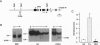Abstract
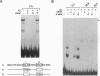
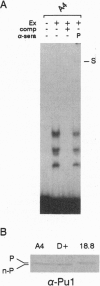
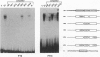
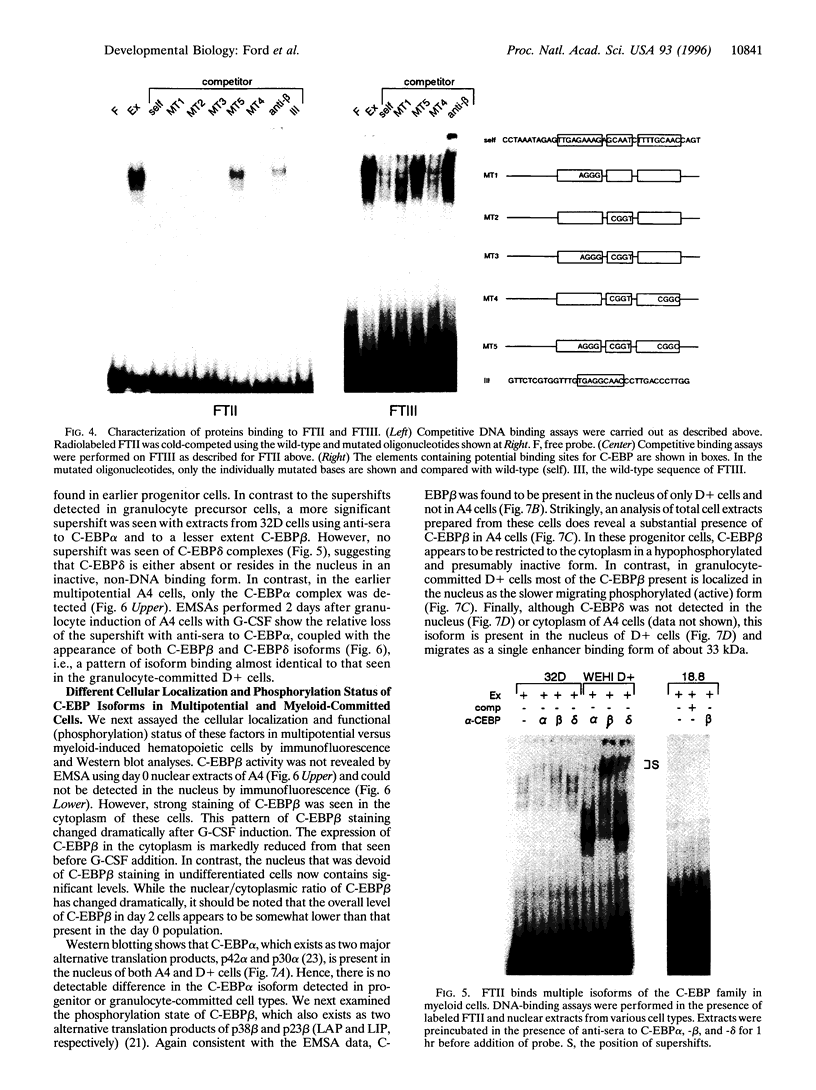
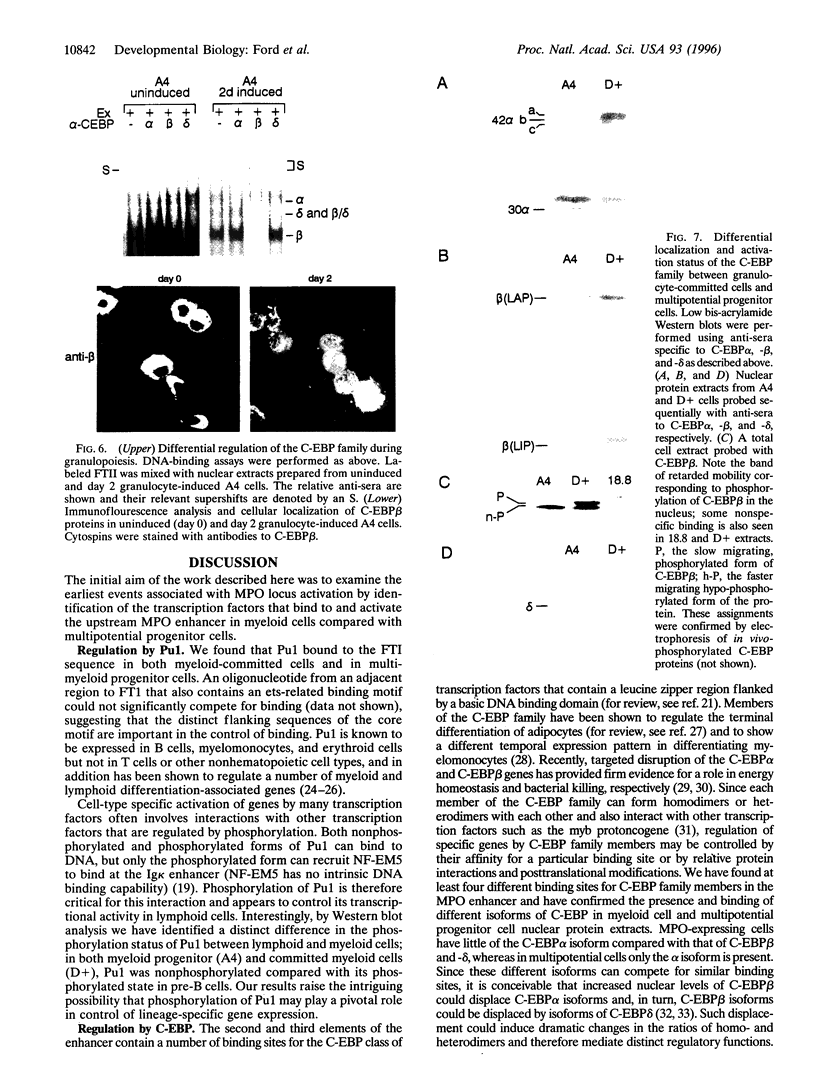
We have compared the molecular architecture and function of the myeloperoxidase upstream enhancer in multipotential versus granulocyte-committed hematopoietic progenitor cells. We show that the enhancer is accessible in multipotential cell chromatin but functionally incompetent before granulocyte commitment. Multipotential cells contain both Pu1 and C-EBP alpha as enhancer-binding activities. Pu1 is unphosphorylated in both multipotential and granulocyte-committed cells but is phosphorylated in B lymphocytes, raising the possibility that differential phosphorylation may play a role in specifying its lymphoid versus myeloid functions. C-EBP alpha exists as multiple phosphorylated forms in the nucleus of both multipotential and granulocyte-committed cells. C-EBP beta is unphosphorylated and cytoplasmically localized in multipotential cells but exists as a phosphorylated nuclear enhancer-binding activity in granulocyte-committed cells. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced granulocytic differentiation of multipotential progenitor cells results in activation of C-EBP delta expression and functional recruitment of C-EBP delta and C-EBP beta to the nucleus. Our results implicate Pu1 and the C-EBP family as critical regulators of myeloperoxidase gene expression and are consistent with a model in which a temporal exchange of C-EBP isoforms at the myeloperoxidase enhancer mediates the transition from a primed state in multipotential cells to a transcriptionally active configuration in promyelocytes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam T., An M. R., Mifflin R. C., Hsieh C. C., Ge X., Papaconstantinou J. trans-activation of the alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene acute phase responsive element by multiple isoforms of C/EBP and glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15681–15688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F., Rosenberg N., Lewis S., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Organization and reorganization of immunoglobulin genes in A-MULV-transformed cells: rearrangement of heavy but not light chain genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashey A., Healy L., Marshall C. J. Proliferative but not nonproliferative responses to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor are associated with rapid activation of the p21ras/MAP kinase signalling pathway. Blood. 1994 Feb 15;83(4):949–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. M., Yang S. Q. Regenerative changes in C/EBP alpha and C/EBP beta expression modulate binding to the C/EBP site in the c-fos promoter. Hepatology. 1994 Feb;19(2):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattori E., Sellitto C., Cappelletti M., Lazzaro D., Bellavia D., Screpanti I., Gulino A., Costantini F., Poli V. Functional analysis of IL-6 and IL-6DBP/C/EBP beta by gene targeting. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Jul 21;762:262–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb32331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. M., Bennett C. A., Healy L. E., Navarro E., Spooncer E., Greaves M. F. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain and CD3 delta-chain gene enhancers are DNase I-hypersensitive in hemopoietic progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3424–3428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. M., Healy L. E., Bennett C. A., Navarro E., Spooncer E., Greaves M. F. Multilineage phenotypes of interleukin-3-dependent progenitor cells. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):1962–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Humphries R. K., Eaves C. J., Eckner R. J. Demonstration of permanent factor-dependent multipotential (erythroid/neutrophil/basophil) hematopoietic progenitor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B. Serological analysis of cell surface antigens of tumors induced by murine leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Jan;48(1):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez G., Griffiths S. D., Ford A. M., Greaves M. F., Enver T. Activation of the beta-globin locus control region precedes commitment to the erythroid lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10618–10622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowenz-Leutz E., Twamley G., Ansieau S., Leutz A. Novel mechanism of C/EBP beta (NF-M) transcriptional control: activation through derepression. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 15;8(22):2781–2791. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.22.2781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Adam B., Strobl L. J., Moreau-Gachelin F. The Spi-1/PU.1 and Spi-B ets family transcription factors and the recombination signal binding protein RBP-J kappa interact with an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 responsive cis-element. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5624–5632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., MacDougald O. A., Diehl A. M., Lane M. D. A 30-kDa alternative translation product of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha message: transcriptional activator lacking antimitotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9606–9610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Transcriptional regulation of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:345–373. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney C. W., Shuman J., McKnight S. L., Chen H. C., Huang K. P. Phosphorylation of CCAAT-enhancer binding protein by protein kinase C attenuates site-selective DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19396–19403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagulapalli S., Pongubala J. M., Atchison M. L. Multiple proteins physically interact with PU.1. Transcriptional synergy with NF-IL6 beta (C/EBP delta, CRP3). J Immunol. 1995 Nov 1;155(9):4330–4338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Engel J. D. Vintage reds and whites: combinatorial transcription factor utilization in hematopoietic differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Oct;4(5):718–724. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90139-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Kowenz-Leutz E., Casini T., Graf T., Leutz A. Myb and NF-M: combinatorial activators of myeloid genes in heterologous cell types. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):749–759. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchprayoon I., Meyers S., Scott L. M., Suzow J., Hiebert S., Friedman A. D. PEBP2/CBF, the murine homolog of the human myeloid AML1 and PEBP2 beta/CBF beta proto-oncoproteins, regulates the murine myeloperoxidase and neutrophil elastase genes in immature myeloid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5558–5568. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. GATA-binding transcription factors in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1992 Aug 1;80(3):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahl H. L., Scheibe R. J., Zhang D. E., Chen H. M., Galson D. L., Maki R. A., Tenen D. G. The proto-oncogene PU.1 regulates expression of the myeloid-specific CD11b promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5014–5020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):368–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Van Beveren C., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. Effect of PU.1 phosphorylation on interaction with NF-EM5 and transcriptional activation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.8456286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Ray B. K. Serum amyloid A gene expression under acute-phase conditions involves participation of inducible C/EBP-beta and C/EBP-delta and their activation by phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4324–4332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Simon M. C., Anastasi J., Singh H. Requirement of transcription factor PU.1 in the development of multiple hematopoietic lineages. Science. 1994 Sep 9;265(5178):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.8079170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott L. M., Civin C. I., Rorth P., Friedman A. D. A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1725–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooncer E., Boettiger D., Dexter T. M. Continuous in vitro generation of multipotential stem cell clones from src-infected cultures. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):228–230. doi: 10.1038/310228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzow J., Friedman A. D. The murine myeloperoxidase promoter contains several functional elements, one of which binds a cell type-restricted transcription factor, myeloid nuclear factor 1 (MyNF1). Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2141–2151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtieri M., Tweardy D. J., Caracciolo D., Johnson K., Mavilio F., Altmann S., Santoli D., Rovera G. Cytokine-dependent granulocytic differentiation. Regulation of proliferative and differentiative responses in a murine progenitor cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N. D., Finegold M. J., Bradley A., Ou C. N., Abdelsayed S. V., Wilde M. D., Taylor L. R., Wilson D. R., Darlington G. J. Impaired energy homeostasis in C/EBP alpha knockout mice. Science. 1995 Aug 25;269(5227):1108–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.7652557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Moore M. A., Metcalf D. A transplantable myelomonocytic leukemia in BALB-c mice: cytology, karyotype, and muramidase content. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):963–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. B., Kiledjian M., Shen C. P., Benezra R., Zwollo P., Dymecki S. M., Desiderio S. V., Kadesch T. Repression of immunoglobulin enhancers by the helix-loop-helix protein Id: implications for B-lymphoid-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6185–6191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. D. The myeloid-lineage specific enhancer of the mouse myeloperoxidase gene consists of three cis-elements defined as in vitro DNase I footprints. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 21;339(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Bennett C. A., MacGregor A. D., Greaves M. F., Goodwin G. H., Ford A. M. A myeloid-lineage-specific enhancer upstream of the mouse myeloperoxidase (MPO) gene. Leukemia. 1994 May;8(5):717–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]