. J. Five alpha-D-galactopyranosyl-binding isolectins from Bandeiraea simplicifolia seeds. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4739–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata Y., Yamashiro S., Yodoi J., Lloyd K. O., Shiku H., Furukawa K. Expression cloning of beta 1,4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase cDNAs that determine the expression of GM2 and GD2 gangliosides. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12082–12089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara K., Watanabe Y., Maruyama K., Kasahara K., Nagai Y., Sanai Y. Expression cloning of a CMP-NeuAc:NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1'Cer alpha 2,8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase) from human melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara K., Watanabe Y., Maruyama K., Kasahara K., Nagai Y., Sanai Y. Expression cloning of a CMP-NeuAc:NeuAc alpha 2-3Gal beta 1-4Glc beta 1-1'Cer alpha 2,8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase) from human melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):7952–7956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Kurata K., Kojima N., Kurosawa N., Ohta S., Hanai N., Tsuji S., Nishi T. Expression cloning of a GM3-specific alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase (GD3 synthase). J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15950–15956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui B., Hakomori S. A revised structure for the Forssman glycolipid hapten. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5766–5769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Lowe J. B. Molecular cloning of a murine N-acetylgalactosamine transferase cDNA that determines expression of the T lymphocyte-specific CT oligosaccharide differentiation antigen. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15162–15171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K. R., Stern P. L. Expression of a Forssman antigenic specificity in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):785–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto F., Clausen H., White T., Marken J., Hakomori S. Molecular genetic basis of the histo-blood group ABO system. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):229–233. doi: 10.1038/345229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto F., Hakomori S. Sugar-nucleotide donor specificity of histo-blood group A and B transferases is based on amino acid substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19257–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto F., McNeill P. D., Hakomori S. Genomic organization of human histo-blood group ABO genes. Glycobiology. 1995 Feb;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.1093/glycob/5.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Genderen I. L., van Meer G., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Voorhout W. F. Subcellular localization of Forssman glycolipid in epithelial MDCK cells by immuno-electronmicroscopy after freeze-substitution. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1009–1019. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]