Abstract
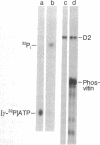
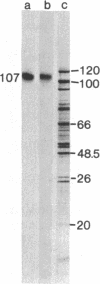
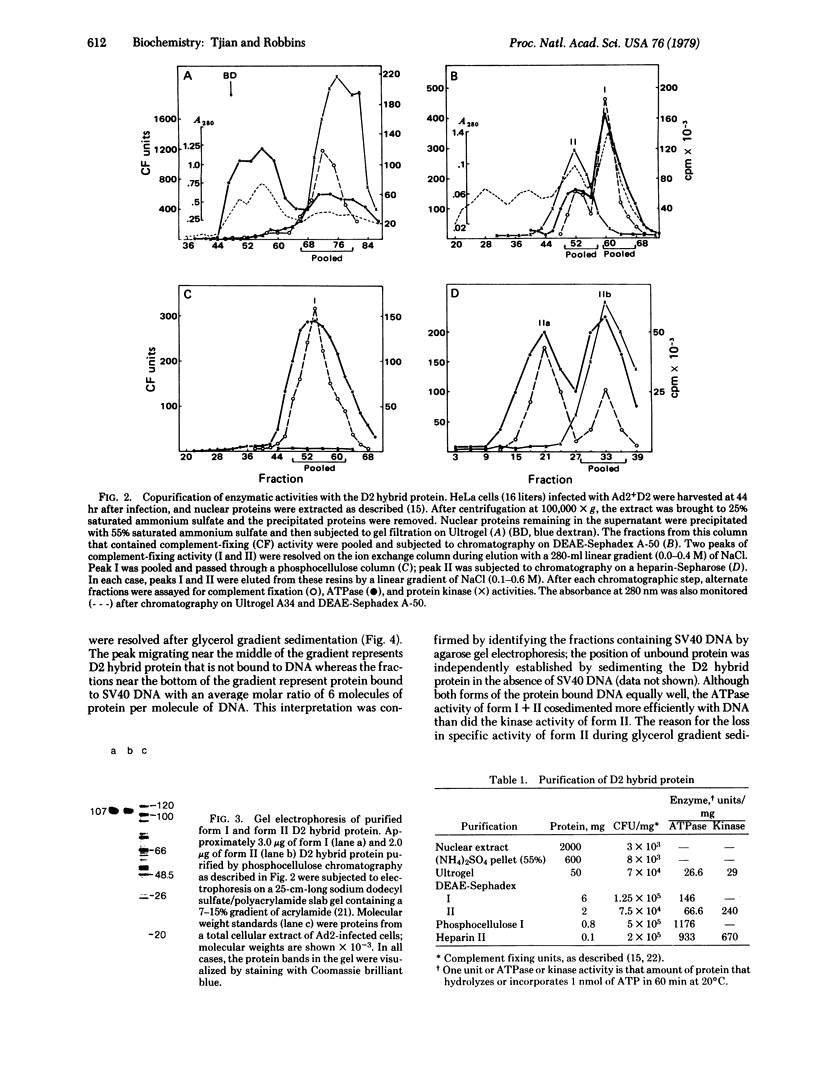
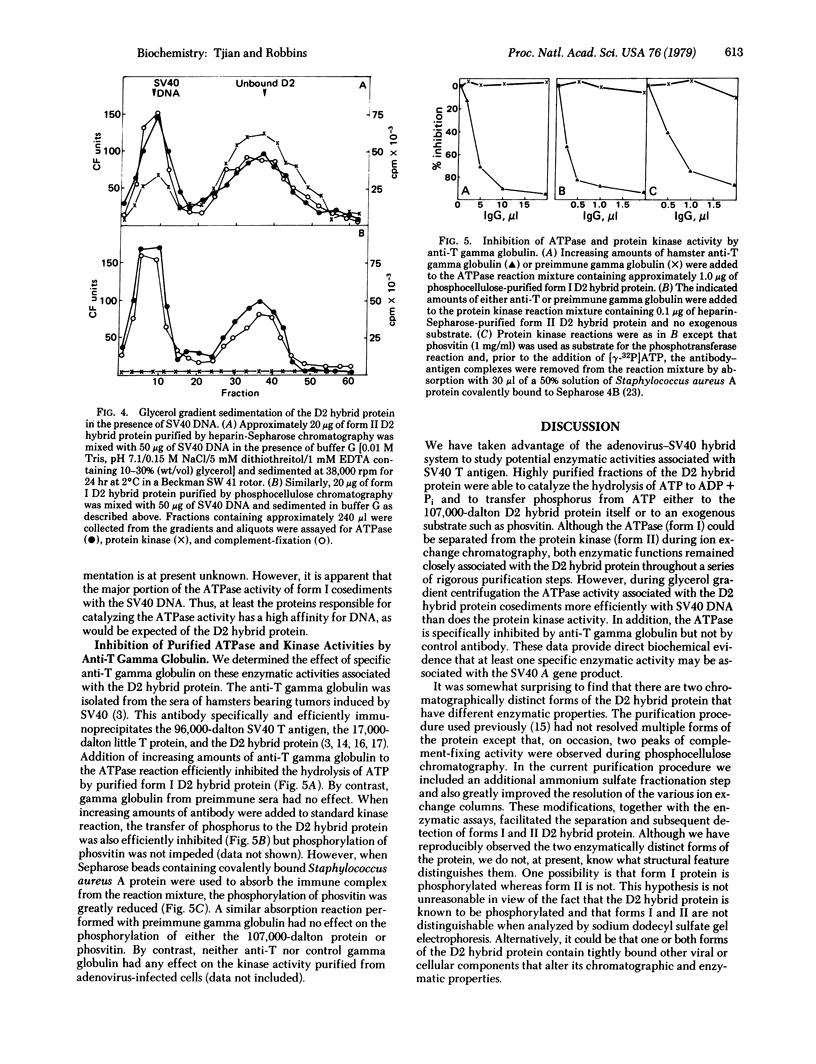
A protein antigenically related to the simian virus (SV 40) A gene product has been purified to near homogeneity from cells infected with the adenovirus-SV 40 hybrid virus Ad2+D2 and shown to contain ATPase (ATP phosphohydrolase, EC 3.6.1.3) and protein kinase (ATP:phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37) activity. Both enzymatic activities copurify with the protein through six stages including one gel filtration column, two ion exchange columns, and a heparin affinity column. Analogous fractions from extracts of cells uninfected or infected with adenovirus 2 alone do not contain these enzymatic activities. The D2 hybrid protein resolves into two forms (I and II) during ion exchange chromatography. Form I, the major species (85%) of the D2 hybrid protein, elutes from DEAE-Sephadex in 0.37 M NaCl and is able to catalyze the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + Pi at a rate of 3 μmol/hr per mg. The remaining 10-15% of the D2 hybrid protein consists of form II which elutes from DEAE-Sephadex in 0.29 M NaCl and is able to hydrolyze ATP as well as to incorporate phosphorus from ATP into either the D2 hybrid protein itself or other protein acceptors such as phosvitin. Although both forms are able to bind DNA, the ATPase activity of form I cosediments with SV 40 DNA more efficiently than does the protein kinase activity of form II during glycerol gradient centrifugation. The ATPase activity of form I is efficiently inhibited by addition of anti-T gamma globulin to the reaction mixture whereas control gamma globulin has no effect. Similarly, the phosphorylation of the D2 hybrid protein by form II is inhibited by anti-T gamma globulin. By contrast, phosphorylation of phosvitin is specifically inhibited by antibody only when the immune complex is removed from the reaction mixture. Thus, it appears likely that one and possibly two enzymatic activities are carried out by the D2 hybrid protein. These findings are discussed in terms of mechanisms of SV 40 DNA replication and virally induced transformation.
Keywords: adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid, D2 hybrid protein, ATPase, protein kinase, antibody inhibition
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Roberts J. M., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. A map of cytoplasmic RNA transcripts from lytic adenovirus type 2, determined by electron microscopy of RNA:DNA hybrids. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):819–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K., Tegtmeyer P., Anthony D. D. Relationship of replication and transcription of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1927–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell J. A., Lukanidin E., Fey G., Sambrook J. The structure and expression of two defective adenovirus 2/simian virus 40 hybrids. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):209–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Dulbecco R. A temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40 affecting transforming ability. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):529–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. The origin and destiny of adenovirus proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):581–590. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Topp W. C., Hanich R., Sambrook J. F. Mutants of SV40 with an altered small t protein are reduced in their ability to transform cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg B., Pollack R., Topp W., Botchan M. Isolation and characterization of T antigen-negative revertants from a line of transformed rat cells containing one copy of the SV40 genome. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Fey G., Graessmann A. Biological activity of purified simian virus 40 T antigen proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Stinchcomb D., Losick R. Antibody directed against Bacillus subtilis rho factor purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate slab gel electrophoresis. Effect on transcription by RNA polymerase in crude extracts of vegetative and sporulating cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8824–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner S., Wright M., Hurwitz J. Association of DNA-dependent and -independent ribonucleoside triphosphatase activities with dnaB gene product of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):783–787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]