Abstract
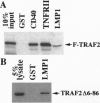
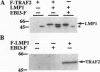
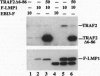
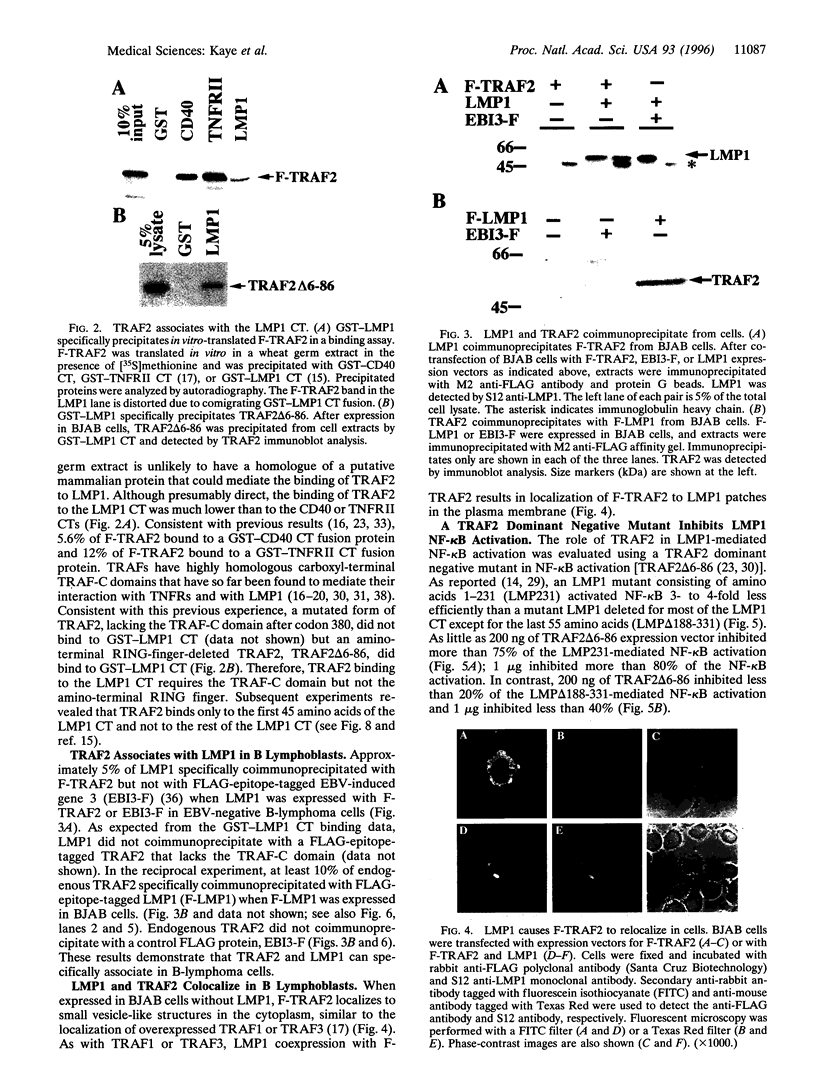
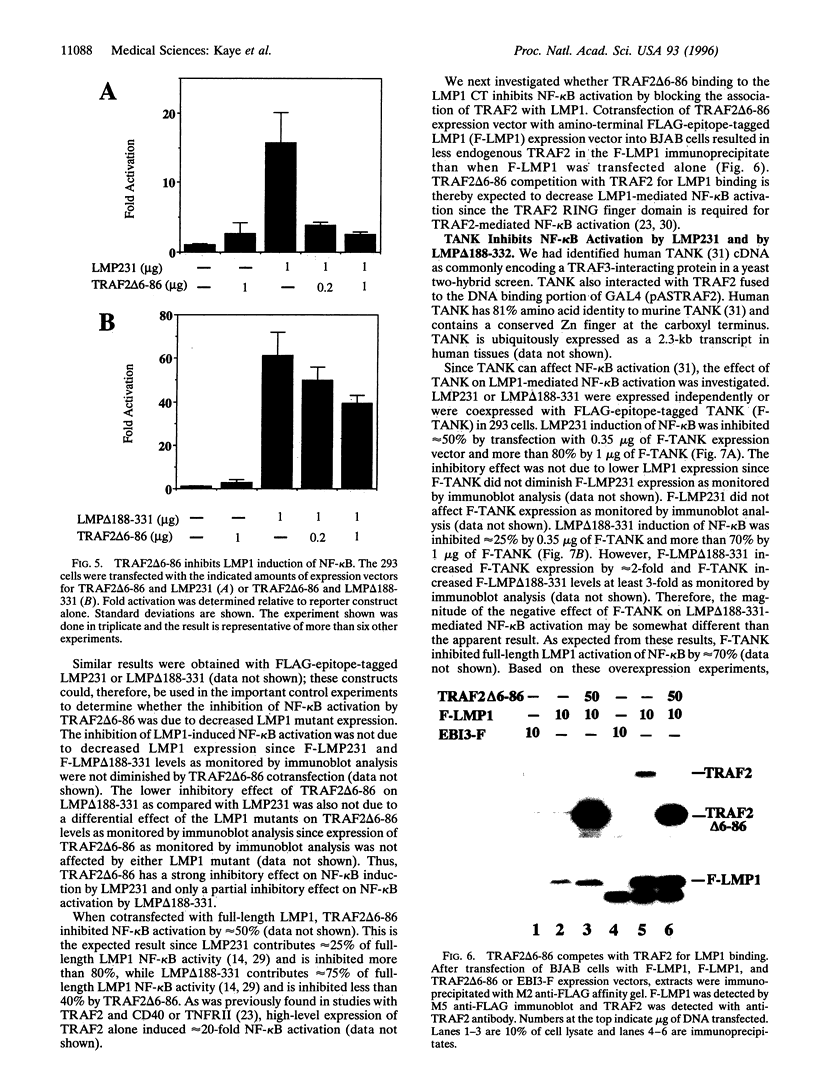
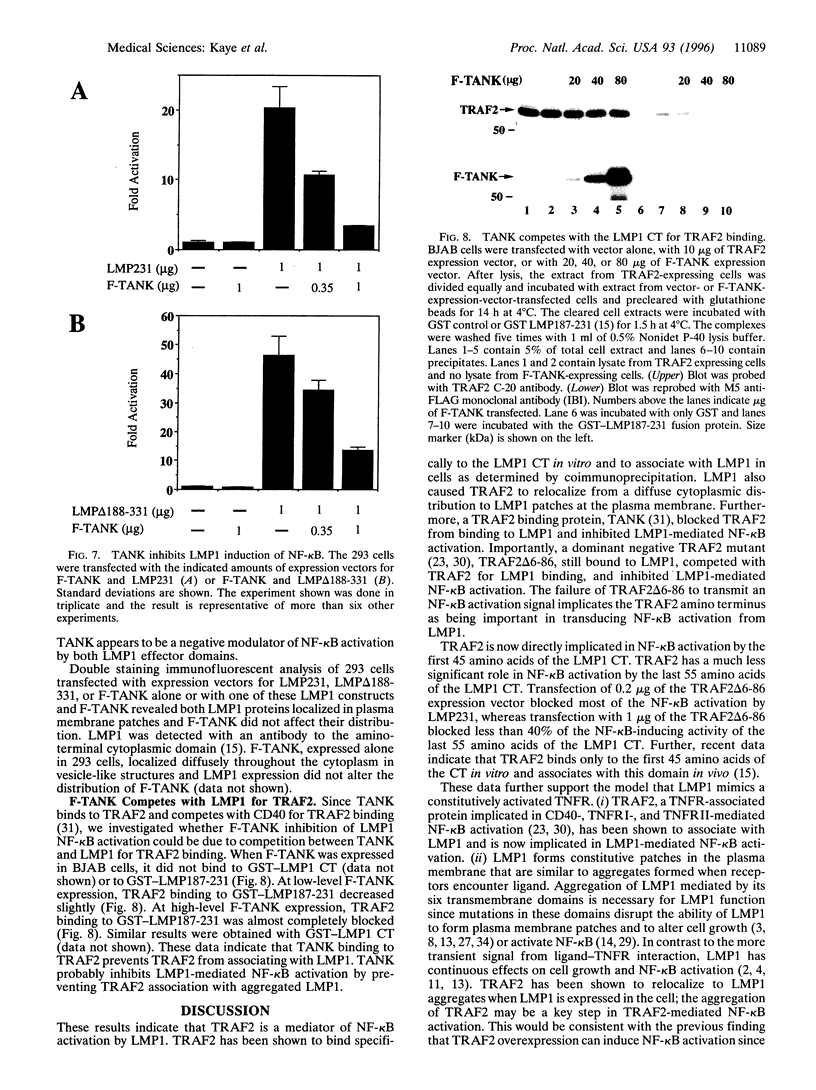
Latent infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1), the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein, associates with tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) associated factor 1 (TRAF1) and TRAF3. Since TRAF2 has been implicated in TNFR-mediated NF-kappa B activation, we have evaluated the role of TRAF2 in LMP1-mediated NF-kappa B activation. TRAF2 binds in vitro to the LMP1 carboxyl-terminal cytoplasmic domain (CT), coprecipitates with LMP1 in B lymphoblasts, and relocalizes to LMP1 plasma membrane patches. A dominant negative TRAF2 deletion mutant that lacks amino acids 6-86 (TRAF/ delta 6-86) inhibits NF-kappa B activation from the LMP1 CT and competes with TRAF2 for LMP1 binding. TRAF2 delta 6-86 inhibits NF-kappa B activation mediated by the first 45 amino acids of the LMP1 CT by more than 75% but inhibits NF-kappa B activation through the last 55 amino acids of the CT by less than 40%. A TRAF interacting protein, TANK, inhibits NF-kappa B activation by more than 70% from both LMP1 CT domains. These data implicate TRAF2 aggregation in NF-kappa B activation by the first 45 amino acids of the LMP1 CT and suggest that a different TRAF-related pathway may be involved in NF-kappa B activation by the last 55 amino acids of the LMP1 CT.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. The multiple membrane-spanning segments of the BNLF-1 oncogene from Epstein-Barr virus are required for transformation. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banchereau J., Bazan F., Blanchard D., Brière F., Galizzi J. P., van Kooten C., Liu Y. J., Rousset F., Saeland S. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenbach M., Josefsen K., Yalamanchili R., Lenoir G., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2209–2220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2209-2220.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G., Baltimore D. TANK, a co-inducer with TRAF2 of TNF- and CD 40L-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Genes Dev. 1996 Apr 15;10(8):963–973. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.8.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G., Cleary A. M., Ye Z. S., Hong D. I., Lederman S., Baltimore D. Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1494–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.7533327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson C. W., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein inhibits human epithelial cell differentiation. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):777–780. doi: 10.1038/344777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devergne O., Hummel M., Koeppen H., Le Beau M. M., Nathanson E. C., Kieff E., Birkenbach M. A novel interleukin-12 p40-related protein induced by latent Epstein-Barr virus infection in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1996 Feb;70(2):1143–1153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.2.1143-1153.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Rymo L., Rhim J. S., Klein G. Morphological transformation of human keratinocytes expressing the LMP gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):447–449. doi: 10.1038/345447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Simurda M. C. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein transactivates the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat through induction of NF-kappa B activity. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6496–6501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6496-6501.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Shu H. B., Pan M. G., Goeddel D. V. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):299–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80984-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H. M., O'Rourke K., Boguski M. S., Dixit V. M. A novel RING finger protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD40. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30069–30072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huen D. S., Henderson S. A., Croom-Carter D., Rowe M. The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) mediates activation of NF-kappa B and cell surface phenotype via two effector regions in its carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 2;10(3):549–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi K. M., Kaye K. M., Kieff E. D. Epstein-Barr virus recombinant molecular genetic analysis of the LMP1 amino-terminal cytoplasmic domain reveals a probable structural role, with no component essential for primary B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4369–4376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4369-4376.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Mosialos G., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 cytoplasmic carboxy terminus is essential for B-lymphocyte transformation; fibroblast cocultivation complements a critical function within the terminal 155 residues. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):675–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.675-683.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laherty C. D., Hu H. M., Opipari A. W., Wang F., Dixit V. M. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24157–24160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Mannick J., Takada K., Kieff E. Phenotypes of Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 deletion mutants indicate transmembrane and amino-terminal cytoplasmic domains necessary for effects in B-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4612–4616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4612-4616.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebowitz D., Wang D., Kieff E. Orientation and patching of the latent infection membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.233-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T., Sugden B. Stimulation of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription by mutant derivatives of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1995 May;69(5):2968–2976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.5.2968-2976.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Birkenbach M., Yalamanchili R., VanArsdale T., Ware C., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Pan M. G., Henzel W. J., Ayres T. M., Goeddel D. V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1243–1252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Sarma V., Dixit V. M., Goeddel D. V. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.7544915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Wong S. C., Henzel W. J., Goeddel D. V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):681–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Xiong J., Shu H. B., Williamson K., Goddard A., Goeddel D. V. I-TRAF is a novel TRAF-interacting protein that regulates TRAF-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8241–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Peng-Pilon M., Huen D. S., Hardy R., Croom-Carter D., Lundgren E., Rickinson A. B. Upregulation of bcl-2 by the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein LMP1: a B-cell-specific response that is delayed relative to NF-kappa B activation and to induction of cell surface markers. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5602–5612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5602-5612.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Irie S., Reed J. C. A novel member of the TRAF family of putative signal transducing proteins binds to the cytosolic domain of CD40. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 23;358(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01406-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H. Y., Donner D. B. Association of a RING finger protein with the cytoplasmic domain of the human type-2 tumour necrosis factor receptor. Biochem J. 1995 Aug 1;309(Pt 3):825–829. doi: 10.1042/bj3090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2337-2346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. B., Weinberg W., Johnson R., Yuspa S., Levine A. J. Expression of the BNLF-1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus in the skin of transgenic mice induces hyperplasia and aberrant expression of keratin 6. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1315–1327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90695-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]