Abstract
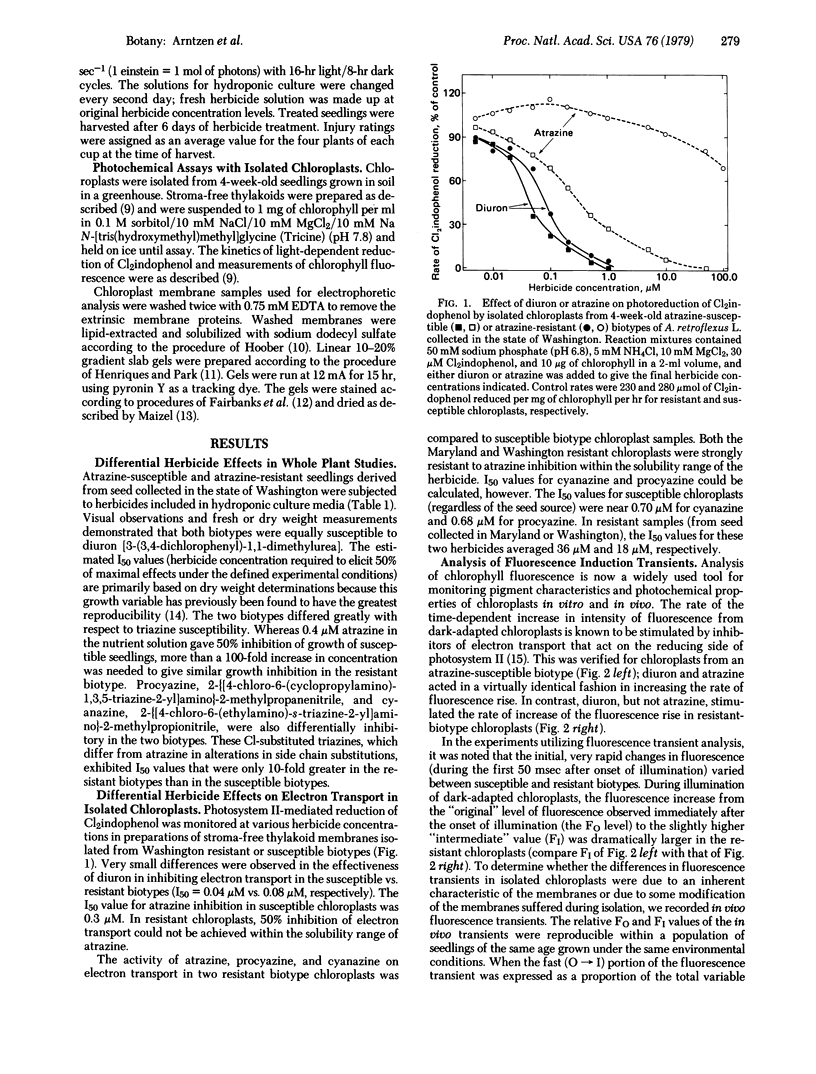
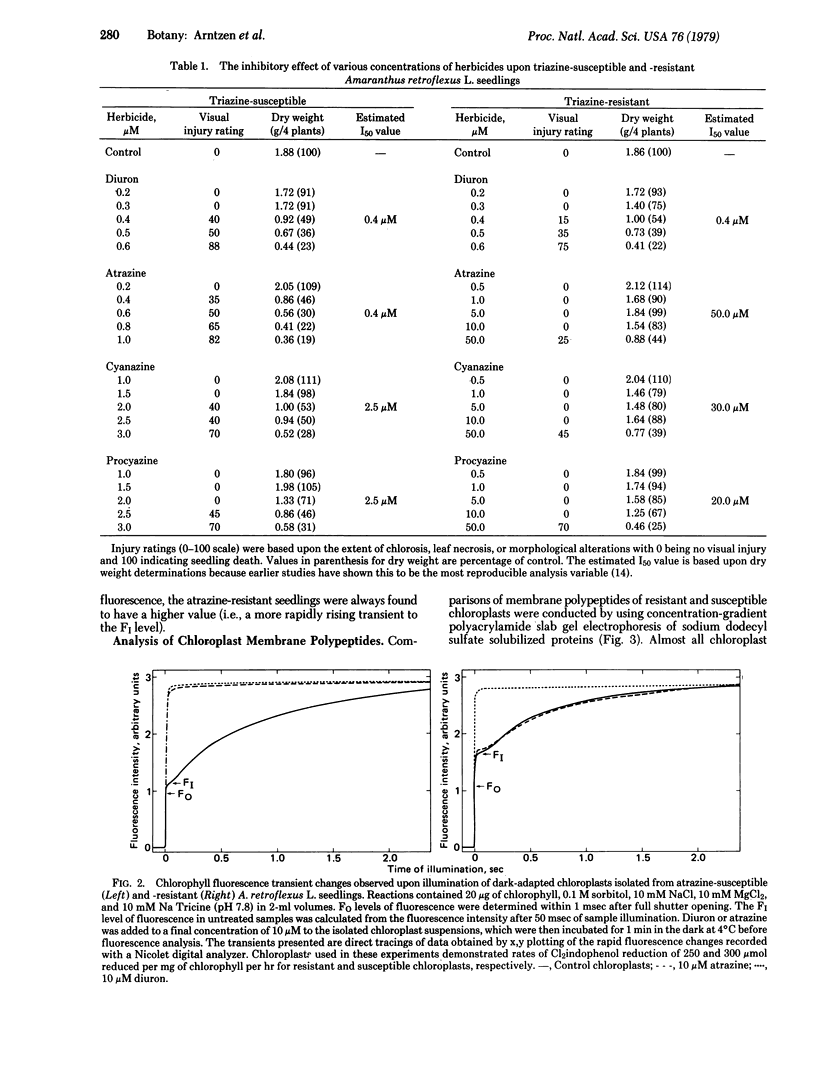
The effectiveness of diuron, atrazine, procyazine, and cyanazine were compared in controlling growth of redroot pigweed (Amaranthus retroflexus L.) in hydroponic culture. A very marked differential inhibition response was observed for atrazine between resistant and susceptible biotypes. Procyazine and cyanazine exhibited less dramatic differential responses, whereas diuron was equally effective in controlling growth in both biotypes. Photosystem II activity of chloroplasts from both triazine-resistant and triazine-susceptible biotypes was inhibited by diuron but only the chloroplasts from triazine-susceptible biotypes were inhibited significantly by atrazine. The photochemical activity of chloroplasts from triazine-resistant biotypes was partially resistant to procyazine or cyanazine inhibition. The parallel lack of diuron differential effects, partial procyazine and cyanazine differential response, and very marked atrazine differential response in both whole plant and chloroplast assays indicates that the chloroplast is the site of selective herbicide tolerance in these triazine-resistant redroot pigweed biotypes.
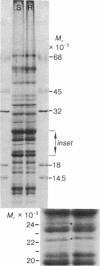
Photosystem II photochemical properties were characterized by analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence transients in the presence or absence of herbicides. Data with susceptible chloroplasts indicated that both diuron and atrazine inhibit electron flow very near the primary electron acceptor of photosystem II. Only diuron altered the fluorescence transient in resistant chloroplasts. In untreated preparations there were marked differences in the fast phases of the fluorescence increase in resistant vs. susceptible chloroplasts; these data are interpreted as showing that the resistant plastids have an alteration in the rate of reoxidation of the primary photosystem II electron acceptor. Electrophoretic analysis of chloroplast membrane proteins of the two biotypes showed small changes in the electrophoretic mobilities of two polypeptide species. The data provide evidence for the following herbicide resistance mechanism: genetically controlled modification of the herbicide target site.
Keywords: triazine herbicides, diuron, photosystem II, pesticide resistance
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke J. J., Ditto C. L., Arntzen C. J. Involvement of the light-harvesting complex in cation regulation of excitation energy distribution in chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 15;187(1):252–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriques F., Park R. B. Further Chemical and Morphological Characterization of Chloroplast Membranes from a Chlorophyll b-less Mutant of Hordeum vulgare. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):763–767. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K. Sites of synthesis of chloroplast membrane polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardi y-1. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4327–4334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renger G. Studies on the structural and functional organization of system II of photosynthesis. The use of trypsin as a structurally selective inhibitor at the outer surface of the thylakoid membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 13;440(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer W., Strotmann H. Relationship between inhibitor binding by chloroplasts and inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 11;460(1):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zankel K. L., Kok B. Estimation of pool sizes and kinetic constants. Methods Enzymol. 1972;24:218–238. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(72)24070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]