Abstract
Partially purified adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1] from bovine brain cortex was fractionated into two separate forms by calcium-dependent regulatory protein (CDR)-Sepharose affinity chromatography. The major form of the enzyme, comprising approximately 80% of the applied activity, did not bind to the affinity column in the presence of Ca2+ and was insensitive to the CDR. Approximately 20% of adenylate cyclase activity was absorbed to CDR-Sepharose in the presence of Ca2+. This activity was stimulated by Ca2+ and CDR. This study directly demonstrates that brain cortex contains Ca2+-CDR-sensitive and -insensitive forms of adenylate cyclase and indicates that CDR-Sepharose may be a useful tool for purification of adenylate cyclase. The Ca2+ -stimulated adenylate cyclase was purified at least 55-fold with a 13% yield.
Full text
PDF
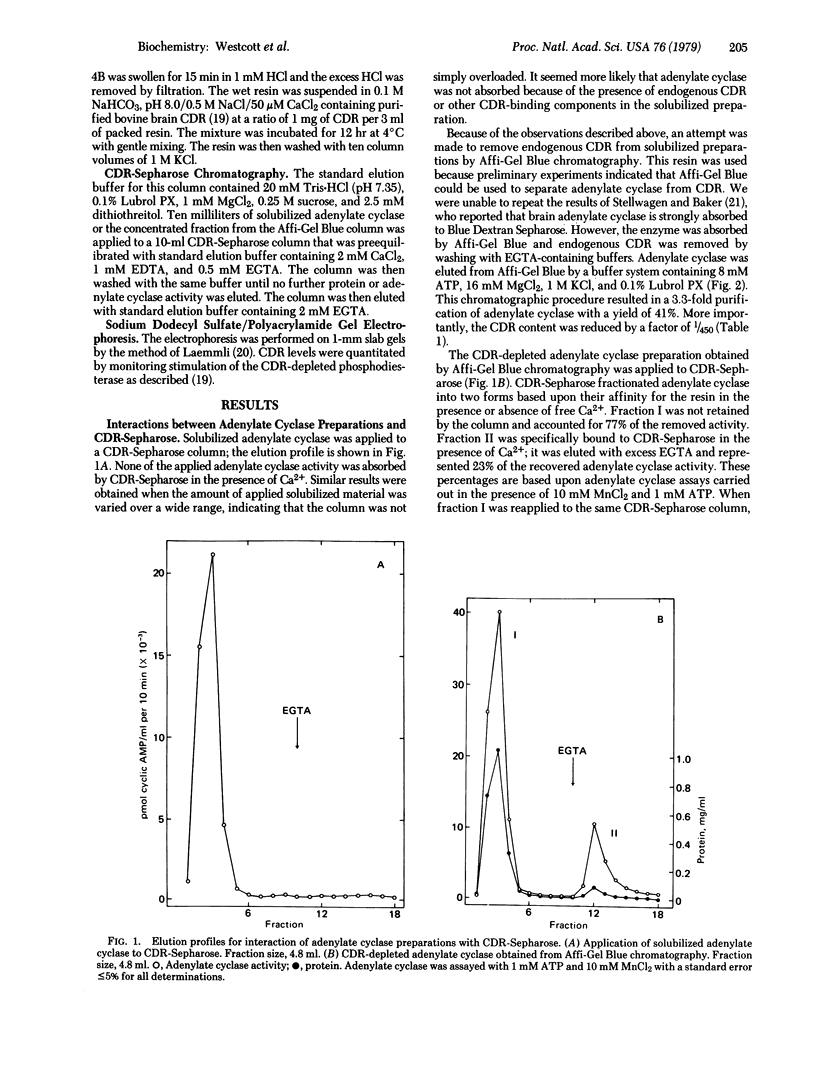
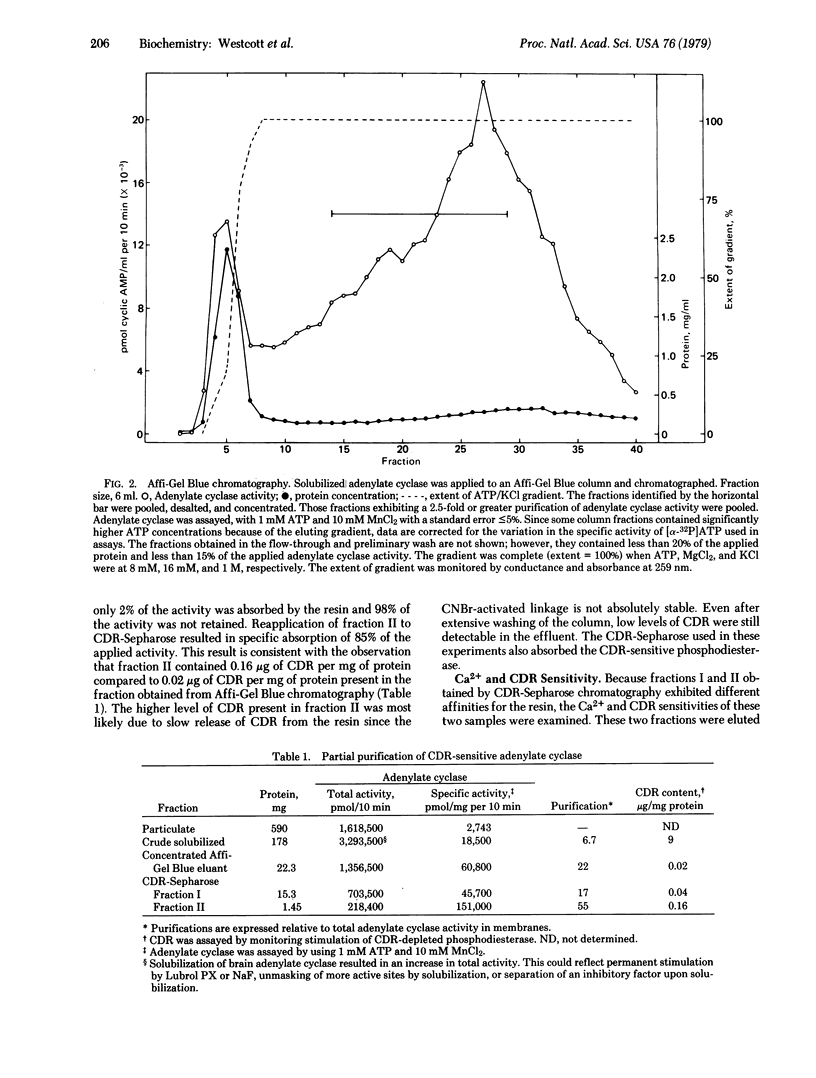
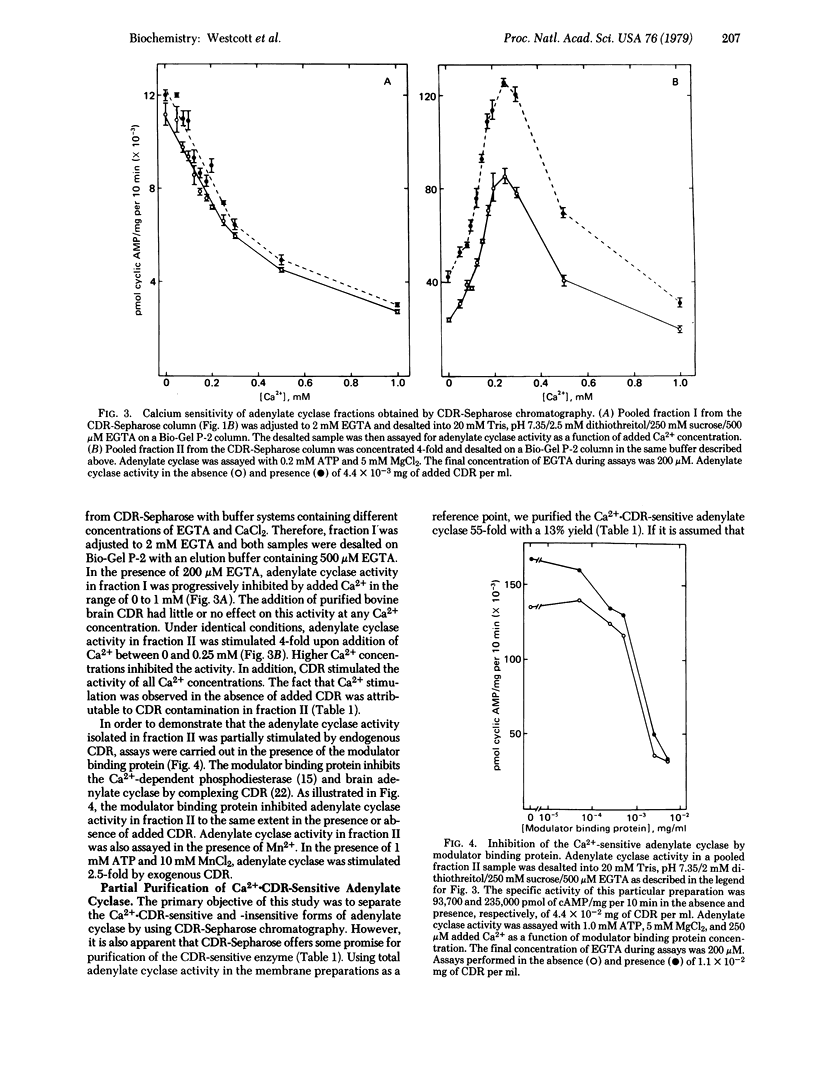

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradham L. S., Holt D. A., Sims M. The effect of Ca2+ on the adenyl cyclase of calf brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 24;201(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A., Wolff D. J. Calcium-dependent adenylate cyclase from rat cerebral cortex. Reversible activation by sodium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5677–5685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Brostrom C. O., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Regulation of adenylate cyclase from glial tumor cells by calcium and a calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4744–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Bradham L. S., Lynch T. J., Lin Y. M., Tallant E. A. Protein activator of cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of bovine or rat brain also activates its adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. C., Wirch E., Stevens F. C., Wang J. H. Purification of a Ca2+-activatable cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from bovine heart by specific interaction with its Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C., Wrenn S., Haber E. Affinity purification of cardiac adenylate cyclase: dependence on prior hydrophobic resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Sutherland E. W. Detergent-dispersed adenylate cyclase from rat brain. Effects of fluoride, cations, and chelators. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5114–5121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R., Teshima Y., Uenishi K. Regulation of nucleoside cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity from rat brain by a modulator and Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Storm D. R. Detection of calcium-dependent regulatory protein binding components using 125I-labeled calcium-dependent regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3374–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Resolution of beta-adrenergic receptor binding and adenylate cyclase activity by gel exclusion chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. M., Liu Y. P., Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Purification, characterization, and active form of the protein activator from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4943–4954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Ca++-dependent formation of brain adenylate cyclase-protein activator complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):616–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I. A. Differentiation of fluorides-stimulated and non-fluoride-stimulated components of beef brain cortex adenylate cyclase cy calcium ions, ethyleneglycol-bis-(beta-aminoethyl ether) N,N'-tetraacetic acid and Triton X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 27;397(1):244–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naya-Vigne J., Johnson G. L., Bourne H. R., Coffino P. Complementation analysis of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1978 Apr 20;272(5655):720–722. doi: 10.1038/272720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. Size and detergent binding of adenylate cyclase from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1498–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orly J., Schramm M. Coupling of catecholamine receptor from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4410–4414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by guanylnucleotide analogues and separation of a nucleotide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):867–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity: interactions of solubilized components with receptor-replete membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Baker B. Proposed structure for brain adenylate cyclase purified using blue dextran-Sepharose chromatography. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):719–720. doi: 10.1038/261719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai K., Kurashina Y., Hayaishi O. Adenylate cyclase from Brevibacterium liquefaciens. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:160–169. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hungen K., Roberts S. Catecholamine and Ca 2+ activation of adenylate cyclase systems in synaptosomal fractions from rat cerebral cortex. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 14;242(115):58–60. doi: 10.1038/newbio242058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. An endogenous inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Teo T. S., Ho H. C., Stevens F. C. Bovine heart protein activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Vanaman T. C. Affinity chromatography purification of a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase using immobilized modulator protein, a troponin C-like protein from brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 8;73(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Brostrom C. O. Calcium-binding phosphoprotein from pig brain: identification as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90486-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



