Abstract
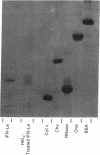
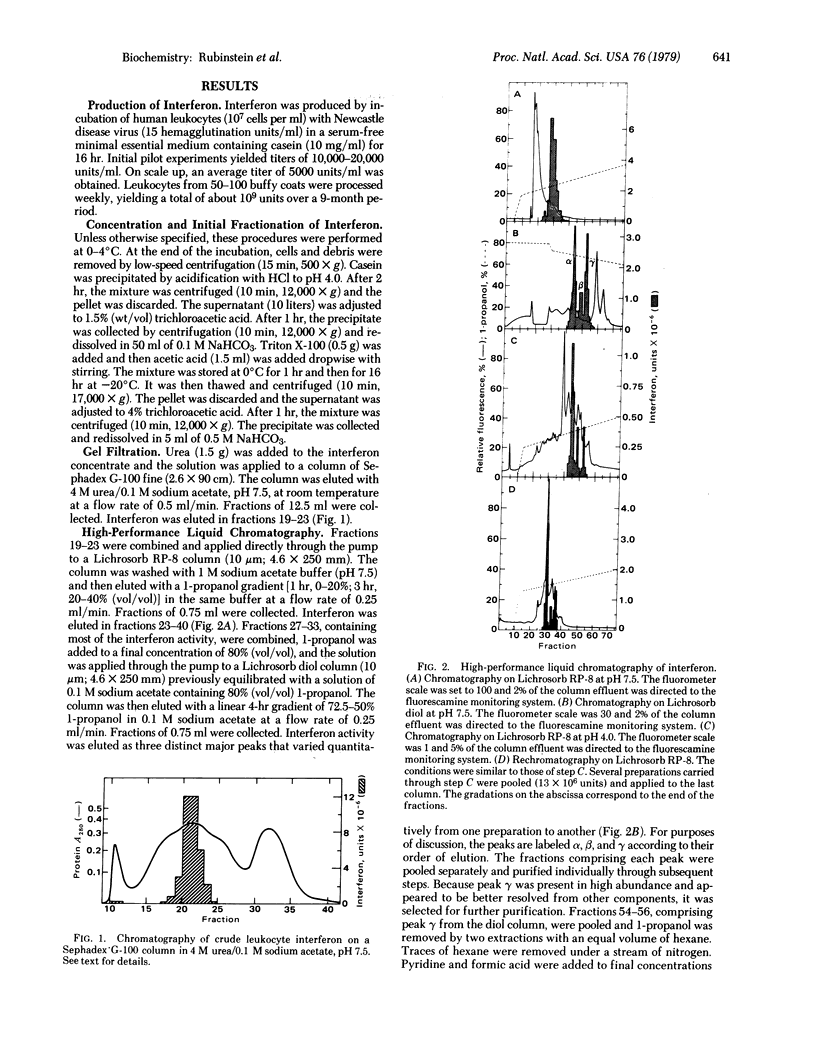
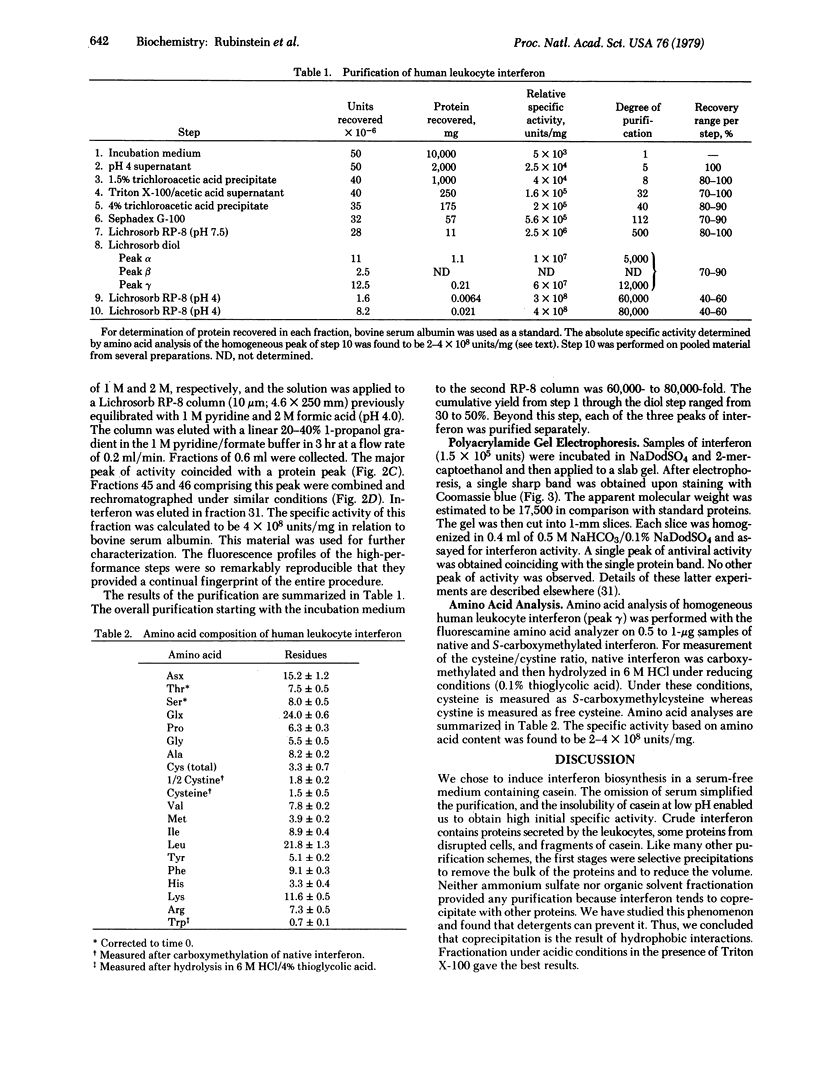
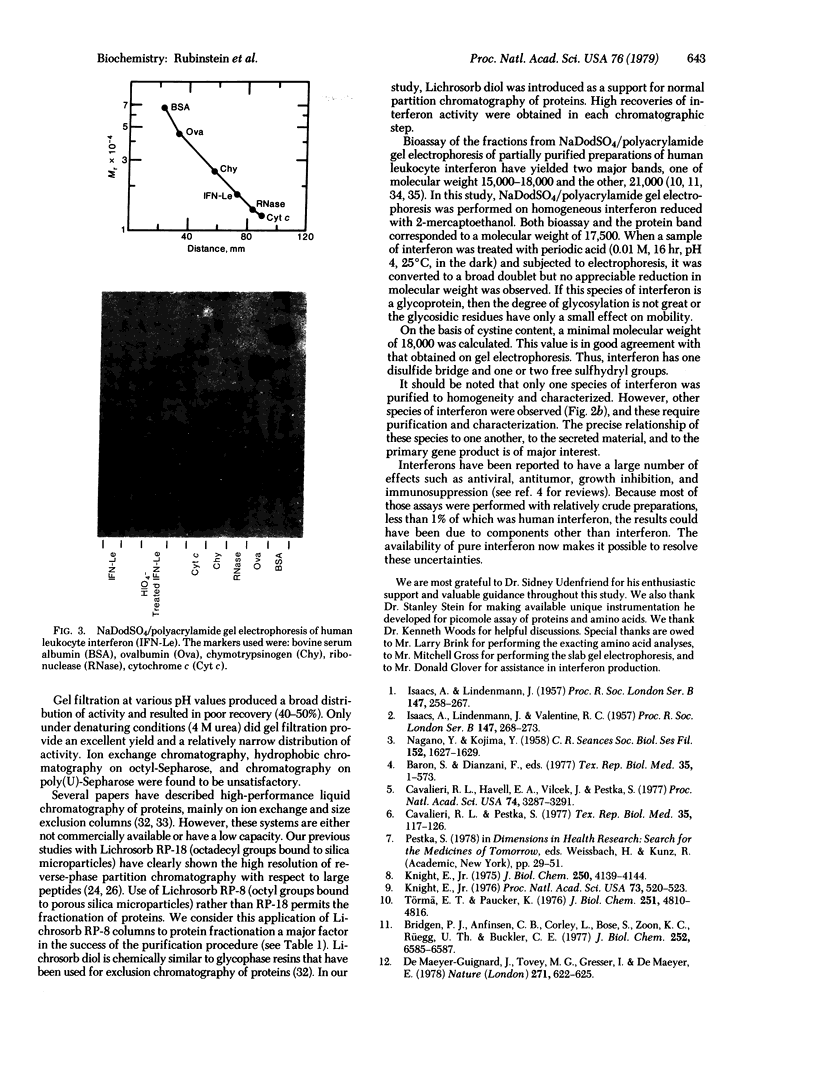
A method of fractionating proteins by high-performance liquid partition chromatography has been developed and used for isolation and purification to homogeneity of one of the species of human leukocyte interferon. The homogeneous interferon exhibited a sharp peak on high-performance liquid chromatography and a single narrow band on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol. Extraction of the gel gave a single sharp peak of antiviral activity coinciding with the protein band. The specific activity of pure interferon was found to be 2--4 X 10(8) units/mg, based on amino acid analysis. The molecular weight is 17,500--18,000.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B., Bose S., Corley L., Gurari-Rotman D. Partial purification of human interferon by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3139–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K., Ogburn C. A., Paucker K., Mogensen K. E., Cantell K. Affinity chromatography of human leukocyte and diploid cell interferons on sepharose-bound antibodies. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold W., Tan C., Tan Y. H. Purification and in vitro labeling of interferon from a human fibroblastoid cell line. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5206–5212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S., Gurari-Rotman D., Ruegg U. T., Corley L., Anfinsen C. B. Apparent dispensability of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon for antiviral activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1659–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Corley L., Bose S., Zoon K. C., Rüegg U. T., Buckler C. E. Human lymphoblastoid interferon. Large scale production and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6585–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Stone J., Udenfriend S. Automatic Monitoring of primary amines in preparative column effluents with fluorescamine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):438–445. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Tovell D. R. Substitution of milk for serum in the production fo human leukocyte interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):625–628. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.625-628.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. L., Havell E. A., Vilcek J., Pestka S. Synthesis of human interferon by Xenopus laevis oocytes: two structural genes for interferons in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. L., Pestka S. Synthesis of interferon in heterologous cells, cell-free extracts, and Xenopus laevis oocytes. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1977;35:117–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadha K. C., Sclair M., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular size heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):196–200. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Noel R., Regnier F. E. High speed ion exchange chromatography of proteins. Anal Chem. 1976 Nov;48(13):1839–1845. doi: 10.1021/ac50007a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human, mouse, and rabbit interferons with immobilized hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7620–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., LINDENMANN J., VALENTINE R. C. Virus interference. II. Some properties of interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Sep 12;147(927):268–273. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., LINDENMANN J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 Sep 12;147(927):258–267. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita M., Cabrer B., Taira H., Rebello M., Slattery E., Weideli H., Lengyel P. Purification of interferon from mouse Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Heterogeneity of purified mouse interferons. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4139–4144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Interferon: purification and initial characterization from human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):520–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGANO Y., KOJIMA Y. Inhibition de l'infection vaccinale par un facteur liquide dans le tissu infecté par le virus homologue. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1958;152(11):1627–1629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnier F. E., Noel R. Glycerolpropylsilane bonded phases in the steric exclusion chromatography of biological macromolecules. J Chromatogr Sci. 1976 Jul;14(7):316–320. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/14.7.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Gross M. S., Miller R. S., Waldman A. A., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon purified to homogeneity. Science. 1978 Dec 22;202(4374):1289–1290. doi: 10.1126/science.725605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Gerber L. D., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3052–3055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Isolation and characterization of the opioid peptides from rat pituitary: beta-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4969–4972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Böhlen P., Stone J., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Amino acid analysis with fluorescamine at the picomole level. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):202–212. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Desmyter J. Molecular heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon: two populations differing in molecular weights, requirements for renaturation, and cross-species antiviral activity. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Davey M. W., Carter W. A. Interaction of human interferons with immobilized hydrophobic amino acids and dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5381–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P., Pestka S. De novo synthesis and glycosylation of the MOPC-46B mouse immunoglobulin light chain in cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4474–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törmä E. T., Paucker K. Purification and characterization of human leukocyte interferon components. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4810–4816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F. Virus replication and high-titered interferon production in human leukocyte cultures inoculated with Newcastle disease virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1415–1421. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1415-1421.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Kawade Y. Purification of two components of mouse L cell interferon: electrophoretic demonstration of interferon proteins. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):225–236. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]