Abstract
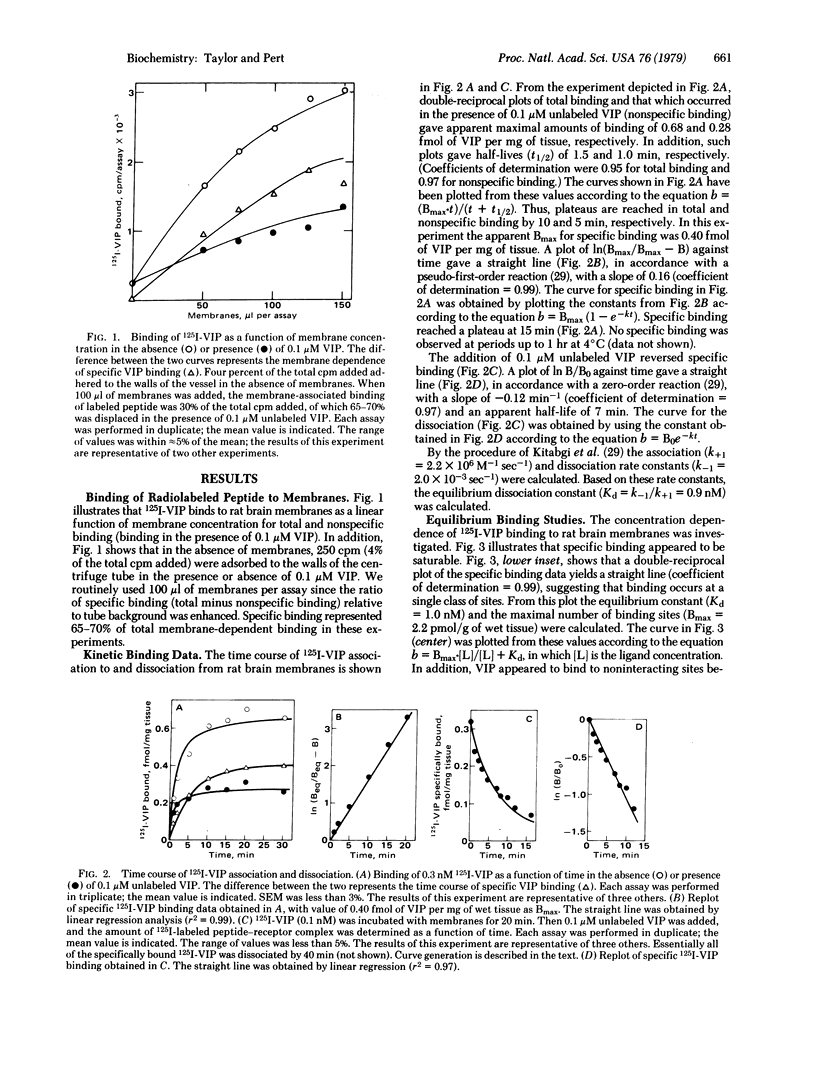
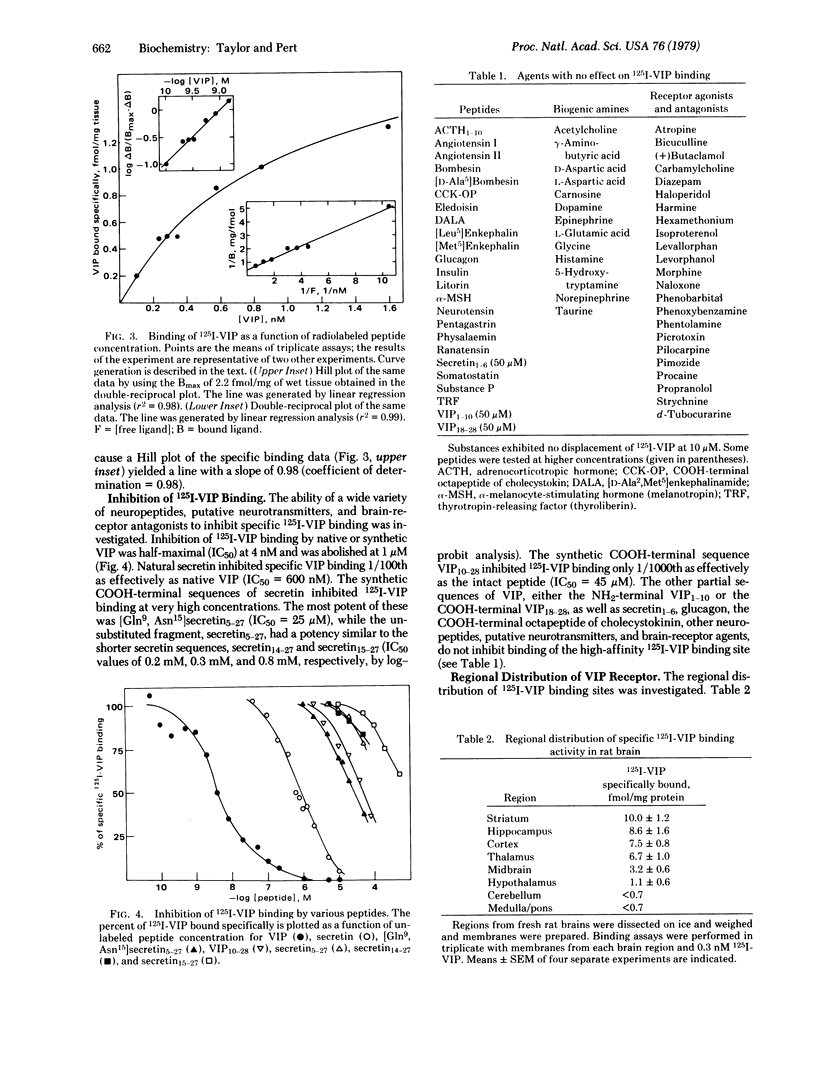
The binding of radiolabeled vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to rat brain membranes was investigated. Specific binding of 125I-labeled VIP was reversible and saturable (Bmax = 2.2 pmol/g of wet tissue). Brain membranes exhibited a high affinity for 125I-labeled VIP (KD = 1 nM) at a single class of noninteracting sites. Binding of 125I-labeled VIP paralleled its immunohistochemical localization, being enriched in cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and thalamus, with the notable exception of the hypothalamus, which had low levels of binding. The density of sites was greater in synaptosomal fractions relative to mitochondrial or nuclear fractions. Secretin and partial sequences of it and VIP inhibited binding to brain membranes with an order of potency similar to that found in other systems. The findings suggest the existence of a unique new class of brain receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm P., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Peptidergic (vasoactive intestinal peptide) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience. 1977;2(5):751–754. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbezat G. O., Grossman M. I. Intestinal secretion: stimulation by peptides. Science. 1971 Oct 22;174(4007):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4007.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bataille D., Freychet P., Rosselin G. Interactions of glucagon, gut glucagon, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and secretin with liver and fat cell plasma membranes: binding to specific sites and stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):713–721. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodanszky M., Henes J. B., Yiotakis A. E., Said S. I. Synthesis and pharmacological properties of the N-terminal decapeptide of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP). J Med Chem. 1977 Nov;20(11):1461–1464. doi: 10.1021/jm00221a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodanszky M., Klausner Y. S., Said S. I. Biological activities of synthetic peptides corresponding to fragments of and to the entire sequence of the vasoactive intestinal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):382–384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. G., Polak M. M., Modlin I., Bloom S. R., Albuquerque R. H., Pearse A. G. Possible dual role for vasoactive intestinal peptide as gastrointestinal hormone and neurotransmitter substance. Lancet. 1976 May 8;1(7967):991–993. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Snyder S. H. Beta adrenergic receptor binding in membrane preparations from mammalian brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):568–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christophe J. P., Conlon T. P., Gardner J. D. Interaction of porcine vasoactive intestinal peptide with dispersed pancreatic acinar cells from the guinea pig. Binding of radioiodinated peptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4629–4634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuguois B., Laudat M. H., Laudat P. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and glucagon: stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity via distinct receptors in liver and fat cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1187–1194. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90590-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Robberecht P., Christophe J. Characterization of VIP-sensitive adenylate cyclase in guinea pig brain. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80645-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont C., Amiranoff B., Laburthe M., Rosselin G. Récepteurs du peptide intestinal vasoactif (VIP) dans les membranes d'adénocarcinome colique humain: liaison spécifique et stimulation de l'adénylate cyclase. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 Jan 16;286(2):209–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B., Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP): vesicular localization and potassium evoked release from rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 17;143(1):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90762-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. L., Bodanszky M. Secretin. VI. Simultaneous "in situ" syntheses of three analogues of the C-terminal tricosapeptide and a study of their conformation. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Feb 18;98(4):974–977. doi: 10.1021/ja00420a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P., Fink M. L., Bodanszky M. Interaction of peptides related to secretin with hormone receptors on pancreatic acinar cells. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):965–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti A., Said S. I., Reynolds R. C., Koniges F. C. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in brain: localization in and release from isolated nerve terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3424–3428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. D., Grillo M., Margolis F. L. Ligand binding studies in the mouse olfactory bulb: identification and characterization of a L-[3H]carnosine binding site. Brain Res. 1978 Dec 15;158(2):407–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90684-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Van Rietschoten J., Granier C., Morgat J. L., Menez A., Leeman S., Freychet P. Neurotensin: specific binding to synaptic membranes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Bataille D., Rosselin G. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): variation of the jejuno-ileal content in the developing rat as measured by radioreceptorassay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1977 Mar;84(3):588–599. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0840588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Besson J., Bon Hoa D. H., Rosselin G. Récepteurs du peptide intestinal vasoactif (VIP) dans les entérocytes: liaison spécifique et stimulation de l'AMP cyclique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1977 Jun 6;284(21):2139–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Rousset M., Boissard C., Chevalier G., Zweibaum A., Rosselin G. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a potent stimulator of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate accumulation in gut carcinoma cell lines in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2772–2775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Edvinsson L., Fahrenkrug J., Håkanson R., Owman C., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O., Sundler F. Immunohistochemical localization of a vasodilatory polypeptide (VIP) in cerebrovascular nerves. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 27;113(2):400–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90951-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Holst J. J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B. Innervation of the pancreas by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) immunoreactive nerves. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(9):773–780. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90246-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Rehfeld J. R. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3197–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide occurs in nerves of the female genitourinary tract. Science. 1977 Sep 30;197(4311):1374–1375. doi: 10.1126/science.897673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makhlouf G. M., Zfass A. M., Said S. I., Schebalin M. Effects of synthetic vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), secretin and their partial sequences on gastric secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Apr;157(4):565–568. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T. W., Pert C. B., Rivier J., Brown M. R. Bomebesin: specific binding to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. The newer gut hormones. Cellular sources, physiology, pathology, and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):746–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Kirkpatrick J. R., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide excitation of central neurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;56(2):337–340. doi: 10.1139/y78-052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Said S. I., Vane J. R. Effects on smooth muscle preparations of unidentified vasoactiv peptides from intestine and lung. Nature. 1970 Mar 21;225(5238):1144–1146. doi: 10.1038/2251144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racusen L. C., Binder H. J. Alteration of large intestinal electrolyte transport by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 1):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., Conlon T. P., Gardner J. D. Interaction of porcine vasoactive intestinal peptide with dispersed pancreatic acinar cells from the guinea pig. Structural requirements for effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide and secretin on cellular adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4635–4639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht P., De Neef P., Lammens M., Deschodt-Lanckman M., Christophe J. P. Specific binding of vasoactive intestinal peptide to brain membranes from the guinea pig. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Mutt V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: isolation from small intestine. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1217–1218. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Rosenberg R. N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science. 1976 May 28;192(4242):907–908. doi: 10.1126/science.1273576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B., Fahrenkrug J., Holst J. J. Release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) by electric stimulation of the vagal nerves. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):373–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schebalin M., Said S. I., Makhlouf G. M. Stimulation of insulin and glucagon secretion by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Am J Physiol. 1977 Feb;232(2):E197–E200. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.232.2.E197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Ingemansson S., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. VIP innervation of the gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jun;72(6):1375–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Bennett J. P., Jr, Snyder S. H. Neurotensin, a central nervous system peptide: apparent receptor binding in brain membranes. Brain Res. 1977 Jul 15;130(2):299–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier C., Brown M. Regulatory peptides of the hypothalamus. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:473–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Muscarinic cholinergic binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


