Abstract
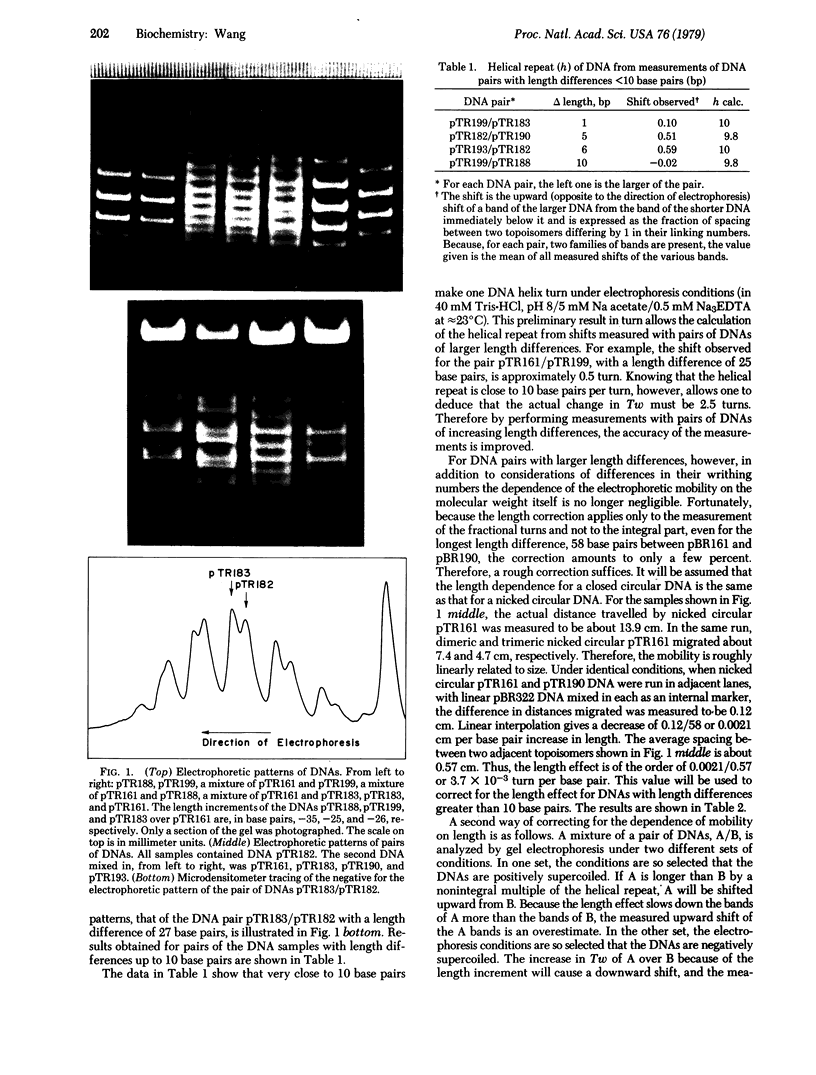
The helical repeat of DNA in solution has been measured directly by analyzing the gel electrophoretic patterns of pairs of covalently closed DNAs with length differences between 1 and 58 base pairs, out of a total length of about 4350 base pairs per DNA molecule. The method is based on the observation that for a covalently closed DNA of a fixed size of n base pairs (n of the order of several thousand), under appropriate conditions, two topological isomers (topoisomers) differing by 1 in their linking numbers are well resolved by gel electrophoresis. If the size of the DNA is increased to n + x base pairs, unless x is an integral multiple of the helical repeat h, the bands of the topoisomers with n + x base pairs per molecule are all shifted relative to the bands of the topoisomers with n base pairs per molecule. The magnitude of the shift is directly related to the nonintegral residual of x/n. Analysis of the set with x ranging from 1 to 58 gives the DNA helix repeat in solution as 10.4 base pairs per turn under physiological conditions, with an estimated probable error of +/- 0.1. This result strongly supports the double helix structure of DNA and rejects the side-by-side model of Rodley et al. [Rodley, G.A., Scobie, R.S., Bates, R.H. T & Lewitt, R.M. (1976) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 2959-2963]. The helical repeat of DNA measured in solution is significantly different from the value 10.0 base pairs per turn for the B form fiber structure.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bram S. The secondary structure of DNA in solution and in nucleohistone. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H. Linking numbers and nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2639–2643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F. B. The writhing number of a space curve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. How many base-pairs per turn does DNA have in solution and in chromatin? Some theoretical calculations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodley G. A., Scobie R. S., Bates R. H., Lewitt R. M. A possible conformation for double-stranded polynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunis-Schneider M. J., Maestre M. F. Circular dichroism spectra of oriented and unoriented deoxyribonucleic acid films--a preliminary study. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):521–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J. Physical and topological properties of circular DNA. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):103–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D., CRICK F. H. Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid. Nature. 1953 Apr 25;171(4356):737–738. doi: 10.1038/171737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Variation of the average rotation angle of the DNA helix and the superhelical turns of covalently closed cyclic lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]