Abstract
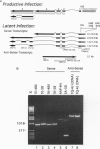
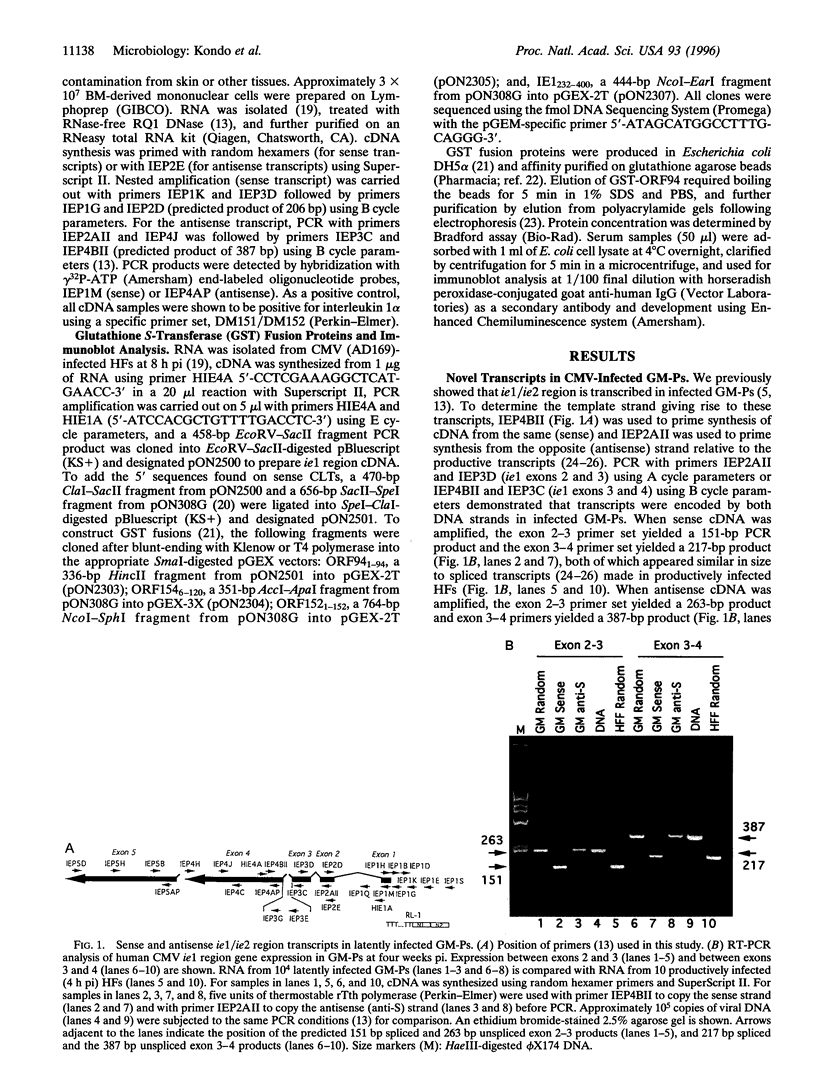
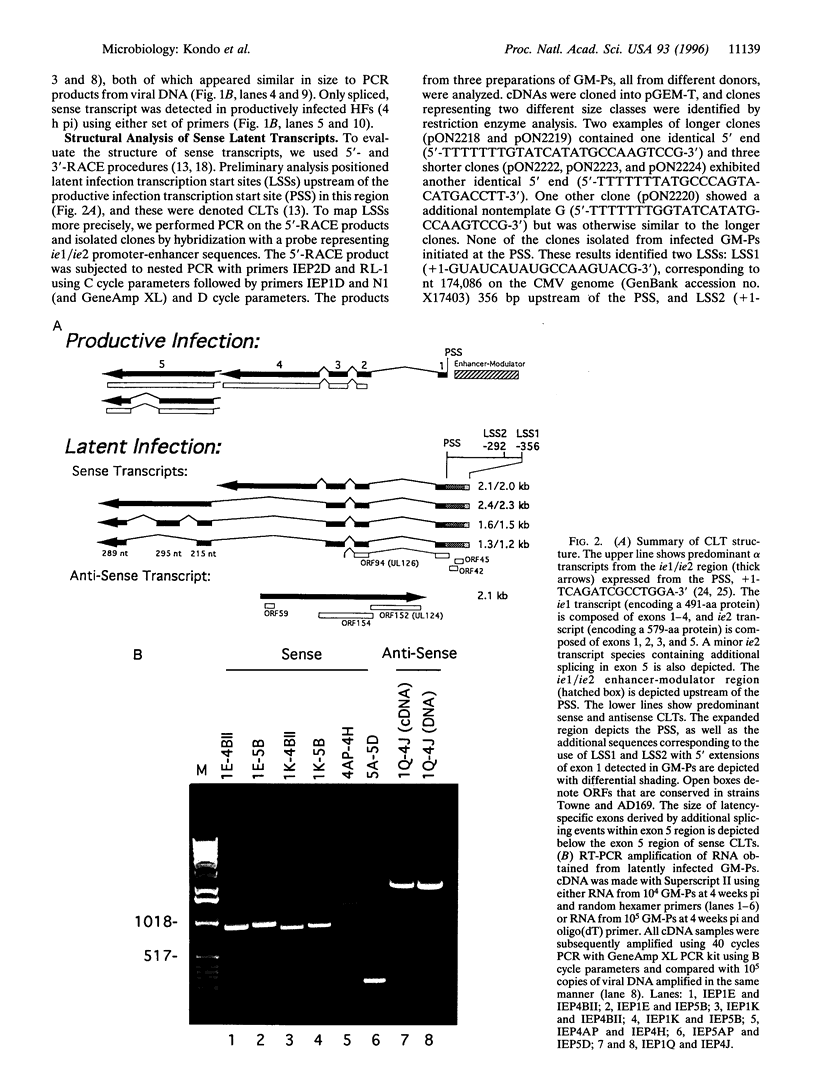
Following infection with cytomegalovirus, human granulocyte-macrophage progenitors carry the viral genome but fail to support productive replication. Viral transcripts arise from a region encompassing the major regulatory gene locus; however, their structure differs significantly from productive phase transcripts. One class, sense transcripts, is encoded in the same direction as productive phase transcripts but uses two novel start sites in the ie1/ie2 promoter/enhancer region. These transcripts have the potential to encode a novel 94 aa protein. The other class, antisense transcript, is unspliced and complimentary to ie1 exons 2-4, and has the potential to encode novel 154 and 152 aa proteins. Consistent with a role in latency, these transcripts are present in bone marrow aspirates from naturally infected, healthy seropositive donors but are not present in seronegative controls. Sense latent transcripts are present in a majority of seropositive individuals. Consistent with the expression of latent transcripts, antibody to the 94 aa and 152 aa proteins is detectable in the serum of seropositive individuals. Thus, latent infection by cytomegalovirus is accompanied by the presence of latency-associated transcripts and expression of immunogenic proteins. Overall, these results suggest that bone marrow-derived myeloid progenitors are an important natural site of viral latency.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baines P., Masters G., Booth M., Jacobs A. Enrichment of progenitor cells from human marrow. Exp Hematol. 1987 Aug;15(7):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan I. S., Daw R. A., Day P. J., Ala F. A., Walker M. R. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of human cytomegalovirus infection in a blood donor population. Br J Haematol. 1991 May;78(1):94–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1991.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumik D., Yang B., Trangas T., Bartlett J. S., Coleman M. S., Sorscher D. H. Identification of a tripartite basal promoter which regulates human terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15861–15867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangioni J. V., Neel B. G. Solubilization and purification of enzymatically active glutathione S-transferase (pGEX) fusion proteins. Anal Biochem. 1993 Apr;210(1):179–187. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerry J. A., Sehgal A., Barlow S. W., Cavanaugh V. J., Fish K., Nelson J. A., Stenberg R. M. Isolation and characterization of a low-abundance splice variant from the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1995 Jun;69(6):3868–3872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.6.3868-3872.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Kaneshima H., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus latent infection of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11879–11883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Mocarski E. S. Cytomegalovirus latency and latency-specific transcription in hematopoietic progenitors. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1995;99:63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minton E. J., Tysoe C., Sinclair J. H., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus infection of the monocyte/macrophage lineage in bone marrow. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):4017–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.4017-4021.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Dorit R. L., Gilbert W. One-sided polymerase chain reaction: the amplification of cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plachter B., Britt W., Vornhagen R., Stamminger T., Jahn G. Analysis of proteins encoded by IE regions 1 and 2 of human cytomegalovirus using monoclonal antibodies generated against recombinant antigens. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):642–652. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood lymphocytes in a natural infection. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2997930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorscher D. H., Yang B., Bhaumik D., Trangas T., Philips A. V., Chancellor K. E., Coleman M. S. Initiation of transcription at the human terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase gene promoter: a novel role for the TATA binding protein. Biochemistry. 1994 Sep 13;33(36):11025–11032. doi: 10.1021/bi00202a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Insertion and deletion mutagenesis of the human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7213–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. The alpha sequence of the cytomegalovirus genome functions as a cleavage/packaging signal for herpes simplex virus defective genomes. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):817–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.817-824.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier P., Kitchen A. D., Taylor D. L., Tyms A. S. Detection of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral mononuclear cells and urine samples using PCR. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Feb;6(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Sequence of protein synthesis in cells infected by human cytomegalovirus: early and late virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):686–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.686-701.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Wiedeman J., Sissons J. G., Borysiewicz L. K., Sinclair J. H. Monocytes are a major site of persistence of human cytomegalovirus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2059–2064. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Wiedeman J., Sissons P., Sinclair J. Induction of endogenous human cytomegalovirus gene expression after differentiation of monocytes from healthy carriers. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1597–1604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1597-1604.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Promoter-regulatory region of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Temporal regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription at immediate early and early times after infection. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):446–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.446-459.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Laer D., Meyer-Koenig U., Serr A., Finke J., Kanz L., Fauser A. A., Neumann-Haefelin D., Brugger W., Hufert F. T. Detection of cytomegalovirus DNA in CD34+ cells from blood and bone marrow. Blood. 1995 Dec 1;86(11):4086–4090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]