Abstract
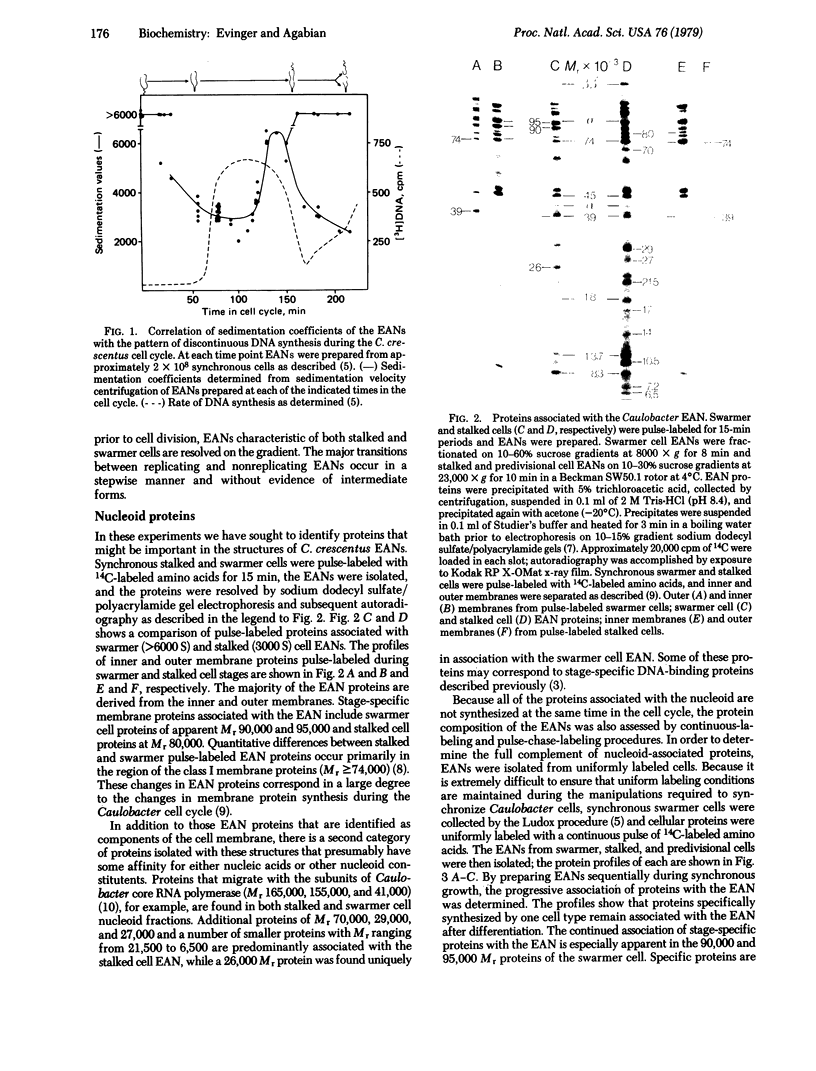
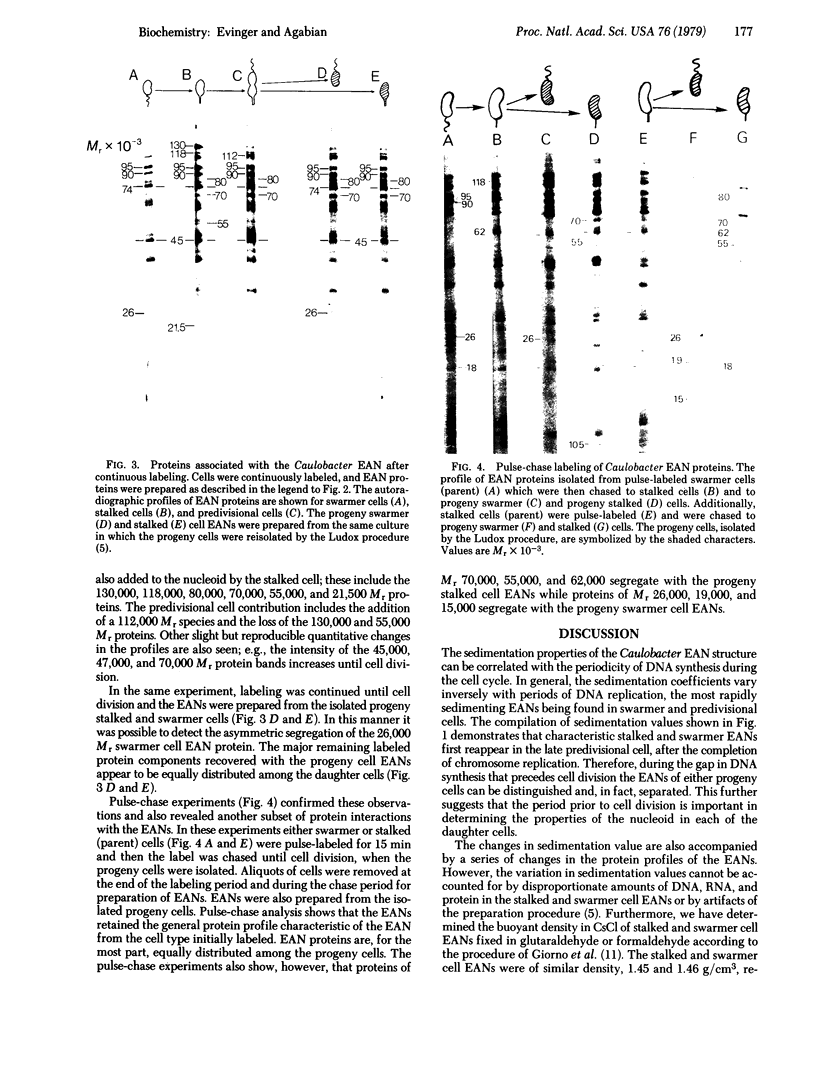
The envelope-associated nucleoid (EAN) of Caulobacter crescentus has been isolated during major developmental stages in the cell cycle. The sedimentation coefficient of the Caulobacter EAN changes as a function of development and is closely correlated with the periodicity of DNA synthesis in this bacterium. The contribution of proteins to the structure of the Caulobacter nucleoid has been analyzed by using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of proteins labeled both for short intervals and continuously throughout the cell cycle. The EAN proteins are derived primarily from membranes and are sequentially associated with the EAN during the cell cycle. Several distinct proteins are isolated with the EAN at specific stages of differentiation. A 26,000 Mr protein, which appears uniquely associated with the swarmer cell EANs, was identified and shown to segregate preferentially with the swarmer cell EAN at cell division.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N., Unger B. Caulobacter crescentus cell envelope: effect of growth conditions on murein and outer membrane protein composition. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):987–994. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.987-994.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemiya K., Wu C. W., Shapiro L. Caulobacter crescentus RNA polymerase. Purification and characterization of holoenzyme and core polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K. K., Newton A. Patterns of protein synthesis during development in Caulobacter crescentus. Dev Biol. 1977 Apr;56(2):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen S. T., Newton A. Chromosome replication during development in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorno R., Hecht R. M., Pettijohn D. Analysis by isopycnic centrifugation of isolated nucleoids of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1559–1567. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. Role of transcription in the temporal control of development in Caulobacter crescentus (stalk-rifampin-RNA synthesis-DNA synthesis-motility). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POINDEXTER J. S. BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION OF THE CAULOBACTER GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:231–295. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.231-295.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Prokaryotic DNA in nucleoid structure. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1976 Nov;4(2):175–202. doi: 10.3109/10409237609105458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L., Agabian-Keshishian N., Hirsch A., Rosen O. M. Effect of dibutyryladenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate on growth and differentiation in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]