Challenges to clinical trial recruitment in palliative care are significant but not insurmountable. Through their experience with designing and deploying a social-marketing based protocol, the authors show that a carefully crafted recruitment and retention protocol can be effective.
Abstract
Purpose:
Palliative care is increasingly viewed as a necessary component of cancer care, especially for patients with advanced disease. Rigorous clinical trials are thus needed to build the palliative care evidence base, but clinical research—especially participant recruitment—is difficult. Major barriers include (1) patient factors, (2) “gatekeeping,” and (3) ethical concerns. Here we discuss an approach to overcoming these barriers, using the Palliative Care Trial (PCT) as a case study.
Patients and Methods:
The PCT was a 2 × 2 × 2 factorial randomized controlled trial (RCT) of different service delivery models to improve pain control in the palliative setting. It used a recruitment protocol that fused evidence-based strategies with principles of “social marketing,” an approach involving the systematic application of marketing techniques. Main components included (1) an inclusive triage algorithm, (2) information booklets targeting particular stakeholders, (3) a specialized recruitment nurse, and (4) standardization of wording across all study communications.
Results:
From an eligible pool of 607 patients, the PCT enrolled 461 patients over 26 months. Twenty percent of patients referred to the palliative care service were enrolled (76% of those eligible after screening). Several common barriers were minimized; among those who declined participation, family disinterest was uncommon (5%), as was the perception of burden imposed (4%).
Conclusion:
Challenges to clinical trial recruitment in palliative care are significant but not insurmountable. A carefully crafted recruitment and retention protocol can be effective. Our experience with designing and deploying a social-marketing–based protocol shows the benefits of such an approach.
Introduction
Palliative care is increasingly viewed as a necessary component of comprehensive cancer care, especially for patients with advanced, incurable disease.1 Caring for this highly symptomatic population will require further development of the palliative care evidence base; rigorous clinical trials in palliative care are needed. Clinical research in this arena, however, can be difficult. Recruitment and retention challenges often impede the development and successful completion of clinical trials in advanced cancer and palliative care.2 Large randomized controlled trials (RCTs), in particular, have historically been considered unfeasible in this setting. This article provides a brief overview of the recruitment challenges unique to palliative care, and presents examples from the Palliative Care Trial (PCT) to highlight strategies to overcome and address these barriers in the setting of a large study.
The 2004 US National Consensus Project for Quality Palliative Care clinical practice guidelines state, “The randomized controlled trial has been difficult to carry out in the field of palliative care—being too intrusive and time consuming to be performed with very sick persons or with families under great stress.”3 The most successful recruitment rates previously described in the palliative care literature leave considerable room for improvement. Ling et al4 recruited 362 participants receiving palliative care for cancer into 23 different clinical trials over a 4-year period. Jordhøy et al5 recruited 434 participants over a period initially set at 24 months, which was then extended to 33 months in order to reach the required sample size. Both of these studies invested a great deal of time into monitoring and adapting recruitment efforts. It is uncommon for palliative care clinical trials to enroll the required number of participants in the given time frame6; the recruitment period often needs to be extended,7 additional sites engaged,8 or recruitment strategies improved.9
There are numerous barriers to palliative care clinical trials accrual, which are discussed at length elsewhere.10 Generally speaking, these barriers can be distilled into three domains: (1) patient issues, (2) “gatekeeping,” and (3) ethical issues. Patient issues include frailty, limited life expectancy or prognostic uncertainty, competing demands, fatigue, and the reminder of impending death. Evidence suggests, however, that patients are often quite interested in research participation and may even benefit from it.11 Gatekeeping occurs when clinicians and/or caregivers make assumptions that research is burdensome or upsetting, that it is of no benefit to the patient, that it would be intrusive, that it could yield false hope, or that it is unethical; prior work shows this to be a common problem.12 Ethical concerns relate to patients' increased vulnerability near the end of life, a decreased capacity to consent in some situations, and concerns about clinical equipoise, as some providers already believe they know and use the most optimal methods of providing care at the end of life. These ethical concerns are often unjustified but rarely insurmountable, and we have discussed them elsewhere.13 Thus we focus here on the patient-related issues and gatekeeping concerns, using the recruitment protocol of the PCT to highlight several effective approaches to these common problems. It is important to note that the eligibility criteria for many palliative care studies may significantly limit the pool of potential participants, so careful planning in this area is key. Because this issue is discussed at length elsewhere, we do not make it a focus of discussion here.14
Patients and Methods
Trial Design
The PCT was a 2 × 2 × 2 factorial RCT designed to test different service delivery models to improve pain control in the palliative care setting; it was conducted in Adelaide, South Australia, from 2001 to 2004. Patients were randomly assigned three times, to (1) individualized interdisciplinary case conference with their general practitioner (GP) versus control, (2) educational outreach visitation to GPs about pain management versus control, and (3) structured educational visitation for patients and caregivers about pain management versus control. Main outcome measures included the Australia-modified Karnofsky Performance Status Score (AKPS), pain scores 60 days after random assignment, and number of hospitalizations. Target enrollment was 460 patients over a 26-month period. Eligible participants were adult, had been referred to the palliative care service, had experienced any form of pain in the preceding 3 months, were mentally competent at enrollment as documented by a Folstein Mini-Mental State Examination score ≥ 24,15 and had a GP willing to participate in the trial. If not capable of doing so themselves, participants could have a legal health care proxy or a GP-identified caregiver provide informed consent,16 though both participant/proxy and GP consent were required for enrollment. Exclusion criteria were (1) patient expected to die within 48 hours of referral, and (2) patient resided outside the geographic service area.
The PCT successfully recruited and enrolled 461 patient participants and their physicians over 26 months. The 461 patients enrolled represent 20% of the 2,305 patients referred to the palliative care service, of whom 607 were eligible for enrollment. The main reasons that people declined participation during the recruitment visit were as follows: “too sick” (40 of 107 reasons cited; 37%), “too busy” (37; 6%), “too stressed or overwhelmed” (15; 14%), “palliative care service involvement not wanted” (6; 6%), “not interested” (6; 6%), “family not interested” (5; 5%), and “trial too burdensome” (4; 4%).
The results, recently published,17 showed that case conferencing reduced hospital admissions by 26% compared with the control condition. This intervention was also associated with maintenance of performance status as measured by AKPS (57.3 v 51.7, P = .0368). Furthermore, among patients with declining functional status (AKPS < 70), case conferencing and educational intervention also appeared to better maintain performance status (55 v 46.5, P = .0143; and 54.7 v 46.8, P = .0206, respectively). Education of GPs did not appear to affect the measured outcomes.
Development of a Tailored Recruitment Plan
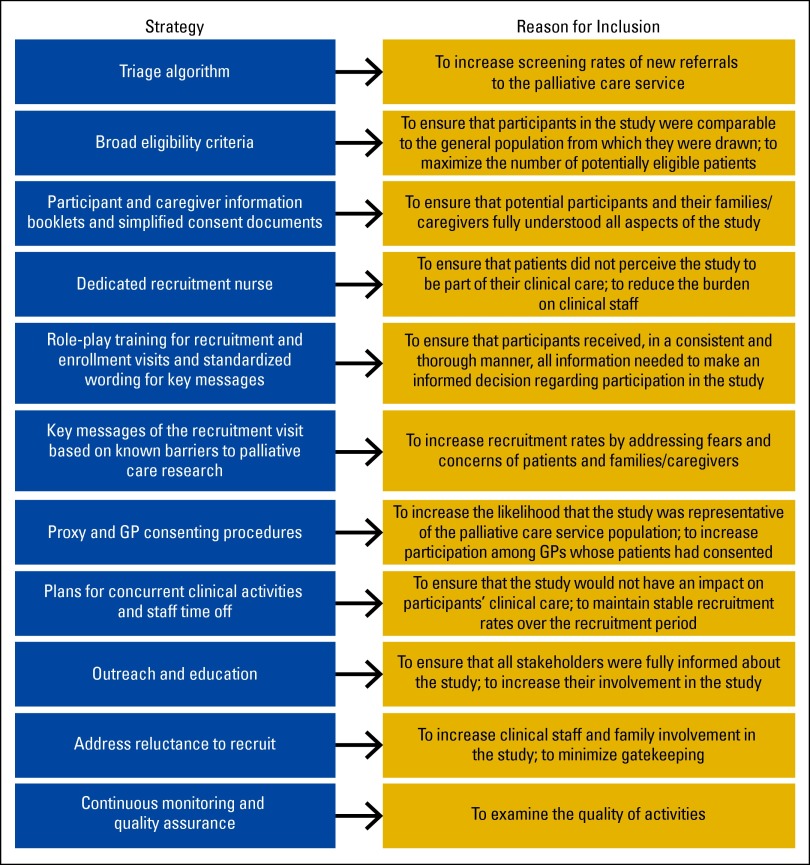
Because difficulty with accrual had been widely documented as a barrier to similar trials preceding the PCT, a recruitment-retention protocol was developed, which aimed to fuse evidence-based strategies with principles of social marketing. Social marketing is defined as the systematic application of marketing techniques aimed at achieving a particular social good.18 After an initial systematic review of the literature regarding large trial recruitment strategies—both in general, and in oncology, palliative care, cardiology, and health services research—study resources were developed, including a triage algorithm, information booklets, and recruitment scripts. This included four key steps and components: (1) developing a triage algorithm, (2) preparing information books targeted to stakeholders, (3) hiring a specialized recruitment nurse, and (4) standardization of wording across study communications. Each component was designed for ease of use, minimization of burden on nonstudy personnel, and likelihood of facilitating patient control over the outcome. As such, the triage algorithm was very inclusive; a different information booklet was developed specifically for caregivers (all at a fifth-grade reading level), and key messages were pilot tested and role-played. See the Data Supplements to view the original screening algorithm, patient information booklet, and general study brochure.
These key elements aimed to increase screening and enrollment efficiency (Figure 1). For example, recruitment was facilitated by broad eligibility criteria; 79% of those screened were deemed eligible for inclusion. The literature highlights restrictive eligibility criteria as one of the main causes of nonparticipation in clinical trials.19 In addition, the appointment of a dedicated recruitment nurse also supported recruitment in several key ways, as demonstrated in other successful trials.4,20 Having a dedicated recruitment nurse ensures consistent knowledge of study quality control measures, appropriate training, strong interpersonal skills, and targeted supplemental communication training when necessary. The presence of a recruitment nurse also relieved clinical nurses of the recruitment burden often posed by studies, typically a significant barrier to recruitment.21 Separating recruitment from clinical care also reduced the pressure on potential participants to consent in order to please their doctors or nurses; this motivation is a major ethical concern for conducting studies with people in a dependent relationship.22
Figure 1.
Successful evidence-based recruitment strategies used in the Palliative Care Trial protocol. GP, general practitioner.
Triage algorithm.
The PCT's referral strategies were designed to maximize the number of potential participants during initial screening. Study staff notified potential referring physicians in advance, using very broad eligibility criteria so they would not have to remember complex rules. Ensuring that clinicians could focus on referring patients to the study, rather than having to know complex eligibility criteria and worry about doing screening themselves, was key to the success of this endeavor. More detailed screening was completed by study personnel, to prevent gatekeeping and to decrease burden on referrers. Incorporation of research screening into the palliative care service's regular triage process maximized the number of patients screened. Clinical triage nurses, explaining that they were not part of the trial staff, first gauged patients' interest and asked potentially eligible patients for permission for trial staff to contact them. Study investigators were concerned that the offer to decline contact by the trial staff would decrease recruitment opportunities; in fact, of 1,948 people screened, 941 (48%) did decline contact. However, the group who permitted contact by trial staff were much more willing to participate in the study (500 of 607; 82%), thereby saving valuable recruitment nurse effort.
Social marketing application.
Implemented marketing strategies included involving clinical staff in study procedure development, multiple presentations to clinic staff, branding materials to promote recognition, and facilitating motivational meetings for stakeholders. Relationship building played an important role in achieving buy-in for the recruitment process. A weekly trial-sponsored coffee hour demonstrated commitment to improving trial procedures in response to the clinical team's concerns. Focus groups provided insight into any problems and demonstrated the positive impact of a coordinated research program on a large palliative care service. Consultation with medical stakeholders, including consultants and GPs, increased awareness of the trial throughout the study period and facilitated recruitment discussions between research staff and stakeholders. Clinical staff involvement in steering committees, regular morning discussions about study progress and other protocols in development, and regular focus groups to monitor burden of research on clinical operations provided constant surveillance of perceptions and attitudes about the study.
Per principles of social marketing, interaction with the target audience was carefully structured to optimize outcomes; specific messaging was established, aimed at ensuring that patients maintained control, thereby minimizing gatekeeping. For example, leaving a blank study withdrawal form with participants and families at the time of consent likely contributed to the study's high consent rate. This practice provided clear assurance that withdrawal was allowed at any time, without compromising ongoing care.
In order to further minimize issues of gatekeeping, each recruitment visit also involved caregivers and was conducted in patients' homes when possible. This ensured that caregivers were adequately informed and received the same key messages as the patients. A focus on fully educating patients, caregivers, and clinical staff about the study, as well as its purposes and practices, ultimately assisted recruitment and retention by building trust among clinical staff and caregivers, which also decreased gate-keeping.
Previously scripted messages intended to ensure consistency were modified over time in response to the particular needs and concerns of patients and their loved ones (eg, the ability to withdraw was important, so this was stated upfront in a clear fashion). All recruitment interactions were scripted and frequently role-played to ensure consistency and quality. Use of standardized wording, together with extensive role-playing, ensured that all potential participants received a consistent and accurate message throughout recruitment.23 The role-playing highlighted potential difficulties and led to problem solving. Key messages are highlighted in Table 1. In addition to communication skills, all study staff were also trained in research ethics.
Table 1.
Key Messages Highlighted During the Home Recruitment Visit
|
(*)Patients taught us that random assignment should never be described as a coin flip. Change the locus of control from something that someone else does to you (eg, coin flip) to a situation in which you control your own destiny (eg, drawing out of a hat, lucky dip). Patients understand that these are all random chance.
Results
This strategic program of social marketing resulted in a favorable recruitment and retention outcome as compared with other published experiences in palliative care clinical trials. Overall, 20% of patients referred to the palliative care service were ultimately enrolled onto the study, representing > 75% of the eligible population. Furthermore, several common barriers were minimized; among those who declined participation, family disinterest was uncommon (5%), as was any perception of excessive burden imposed by the study (4%). The most common reason for declining participation was that patients felt “too sick” (37%).
Discussion
This study demonstrates that, with the use of a multicomponent, evidenced-based recruitment protocol that addresses key barriers to research in palliative care, large palliative care RCTs can accrue sufficient samples. Key features of the demonstrated recruitment protocol were a triage algorithm, broad eligibility criteria, a dedicated recruitment nurse, simplified consent documents and information booklets, carefully planned visits that included standardized wording for key messages, practicing through role-plays, well-defined consenting procedures encompassing proxy and GP scenarios, integration with clinical services, plans for staff relief, focused outreach, public/provider education, plans to address gatekeeping, and continuous monitoring and quality assurance (Figure 1). These strategies could transfer readily to other disciplines that experience difficulties in recruitment, such as geriatrics, rehabilitation, and pediatrics.
This approach was subsequently used in the dyspnea trial, which recruited 239 palliative care patients to a randomized, double-blind trial from 2006 to 2008,24 and it is now considered the standard approach for clinical trials conducted in the Australian Palliative Care Clinical Studies collaborative research network. It was also implemented in a study investigating the efficacy of alvimopan in the treatment of constipation; this study initially had poor enrollment, so a revised recruitment protocol was developed, using principles of social marketing similar to those used in the PCT.25 This quickly resulted in a significant increase in the enrollment rate and successful completion of the study. (Figure 2). Importantly, for each of these studies, the full set of recruitment solutions was tailored and honed for the specific trial; sometimes all of the solutions were used, and at other times, we focused on practically feasible aspects such as development of consistent key messaging, role-plays, and recruitment materials. Practicality is key; the process does not need to be extravagant, just well thought out, based on best evidence, practiced and consistent.
Figure 2.
Impact of the implementation of a revised recruitment plan on increased referrals to the alvimopan study.
Cost
The application of social marketing principles need not be expensive. The majority of its key elements are effectively free, consisting of carefully constructed messaging and materials that ensure consistency in communication about the study. Role-plays require little time but result in further improvements in messaging consistency and efficacy. Though the PCT used a specialized recruitment nurse to facilitate screening, this is not an essential component of a successful application of social marketing principles to clinical research. In applying these principles to several studies to date, we have found them to be remarkably effective and important, regardless of study size, design, or funding.
Conclusions
Research study recruitment and retention is a particular challenge in palliative care trials. This challenge, however, is not an insurmountable one, and is worth pursuing in order to build the palliative care evidence base and advance the science of the field. A carefully crafted recruitment and retention protocol is of particular importance in the successful conduct of clinical trials in palliative care populations. Our experience with designing and deploying a social marketing–based protocol in the PCT shows the benefits of such an approach. This approach is more regimented and time consuming but results in more patient control and reduces issues of gatekeeping, whereby patients who might be interested in participating never have the opportunity as a result of biases on the part of their caregivers or physicians. Repeated refinement of these protocols is necessary, as each trial has different barriers and each patient population has different needs.
Supplementary Material
Authors' Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest
Although all authors completed the disclosure declaration, the following author(s) and/or an author's immediate family member(s) indicated a financial or other interest that is relevant to the subject matter under consideration in this article. Certain relationships marked with a “U” are those for which no compensation was received; those relationships marked with a “C” were compensated. For a detailed description of the disclosure categories, or for more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to the Author Disclosure Declaration and the Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest section in Information for Contributors.
Employment or Leadership Position: Amy P. Abernethy, American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine (C), Advoset (C), Orange Leaf Associates LLC (C) Consultant or Advisory Role: Amy P. Abernethy, Novartis (C), Bristol Myers Squibb (C), Pfizer (C) Stock Ownership: None Honoraria: Amy P. Abernethy, Novartis, Pfizer Research Funding: Thomas W. LeBlanc, Junior Career Development Award from the National Palliative Care Research Center; Amy P. Abernethy, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Biovex, DARA, Helsinn, MiCo, Dendreon, Pfizer, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Genentech Expert Testimony: None Patents, Licenses or Royalties: None Other Remuneration: None
Author Contributions
Conception and design: Thomas W. LeBlanc, David C. Currow, Amy P. Abernethy
Financial support: Amy P. Abernethy
Administrative support: Amy P. Abernethy
Collection and assembly of data: Thomas W. LeBlanc, David C. Currow, Amy P. Abernethy
Data analysis and interpretation: All authors
Manuscript writing: All authors
Final approval of manuscript: All authors
STATEMENT OF OWNERSHIP MANAGEMENT AND CIRCULATION (Required by 39 U.S.C. 3685).
Publication title: JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY PRACTICE.
Publication no.: 1554-7477.
Filing date: October 1, 2013.
Issue frequency: 6 times/year; Bimonthly
No. of issues published annually: 6.
Annual subscription price: $50.00.
Complete mailing address of known office of publication: 2318 Mill Road, Suite 800, Alexandria, VA 22314-4609.
Complete mailing address of the headquarters or general business offices of the publisher: 2318 Mill Road, Suite 800, Alexandria, VA 22314-4609.
Full names and complete mailing addresses of publisher, editor, and managing editor: Publisher: David Sampson, Publisher, Journal of Oncology Practice, 2318 Mill Road, Suite 800, Alexandria, VA 22314-4609. Editor: John V. Cox, DO, MBA, FACP, Editor-in-Chief, Journal of Oncology Practice, Texas Oncologist Methodist, 3555 West Wheatland Road, Dallas, TX 7523-3461. Managing Editor: Kenneth G. Kornfield, Managing Editor, Journal of Oncology Practice, 2318 Mill Road, Suite 800, Alexandria, VA 22314-4609.
Owner: American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2318 Mill Road, Suite 800, Alexandria, VA 22314-4609.
Known bondholders, mortgagees, and other security holders owning or holding 1 percent or more of total amount of bonds, mortgages, or other securities: None.
Purpose, function, and nonprofit status: Has not changed during preceding 12 months.
Publication title: JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY PRACTICE.
Issue date for circulation data: Volume 9, Issue 5 (September 2013).
Extent and nature of circulation: Average number of copies each issue during preceding 12 months: (a) Total no. copies (net press run), 22,084. (b) Paid and/or requested circulation: (1) Paid/requested outside-county mail subscriptions stated on Form 3541 (include advertiser's proof and exchange copies): 16,513; (2) Paid in-county subscriptions stated on Form 3541 (include advertiser's proof and exchange copies): N/A; (3) Sales through dealers and carriers, street vendors, counter sales, and other non-USPS paid distribution: 64; (4) Other classes mailed through the USPS: N/A. (c) Total paid and/or requested circulation (sum of 15b (1), (2), (3), and (4)): 16,577. (d) Free distribution by mail (samples, complimentary, and other free): (1) Outside-county as stated on form 3541: 2,677; (2) In-county as stated on form 3541: N/A; (3) Other classes mailed through the USPS: N/A; (4) Free distribution outside the mail (carriers or other means): 355. (e) Total free distribution (sum of 15d (1), (2), (3) and (4)): 3,032. (f) Total distribution (sum of 15c and 15e): 19,609. (g) Copies not distributed: 2,475. (h) Total (sum of 15f and 15g): 22,084. (i) Percent paid and/or requested circulation (15c/15f x 100): 85%. Actual no. copies of single issue published nearest to filing date: (a) Total no. copies (net press run): 23,868. (b) Paid and/or requested circulation: (1) Paid/requested outside-county mail subscriptions stated on Form 3541 (include advertiser's proof and exchange copies): 19,052; (2) Paid in-county subscriptions stated on Form 3541 (include advertiser's proof and exchange copies): N/A; (3) Sales through dealers and carriers, street vendors, counter sales, and other non-USPS paid distribution: 76; (4) Other classes mailed through the USPS: N/A. (c) Total paid and/or requested circulation (sum of 15b(1), (2), (3), and (4)): 19,128. (d) Free distribution by mail (samples, complimentary, and other free copies): (1) Outside-county as stated on Form 3541: 652; (2) In-county as stated on Form 3541: N/A; (3) Other classes mailed through the USPS: N/A; (4) Free distribution outside the mail (carriers or other means): 355. (e) Total free distribution (sum of 15d (1), (2), (3) and (4)): 1,007. (f) Total distribution (sum of 15c and 15e): 20,135. (g) Copies not distributed: 3,733. (h) Total (sum of 15f and 15g): 23,868. (i) Percent paid and/or requested circulation (15c/15f x 100): 95%.
Total circulation includes electronic copies. Report circulation on PS Form 3526-X worksheet. N/A.
This Statement of Ownership will be printed in Volume 9, Issue 6 (November 2013).
I certify that the statements made by me above are correct and complete.
David Sampson, Publisher
References
- 1.Smith TJ, Temin S, Alesi ER, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology provisional clinical opinion: The integration of palliative care into standard oncology care. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(8):880–887. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.5161. doi: 10.1200/JCO. 2011.38.5161. Epub 2012 Feb 6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rinck G, Kleijnen J, Van den Bos TG, et al. Trials in palliative care. BMJ. 1995;310:598–599. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6979.598c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.National Consensus Project for Quality Palliative Care. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Quality Palliative Care. New York, NY: National Consensus Project for Quality Palliative Care; 2004. p. 42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ling J, Rees E, Hardy J. What influences participation in clinical trials in palliative care in a cancer centre? Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:621–626. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(99)00330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jordhøy MS, Kaasa S, Fayers P, et al. Challenges in palliative care research; recruitment, attrition and compliance: Experience from a randomized controlled trial. Palliat Med. 1999;13:299–310. doi: 10.1191/026921699668963873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hollis JF, Satterfield S, Smith F, et al. Recruitment for phase II of the Trials of Hypertension Prevention. Effective strategies and predictors of randomization. Trials of Hypertension Prevention (TOHP) Collaborative Research Group. Ann Epidemiol. 1995;5:140–148. doi: 10.1016/1047-2797(94)00058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chang BH, Hendricks AM, Slawsky MT, et al. Patient recruitment to a randomized clinical trial of behavioral therapy for chronic heart failure. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2004;4:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-4-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Agras WS, Marshall G. Recruitment for the Coronary Primary Prevention Trial. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979;25:688–690. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979255part2688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Benedict G. LRC Coronary Prevention Trial: Baltimore. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979;25:685. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979255part2685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fischer DJ, Burgener SC, Kavanaugh K, et al. Conducting research with end-of-life populations: Overcoming recruitment challenges when working with clinical agencies. Appl Nurs Res. 2012;25:258–263. doi: 10.1016/j.apnr.2011.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.White C, Hardy J. What do palliative care patients and their relatives think about research in palliative care?-A systematic review. Support Care Cancer. 2010;18:905–911. doi: 10.1007/s00520-009-0724-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.White C, Gilshenan K, Hardy J. A survey of the views of palliative care healthcare professionals towards referring cancer patients to participate in randomized controlled trials in palliative care. Support Care Cancer. 2008;16:1397–1405. doi: 10.1007/s00520-008-0441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.LeBlanc TW, Wheeler JL, Abernethy AP. Research in end-of-life settings: An ethical inquiry. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2010;24:244–250. doi: 10.3109/15360288.2010.493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Currow DC, Shelby-James TM, Agar M, et al. Planning phase III multi-site clinical trials in palliative care: The role of consecutive cohort audits to identify potential participant populations. Support Care Cancer. 2010;18:1571–1579. doi: 10.1007/s00520-009-0780-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. “Mini-mental state.” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Masso M, Dodds S, Fildes D, et al. Ethical Research in Palliative Care: A Guide Through the Human Research Ethics Committee Process. Canberra, Australia: Commonwealth of Australia Department of Health and Ageing; 2004. pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abernethy AP, Currow DC, Shelby-James T, et al. Delivery strategies to optimize resource utilization and performance status for patients with advanced life-limiting illness: Results From the “Palliative Care Trial” [ISRCTN81117481] J Pain Symptom Manage. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.02.024. pii: S0885-3924(12)00274-6. [epub ahead of print on October 23, 2012] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Etkin CD, Farran CJ, Barnes LL, Shah RC. Recruitment and enrollment of caregivers for a lifestyle physical activity clinical trial. Res Nurs Health. 2012 Feb;35:70–81. doi: 10.1002/nur.20466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gotay CC. Accrual to cancer clinical trials: Directions from the research literature. Soc Sci Med. 1991;33:569–577. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lovato LC, Hill K, Hertert S, et al. Recruitment for controlled clinical trials: Literature summary and annotated bibliography. Control Clin Trials. 1997;18:328–352. doi: 10.1016/s0197-2456(96)00236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hudson P, Aranda S, McMurray N. Randomized controlled trials in palliative care: Overcoming the obstacles: Int J Palliat Nurs. 2001;7:427–434. doi: 10.12968/ijpn.2001.7.9.9301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Karim K. Conducting research involving palliative patients. Nurs Stand. 2000;15:34–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kiev A. Management of clinical trials with new medications for cocaine dependence and abuse. Natl Inst Drug Abuse Res Monogr Ser. 1997;175:96–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abernethy AP, McDonald CF, Frith PA, et al. Effect of palliative oxygen versus room air in relief of breathlessness in patients with refractory dyspnoea: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:784–793. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61115-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Abernethy AP, Currow DC, Wurzelmann J, et al. Enhancing enrollment in palliative care trials: Key insights from a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Support Oncol. 2010;8:139–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.