Abstract
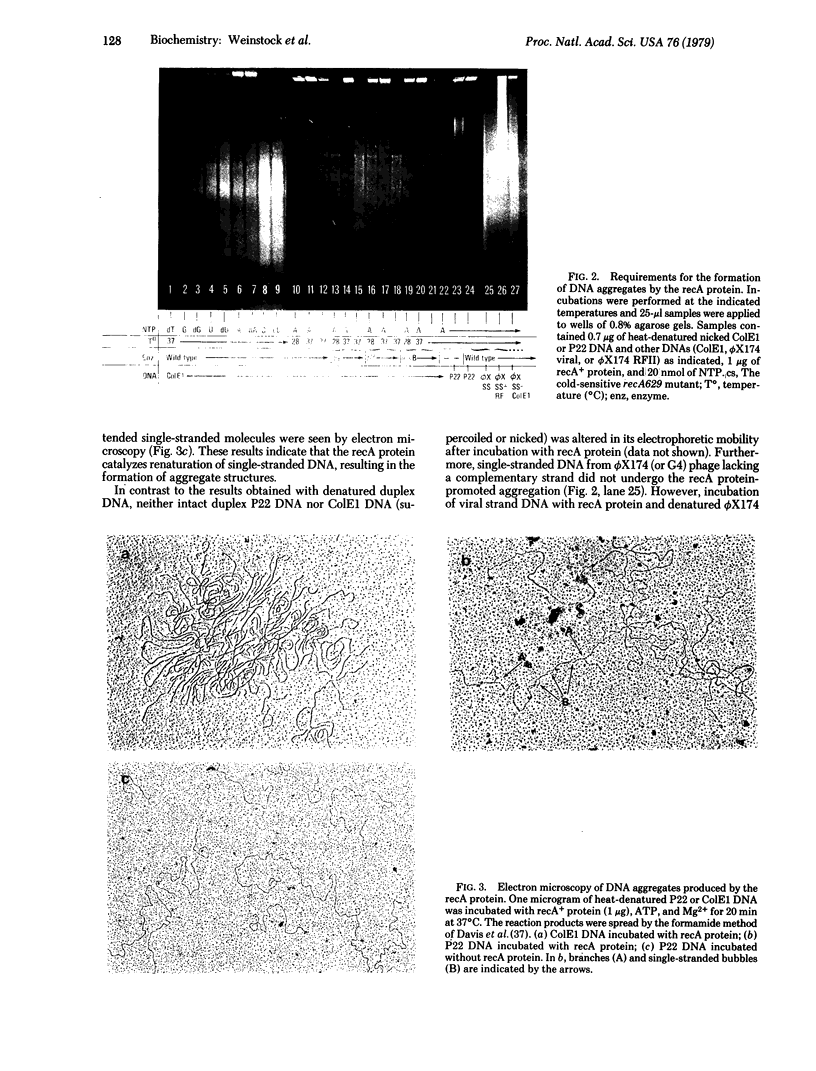
The product of the recA gene of Escherichia coli has been purified to near-homogeneity by a simple three-step procedure. Incubation of the recA protein with complementary single strands of DNA, Mg2+, and ATP results in the rapid formation of large DNA aggregates containing many branched structures. As judged by resistance to S1 nuclease and by electron microscopy, these aggregates contain both duplex and single-stranded regions. The renaturation and aggregation of DNA catalyzed by the recA protein is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP. The recA protein purified from a cold-sensitive recA mutant does not catalyze DNA renaturation or aggregation at 28 degrees C, but does so at 37 degrees C, a finding which correlates with the recombination defect observed in vivo and indicates that this activity is an intrinsic function of the recA protein. These results suggest that the recA protein plays a specific role in strand transfer during recombination and possibly in postreplication repair of damaged DNA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zuccarelli A. J., Sinsheimer R. L. Recombinant DNA molecules of bacteriophage phi chi174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):235–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans H. E., Hoekstra W. P., Zuidweg E. M. Conjugation in Escherichia coli: a study of recombination and the fate of donor DNA at the level of the zygote. Mol Gen Genet. 1975;137(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00332536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birge E. A., Low K. B. Detection of transcribable recombination products following conjugation in rec+, reCB- and recC-strains of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D. Synthesis and maturation of phage P22 DNA. I. Identification of intermediates. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):621–641. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellazzi M., George J., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. I. Further characterization of the thermosensitive mutation tif-1 whose expression mimics the effect of UV irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00269133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen C., Baldwin R. L. Catalysis of DNA reassociation by the Escherichia coli DNA binding protein: A polyamine-dependent reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Chamberlin M., Boyce R. P., Howard-Flanders P. Abnormal metabolic response to ultraviolet light of a recombination deficient mutant of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):442–454. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Recombination deficient mutants of E. coli and other bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:67–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson P. T., West S. C. Identification of protein X of Escherichia coli as the recA+/tif+ gene product. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 21;155(1):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00268563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Mount D. W. Identification of the recA (tif) gene product of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5280–5284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloman W. K., Radding C. M. Recombination promoted by superhelical DNA and the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3910–3914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P. DNA repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:175–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Flanders P., Theriot L. Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in DNA repair and in genetic recombination. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1137–1150. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jendrisak J. J., Burgess R. R. A new method for the large-scale purification of wheat germ DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4639–4645. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Scott J. F., Bertsch L. L. ATP utilization by rep protein in the catalytic separation of DNA strands at a replicating fork. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3298–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Kleid D. G. Escherichia coli protein X is the recA gene product. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6251–6252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K. Genetic analysis of the Escherichia coli K-12 srl region. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.904-911.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Hesse J. E., Epstein W. Identification and radiochemical purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K. Protein X is the product of the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5275–5279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morand P., Blanco M., Devoret R. Characterization of lexB mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):572–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.572-582.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W. A mutant of Escherichia coli showing constitutive expression of the lysogenic induction and error-prone DNA repair pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H., Dressler D. On the mechanism of genetic recombination: electron microscopic observation of recombination intermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Genetic recombination: strand transfer and mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:847–880. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Molecular mechanisms in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W., Craig N. L. Escherichia coli recA gene product inactivates phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4714–4718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. C., Meun D. H. Repair of radiation-induced damage in Escherichia coli. I. Effect of rec mutations on post-replication repair of damage due to ultraviolet radiation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. M. Chromosome transfer from F-lac+ strains of Escherichia coli K-12 mutant at recA, recB, or recC. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):599–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.599-604.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]