Abstract
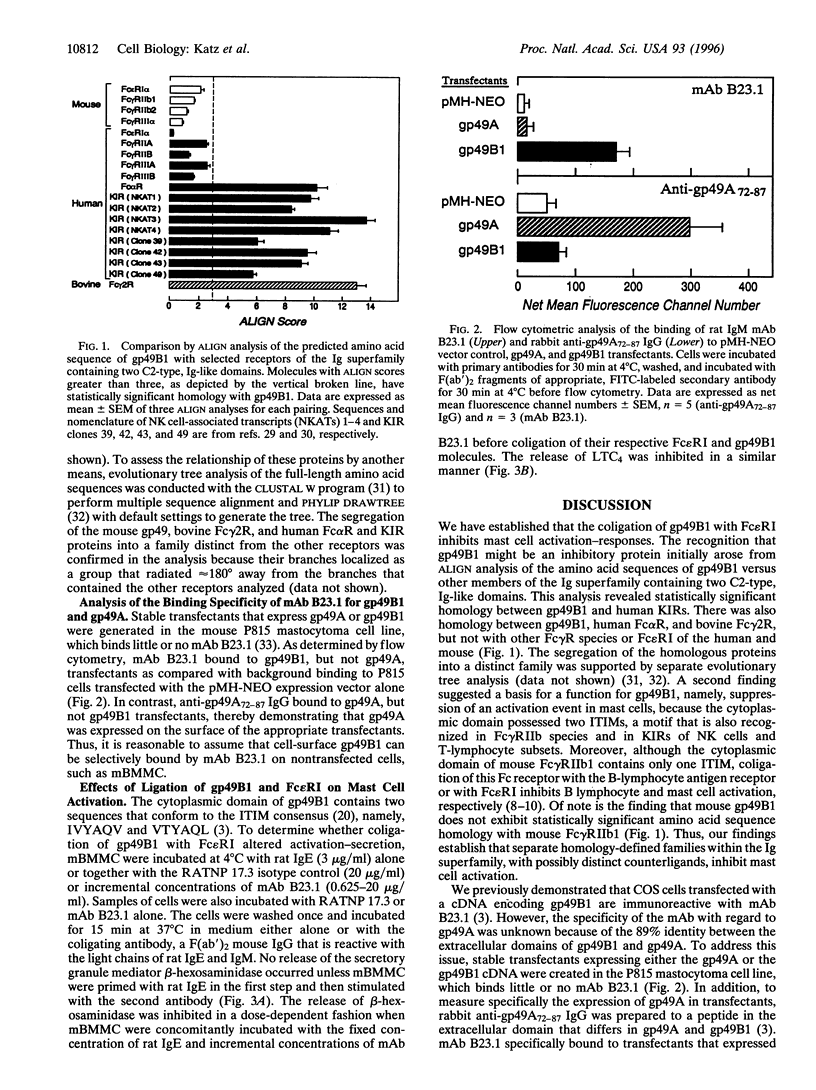
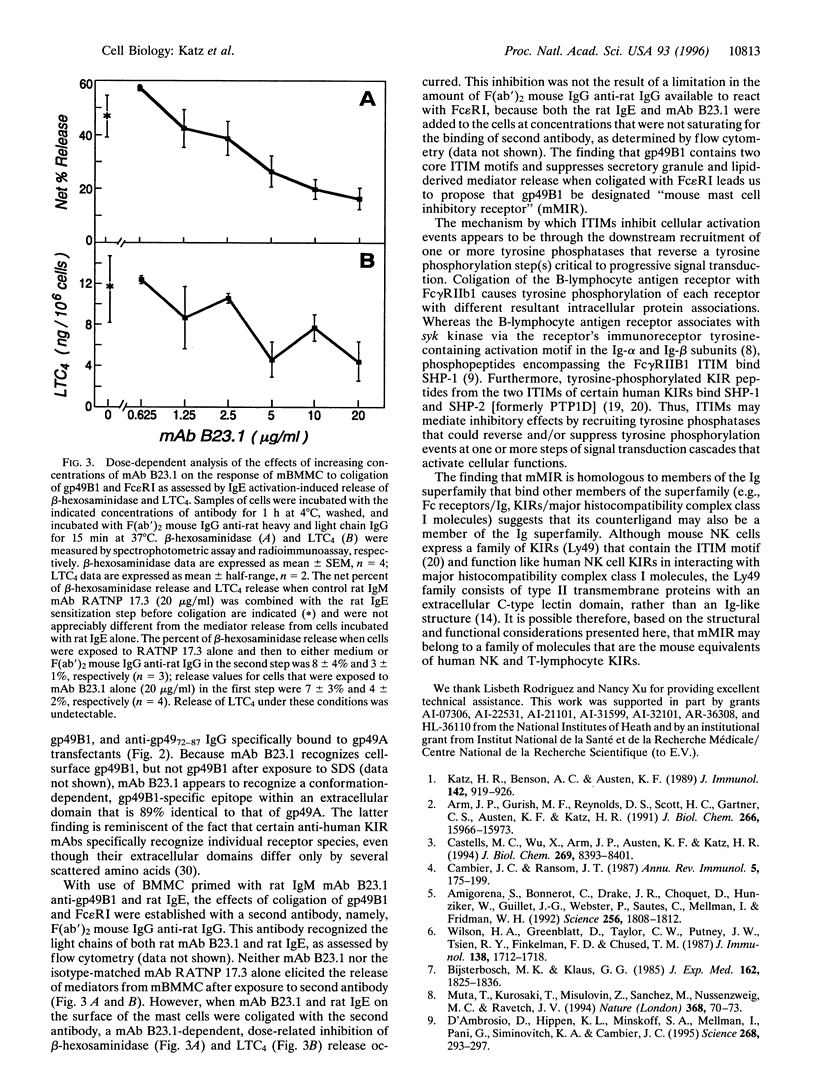
Mouse mast cells express gp49B1, a cell-surface member of the Ig superfamily encoded by the gp49B gene. We now report that by ALIGN comparison of the amino acid sequence of gp49B1 with numerous receptors of the Ig superfamily, a newly recognized family has been established that includes gp49B1, the human myeloid cell Fc receptor for IgA, the bovine myeloid cell Fc receptor for IgG2, and the human killer cell inhibitory receptors expressed on natural killer cells and T lymphocyte subsets. Furthermore, the cytoplasmic domain of gp49B1 contains two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs that are also present in killer cell inhibitory receptors; these motifs downregulate natural killer cell and T-cell activation signals that lead to cytotoxic activity. As assessed by flow cytometry with transfectants that express either gp49B1 or gp49A, which are 89% identical in the amino acid sequences of their extracellular domains, mAb B23.1 was shown to recognize only gp49B1. Coligation of mAb B23.1 bound to gp49B1 and IgE fixed to the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgE on the surface of mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells inhibited exocytosis in a dose-related manner, as defined by the release of the secretory granule constituent beta-hexosaminidase, as well as the generation of the membrane-derived lipid mediator, leukotriene C4. Thus, gp49B1 is an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif-containing integral cell-surface protein that downregulates the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgE-mediated release of proinflammatory mediators from mast cells. Our findings establish a novel counterregulatory transmembrane pathway by which mast cell activation can be inhibited.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Erickson B. W. Optimal sequence alignment using affine gap costs. Bull Math Biol. 1986;48(5-6):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF02462326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigorena S., Bonnerot C., Drake J. R., Choquet D., Hunziker W., Guillet J. G., Webster P., Sautes C., Mellman I., Fridman W. H. Cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity and functions of IgG Fc receptors in B lymphocytes. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1535455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arm J. P., Gurish M. F., Reynolds D. S., Scott H. C., Gartner C. S., Austen K. F., Katz H. R. Molecular cloning of gp49, a cell-surface antigen that is preferentially expressed by mouse mast cell progenitors and is a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15966–15973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Klaus G. G. Crosslinking of surface immunoglobulin and Fc receptors on B lymphocytes inhibits stimulation of inositol phospholipid breakdown via the antigen receptors. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1825–1836. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burshtyn D. N., Scharenberg A. M., Wagtmann N., Rajagopalan S., Berrada K., Yi T., Kinet J. P., Long E. O. Recruitment of tyrosine phosphatase HCP by the killer cell inhibitor receptor. Immunity. 1996 Jan;4(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80300-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Ransom J. T. Molecular mechanisms of transmembrane signaling in B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:175–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castells M. C., Wu X., Arm J. P., Austen K. F., Katz H. R. Cloning of the gp49B gene of the immunoglobulin superfamily and demonstration that one of its two products is an early-expressed mast cell surface protein originally described as gp49. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8393–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna M., Samaridis J. Cloning of immunoglobulin-superfamily members associated with HLA-C and HLA-B recognition by human natural killer cells. Science. 1995 Apr 21;268(5209):405–408. doi: 10.1126/science.7716543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio D., Hippen K. L., Minskoff S. A., Mellman I., Pani G., Siminovitch K. A., Cambier J. C. Recruitment and activation of PTP1C in negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling by Fc gamma RIIB1. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):293–297. doi: 10.1126/science.7716523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M., Malbec O., Latour S., Arock M., Fridman W. H. Regulation of high-affinity IgE receptor-mediated mast cell activation by murine low-affinity IgG receptors. J Clin Invest. 1995 Feb;95(2):577–585. doi: 10.1172/JCI117701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumperz J. E., Parham P. The enigma of the natural killer cell. Nature. 1995 Nov 16;378(6554):245–248. doi: 10.1038/378245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. C., Menzin E., Saito T., Germain R. N., Bierer B. E. The complete sequences of plasmids pFNeo and pMH-Neo: convenient expression vectors for high-level expression of eukaryotic genes in hematopoietic cell lines. Gene. 1993 May 30;127(2):267–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90731-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H. R., Benson A. C., Austen K. F. Activation- and phorbol ester-stimulated phosphorylation of a plasma membrane glycoprotein antigen expressed on mouse IL-3-dependent mast cells and serosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):919–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H. R., Raizman M. B., Gartner C. S., Scott H. C., Benson A. C., Austen K. F. Secretory granule mediator release and generation of oxidative metabolites of arachidonic acid via Fc-IgG receptor bridging in mouse mast cells. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):868–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H. Inhibitory MHC class I receptors on NK cells and T cells. Immunol Today. 1996 Feb;17(2):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80585-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc P. A., Biron C. A. Mononuclear phagocyte maturation: a cytotoxic monoclonal antibody reactive with postmonoblast stages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Feb;83(2):242–254. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mingari M. C., Vitale C., Cambiaggi A., Schiavetti F., Melioli G., Ferrini S., Poggi A. Cytolytic T lymphocytes displaying natural killer (NK)-like activity: expression of NK-related functional receptors for HLA class I molecules (p58 and CD94) and inhibitory effect on the TCR-mediated target cell lysis or lymphokine production. Int Immunol. 1995 Apr;7(4):697–703. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.4.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Bottino C., Vitale M., Pende D., Biassoni R., Mingari M. C., Moretta L. Receptors for HLA class-I molecules in human natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:619–648. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ciccone E., Mingari M. C., Biassoni R., Moretta A. Human natural killer cells: origin, clonality, specificity, and receptors. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:341–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muta T., Kurosaki T., Misulovin Z., Sanchez M., Nussenzweig M. C., Ravetch J. V. A 13-amino-acid motif in the cytoplasmic domain of Fc gamma RIIB modulates B-cell receptor signalling. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):70–73. doi: 10.1038/368070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olcese L., Lang P., Vély F., Cambiaggi A., Marguet D., Bléry M., Hippen K. L., Biassoni R., Moretta A., Moretta L. Human and mouse killer-cell inhibitory receptors recruit PTP1C and PTP1D protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4531–4534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Gumperz J. E., Parham P., Lanier L. L. Superantigen-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity inhibited by MHC class I receptors on T lymphocytes. Science. 1995 Apr 21;268(5209):403–405. doi: 10.1126/science.7716542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Correa I., Corral L., Dorfman J., Wu M. F. Inhibitory effects of class I molecules on murine NK cells: speculations on function, specificity and self-tolerance. Semin Immunol. 1995 Apr;7(2):103–107. doi: 10.1006/smim.1995.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Ihle J. N., Seldin D., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Katz H. R., LeBlanc P. A., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Interleukin 3: A differentiation and growth factor for the mouse mast cell that contains chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1479–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Stevens R. L., Lewis R. A., Liu F. T., Corey E., Austen K. F. IgE-mediated release of leukotriene C4, chondroitin sulfate E proteoglycan, beta-hexosaminidase, and histamine from cultured bone marrow-derived mouse mast cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):189–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Stirling J. L. N-Acetyl-beta-glucosaminidases in human spleen. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1070321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. D., Higgins D. G., Gibson T. J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Nov 11;22(22):4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagtmann N., Biassoni R., Cantoni C., Verdiani S., Malnati M. S., Vitale M., Bottino C., Moretta L., Moretta A., Long E. O. Molecular clones of the p58 NK cell receptor reveal immunoglobulin-related molecules with diversity in both the extra- and intracellular domains. Immunity. 1995 May;2(5):439–449. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. A., Greenblatt D., Taylor C. W., Putney J. W., Tsien R. Y., Finkelman F. D., Chused T. M. The B lymphocyte calcium response to anti-Ig is diminished by membrane immunoglobulin cross-linkage to the Fc gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1712–1718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama W. M., Daniels B. F., Seaman W. E., Hunziker R., Margulies D. H., Smith H. R. A family of murine NK cell receptors specific for target cell MHC class I molecules. Semin Immunol. 1995 Apr;7(2):89–101. doi: 10.1006/smim.1995.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



