Abstract
The brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has available the necessary functional components to produce the active ligands angiotensins II (AngII), angiotensin III, angiotensins (IV), angiotensin (1–7), and angiotensin (3–7). These ligands interact with several receptor proteins including AT1, AT2, AT4, and Mas distributed within the central and peripheral nervous systems as well as local RASs in several organs. This review first describes the enzymatic pathways in place to synthesize these ligands and the binding characteristics of these angiotensin receptor subtypes. We next discuss current hypotheses to explain the disorders of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as research efforts focused on the use of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), in their treatment. ACE inhibitors and ARBs are showing promise in the treatment of several neurodegenerative pathologies; however, there is a need for the development of analogs capable of penetrating the blood-brain barrier and acting as agonists or antagonists at these receptor sites. AngII and AngIV have been shown to play opposing roles regarding memory acquisition and consolidation in animal models. We discuss the development of efficacious AngIV analogs in the treatment of animal models of AD and PD. These AngIV analogs act via the AT4 receptor subtype which may coincide with the hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met receptor system. Finally, future research directions are described concerning new approaches to the treatment of these two neurological diseases.
Keywords: angiotensin II, angiotensin IV, hepatocyte growth factor, angiotensin receptors, c-Met receptor, Mas receptor, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease
As life expectancy has increased the incidences of dementia and Parkinson’s disease (PD) have also increased. The number of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients in the U.S. is presently estimated to be 4.5 million, with approximately 37 million worldwide (1, 2). By 2040 the worldwide number is predicted to reach 81 million with 4.6 million new patients diagnosed per year (3). There is a 3% occurrence of AD between the ages of 65–74 years, and upwards of 50% for those 85 years of age and older (4). Beyond the cost associated with treatment (estimated range from $70 to 150 billion annually in the U.S. alone) are the personal hardships and sacrifices suffered by family members and other care givers accompanied by the frustrations experienced by the patient and health care professionals as cognitive abilities continue to slowly deteriorate with no efficacious drug treatment available. It is clear that the brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a potential contributor to dementia and blockade of this system has been shown to be important (5–9). However, the precise role(s) played by the brain RAS is unclear and somewhat convoluted given that the octapeptide angiotensin II (AngII) has been shown to disrupt learning and memory; while the hexapeptide angiotensin IV (AngIV) facilitates memory acquisition and consolidation. A second major neurodegenerative disease, PD, was first described by James Parkinson in 1867 and now affects about 10 million people in the U.S. Around the world PD impacts approximately 1% of the population over 50 years of age and 1.5% over 65 years (10). There is accumulating evidence that the brain RAS is important in the etiology of PD as well, and this recently discovered link with the RAS will be discussed.
This review initially describes the presently identified angiotensin ligands and their interaction with specific receptor proteins (AT1, AT2, and AT4). The AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes have been well characterized (11, 12); however, the AT4 subtype has only been partially sequenced (13). Next we discuss the current hypotheses offered to explain the causes of AD and PD, and the drugs thus far developed to treat these dysfunctions. The role of angiotensins in memory formation and PD is discussed, followed by current attempts to develop new and efficacious treatments for AD and PD. Related to these efforts we describe an AngIV related analog effective in delaying or reversing symptoms in animal models of AD and PD. We conclude with thoughts concerning future directions in these important clinical areas of research.
Formation of Angiotensin Ligands
Angiotensin peptides are derived from the precursor protein angiotensinogen via several enzymatic conversion pathways [Figure 1; Ref. (14–16)]. Briefly, the decapeptide angiotensin I (AngI) is formed by renin (EC 3.4.23.15) acting upon the amino terminal of angiotensinogen. AngI serves as a substrate for angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE; EC 3.4.15.1) that hydrolyzes the carboxy terminal dipeptide His-Leu to form the octapeptide AngII (14). AngII is converted to the heptapeptide angiotensin III (AngIII) by glutamyl aminopeptidase A (AP-A; EC 3.4.11.7) that cleaves the Asp residue at the N-terminal (17–19). Membrane alanyl aminopeptidase N (AP-N; EC 3.4.11.2) cleaves Arg at the N-terminal of AngIII to form the hexapeptide angiotensin IV (AngIV). AngIV can be further converted to Ang(3–7) by carboxypeptidase P (Carb-P) and prolyl oligopeptidase (PO) cleavage of the Pro-Phe bond to form Ang(3–7).
Figure 1.
The renin-angiotensin pathway including active ligands (bold), enzymes, receptors, and inhibitors involved in central angiotensin mediated blood pressure. Abbreviations: ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE2, angiotensin converting enzyme 2; AP-A, aminopeptidase A; AP-N, aminopeptidase N; ARBs, angiotensin receptor blockers.
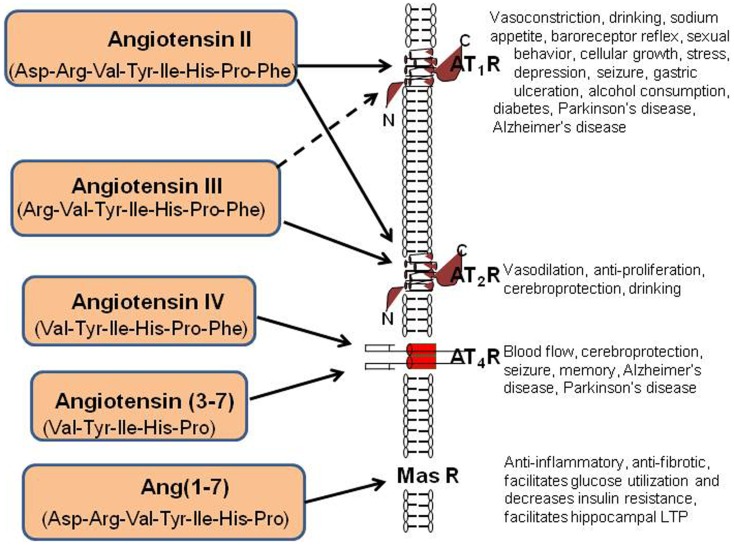
AngII can also be converted to Ang(1–7) by Carb-P cleavage of Phe (20), by the mono-peptidase ACE2 (21), or by ACE cleavage of the dipeptide Phe-His from Ang(1–9) (22). Note that the functional role of insertion of Alu in intron 16 of the human ACE gene has been questioned; however, Wu et al. (23) has shown this form of ACE to upregulate ACE promoter transcriptional activity by approximately 70%. Ang(1–7) is converted to Ang(2–7) by AP-A acting at the Asp-Arg bond (24). AngI is biologically inactive; while AngII and AngIII are full agonists at the AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes and mediate pressor and dipsogenic functions [Figure 2; reviewed in Ref. (11)]. AngIV binds with low affinity to the AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes (25, 26), but with high affinity and selectivity to the AT4 receptor subtype (26–28).
Figure 2.
Description of the peptide structures and enzymes involved in the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I through shorter angiotensins. The biologically active forms include angiotensin II, III, IV, angiotensin (3–7), and angiotensin (1–7). The respective receptors where these active angiotensins bind are indicated by arrows.
Finally, AngII can be converted to Ang(1–7) by ACE2 (29). Recent evidence indicates that this Ang(1–7)/Mas receptor system is important with regard to counteracting peripheral organ inflammation and fibrosis, increasing glucose utilization and decreasing insulin resistance (30, 31). The Mas receptor has been identified in the brain with particularly high concentrations within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and piriform cortex (32). In agreement with these memory-related brain distributions of Mas, Ang(1–7) has been shown to facilitate hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) (33) suggesting its potential importance in learning and memory. The Ang(1–7)/Mas receptor system also plays a neuroprotective role in responding to cerebral ischemia (34). The reader is referred to the following reviews for detailed characterizations of the angiotensin receptor subtypes (8, 11, 30, 35).
Current Hypotheses of Alzheimer’s Disease
Two prominent theories are presently offered to explain the neurochemical changes underlying AD. These are the cholinergic and amyloid cascade hypotheses. Based on the cholinergic hypothesis of memory formation it was originally proposed that drugs designed to inhibit central and peripheral acetylcholine esterase (AChE), and serve as a muscarinic M2 autoreceptor antagonist, would result in facilitated release of ACh. Further, AChE binding to the non-amyloidogenic form of β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) appears to facilitate a conformational shift to the amyloidogenic form (36–38). Treatment with an AChE inhibitor would be expected to neutralize the catalytic site of the enzyme and reduce Aβ peptide aggregation as facilitated by active AChE. To date the cholinergic hypothesis of memory formation has driven the development of the major marketed drugs in the form of AChE inhibitors (Tacrine®, Donepezil®, Rivastigmine®, and Galantamine®) which will go generic in the near future (9). These drugs are only marginally helpful in treating symptoms and do not appear to impact the underlying neuropathology of this disease (39). The FDA approved Namenda®(Memantine HCl) in 2004, an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist designed to limit glutamate excitotoxicity and intended to treat moderate to severe AD patients (40). Namenda is also limited regarding its ability to slow disease progression and does little to stem the neuropathology. Recent research has focused on the accumulation of brain Aβ as an important target in the pathogenesis of AD (41). There may be a link between Aβ accumulation and NMDA receptor over activation in that oxidative stress, plus the elevated intracellular calcium generated due to Aβ accumulation, appear to enhance glutamate mediated neurotoxicity via increased NMDA receptor activation (42).
There are many possible reasons for the lack of an effective therapy for AD including the complexity of the disease process and the resulting inability to identify reliable biomarkers. In addition, it is now apparent that AD is multifactorial rather than a single disease (43). To further complicate drug development and diagnosis those AD criteria behaviors denoting cognitive decline can also result from a number of other clinical conditions including vascular disease (44, 45), frontotemporal dementia, PD-induced dementia, HIV infection (46, 47), as well as cumulative oxidative damage and toxicities accompanying normal aging (48). The ultimate goal of development must be a drug that prevents the progressive loss of synapses and neurons and reverses this degenerative process.
The second major hypothesis concerns amyloid peptides that range in length from 39 to 42 amino acids and are produced by the conversion of amyloid precursor protein (APP) (49). It is suggested that the cellular accumulation of Aβ(1–42) causes the neurodegenerative characteristics of AD (41). Treatment with the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) Valsartan has been shown to discourage amyloid β-mediated cognitive dysfunction in the Tg 2576 mouse model of AD (50). Along these lines, intranasal injection of Losartan (also an ARB) resulted in neuroprotection, presumably via its Aβ-reducing plus anti-inflammatory effects (51).
With the recent clinical trials failure of so called “β-amyloid buster compounds” by Lilly and Pfizer Pharmaceuticals it now appears that both of these hypotheses are much too simple and new approaches must be developed and tested. One very attractive potential upstream contributor to dementia is the brain RAS. A potential role for the brain RAS in learning and memory was proposed some time ago and thus provides justification for the identification of brain RAS components that may serve as targets for the treatment of AD [reviewed in Ref. (52–56)]. Recent findings suggest that many of the memory enhancing effects initially attributed to AngII are likely due to the conversion of AngII to AngIV, and it is this peptide acting as an agonist at the AT4 receptor subtype, that is responsible for cognitive facilitation (20, 57, 58). Taken as a whole research findings now suggest that AngII interferes with performance on most memory tasks used with animal models; while AngIV facilitates performance (59). This AngIV memory facilitation hypothesis is consistent with the finding that ARBs improve cognitive processing (60–64). It remains to be determined whether blockade of the AT1 receptor subtype permits conversion of excess endogenous AngII to AngIV which then activates the AT4 receptor. This notion is also supported by the observation that ACE inhibitors enhance cognitive processing in both humans (65, 66) and animal models (67). Specifically, resulting increases in AngI levels are likely converted to Ang(1–9) and then to AngIII, AngIV, and Ang(3–7). Both AngIV and Ang(3–7) act as agonists at the AT4 receptor subtype. See below for further details concerning AngIV-induced memory facilitation. It should be noted that ACE has been shown to convert Aβ1–42 to Aβ1–40 (39). Aβ1–42 is the form that appears to be responsible for brain amyloid deposition (9). Thus, treatment with an ACE inhibitor could, over time, result in greater accumulations of amyloid plaques.
A Role for Angiotensins in Memory Consolidation
A number of studies indicate that AngIV, and AngIV analogs such as Nle1-AngIV, facilitate LTP, learning, and memory consolidation (68–72). Studies using various animal models of dementia to test the influence of Nle1-AngIV have demonstrated reversal of deficits initiated by: (1) treatment with scopolamine (73); (2) kainic acid injections into the hippocampus (74); (3) perforant path knife-cuts (72); and (4) ischemia resulting from transient four-vessel occlusion (12). Consistent with these behavioral and electrophysiological results, brain autoradiography-determined binding sites for [125I]-AngIV have been localized in structures known to mediate cognitive processing including the neocortex, hippocampus, and basal nucleus of Meynert (26, 56, 75). Denny and colleagues (76) reported that AngII blocked hippocampal LTP in vivo in perforant path stimulated dentate gyrus neurons. This inhibition appeared to be dependent upon AngII binding at the AT1 receptor subtype given that co-application of Losartan with AngII significantly attenuated this inhibition; while application of the AT2 receptor antagonist PD123, 319 failed to interfere with this AngII-induced inhibition (77). Recently it has been established that AngII, chronically perfused via subcutaneous osmotic pump in mice, resulted in hypertension and impaired spatial memory as measured using the Morris water maze task beginning during the third week of treatment (78). Such AngII-induced spatial memory impairment has also been reported in rats following acute intracerebroventricular infusion (79). Significant reductions in cerebral blood flow and brain acetylcholine levels, as well as oxidative stress, were measured 60 min following AngII injection. Taken together these results indicate that AngII generally interferes with learning and memory acquisition.
Current Hypotheses of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is due to a progressive loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. The striatum is the primary projection field of these substantia nigra neurons, thus the loss of DA results in insufficient stimulation of striatal dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors (80, 81). Decreased availability of DA triggers the symptomatic triad of bradykinesia, tremors-at-rest, and rigidity. There is evidence from animal models and PD patients that neuro-inflammatory processes, triggered by reactive oxygen species (ROS), damage mitochondrial membrane permeability, enzymes, and mitochondrial genome resulting in DA cell death (82, 83). l-DOPA is efficacious at controlling motor symptoms in the majority of patients but is ineffective regarding non-motor symptoms. Current treatment strategies to relieve these symptoms include DA replacement via Levodopa (l-DOPA, the precursor of DA), DA receptor agonists, monoamine oxidase B inhibitors, and catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors, to protect the DA that is formed (84, 85). As the disease progresses periods of decreased mobility, dyskinesia, and spontaneous involuntary movements complicate treatment (86). Thus, in addition to treatment with the DA receptor agonists apomorphine and Levodopa, surgical techniques including pallidotomy and deep brain electrical stimulation may be required (87, 88). Progressive neurodegeneration also impacts additional non-dopaminergic neurotransmitter systems including noradrenergic, cholinergic, and serotonergic (89). As a result, non-motor symptoms may develop including depression, sleep disturbances, dementia, and autonomic nervous system failure (90, 91). l-DOPA is reasonably ineffective at combating non-motor symptoms (90). Current research efforts are three-pronged and directed at extending the duration of Levodopa’s efficacy, controlling these additional non-motor symptoms, and developing new strategies designed to offer neuroprotection and overall disease reversal benefits. Attaining the goal of slowing or reversing the rate of DA neuron loss may also result in the protection of non-DA neurotransmitter systems.
A Role for Angiotensins in Parkinson’s Disease
Allen et al. (92) were first to suggest a potential relationship between the brain RAS and PD. These investigators measured decreased angiotensin receptor binding in the substantia nigra and striatum in post mortem brains of PD patients. A number of studies support an important role for ACE in this disease. ACE is present in the nigra-striatal pathway and basal ganglia structures (93–95). PD patients treated with the ACE inhibitor perindopril revealed improved motor responses to the DA precursor 3,4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine (96). Relative to this treatment with perindopril, elevated striatal DA levels have been measured in mice (97). In addition, ACE has been shown to metabolize bradykinin and thus modulate inflammation, a contributing factor in PD. Activation of the AT1 receptor subtype by AngII promotes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent oxidases, a significant source of ROS (98, 99). Treatment with ACE inhibitors has been shown to offer protection against the loss of DA neurons in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) animal models (100, 101), as well as the 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) rat model (102). The likely mechanism underlying this ACE inhibitor-induced protection is a reduction in the synthesis of AngII acting at the AT1 receptor subtype [reviewed in Ref. (103)]. It is known that AngII binding at the AT1 subtype activates the NADPH oxydase complex, thus providing a major source of ROS (104–106). Further, activation of the AT1 receptor results in the stimulation of the NF-kB signal transduction pathway facilitating the synthesis of chemokine, cytokines, and adhesion molecules, all important in the migration of inflammatory cells into regions of tissue injury (107).
If AngII activation of the AT1 receptor subtype results in facilitation of the NADPH oxidase complex and formation of free radicals, then blockade of the AT1 receptor should serve a protective function. This appears to be the case. Treatment with an AT1 receptor blocker (ARB) protects DA neurons in both 6-OHDA (108–110) and MPTP animal models (105, 111, 112). ARBs have been shown to reduce the formation of NADPH oxidase-derived ROS following administration of 6-OHDA (113). While the risk of developing PD is reduced with the use of calcium channel blockers to control hypertension, the positive influences of ACE inhibitors, β-blockers, and ARBs are not clear (114). Of relevance to this issue is the PD patient who showed exacerbated motor dysfunction when treated with an ARB [Losartan; Ref. (115)]. This patient experienced severe bradykinesia while on Losartan, accompanied by frequent episodes of freezing.
The AT2 receptor subtype is present in several fetal tissues including uterus, ovary, adrenal gland, heart, vascular endothelium, kidney, and brain (particularly neocortex and hippocampus) (11, 116–119). As the animal matures the expression of the AT2 receptor decreases. It appears that adult mammalian brain levels of this receptor in the striatum and substantia nigra are reasonably low (56, 120). The AT2 receptor has been linked with cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue regeneration (121, 122). The results from a study utilizing mesencephalic precursor cells indicated that AngII, acting at the AT2 receptor, facilitated differentiation of precursor cells into DA neurons (123). Along these lines, activation of the AT2 receptor has been shown to inhibit NADPH oxidase activation (124). However, Rodriguez-Pallares et al. (99) found that AngII treatment of the 6-OHDA lesioned rat increased DA cell death. This could be due to the much greater numbers of brain AT1 receptors, as compared with AT2 receptors, such that the beneficial effects of AT2 receptor activation was overwhelmed by AT1 activation. Finally, the expression of AT2 receptors in PD patients appears to be decreased in the caudate nucleus but is unchanged in the substantia nigra and putamen (125).
Basal ganglia structures possess a local RAS that evidences increased activity during dopaminergic degeneration (109, 126, 127). Villar-Cheda et al. (128) have reported that reserpine-induced decreases in DA resulted in a significant increase in the expression of AT1 and AT2 receptors. A similar pattern was seen with 6-OHDA-induced DA denervation in which a decrease in receptor expression was noted with l-DOPA treatment. These results indicate a direct interaction between the RAS and the dopaminergic system in basal ganglia structures. Related to this, Rodriguez-Perez and colleagues (110, 129) used intrastriatal 6-OHDA injections to produce dopaminergic degeneration and noted a significant decrease in DA neurons in ovariectomized rats. This loss of neurons was attenuated by treatment with the AT1 receptor antagonist Candesartan, or estrogen replacement. Estrogen replacement also resulted in a down-regulation of AT1 receptors and NADPH complex in the substantia nigra, accompanied by an up-regulation of the AT2 receptor subtype. These results suggest an important relationship among estrogen levels, brain DA receptors, and the RAS. An increase in the expression of AT1 receptors and decreased expression of AT2 receptors has been reported in aged rats (130). This observation is of major importance given the potentially deleterious consequences of AT1 receptor activation on basal ganglia structures.
Recently Rodriguez-Perez et al. (131) have reported that chronic hypoperfusion in rats resulted in a reduction in striatal DA levels accompanied by a large decline in DA neurons and striatal terminals. This DA neuron loss was countered by orally administered Candesartan. Further, AT1 receptor expression was highest in the substantia nigra; while AT2 expression was lower in rats that experienced chronic hypoperfusion as compared with controls. Again, Candesartan attenuated such changes in receptor expression. Taken together these findings argue that inhibition of AT1 receptor activity serves a neuroprotective role in PD.
The involvement of AngIV in PD has been initially investigated (132). A genetic in vitro PD model was used consisting of the α-synuclein over-expression of the human neuroglioma H4 cell line. Results indicated a significant reduction in α-synuclein-induced toxicity with Losartan treatment combined with the AT2 receptor antagonist PD123319, in the presence of AngII. Under these same conditions AngIV was only moderately effective. Our laboratory has recently synthesized a metabolically stable AngIV analog that acts by way of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met receptor system (133–136) to overcome the motor dysfunctions that follow 6-OHDA-induced lesions of the substantia nigra pars compacta in the rat (unpublished results). This compound, called Dihexa, significantly improved both rope hang times and stride length over the course of a 48-day treatment period.
Taken together these findings suggest that treatment with an ARB may offer some protection against the risk of developing PD. However, much additional work employing angiotensin mimetics must be completed to better understand the relationship among brain angiotensin receptors, angiotensin ligands, inflammation, and ROS as related to PD.
AngIV, HGF, and the Brain DA System
Aging is one of the major risk factors predisposing individuals to neurodegenerative diseases (130, 137, 138). The neurodegeneration accompanying aging is dependent in part upon oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and microglial NADPH oxidase activity. Each is of significant importance regarding DA neuron loss (106, 139). Activation of AT1 receptors by AngII has been shown to facilitate DA neuron degeneration by activating microglial NADPH oxidase (109). The activation of AT1 receptors by AngII failed to cause DA neuron degeneration when microglial cells were absent (99). Of related importance, Zawada and colleagues (140) recently reported that nigral dopaminergic neurons responded to neurotoxicity-induced superoxide in two waves. First, a spike in mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide was measured 3 h following treatment with an MPTP metabolite (MPP+). Second, by 24 h following treatment hydrogen peroxide levels were further elevated. Treatment with Losartan suppressed this nigral superoxide production suggesting a potentially important role for ARBs in the treatment of PD. Further, AngII binding at the AT1 receptor increased DA neuron degeneration initiated by subthreshold doses of DA neurotoxins by stimulating intraneuronal levels of ROS and neuroinflammation by activation of microglial NADPH oxidase (141–144).
From the above observations it follows that AT1 receptor blockade should have a neuroprotective effect on DA neurons in PD patients as demonstrated in animal models (112). Less obvious is the likelihood that AT1 receptor blockade results in accumulating levels of AngII that are converted to AngIII and then to AngIV. This conversion cascade has been shown to occur intracellularly (145). In fact, this conversion of AngII appears to be necessary for DA release to occur in the striatum (146). Thus, an intriguing alternative explanation of these AT1 receptor antagonist results is that the increased endogenous levels of AngIV facilitate activation of the HGF/c-Met receptor system and neuroprotection of DA neurons. In this way AngIV may act in combination with AT1 receptor blockade to protect DA neurons. Our laboratory has offered evidence that AngIV, and AngIV analogs, are capable of facilitating HGF/c-Met activity (133). Support for this claim is presented in several recent reports. First we found that the action of AT4 receptor antagonists depends on inhibiting the HGF/c-Met receptor system by binding to and blocking HGF dimerization (134, 147). In contrast, AT4 receptor agonists facilitate cognitive processing and synaptogenesis by acting as mimics of the dimerization domain of HGF [hinge region; Ref. (135, 148)]. This work has culminated in the synthesis of a small molecule AT4 receptor agonist capable of penetrating the blood-brain barrier and facilitating cognitive processing presumably by increasing synaptogenesis (133). This small molecule (MM-201) has a Kd for HGF ≈6.5 or 13 pM (136). This AngIV-HGF/c-Met interaction could explain earlier reports indicating that activation of the AT4 receptor facilitates cerebral blood flow and neuroprotection (149–151).
In agreement with the above findings, HGF has been shown to positively impact ischemic-induced injuries such as cardiac (152) and hind limb ischemia (153, 154). HGF has also been shown to eliminate hippocampal neuronal cell loss in transient global cerebral ischemic gerbils (155), and transient focal ischemic rats (156). Date and colleagues (157, 158) have reported HGF-induced improvements in escape latencies by microsphere embolism-cerebral ischemic rats using a circular water maze task. These authors measured reduced damage to cerebral endothelial cells in ischemic animals treated with HGF. Shimamura et al. (159) have recently shown that over-expression of HGF following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion resulted in significant recovery of performance in the Morris water maze and passive avoidance conditioning tasks. Treatment with HGF was also found to increase the number of arteries in the neocortex some 50 days following the onset of ischemia.
In sum, these results suggest a role for the HGF/c-Met receptor system in cerebroprotection and are consistent with the notion that AngIV increases blood flow by a NO-dependent mechanism (141). In support of this hypothesis a report by Faure et al. (160) indicated that increasing doses of AngIV via the internal carotid artery significantly decreased mortality and cerebral infarct size in rats 24 h following embolic stroke due to the intracarotid injection of calibrated microspheres. Pretreatment with the AT4 receptor antagonist Divalinal-AngIV, or the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME), abolished this protective effect. Sequential cerebral autoradiography indicated that AngIV caused the redistribution of blood flow to ischemic areas within a few minutes. Thus, AngIV may yield its cerebral protective effect against acute cerebral ischemia via an intracerebral-hemodynamic c-Met receptor-mediated NO-dependent mechanism. Should these relationships hold then a metabolically stable blood-brain barrier penetrant small molecule that activates the HGF/c-Met system could prove highly efficacious in the treatment of PD.
Future Research Directions
The use of ACE inhibitors and AT1 and/or AT2 receptor blockers have shown preliminary experimental promise in the treatment of stress, depression, alcohol consumption, seizure, AD, PD, and diabetes. A number of AT1 receptor antagonists, capable of penetrating the BBB, are now available with new ones in clinical trials (161, 162); however, the vast majority of clinical studies concerned with the use of antihypertensive agents to treat dementia have focused on ACE inhibitors and diuretics (163, 164). This is also true of studies concerned with cerebroprotection against stroke (165). Traditional antidepressant drugs for patients suffering from depression and migraine pathophysiology have taken precedence over the use of ARBs (166). Similarly, the testing of ARBs with seizure and PD patients has yet to gain momentum. The treatment of diabetic patients with ARBs is just now receiving attention (167), particularly with patients suffering diabetic related nephropathy (168, 169). The AngIV/AT4 receptor system has been implicated in memory facilitation, cerebroprotection, seizure, Alzheimer’s, and PDs. The lack of BBB penetrating AT4 receptor agonists and antagonists has limited our understanding concerning the relative importance of brain AT1 and AT4 receptor subtypes in the etiology and treatment of dementias, stroke, and related memory dysfunctions. Although current drug development efforts show promise regarding small molecules that interact specifically with the AT4 receptor, much additional effort is needed in this important research area.
There remain a number of important unanswered questions regarding whether the observed biological effects of AngIV and its analogs are mediated by the HGF/c-Met system. (1) What is the complete brain distribution of the c-Met receptor and is this receptor expressed in significant levels within cognitive mediating brain structures? (2) Can AngIV, and AngIV analogs, specifically activate the HGF/c-Met receptor system in vivo to induce AngIV/AT4 receptor associated functions? (3) Are the levels of endogenous AngIV sufficient to augment the HGF-dependent activation of brain c-Met receptors? This is a very significant issue in that the in vivo half-life of AngIV appears to be very short. Related to this point, what is the affinity of AngIV for HGF? (4) Does LVV-H7 bind to HGF, and if so, at what affinity? and (5) Does the activation of brain c-Met receptors produce neurogenesis, and if so can this phenomenon be utilized to replace experimentally and clinically damaged pathways? Until these questions are answered an understanding of the true mechanism of action of AngIV and its analogs will remain uncertain.
Conclusion
The classic RAS was originally described as a circulating hormonal system involved in cardiovascular regulation, vasopressin release, sympathetic activation, and body water/electrolyte balance. These functions appear to be primarily mediated by the AT1 receptor subtype. With the recognition that local tissue RASs exist has come research interest in additional physiological and pharmacological functions that permit better understanding of clinical dysfunctions such as inflammation, cellular proliferation, apoptosis, and fibrosis accompanied by an increased appreciation for the role of both the AT1 and AT2 receptor subtypes [reviewed in Ref. (170, 171)]. It is now clear that the brain RAS is involved in a number of novel physiologies and behaviors that have important implications for the design and development of new drug treatment strategies. This review focused on the importance of the RAS with regard to two neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer’s and PDs. The use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs with Alzheimer’s patients suggests an involvement by the brain RAS in this dysfunction. Such positive results force the need to further investigate the potential roles of several angiotensins, not only the AngII/AT1 receptor system. Clearly the AngII/AT2 receptor and AngIV/AT4 (c-Met) receptor systems have been shown to exert positive influences on memory acquisition and retrieval and are worthy of additional attention. The Ang(1–7)/Mas receptor system has been implicated in neuroprotection and the facilitation of LTP and also deserves further experimental evaluation.
Taken together these findings encourage new clinically relevant approaches to understanding the memory enhancing effects, especially of the angiotensin IV system, on cerebral blood flow, neuroprotection, stress and depression, alcohol consumption, seizure, Alzheimer’s and PDs, and diabetes (12, 172, 173). The development of blood-brain barrier permeable AT4 receptor agonists and antagonists presents a novel and promising new strategy for the treatment of several of these clinical dysfunctions (174–177).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Research from our laboratory presented in this review was supported by the E. Edward and Lucille I. Lainge Endowment for Alzheimer’s Research, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and funds provided for Medical and Biological Research by the State of Washington Initiative Measure No. 171.
References
- 1.McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging – Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (2011) 7:263–9 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yaari R, Corey-Bloom J. Alzheimer’s disease. Sem Neurol (2007) 27:32–41 10.1055/s-2006-956753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglion L, Ganguli M, et al. Alzheimer’s disease international. Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet (2005) 366:2112–7 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Clark CM. Clinical manifestations and diagnostic evaluation of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. In: Clark CM, Trajanowski JQ, editors. Neurodegenerative Dementias: Clinical Features and Pathological Mechanisms. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; (2000). p. 95–114 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fletcher A. Quality of life in the management of hypertension. Clin Exper Hypertens (1999) 21:961–72 10.3109/10641969909061024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fogari R, Zoppi A. Effect of antihypertensive agents on quality of life in the elderly. Drugs Aging (2004) 21:377–93 10.2165/00002512-200421060-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Iwanami U, Mogi M, Iwai M, Horiuchi M. Inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system and target organ protection. Hypertens Res (2009) 32:229–37 10.1038/hr.2009.5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wright JW, Harding JW. The brain angiotensin IV/AT4 receptor system as a new target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev Res (2009) 70:472–80 10.1002/ddr.20328 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wright JW, Harding JW. The brain RAS and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol (2010) 223:326–33 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Olanow CW, Stern MB, Sethi K. The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Neurology (2009) 72(Suppl 4):S1–136 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a1d44c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger T. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev (2000) 52:415–72 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wright JW, Harding JW. Brain renin-angiotensin: a new look at an old system. Prog Neurobiol (2011) 95:49–67 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.07.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Albiston AL, Peck GR, Yeatman HR, Fernando R, Ye S, Chai SY. Therapeutic targeting of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase: heads and tails? Pharmacol Ther (2007) 116:417–27 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Johnston CI. Biochemistry and pharmacology of the renin-angiotensin system. Drugs (1990) 39:21–31 10.2165/00003495-199000391-00005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Karamyan VT, Speth RC. Enzymatic pathways of the brain renin-angiotensin system: unsolved problems and continuing challenges. Regul Pept (2007) 143:15–27 10.1016/j.regpep.2007.03.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Speth RC, Karamyan VT. The significance of brain aminopeptidases in the regulation of the actions of angiotensin peptides in the brain. Heart Fail Rev (2008) 13:299–309 10.1007/s10741-007-9078-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chauvel EN, Llorens-Cortes C, Coric P, Wilk S, Roques BP, Fournié-Zaluski MC. Differential inhibition of aminopeptidase A and aminopeptidase N by new beta-amino thiols. J Med Chem (1994) 37:2950–7 10.1021/jm00044a016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rich DH, Moon BJ, Harbeson S. Inhibition of aminopeptidases by amastatin and bestatin derivatives, effect of inhibitor structure on slow-binding processes. J Med Chem (1984) 27:417–22 10.1021/jm00370a001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wilk S, Healy DP. Glutamyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase A), the BP-1/6C3 antigen. Adv Neuroimmunol (1993) 3:195–207 10.1016/S0960-5428(05)80021-X [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wright JW, Bechtholt AJ, Chambers SL, Harding JW. Angiotensin III and IV activation of the brain AT1 receptor subtype in cardiovascular function. Peptides (1996) 17:1365–71 10.1016/S0196-9781(96)00226-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ferrario CM, Chappell MD. Novel angiotensin peptides. Cell Mol Life Sci (2004) 61:2720–7 10.1007/s00018-004-4243-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vauquelin G, Michotte Y, Smolders I, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Dupont A, et al. Cellular targets for angiotensin II fragments: pharmacological and molecular evidence. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst (2002) 3:195–204 10.3317/jraas.2002.041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wu SJ, Hsieh TJ, Kuo MC, Tsai ML, Tsai KL, Chen CH, et al. Functional regulation of Alu element of human angiotensin-converting enzyme gene in neuron cells. Neurobiol Aging (2013) 34(7):e1–7 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mentlein R, Roos T. Proteases involved in the metabolism of angiotensin II, bradykinin, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), and neuropeptide Y by vascular smooth muscle cells. Peptides (1996) 17:709–20 10.1016/0196-9781(96)00066-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bennett JP, Jr, Snyder SH. Angiotensin II binding to mammalian brain membranes. J Biol Chem (1976) 251:7423–30 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Harding JW, Cook VI, Miller-Wing AV, Hanesworth JM, Sardinia MF, Hall KL, et al. Identification of an AII (3-8) [AIV] binding site in guinea pig hippocampus. Brain Res (1992) 583:340–3 10.1016/S0006-8993(10)80047-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bernier SG, Bellemare JM, Escher E, Guillemette G. Characterization of AT4 receptor from bovine aortic endothelium photosensitive analogues of angiotensin IV. Biochemistry (1998) 37:4280–7 10.1021/bi972863j [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jarvis MF, Gessner GW, Ly CG. The angiotensin hexapeptide 3-8 fragment potently inhibits [125I] angiotensin II binding to non-AT1 or -AT2 recognition sites in bovine adrenal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol (1992) 219:319–22 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90312-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ohishi M, Yamamoto K, Rakugi H. Angiotensin (1-7) and other angiotensin peptides. Curr Pharm Des (2013) 19:3060–4 10.2174/1381612811319170013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Passos-Silva DG, Verano-Braga T, Santos RA. Angiotensin-(1-7): beyond the cardio-renal actions. Clin Sci (Lond) (2013) 124:443–56 10.1042/CS20120461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simões e Silva AC, Silveira KD, Ferreira AJ, Teixeira MM. ACE2, angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor axis in inflammation and fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol (2013) 169:477–92 10.1111/bph.12159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Freund M, Walther T, von Bohlen und Halbach O. Immunohistochemical localization of the angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas in the murine forebrain. Cell Tissue Res (2012) 348:29–35 10.1007/s00441-012-1354-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hellner K, Walther T, Schubert M, Albrecht D. Angiotensin-(1-7) enhances LTP in the hippocampus through the G-protein-coupled receptor Mas. Mol Cell Neurosci (2005) 29:427–35 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jiang T, Gao L, Guo J, Lu J, Wang Y, Zhang Y. Suppressing inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway contributes to the neuroprotective effect of angiotensin-(1-7) in rats with permanent cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol (2012) 167:1520–32 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02105.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dasgupta C, Zhang L. Angiotensin II receptors and drug discovery in cardiovascular disease. Drug Discov Today (2011) 16:22–34 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.11.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.DeFerrari GV, Canales MA, Shin I, Weiner LM, Silman I, Inestrosa NC. A structural motif of acetylcholinesterase that promotes amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation. Biochemistry (2001) 40:10447–57 10.1021/bi0101392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Inestrosa NC, Alvarez A, Perez CA, Moreno RD, Vicente M, Linger C, et al. Acetylcholinesterase accelerates assembly of amyloid-beta-peptides into Alzheimer’s fibrils: possible role of the peripheral site of the enzyme. Neuron (1996) 16:881–91 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80108-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rees T, Hammond PI, Soreq H, Younkin S, Brimijoin S. Acetylcholinesterase promotes beta-amyloid plaques in cerebral cortex. Neurobiol Aging (2003) 24:777–87 10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00230-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhu Y, Xiao K, Ma L, Xiong B, Fu Y, Yu H, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and β-secretase. Bioorg Med Chem (2009) 17:1600–13 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.12.067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Melnikova I. Therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2007) 6:341–2 10.1038/nrd2314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science (2002) 297:353–6 10.1126/science.1072994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lipton SA. The molecular basis of memantine action in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurologic disorders: low-affinity, uncompetitive antagonism. Curr Alzheimer Res (2005) 2:155–65 10.2174/1567205053585846 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schubert D, Maher P. An alternative approach to drug discovery for Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Future Med Chem (2012) 4:1681–8 10.4155/fmc.12.109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Polidori MC, Pientka L. Bridging the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease with vascular pathology: the feed-back, the feed-forward, and oxidative stress. J Alzheimers Dis (2012) 28:1–9 10.3233/JAD-2011-111034 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Bang W, Bennett DA. Mixed brain pathologies account for most dementia cases in community-dwelling older persons. Neurology (2007) 69:2197–204 10.1212/01.wnl.0000271090.28148.24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Brayne C, Matthews FE, Xuereb JH. Pathological correlates of late onset dementia in a multicentre, community-based population in England and Wales. Neuropathology Group of the Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study (MRC CFAS). Lancet (2001) 357:169–75 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03589-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chen M, Maleski JJ, Sawmiller DR. Scientific truth or false hope: understanding Alzheimer’s disease from an aging perspective. J Alzheimers Dis (2011) 24:3–10 10.3233/JAD-2010-101638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ding Q, Dimayuga E, Keller JN. Proteasome regulation of oxidative stress in aging and age-related disease of the CNS. Antioxid Redox Signaling (2006) 8:163–72 10.1089/ars.2006.8.163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Van Nostrand WE, Davis-Salinas J, Saporito-Irwin SM. Amyloid beta-protein induces the cerebrovascular cellular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci (1996) 777:297–302 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb34436.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wang J, Ho L, Chen L, Zhoa Z, Zhao W, Qian X, et al. Valsartan lowers brain beta-amyloid protein levels and improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest (2007) 117:3393–402 10.1172/JCI31547 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Danielyan L, Klein R, Hanson LR, Buadze M, Schwab M, Gleiter CH, et al. Protective effects of intranasal losartan in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Rejuvenation Res (2010) 13:195–201 10.1089/rej.2009.0944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gard PR. The role of angiotensin II in cognition and behaviour. Eur J Pharmacol (2002) 438:1–14 10.1016/S0014-2999(02)01283-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gard PR. Angiotensin as a target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, anxiety and depression. Expert Opin Ther Targets (2004) 8:7–14 10.1517/14728222.8.1.7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mustafa T, Lee JH, Chai SY, Albiston AL, McDowall SG, Mendelsohn FA. Bioactive angiotensin peptides: focus on angiotensin IV. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst (2001) 2:205–10 10.3317/jraas.2001.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.von Bohlen und Halbach O. Angiotensin IV in the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res (2003) 311:1–9 10.1007/s00441-002-0655-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wright JW, Harding JW. Important roles for angiotensin III and IV in the brain renin-angiotensin system. Brain Res Rev (1997) 25:96–124 10.1016/S0165-0173(97)00019-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Braszko JJ, Walesiuk A, Wielgat P. Cognitive effects attributed to angiotensin II may result from its conversion to angiotensin IV. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst (2006) 7:168–74 10.3317/jraas.2006.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chai SY, Fernando R, Peck G, Ye SY, Mendelsohn FA, Jenkins TA, et al. The angiotensin IV/AT4 receptor. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci (2004) 61:2728–37 10.1007/s00018-004-4246-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wright JW, Harding JW. The brain angiotensin system and extracellular matrix molecules in neural plasticity, learning, and memory. Prog Neurobiol (2004) 72:263–93 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2004.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Basso N, Paglia N, Stella I. Protective effect of the inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system on aging. Regul Pept (2005) 128:247–52 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.12.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hajjar IM, Keown M, Frost B. Antihypertensive agents for aging patients who are at risk for cognitive dysfunction. Curr Hypert Rep (2005) 7:466–73 10.1007/s11906-005-0043-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Khachaturian AS, Zandi PP, Lyketsos CG, Hayden KM, Skoog I, Norton MC, et al. Antihypertensive medication use and incident Alzheimer disease: the Cache County Study. Arch Neurol (2006) 63:686–92 10.1001/archneur.63.5.noc60013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Li NC, Lee A, Whitmer RA, Kivipelto M, Lawler E, Kazis LE. Use of angiotensin receptor blockers and risk of dementia in a predominantly male population: prospective cohort analysis. BMJ (2010) 340:b5465. 10.1136/bmj.b5465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mogi M, Horiuchi M. Effects of angiotensin II receptor blockers on dementia. Hypertens Res (2009) 32:738–40 10.1038/hr.2009.110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kehoe PG, Wilcock GK. Is inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system a new treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease? Lancet Neurol (2007) 6:373–8 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70077-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ohrui T, Tomita N, Sato-Nakagawa T, Matsui T, Maruyama M, Niwa K, et al. Effects of brain-penetrating ACE inhibitors on Alzheimer disease progression. Neurology (2004) 63:1324–35 10.1212/01.WNL.0000140705.23869.E9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yamada K, Horita T, Takayama M, Takahashi S, Takaba K, Nagata Y, et al. Effect of a centrally active angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril, on cognitive performance in chronic cerebral hypo-perfusion rats. Brain Res (2011) 1421:110–20 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.09.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Albiston AL, Allen AM, Mendelsohn FA, Ping SE, Barrett GL, Murphy M, et al. Effect of I.C.V. injection of AT4 receptor ligands, NLE1-angiotensin IV and LVV-hemorphin 7, on spatial learning in rats. Neuroscience (2004) 124:341–9 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Albiston AL, Pederson ES, Burns P, Purcell B, Wright JW, Harding JW, et al. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced learning deficits by LVV-hermorphin-7 in rats in the passive avoidance and water maze paradigms. Behav Brain Res (2004) 154:239–43 10.1016/j.bbr.2004.02.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Braszko JJ, Kupryszewski G, Witczuk B, Wisniewski K. Angiotensin II (3-8)-hexapeptide affects motor activity, performance of passive avoidance, and a conditioned avoidance response in rats. Neuroscience (1988) 27:777–83 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90182-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kramár EA, Armstrong DL, Ikeda S, Wayner MJ, Harding JW, Wright JW. The effects of angiotensin IV analogs on long-term potentiation within the CA1 region of the hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res (2001) 897:114–21 10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02100-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wright JW, Stubley L, Pederson ES, Kramár EA, Hanesworth JM, Harding JW. Contributions of the brain angiotensin IV-AT4 receptor subtype system to spatial learning. J Neurosci (1999) 19:3952–61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pederson ES, Krishnan R, Harding JW, Wright JW. A role for the angiotensin AT4 receptor subtype in overcoming scopolamine-induced spatial memory deficits. Regul Pept (2001) 102:147–56 10.1016/S0167-0115(01)00312-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stubley-Weatherly L, Harding JW, Wright JW. Effects of discrete kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions on spatial and contextual learning and memory in rats. Brain Res (1996) 716:29–38 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01589-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chai SY, Bastias MA, Clune EF, Matsacos DJ, Mustafa T, Lee JH, et al. Distribution of angiotensin IV binding sites (AT4 receptor) in the human forebrain, midbrain and pons as visualized by in vitro receptor autoradiography. J Chem Neuroanat (2000) 20:339–48 10.1016/S0891-0618(00)00112-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Denny JB, Polan-Curtain J, Wayner MJ, Armstrong DL. Angiotensin II blocks hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res (1991) 567:321–4 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90812-A [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.von Bohlen und Halbach O, Albrecht D. Angiotensin II inhibits long-term potentiation within the lateral nucleus of the amygdala through AT1 receptors. Peptides (1998) 19:1031–6 10.1016/S0196-9781(98)00044-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Duchemin S, Belanger E, Wu R, Ferland G, Girouard H. Chronic perfusion of angiotensin II causes cognitive dysfunctions and anxiety in mice. Physiol Behav (2013) 109:63–8 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.10.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tota S, Goel R, Pachauri SD, Rajasekar N, Najmi AK, Hanif K, et al. Effect of angiotensin II on spatial memory, cerebral blood flow, cholinergic neurotransmission, and brain derived neurotrophic factor in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) (2013) 226:357–69 10.1007/s00213-012-2913-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Schapira AH. Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson disease. Neurol Clin (2009) 27:583–603 10.1016/j.ncl.2009.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Welchko RM, Leveque XT, Dunbar GL. Genetic rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis (2012) 2012:128356. 10.1155/2012/128356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Tufekci KU, Genc S, Genc K. The endotoxin-induced neuroinflammation model of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis (2011) 2011:487450. 10.4061/2011/487450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Witte ME, Geurts JG, deVries HE, van der Valk P, van Horssen J. Mitochondrial dysfunction: a potential link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration? Mitochondrion (2010) 10:411–8 10.1016/j.mito.2010.05.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kaplan S, Tarsy D. Initial treatment of Parkinson’s disease: an update. Curr Treat Options Neurol (2013) 15:377–84 10.1007/s11940-013-0236-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Lipski J, Nistico R, Berretta N, Guatteo E, Bernardi G, Mercuri NB. A scapegoat for accelerated neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease? Prog Neurobiol (2011) 94:389–407 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.06.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Marsden CD. Basal ganglia disease. Lancet (1982) 2:1141–7 10.1016/S0140-6736(82)92797-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Valkmann J, Schafer H, Botzel K. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med (2006) 355:896–908 10.1056/NEJMoa060281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Garcia PJ, Ruiz-Matus C. Efficacy of long-term continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion in advanced Parkinson’s disease with motor fluctuations: a multicenter study. Mov Disord (2008) 23:1130–6 10.1002/mds.22063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Meissner WG, Frasier M, Gasser T, Goetz CG, Lozano A, Piccini P, et al. Priorities in Parkinson’s disease research. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2011) 10:377–93 10.1038/nrd3430 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Chaudhuri KR, Schapira AH. The non motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: dopaminergic pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Neurol (2009) 8:464–744 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70068-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chaudhuri KR, Odin P, Antonini A, Martinez-Martin P. Parkinson’s disease: the non-motor issues. Parkinsonism Related Disord (2011) 17:717–23 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.02.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Allen AM, MacGregor DP, Chai SY, Donnan GA, Daczmarczyk S, Richardson K, et al. Angiotensin II receptor binding associated with nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in human basal ganglia. Ann Neurol (1992) 32:339–44 10.1002/ana.410320306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chai SY, Mendelsohn FA, Paxinos G. Angiotensin converting enzyme in rat brain visualized by quantitative in vitro autoradiography. Neuroscience (1987) 20:615–27 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90114-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chai SY, McKenzie JS, McKinley MJ, Mendelsohn FA. Angiotensin converting enzyme in the human basal forebrain and midbrain visualized by in vitro autoradiography. J Comp Neurol (1990) 291:179–94 10.1002/cne.902910203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Strittmatter SM, Thiele EA, Kapiloff MS, Snyder SH. A rat brain isozyme of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Unique specificity for amidated peptide substrates. J Biol Chem (1985) 260:9825–32 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Reardon KA, Mendelsohn FA, Chai SY, Horne MK. The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, perindopril, modifies the clinical features of Parkinson’s disease. Aust N Z J Med (2000) 30:48–53 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2000.tb01054.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Jenkins TA, Mendelsohn FA, Chai SY. Angiotensin-converting enzyme modulates dopamine turnover in the striatum. J Neurochem (1997) 68:1304–11 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.68031304.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Chabrashvili T, Kitiyakara C, Blau J. Effects of ANGII type 1 and 2 receptors on oxidative stress, renal NADPH oxidase, and SOD expression. Am J Physiol (2003) 285:R117–24 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rey P, Parga JA, Munoz A, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Brain angiotensin enhances dopaminergic cell death via microglial activation and NADPH-derived ROS. Neurobiol Dis (2008) 31:58–73 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Jenkins TA, Wong JY, Howells DW, Mendelsohn FA, Chai SY. Effect of chronic angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on striatal dopamine content in the MPTP-treated mouse. J Neurochem (1999) 73:214–9 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730214.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Munoz A, Rey P, Guerra MJ. Reduction of dopaminergic degeneration and oxidative stress by inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme in a MPTP model of parkinsonism. Neuropharmacology (2006) 51:112–20 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lopez-Real A, Rey P, Soto-Otero R, Mendez-Alvarez E, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition reduces oxidative stress and protects dopaminergic neurons in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of parkinsonism. J Neurosci Res (2005) 81:865–73 10.1002/jnr.20598 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Mertens B, Vanderheyden P, Michotte Y, Sarre S. The role of the central renin-angiotensin system in Parkinson’s disease. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst (2010) 11:49–56 10.1177/1470320309347789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Babior BM. NADPH oxidase. Curr Opin Immunol (2004) 16:42–7 10.1016/j.coi.2003.12.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Joglar B, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Rodriguez-Peres AI, Rey P, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. The inflammatory response in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease is mediated by brain angiotensin: relevance to progression of the disease. J Neurochem (2009) 109:656–69 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05999.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Rodriguez-Pallares J, Parga JA, Munoz A, Rey P, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Mechanism of 6-hydroxydopamine neurotoxicity: the role of NADPH oxidase and microglial activation in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. J Neurochem (2007) 103:145–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Okamura A, Rakugi H, Ohishi M, Yanagitani Y, Takiuchi S, Moriguchi K, et al. Upregulation of renin-angiotensin system during differentiation of monocytes to macrophages. J Hypertens (1999) 17:537–45 10.1097/00004872-199917040-00012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Mertens B, Varcin M, Michotte Y, Sarre S. The neuroprotective action of candesartan is related to interference with the early stages of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death. Eur J Neurosci (2011) 34:1141–8 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07840.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Rodriguez-Perez AI, Valenzuela R, Joglar B, Garrido-Gil P, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Renin angiotensin system and gender differences in dopaminergic degeneration. Mol Neurodegener (2011) 6:58–70 10.1186/1750-1326-6-58 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Rodriguez-Perez AI, Valenzuela R, Villar-Cheda B, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Dopaminergic neuroprotection of hormonal replacement therapy in young and aged menopausal rats: role of the brain angiotensin system. Brain (2012) 135:124–38 10.1093/brain/awr320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Garrido-Gil P, Joglar B, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Involvement of PPAR-gamma in the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of angiotensin type 1 receptor inhibition: effects of the receptor antagonist telmisartan and receptor deletion in a mouse MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation (2012) 9:38. 10.1186/1742-2094-9-38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Grammatopoulos TN, Jones SM, Ahmadi FA, Hoover BR, Snell LD, Skoch J, et al. Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist losartan, reduces MPTP-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. Mol Neurodegener (2007) 2:1. 10.1186/1750-1326-2-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Rey P, Lopez-Real A, Sanchez-Iglesias S, Munoz A, Soto-Otero R, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Angiotensin type-1-receptor antagonists reduce 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity for dopaminergic neurons. Neurobiol Aging (2007) 28:555–67 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.02.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Becker C, Jick SS, Meier CR. Use of antihypertensives and the risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology (2008) 70:438–44 10.1212/01.wnl.0000303818.38960.44 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sarma GR, Kamath V, Mathew T, Roy AK. A case of Parkinsonism worsened by losartan: a probable new adverse effect. Mov Disord (2008) 23:1055. 10.1002/mds.21945 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Grady EF, Sechi LA, Griffin CA, Schambelan M, Kalinyak JE. Expression of AT2 receptors in the developing rat fetus. J Clin Invest (1991) 88:921–33 10.1172/JCI115395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C. Distribution of angiotensin II type-2 receptor (AT2) mRNA expression in the adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol (1996) 373:322–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Nielsen AH, Schauser K, Winther H, Dantzer V, Poulsen K. Angiotensin II receptors and renin in the porcine uterus: myometrial AT2 and endometrial AT1 receptors are down-regulated during gestation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol (1997) 24:309–14 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1997.tb01193.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Song K, Allen AM, Paxinos G, Mendelsohn FA. Mapping of angiotensin II receptor subtype heterogeneity in rat brain. J Comp Neurol (1992) 316:467–84 10.1002/cne.903160407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Nuyt AM, Lenkei Z, Palkovits M, Corvol P, Llorens-Cortes C. Ontogeny of angiotensin II type 2 receptor mRNA expression in fetal and neonatal rat brain. J Comp Neurol (1999) 407:193–206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Cote F, Do TH, Laflamme I, Gallo JM, Gallo-Payet N. Activation of the AT(2) receptor of angiotensin II induces neurite outgrowth and cell migration in microexplant cultures of the cerebellum. J Biol Chem (1999) 274:31686–92 10.1074/jbc.274.44.31686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Li J, Culman J, Hortnagl H, Zhao Y, Gerova N, Timm M, et al. Angiotensin AT2 receptor protects against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury. FASEB J (2005) 19:617–9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Rodriguez-Pallares J, Quiroz CR, Parga JA, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Angiotensin II increases differentiation of dopaminergic neurons from mesencephalic precursors via angiotensin type 2 receptors. Eur J Neurosci (2004) 20:1489–98 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03621.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Sohn HY, Raff U, Hoffmann A, Gloe T, Heermeier TK, Galle J, et al. Differential role of angiotensin II receptor subtypes on endothelial supraoxide formation. Br J Pharmacol (2000) 131:667–72 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703566 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Ge J, Barnes NM. Alterations in angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptor subtype levels in brain regions from patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Pharmacol (1996) 297:299–306 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00762-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Garrido-Gil P, Valenzuela R, Villar-Cheda B, Lanciego JL, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Expression of angiotensinogen and receptors for angiotensin and prorenin in the monkey and human substantia nigra: an intracellular renin-angiotensin system in the nigra. Brain Struct Funct (2012) 218:373–88 10.1007/s00429-012-0402-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Labandeira-Garcia JL, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Villar-Cheda B, Rodriguez-Perz AI, Garrido-Gil P, Guerra MJ. Aging, angiotensin system and dopaminergic degeneration in the substantia nigra. Aging Dis (2011) 2:257–74 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Villar-Cheda B, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Valenzuela R, Munoz A, Guerr MJ, Baltatu OC, et al. Nigral and striatal regulation of angiotensin receptor expression by dopamine and angiotensin in rodents: implications for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci (2010) 32:1695–706 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07448.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rodriguez-Perez AI, Valenzuela R, Villar-Cheda B, Guerra MJ, Lanciego JL, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Estrogen and angiotensin interaction in the substantia nigra. Relevance to postmenopausal Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol (2010) 224:517–26 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Villar-Cheda B, Valenzuela R, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Aging-related changes in the nigral angiotensin system enhances proinflammatory and pro-oxidative markers and 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic degeneration. Neurobiol Aging (2012) 33(204):e1–11 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.08.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Rodriguez-Perez AI, Dominquez-Meijide A, Lanciego JL, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Dopaminergic degeneration is enhanced by chronic brain hypoperfusion and inhibited by angiotensin receptor blockage. Age (Dordr) (2012) 35:1675–90 10.1007/s11357-012-9470-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Grammatopoulos TN, Outeiro TF, Hyman BT, Standaert DG. Angiotensin II protects against α-synuclein toxicity and reduces protein aggregation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2007) 363:846–51 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.09.043 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Benoist CC, Wright JW, Zhu M, Appleyard SM, Wayman GA, Harding JW. Facilitation of hippocampal synaptogenesis and spatial memory by C-terminal truncated Nle1-angiotensin IV analogues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2011) 339:35–44 10.1124/jpet.111.182220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Kawas LH, Yamamoto BJ, Wright JW, Harding JW. Mimics of the dimerization domain of hepatocyte growth factor exhibit anti-Met and anticancer activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2011) 339:509–18 10.1124/jpet.111.185694 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Kawas LH, McCoy AT, Yamamoto BJ, Wright JW, Harding JW. Development of angiotensin IV analogs as hepatocyte growth factor/met modifiers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2012) 340:539–48 10.1124/jpet.111.188136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.McCoy AT, Benoist CC, Kawas LH, Bule J, Zhu M, Appleyard SM, et al. Evaluation of metabolically stabilized angiotensin IV analogs as pro-cognitive/anti-dementia agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2012) 344:141–54 10.1124/jpet.112.199497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Collier TJ, Kipton J, Daley F, Palfi S, Chu Y, Sortwell C, et al. Aging-related changes in the nigrostriatal dopamine system and the response to MPTP in nonhuman primates: diminished compensatory mechanisms as a prelude to parkinsonism. Neurobiol Dis (2007) 26:56–65 10.1016/j.nbd.2006.11.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Cruz-Muros I, Afonso-Oramas D, Abreu P, Perez-Delgado MM, Rodriguez M, Gonsalez-Hernandez T. Aging effects on the dopamine transporter expression and compensatory mechanisms. Neurobiol Aging (2009) 30:973–86 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Wu DC, Jackson-Lewis V, Vila M, Tieu K, Teismann P, Vadseth C, et al. Blockade of microglial activation is neuroprotective in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Neurosci (2002) 22:1763–71 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Zawada WM, Banninger BP, Thornton J, Marriott B, Cantu D, Rachubinski AL, et al. Generation of reactive oxygen species in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) treated dopaminergic neurons occurs as an NADPH oxidase-dependent two-wave cascade. J Neuroinflammation (2011) 8:129. 10.1186/1742-2094-8-129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Kramár EA, Krishnan R, Harding JW, Wright JW. Role of nitric oxide in angiotensin IV-induced increases in cerebral blood flow. Regul Pept (1998) 74:185–92 10.1016/S0167-0115(98)00039-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Qin L, Liu Y, Wang T, Wei SJ, Block ML, Wilson B, et al. NADPH oxidase mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity and proinflammatory gene expression in activated microglia. J Biol Chem (2004) 279:1415–21 10.1074/jbc.M307657200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Seshiah PN, Weber DS, Rocic P, Valppu L, Taniyama Y, Griendlilng KK. Angiotensin II stimulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity: upstream mediators. Circ Res (2002) 91:406–13 10.1161/01.RES.0000033523.08033.16 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Touyz RM, Chen X, Tabet F, Yao G, He G, Quinn MT, et al. Expression of a functionally active gp91 phox-containing neutrophil-type NAD(P)H oxidase in smooth muscle cells from human resistance arteries: regulation by angiotensin II. Circ Res (2002) 90:1205–13 10.1161/01.RES.0000020404.01971.2F [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Stragier B, De Bundel D, Sarre S, Smolders I, Vauguelin G, Dupont A, et al. Involvement of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase in the effects of the renin-angiotensin fragment angiotensin IV: a review. Heart Fail Rev (2008) 13:321–37 10.1007/s10741-007-9062-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Stragier B, Sarre S, Vanderheyden P, Vauquelin G, Fournie-Zaluski MC, Ebinger G, et al. Metabolism of angiotensin II is required for its in vivo effect on dopamine release in the striatum of the rat. J Neurochem (2004) 90:1251–7 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02600.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Yamamoto BJ, Elias PD, Masino JA, Hudson BD, McCoy AT, Anderson ZJ, et al. The angiotensin IV analog Nle-Tyr-Leu-psi-(CH2-NH2)3-4-His-Pro-Phe (norleual) can act as a hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (2010) 333:161–73 10.1124/jpet.109.161711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Kawas LH, Benoist CC, Harding JW, Wayman GA, Abu-Lail NI. (2012). Available from: http://www.nanomedjournal.com/article/S1549-9634(12)00522-9/abstract [DOI] [PubMed]
- 149.Dalmay F, Pesteil F, Allard J, Nisse-Durgeat S, Fernandez L, Fournier A. Angiotensin IV decreases acute stroke mortality in the gerbil. Hypertension (2001) 14:56A. 10.1016/S0895-7061(01)01592-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Kramár EA, Harding JW, Wright JW. Angiotensin II- and IV-induced changes in cerebral blood flow. Roles of AT1, AT2, and AT4 receptor subtypes. Regul Pept (1997) 68:131–8 10.1016/S0167-0115(96)02116-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Naveri L, Stromberg C, Saavedra JM. Angiotensin IV reverses the acute cerebral blood flow reduction after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (1994) 14:1096–9 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Nakamura T, Muzuno S, Matsumoto K, Sawa Y, Matsuda H, Nakamura T. Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by endogenous and exogenous HGF. J Clin Invest (2000) 106:1511–9 10.1172/JCI10226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Morishita R, Nakamura S, Hayashi S, Taniyama Y, Moriguchi A, Nagano T, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis induced by human recombinant hepatocyte growth factor in rabbit hind limb ischemia model as cytokine supplement therapy. Hypertension (1999) 33:1379–84 10.1161/01.HYP.33.6.1379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Van Belle E, Witzenbichler B, Chen D, Silver M, Chang L, Schwall R, et al. Potentiated angiogenic effect of scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor via induction of vascular endothelial growth factor: the case for paracrine amplification of angiogenesis. Circulation (1998) 97:381–90 10.1161/01.CIR.97.4.381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Miyazawa T, Matsumoto K, Ohmichi H, Katoh H, Yamashima T, Hakamura T. Protection of hippocampal neurons from ischemia-induced delayed neuronal death by hepatocyte growth factor: a novel neurotrophic factor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab (1998) 18:345–8 10.1097/00004647-199804000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Tsuzuki N, Miyazawa T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Shima K. Hepatocyte growth factor reduces the infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurol Res (2001) 23:417–24 10.1179/016164101101198659 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Date I, Takagi N, Takagi K, Kago T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced learning dysfunction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2004) 319:1152–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Date I, Takagi N, Takagi K, Kago T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor improved learning and memory dysfunction of microsphere-embolized rats. J Neurosci Res (2004) 78:442–53 10.1002/jnr.20263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Shimamura M, Sato N, Waguri S, Uchiyama Y, Hayashi T, Iida H, et al. Gene transfer of hepatocyte growth factor gene improves learning and memory in the chronic stage of cerebral infarction. Hypertension (2006) 47:742–51 10.1161/01.HYP.0000208598.57687.3e [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Faure S, Chapot R, Tallet D, Javellaud J, Achard JM, Oudart N. Cerebroprotective effect of angiotensin IV in experimental ischemic stroke in the rat mediated by AT(4) receptors. J Physiol Pharmacol (2006) 57:329–42 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Kurtz TW, Klein U. Next generation multifunctional angiotensin receptor blockers. Hypertens Res (2009) 32:826–34 10.1038/hr.2009.135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Siragy HM. Comparing angiotensin II receptor blockers on benefits beyond blood pressure. Adv Ther (2010) 27:257–84 10.1007/s12325-010-0028-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Fournier A, Oprisiu-Fournier R, Serot JM, Godefroy O, Achard JM, Faure S, et al. Prevention of dementia by antihypertensive drugs: how AT1-receptor-blockers and dihydropyridines better prevent dementia in hypertensive patients than thiazides and ACE-inhibitors. Expert Rev Neurother (2009) 9:1413–31 10.1586/ern.09.89 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Shah K, Qureshi SU, Johnson M, Parikh N, Schulz PE, Kunik ME. Does use of antihypertensive drugs affect the incidence or progression of dementia? A systematic review. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother (2009) 7:250–61 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2009.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Fournier A, Messerti FH, Achard JM, Fernandez I. Cerebroprotection mediated by angiotensin II: a hypothesis supported by recent randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol (2004) 43:1343–7 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.10.060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Galletti F, Cupini LM, Corbelli I, Calabresi P, Sarchielli P. Pathophysiological basis of migraine prophylaxis. Prog Neurobiol (2009) 89:176–92 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Gupta M, Honos GN, Velazquez EJ, Chung N, Oigman W, Maggioni AP. Evidence for the efficacy of ARBs across the cardiovascular continuum. Curr Med Res Opin (2010) 26:1203–18 10.1185/03007991003712159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Hoogwerf BJ. Renin-angiotensin system blockade and cardiovascular and renal protection. Am J Cardiol (2010) 105(Suppl):30A–5A 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.10.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Woo KT, Wong KS, Chan CM. Clinical trials of the past decade in the management of chronic kidney disease. Rev Recent Clin Trials (2009) 4:159–62 10.2174/157488709789957646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Cat AN, Touyz RM. A new look at the renin-angiotensin system – focusing on the vascular system. Peptides (2011) 32:2141–50 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Steckelings UM, Rompe F, Kaschina E, Unger T. The evolving story of the RAAS in hypertension, diabetes and CV disease – moving from macrovascular to microvascular targets. Fundam Clin Pharmacol (2009) 23:693–703 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00780.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wright JW, Harding JW. Importance of the brain angiotensin system in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis (2012) 2012:860923. 10.1155/2012/860923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Wright JW, Harding JW. The brain renin-angiotensin system: a diversity of functions and implications for CNS diseases. Pflugers Arch (2013) 465:133–51 10.1007/s00424-012-1102-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Kerins DM, Hao Q, Baughan DE. Angiotensin induction of PAI-1 expression in endothelial cells is mediated by the hexapeptide angiotensin IV. J Clin Invest (1995) 96:2515–20 10.1172/JCI118312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Korhonen L, Sjoholm U, Takei N, Kern MA, Schirmacher P, Castren E, et al. Expression of c-Met in developing rat hippocampus: evidence for HGF as a neurotrophic factor for calbindin D-expressing neurons. Eur J Neurosci (2000) 12:3453–61 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00260.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Matzke A, Sargsyan V, Holtmann B, Aramuni G, Asan E, Sendtner M, et al. Haplo insufficiency of c-Met in cd44-/- mice identifies a collaboration of CD44 and c-Met in vivo. Mol Cell Biol (2007) 27:8797–806 10.1128/MCB.01355-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Olson ML, Olson EA, Qualls JH, Stratton JJ, Harding JW, Wright JW. Norleucine1-angiotensin IV alleviates mecamylamine-induced spatial memory deficits. Peptides (2004) 25:233–41 10.1016/j.peptides.2003.12.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]