Abstract
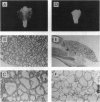
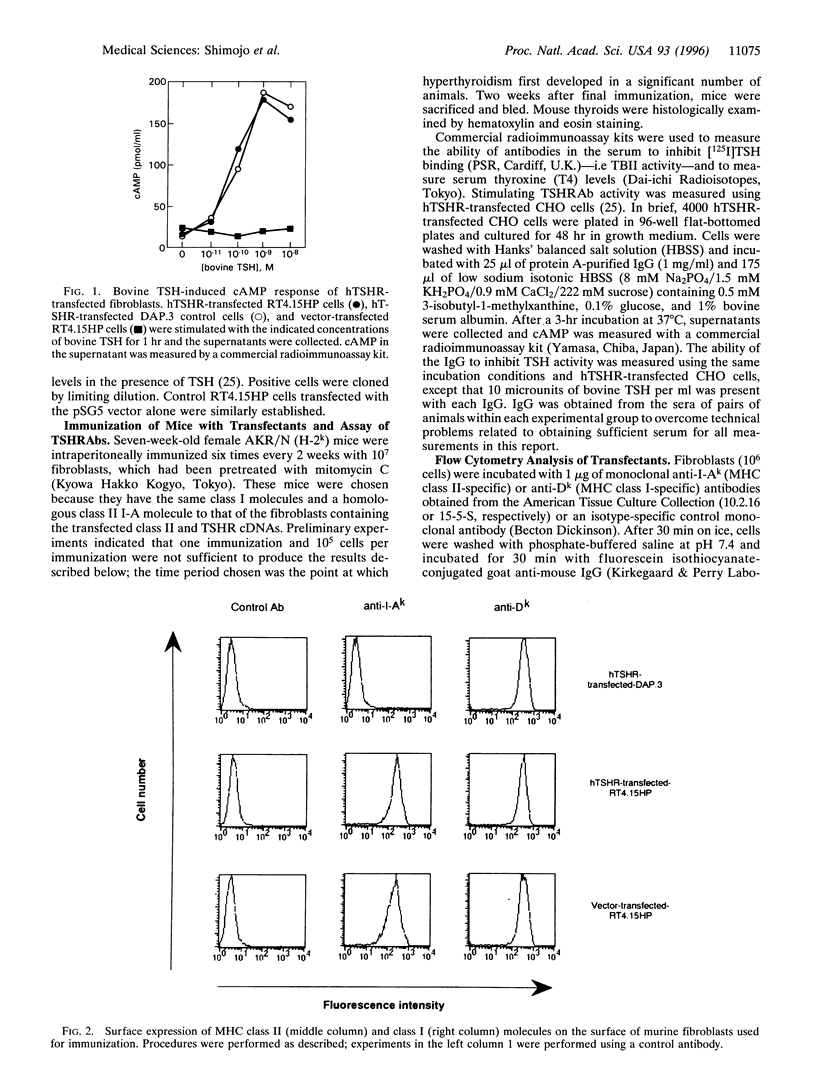
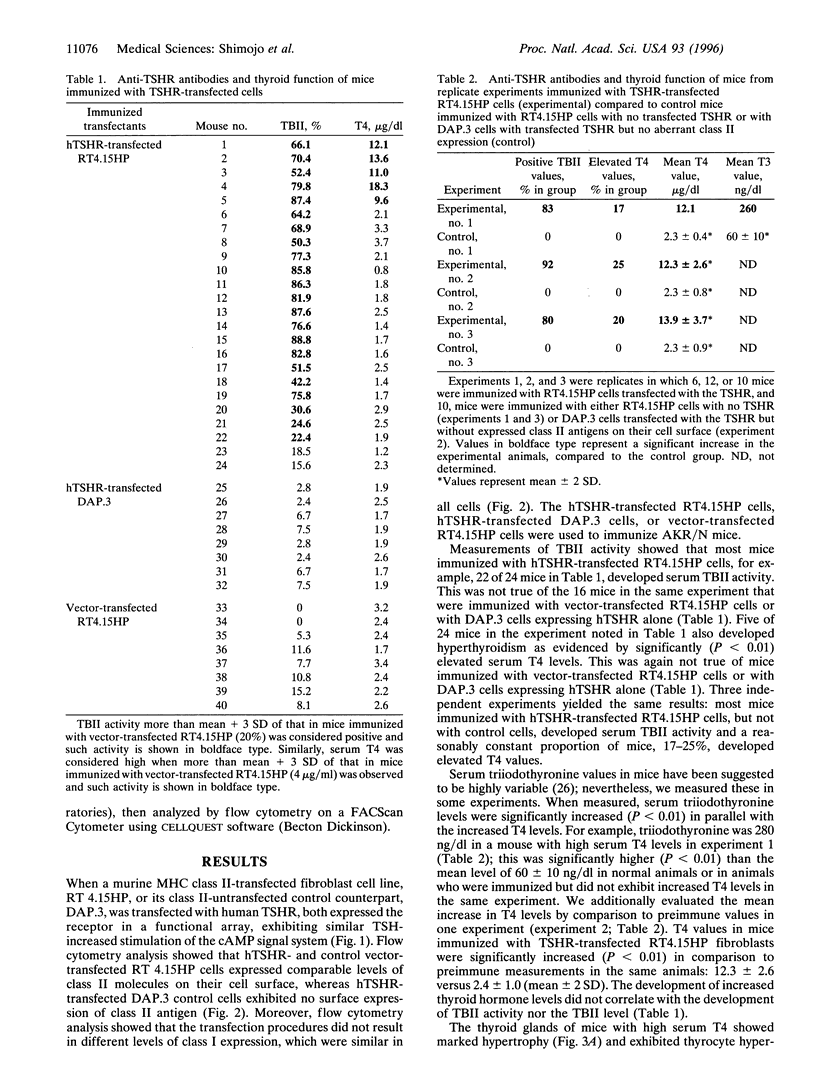
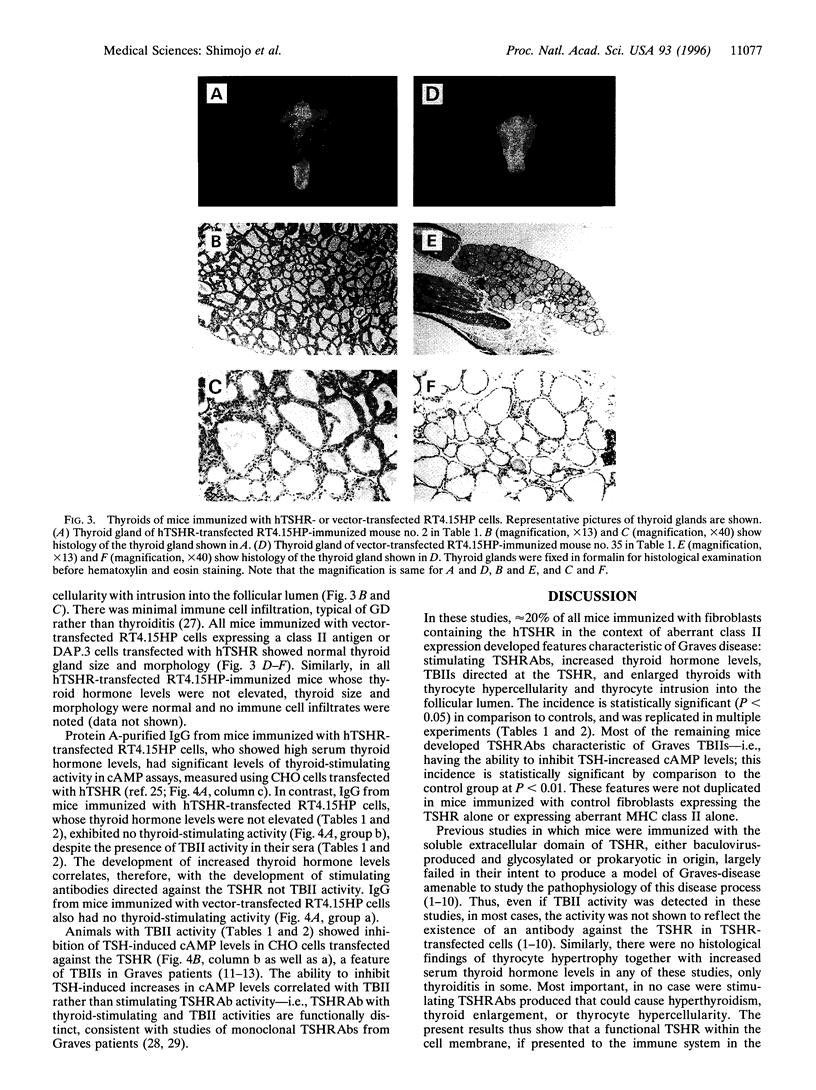
Graves disease is an autoimmune thyroid disease characterized by the presence of antibodies against the thyrotropin receptor (TSHR), which stimulate the thyroid to cause hyperthyroidism and/or goiter. By immunizing mice with fibroblasts transfected with both the human TSHR and a major histocompatibility complex class II molecule, but not by either alone, we have induced immune hyperthyroidism that has the major humoral and histological features of Graves disease: stimulating TSHR antibodies, thyrotropin binding inhibiting immunoglobulins, which are different from the stimulating TSHR antibodies, increased thyroid hormone levels, thyroid enlargement, thyrocyte hypercellularity, and thyrocyte intrusion into the follicular lumen. The results suggest that the aberrant expression of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules on cells that express a native form of the TSHR can result in the induction of functional anti-TSHR antibodies that stimulate the thyroid. They additionally suggest that the acquisition of antigen-presenting ability on a target cell containing the TSHR can activate T and B cells normally present in an animal and induce a disease with the major features of autoimmune Graves.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Pujol-Borrell R., Hanafusa T., Feldmann M. Role of aberrant HLA-DR expression and antigen presentation in induction of endocrine autoimmunity. Lancet. 1983 Nov 12;2(8359):1115–1119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carayanniotis G., Huang G. C., Nicholson L. B., Scott T., Allain P., McGregor A. M., Banga J. P. Unaltered thyroid function in mice responding to a highly immunogenic thyrotropin receptor: implications for the establishment of a mouse model for Graves' disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Feb;99(2):294–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb05548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola S., Alcalde L., Ruf J., Vassart G., Ludgate M. Overexpression of the extracellular domain of the thyrotrophin receptor in bacteria; production of thyrotrophin-binding inhibiting immunoglobulins. J Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Aug;13(1):11–21. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0130011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola S., Alcalde L., Tonacchera M., Ruf J., Vassart G., Ludgate M. Induction of thyrotropin receptor (TSH-R) autoantibodies and thyroiditis in mice immunised with the recombinant TSH-R. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 15;199(2):1027–1034. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola S., Many M. C., Stalmans-Falys M., Tonacchera M., Vassart G., Ludgate M. Recombinant thyrotropin receptor and the induction of autoimmune thyroid disease in BALB/c mice: a new animal model. Endocrinology. 1994 Nov;135(5):2150–2159. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.5.7956939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies T. F. Modeling Graves' disease in the mouse--work still in progress. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Oct;80(10):2846–2847. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.10.7559862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealey P. A., Kohn L. D., Ekins R. P., Marshall N. J. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies derived from lymphocytes from Graves' disease patients in a cytochemical bioassay for thyroid stimulators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 May;58(5):909–914. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-5-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farid N. R., Thompson C. HLA and autoimmune endocrine disease 1985. Mol Biol Med. 1986 Feb;3(1):85–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Ashwell J. D., Lechler R. I., Margulies D. H., Nickerson K. M., Suzuki G., Tou J. Y. "Exon-shuffling" maps control of antibody- and T-cell-recognition sites to the NH2-terminal domain of the class II major histocompatibility polypeptide A beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2940–2944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. B., Cho B. Y., Park H. Y., Lee H. K., Kohn L. D., Tahara K., Koh C. S. Epitopes for thyroid-stimulating antibodies in Graves' sera: a possible link of heterogeneity to differences in response to antithyroid drug treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 May;81(5):1758–1767. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.5.8626830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Alvarez F., Marcocci C., Kohn A. D., Corda D., Hoffman W. E., Tombaccini D., Valente W. A., de Luca M., Santisteban P. Monoclonal antibody studies defining the origin and properties of autoantibodies in Graves' disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;475:157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Kosugi S., Ban T., Saji M., Ikuyama S., Giuliani C., Hidaka A., Shimura H., Akamizu T., Tahara K. Molecular basis for the autoreactivity against thyroid stimulating hormone receptor. Int Rev Immunol. 1992;9(2):135–165. doi: 10.3109/08830189209061788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kündig T. M., Bachmann M. F., DiPaolo C., Simard J. J., Battegay M., Lother H., Gessner A., Kühlcke K., Ohashi P. S., Hengartner H. Fibroblasts as efficient antigen-presenting cells in lymphoid organs. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1343–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.7761853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion S., Braun J. M., Ropars A., Kohn L. D., Charreire J. Induction of autoimmunity by immunization of mice with human thyrotropin receptor. Cell Immunol. 1994 Oct 15;158(2):329–341. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozes E., Kohn L. D., Hakim F., Singer D. S. Resistance of MHC class I-deficient mice to experimental systemic lupus erythematosus. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):91–93. doi: 10.1126/science.8316860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saji M., Moriarty J., Ban T., Singer D. S., Kohn L. D. Major histocompatibility complex class I gene expression in rat thyroid cells is regulated by hormones, methimazole, and iodide as well as interferon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Sep;75(3):871–878. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.3.1381373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharamaiah G. S., Desai R. K., Dallas J. S., Tahara K., Kohn L. D., Prabhakar B. S. Induction of TSH binding inhibitory immunoglobulins with the extracellular domain of human thyrotropin receptor produced using baculovirus expression system. Autoimmunity. 1993;14(4):315–320. doi: 10.3109/08916939309079234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharamaiah G. S., Wagle N. M., Morris J. C., Prabhakar B. S. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the human thyrotropin (TSH) receptor: antibodies can bind to discrete conformational or linear epitopes and block TSH binding. Endocrinology. 1995 Jul;136(7):2817–2824. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.7.7540542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Kohn L. D., Zinger H., Mozes E. Methimazole prevents induction of experimental systemic lupus erythematosus in mice. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):873–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sospedra M., Obiols G., Babi L. F., Tolosa E., Vargas F., Roura-Mir C., Lucas-Martin A., Ercilla G., Pujol-Borrell R. Hyperinducibility of HLA class II expression of thyroid follicular cells from Graves' disease. A primary defect? J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):4213–4222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara K., Ban T., Minegishi T., Kohn L. D. Immunoglobulins from Graves' disease patients interact with different sites on TSH receptor/LH-CG receptor chimeras than either TSH or immunoglobulins from idiopathic myxedema patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91335-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd I., Londei M., Pujol-Borrell R., Mirakian R., Feldmann M., Bottazzo G. F. HLA-D/DR expression on epithelial cells: the finger on the trigger? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;475:241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno H., Sasazuki T., Tamai H., Matsumoto H. Two major genes, linked to HLA and Gm, control susceptibility to Graves' disease. Nature. 1981 Aug 20;292(5825):768–770. doi: 10.1038/292768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlase H., Nakashima M., Graves P. N., Tomer Y., Morris J. C., Davies T. F. Defining the major antibody epitopes on the human thyrotropin receptor in immunized mice: evidence for intramolecular epitope spreading. Endocrinology. 1995 Oct;136(10):4415–4423. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.10.7664661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagle N. M., Dallas J. S., Seetharamaiah G. S., Fan J. L., Desai R. K., Memar O., Rajaraman S., Prabhakar B. S. Induction of hyperthyroxinemia in BALB/C but not in several other strains of mice. Autoimmunity. 1994;18(2):103–112. doi: 10.3109/08916939409007983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagle N. M., Patibandla S. A., Dallas J. S., Morris J. C., Prabhakar B. S. Thyrotropin receptor-specific antibodies in BALB/cJ mice with experimental hyperthyroxinemia show a restricted binding specificity and belong to the immunoglobulin G1 subclass. Endocrinology. 1995 Aug;136(8):3461–3469. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.8.7628382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetman A. P., McGregor A. M. Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr Rev. 1994 Dec;15(6):788–830. doi: 10.1210/edrv-15-6-788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]