Abstract
Introduction:
Say Meyer syndrome is rare X linked condition characterized by developmental delay, short stature and metopic suture synostosis. We are reporting a case of Say Meyer syndrome presented to our hospital for short stature and developmental delay at age 3½ years.
Case Report:
A 3½-year-old boy presented to our hospital for decreased growth velocity from the age of 1 year. History revealed the boy had a birth weight of 2.3 kg, had an episode of seizures in the neonatal period. He was born to non-consanguineous marriage. He had global developmental delay and there was a lack of bowel and bladder control. History did not reveal any hearing or visual impairment. No history of any chronic systemic illnesses. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain revealed mild diffuse frontotemporal atrophy with multiple irregular gliotic areas in bilateral frontal lobes. Diffuse white matter volume loss in bilateral cerebral hemispheres. Diffuse thinning of corpus callosum. Diffuse periventricular hyper intensity on T2W and fluid attenuated inversion recovery sequences.
Conclusion:
Say Meyer syndrome is rare X linked condition characterized by developmental delay, short stature and metopic suture synostosis. Characteristic MRI brain findings include diffuse frontotemporal atrophy with multiple gliotic areas in frontal lobes. Diffuse white matter volume loss in bilateral cerebral hemispheres.
Keywords: Craniosynostosis, frontotemporal atrophy, multiple gliotic areas, Say Meyer syndrome, short stature
INTRODUCTION
Say Meyer syndrome is rare X linked condition characterized by developmental delay, short stature and metopic suture synostosis.
CASE REPORT
A 3½-year-old boy presented to our hospital for decreased growth velocity from the age of 1 year. History revealed the boy had a birth weight of 2.3 kg and he had an episode of seizures in the neonatal period. He was born to non-consanguineous marriage. He had global developmental delay and there was a lack of bowel and bladder control. History did not reveal any hearing or visual impairment. No history of any chronic systemic illnesses.
On clinical examination, height was 88 cm, weight was 9 kg and head circumference was 42 cm. Vitals were normal. Upper segment 44 cm and lower segment was 44 cm. He had hypotelorism, squint and a prominent metopic suture [Figure 1]. Thyroid profile, urine examination, renal parameters, serum calcium, serum bicarbonate were normal. Screening echocardiography and ultrasound abdomen was unremarkable.
Figure 1.
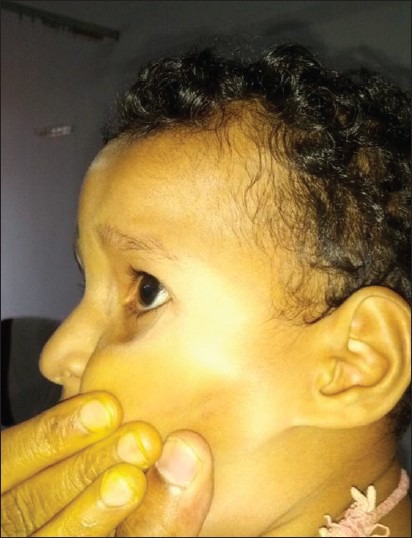
Metopic suture synostosis
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain revealed mild diffuse frontotemporal atrophy with multiple irregular gliotic areas in bilateral frontal lobes. Diffuse white matter volume loss in bilateral cerebral hemispheres [Figure 2]. Diffuse thinning of corpus callosum. Diffuse periventricular hyper intensity on T2W and fluid attenuated inversion recovery sequences.
Figure 2.
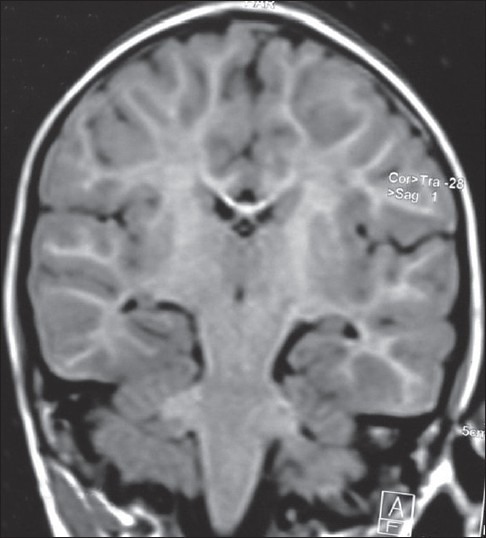
Diffuse white matter volume loss
DISCUSSION
Say Meyer syndrome is a rare X linked disorder characterized by developmental delay, high arched palate, metopic suture synostosis and short stature. It is characterized by hypotelorism, early growth failure, esotropia, long eyelashes, high arched palate and hypospadias.[1]
MRI of the brain typically reveals a decreased volume of white matter with associated a trophy, brainstem, which is smaller in size, thinning of the corpus callosum, unvisualized genu and rostrum, increased signal intensity in the periventrlcular regions suggesting periventricular leukomalacia and enlarged ventricles. Skull radiographs show a decreased interorbital distance and a sclerotic metopic suture.[1]
CONCLUSION
Say Meyer syndrome is one of the rare syndromic causes of short stature, which has to be considered among patients with coexisting dysmorphism and developmental delay.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared
REFERENCE
- 1.Gottesman GS, Silhavy JA, Singh GK, Marlin DS. Say-Meyer syndrome: A new case with Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, cardiacabnormality and X linked dominant inheritance pattern. Genet Med. 2000;2:78–78. [Google Scholar]


