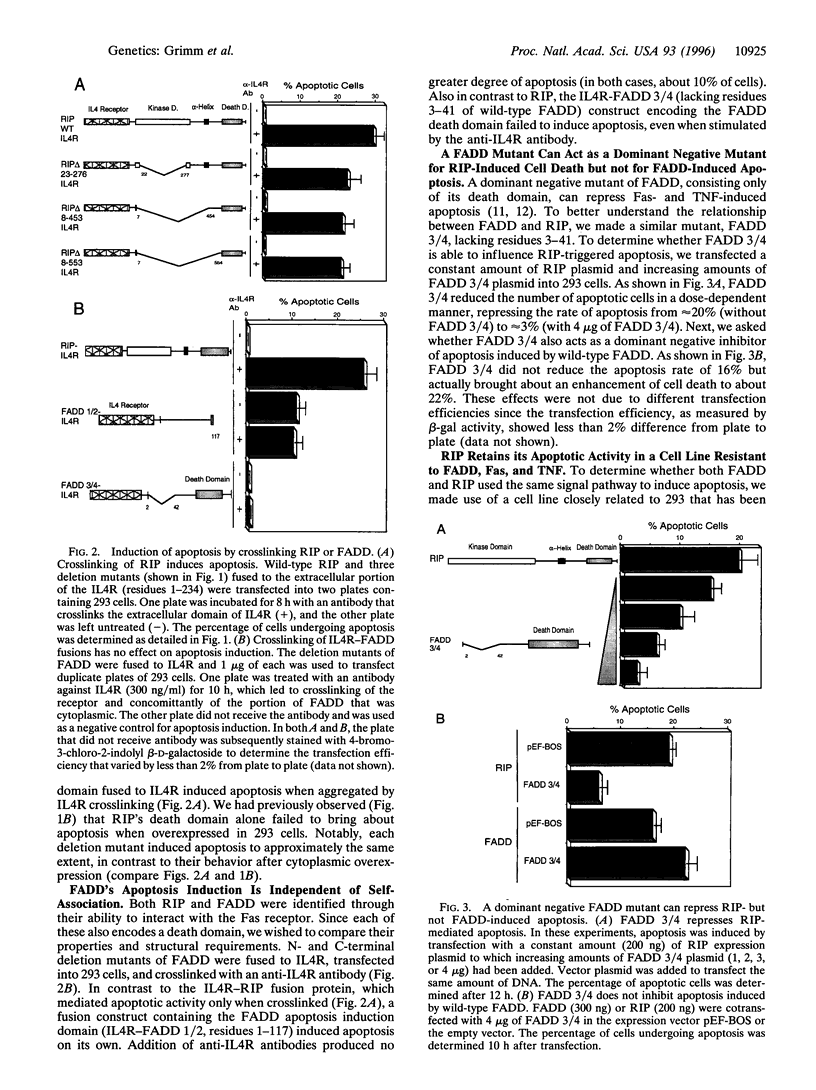
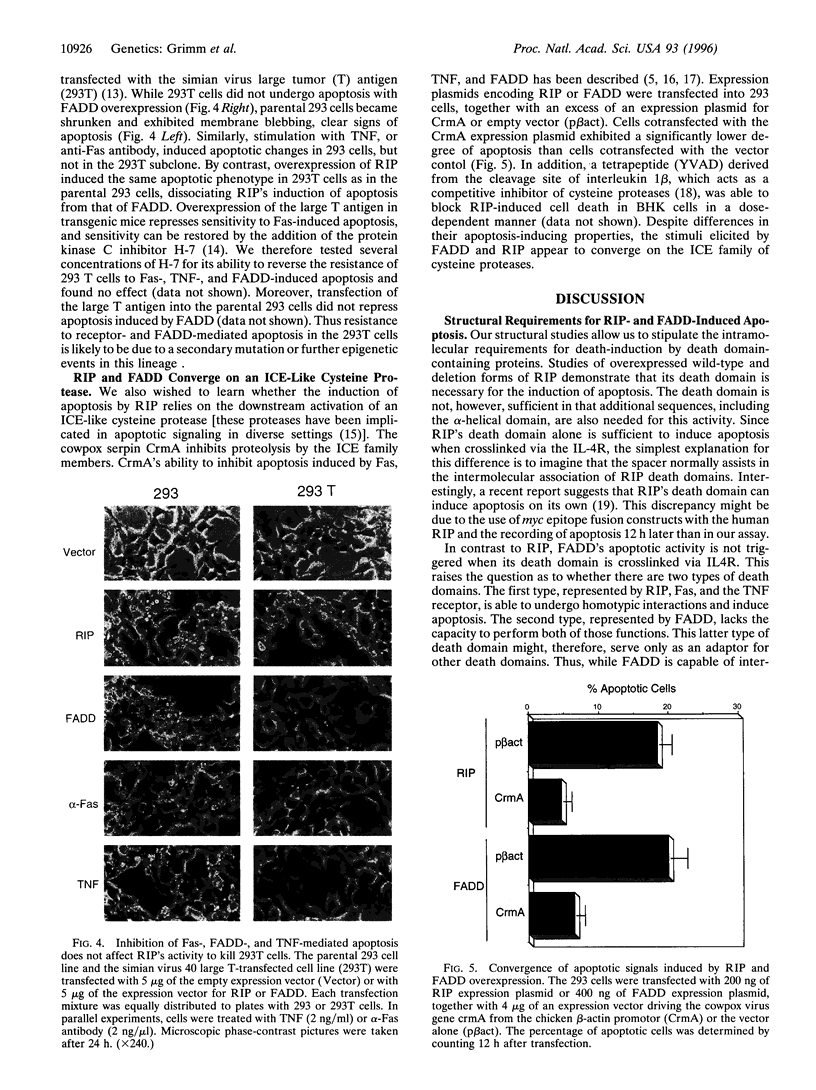
Abstract
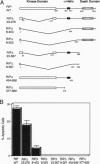
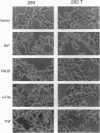
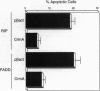
With use of the yeast two-hybrid system, the proteins RIP and FADD/MORT1 have been shown to interact with the "death domain" of the Fas receptor. Both of these proteins induce apoptosis in mammalian cells. Using receptor fusion constructs, we provide evidence that the self-association of the death domain of RIP by itself is sufficient to elicit apoptosis. However, both the death domain and the adjacent alpha-helical region of RIP are required for the optimal cell killing induced by the overexpression of this gene. By contrast, FADD's ability to induce cell death does not depend on crosslinking. Furthermore, RIP and FADD appear to activate different apoptotic pathways since RIP is able to induce cell death in a cell line that is resistant to the apoptotic effects of Fas, tumor necrosis factor, and FADD. Consistent with this, a dominant negative mutant of FADD, lacking its N-terminal domain, blocks apoptosis induced by RIP but not by FADD. Since both pathways are blocked by CrmA, the interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme family protease inhibitor, these results suggest that FADD and RIP can act along separable pathways that nonetheless converge on a member of the interleukin 1 beta converting enzyme family of cysteine proteases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boldin M. P., Goncharov T. M., Goltsev Y. V., Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):803–815. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldin M. P., Varfolomeev E. E., Pancer Z., Mett I. L., Camonis J. H., Wallach D. A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):7795–7798. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.7795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnaiyan A. M., O'Rourke K., Tewari M., Dixit V. M. FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnaiyan A. M., Tepper C. G., Seldin M. F., O'Rourke K., Kischkel F. C., Hellbardt S., Krammer P. H., Peter M. E., Dixit V. M. FADD/MORT1 is a common mediator of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):4961–4965. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):824–830. doi: 10.1126/science.2406902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enari M., Hug H., Nagata S. Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature. 1995 May 4;375(6526):78–81. doi: 10.1038/375078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. ICE family proteases: mediators of all apoptotic cell death? Immunity. 1996 Mar;4(3):195–201. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Huang J., Shu H. B., Baichwal V., Goeddel D. V. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity. 1996 Apr;4(4):387–396. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Shu H. B., Pan M. G., Goeddel D. V. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):299–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80984-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Xiong J., Goeddel D. V. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Nagata S. A novel protein domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human Fas antigen. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):10932–10937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kischkel F. C., Hellbardt S., Behrmann I., Germer M., Pawlita M., Krammer P. H., Peter M. E. Cytotoxicity-dependent APO-1 (Fas/CD95)-associated proteins form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) with the receptor. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5579–5588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nagata S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5322–5322. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio M., Chinnaiyan A. M., Kischkel F. C., O'Rourke K., Shevchenko A., Ni J., Scaffidi C., Bretz J. D., Zhang M., Gentz R. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S. Fas and Fas ligand: a death factor and its receptor. Adv Immunol. 1994;57:129–144. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60672-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Vaillancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., Gareau Y., Griffin P. R., Labelle M., Lazebnik Y. A. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):37–43. doi: 10.1038/376037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouquet N., Allemand I., Molina T., Bennoun M., Briand P., Joulin V. Fas-dependent apoptosis is impaired by SV40 T-antigen in transgenic liver. Oncogene. 1995 Sep 21;11(6):1061–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanger B. Z., Leder P., Lee T. H., Kim E., Seed B. RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Ayres T. M., Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):845–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dixit V. M. Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is inhibited by the poxvirus crmA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3255–3260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varfolomeev E. E., Boldin M. P., Goncharov T. M., Wallach D. A potential mechanism of "cross-talk" between the p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor and Fas/APO1: proteins binding to the death domains of the two receptors also bind to each other. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):1271–1275. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]