Abstract
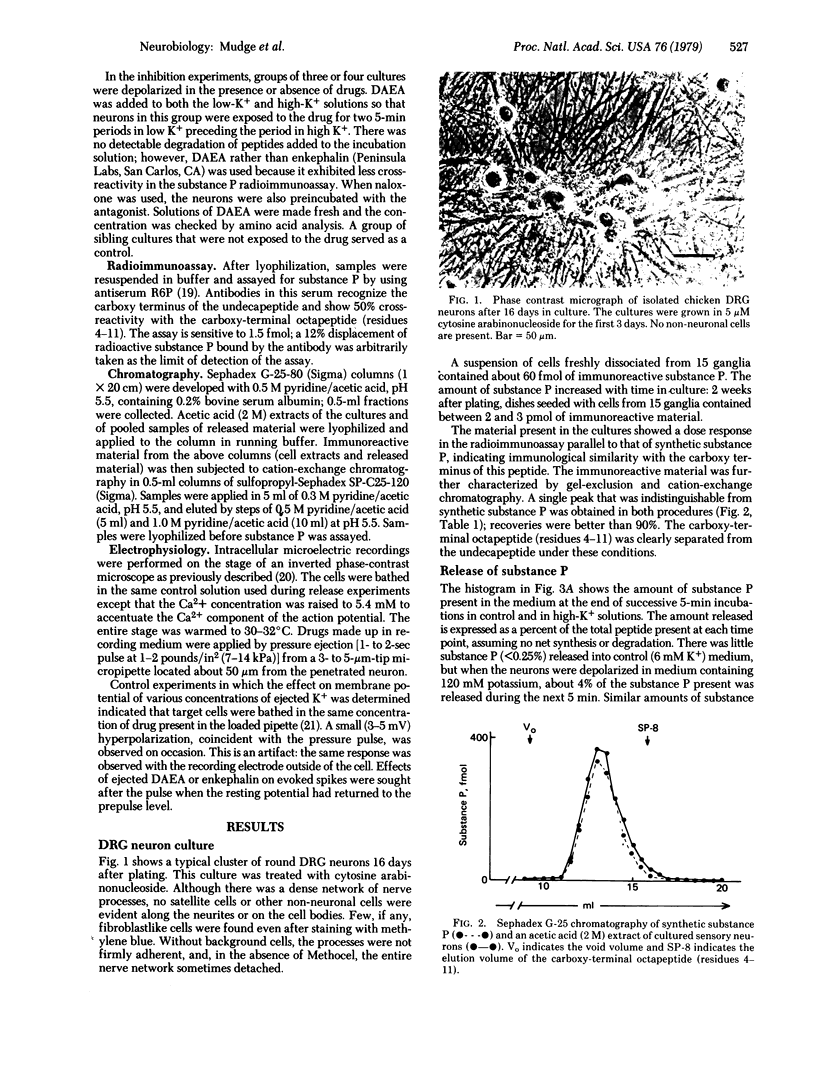
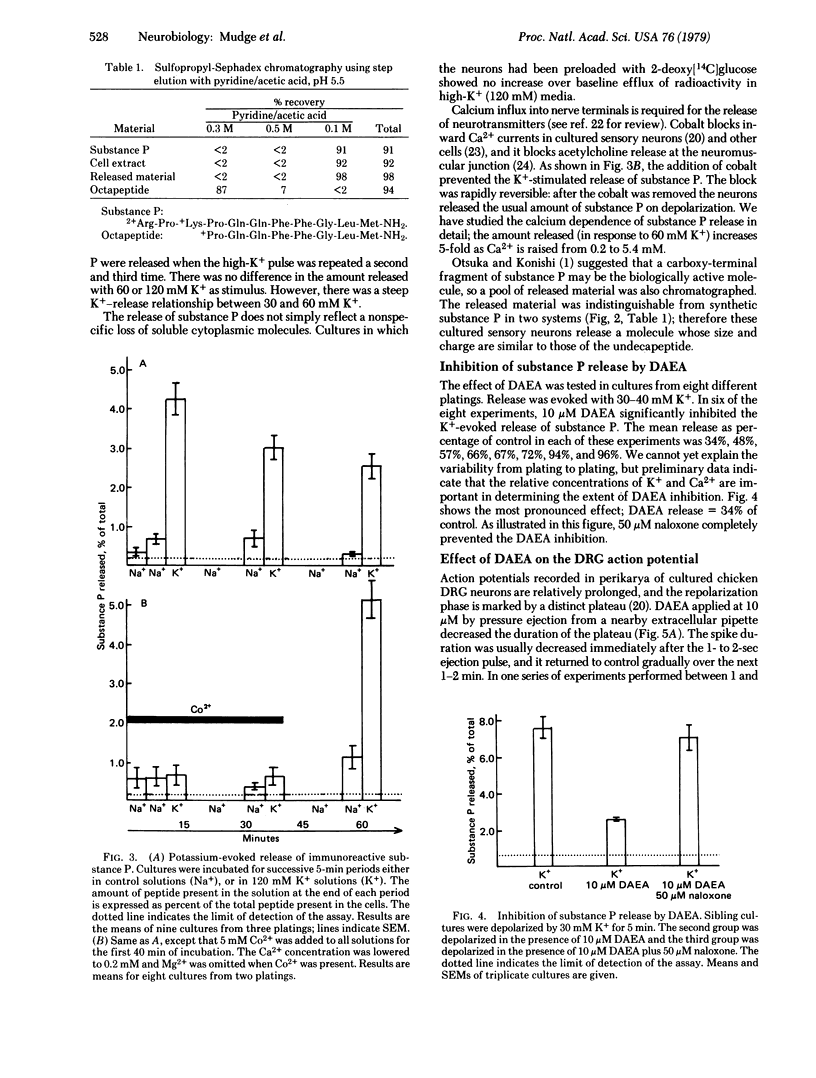
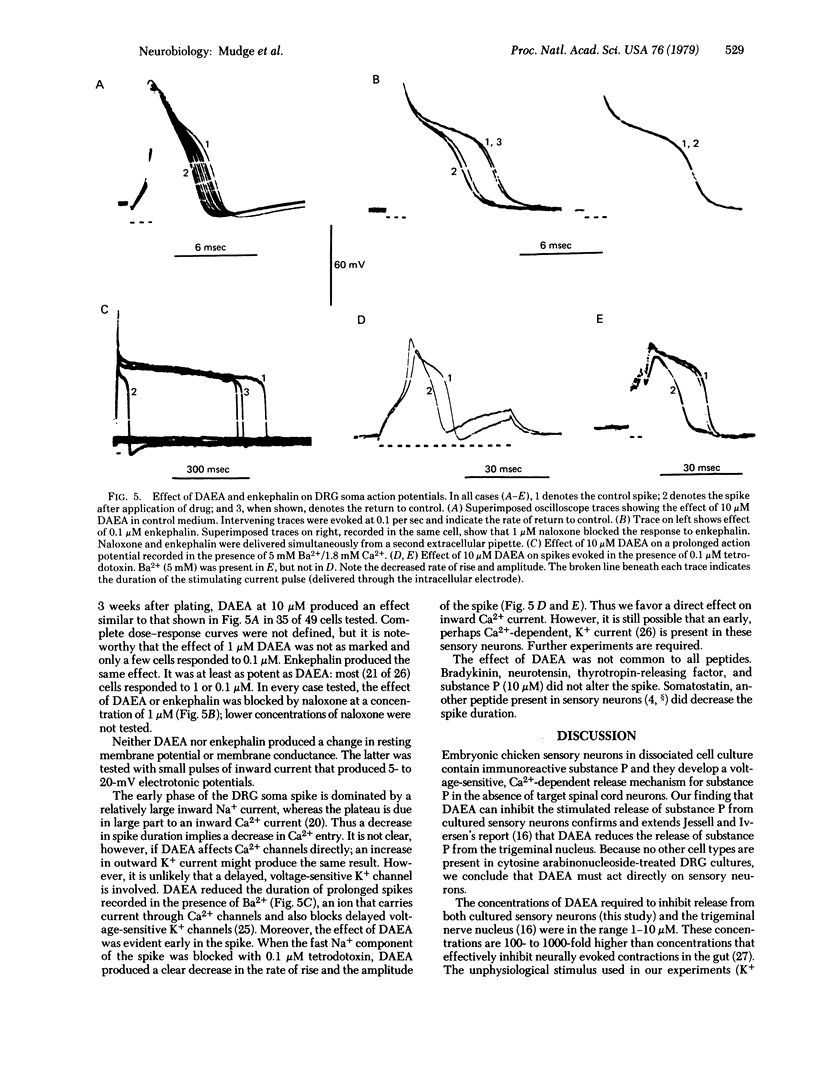
Sensory neurons grown in dispersed cell culture in the absence of non-neuronal cell types contain immunoreactive substance P that is chemically similar to synthetic substance P. When depolarized in high-K+ media (30-120 mM), the neurons release this peptide by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism. An enkephalin analogue, [D-Ala2]enkephalin amide, at 10 micron inhibits the K+-evoked release of substance P. At the same or lower concentrations, [D-Ala2]enkephalin amide and enkephalin decrease the duration of the Ca2+ action potential evoked and recorded in dorsal root ganglion cell bodies without affecting the resting membrane potential or resting membrane conductance. This modulation of voltage-sensitive channels may account for the inhibition of substance P release.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dichter M. A., Fischbach G. D. The action potential of chick dorsal root ganglion neurones maintained in cell culture. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(2):281–298. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Hall J. G., Headley P. M. Enkephalins and dorsal horn neurones of the cat: effects on responses to noxious and innocuous skin stimuli. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;61(3):399–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D. Synapse formation between dissociated nerve and muscle cells in low density cell cultures. Dev Biol. 1972 Jun;28(2):407–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. L. Effects of substance P on functionally identified units in cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):439–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90965-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M. Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antogonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;53(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elde R., Johansson O., Luft R., Nilsson G., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for separate populations of somatostatin-containing and substance P-containing primary afferent neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Kandel E. R. Presynaptic modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ current: mechanism for behavioral sensitization in Aplysia californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3512–3516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Nelson P. G. Specific-opiate-induced depression of transmitter release from dorsal root ganglion cells in culture. Science. 1978 Mar 31;199(4336):1449–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.204015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Tonini M. The mechanism of action of narcotic analgesics in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Dec;61(4):541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Release of substance P-like immunoreactivity from isolated spinal cord of newborn rat. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):83–84. doi: 10.1038/264083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Konishi S. Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:135–143. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Reis D. J., Leeman S. E. Ultrastructural localization of substance P in neurons of rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 25;122(3):534–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90463-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randić M., Miletić V. Effect of substance P in cat dorsal horn neurones activated by noxious stimuli. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 3;128(1):164–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnakre J., Tauc L. Calcium influx in active Aplysia neurones detected by injected aequorin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio242113b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Konishi S., Powell D., Leeman S. E., Otsuka M. Identification of the motoneuron-depolarizing peptide in bovine dorsal root as hypothalamic substance P. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Nomura J., Shooter E. M. The isolation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein in a high molecular weight form. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2202–2209. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. Graded and all-or-none electrogenesis in arthropod muscle. II. The effects of alkali-earth and onium ions on lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:997–1027. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakly J. N. The action of cobalt ions on neuromuscular transmission in the frog. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):597–612. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Bayerl H. The mechanism of inhibition of neuronal activity by opiates in the spinal cord of cat. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):111–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90826-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



