Abstract
Over the past decade, developmental neuroscience has been transformed by the widespread application of confocal and two-photon fluorescence microscopy. Even greater progress is imminent, as recent innovations in microscopy now enable imaging with increased depth, speed, and spatial resolution; reduced phototoxicity; and in some cases without external fluorescent probes. We discuss these new techniques and emphasize their dramatic impact on neurobiology, including the ability to image neurons at depths exceeding 1 mm, to observe neurodevelopment noninvasively throughout embryogenesis, and to visualize neuronal processes or structures that were previously too small or too difficult to target with conventional microscopy.
1. Introduction
The components of the developing nervous system span a wide range of spatial scales--from synaptic vesicles 40 nanometers in diameter to axons several hundred micrometers long, and temporal scales--from processes lasting fractions of a second, to processes which might take years to complete. No single microscope is omniscient, so examining neurodevelopment requires a range of techniques with similar breadth in spatiotemporal resolution, while also allowing imaging to be performed noninvasively, at depth, and in vivo. Confocal and two-photon microscopies are established workhorses that partially satisfy these criteria, but many aspects of neurodevelopment still remain off-limits. We describe here new techniques, many of which have only recently been applied to neuroscience, that will greatly enhance the accessibility of the nervous system to researchers.
2. Imaging Deeper
In the rodent brain, structures like the hippocampus and other deep brain areas are covered by a millimeter or more of tissue that scatter or absorb light, rendering them relatively inaccessible to conventional optical imaging. Scattering of the visible excitation wavelengths used in confocal microscopy limits the penetration depth to less than 100 μm. In two-photon microscopy, two longer-wavelength (usually near-infrared) excitation photons are absorbed instead of a single photon. Since this process depends on the near-simultaneous absorption of two photons, it is strongly enhanced when the excitation is concentrated in time (achieved with a pulsed excitation source) and in space (at the excitation focus). The resulting fluorescence is tightly confined to the focal region, and out-of-focus background is drastically reduced relative to single-photon microscopy. In addition, near-infrared excitation reduces scattering. These advantages improve depth penetration, enabling the study of neuronal activity and anatomy in the cortex (Fig. 1a), sometimes at depths exceeding 800 μm (Fig. 1b) [1].
Fig. 1.
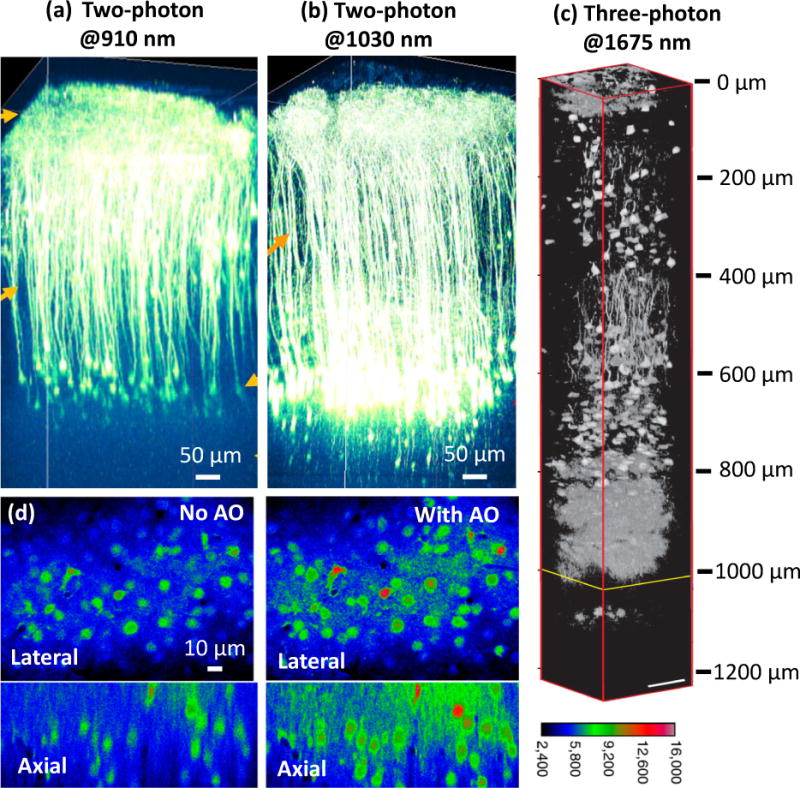
(a–c) Deep in vivo fluorescence imaging with NIR excitation. Two-photon fluorescence imaging of cortical pyramidal neurons with (a) 910-nm and (b) 1030-nm excitation in an adult eYFP-labelled mouse brain. (c) Three-photon fluorescence imaging with 1675-nm excitation of RFP-labelled pyramidal neurons in a mouse brain. (d) AO correction improves calcium imaging. Left: OGB-1 AM labeled neurons 155 μm below the brain surface without AO correction. Right: The same neurons with AO correction. Panels a-b are reprinted from R. Kawakami, et al. [1] with permission from Science; panel c is adapted from N. G. Horton, et al. [3] with permission from Nature; panel d is adapted from N. Ji, et al. [6] with permission from PNAS.
Imaging deeper than 1 mm is difficult, as the fluorescence originating from the focal plane gets progressively scattered and attenuated at depth. Increasing the two-photon intensity or using even longer wavelengths to further reduce scattering helps [2], but only to a point. Beyond a certain depth, the out-of-focus fluorescence background generated at superficial layers overwhelms the increasingly faint signal at the focal plane. Near-simultaneous absorption of three photons results in fluorescence emission that is better confined to the focal plane and further reduces background, breaking the depth limit inherent to two-photon microscopy. Such three-photon microscopy requires pulsed lasers with higher energy and longer wavelengths for exciting the same fluorophores as in two-photon microscopy. The advent of high-pulse-energy lasers at ~1700 nm makes three-photon excitation of red fluorescent proteins practical, extending the imaging of mouse hippocampus from 1,060 to 1,120 μm (Fig. 1c) and enabling vascular imaging to 1.4 mm depth within the brain [3]. Even higher-order multiphoton microscopy is conceivable, although the risk of photodamage increases due to the increasingly intense excitation required. Finally, we note that cleverly combining ultrasound with visible excitation has enabled fluorescence imaging at an unprecedented depth of 2.5 mm within ex vivo tissue, albeit at a lateral resolution of tens of microns [4].
Besides scattering, optical aberrations resulting from imperfect optics and heterogeneity in sample refractive index prevent the formation of a diffraction-limited focus, also limiting imaging depth. Adaptive optics (AO) methods measure these aberrations and iteratively change the shape, phase, or intensity of the excitation in order to improve imaging. AO has been most useful in two-photon microscopy, where depth penetration, signal, and resolution are critically dependent on forming a high-quality excitation focus. AO has improved imaging at depth [5], provided near diffraction-limited imaging 450 μm inside tissue, enabled a fivefold signal enhancement for small neuronal structures, and increased axial resolution threefold when performing functional Ca2+ imaging in single neurons (Fig. 1d) [6]. More recently, AO was used to reduce excitation scattering in mouse brain, thereby improving signal strength 10–100 fold at a depth of 400 μm in vivo, and operating at speeds ~10x faster than previous efforts [7].
3. Imaging Faster
Conventional technology is often too slow for capturing rapid neurodevelopmental dynamics. For example, the slow serial scanning employed in most two-photon microscopy systems restricts recording of neurophysiological signals to a single 2D plane. Observing neuronal activity (occurring on the millisecond timescale) through a population of neurons requires faster acquisition capable of interrogating neuronal activity in 3D. Advances in two-photon imaging and light-sheet microscopy now allow the interrogation of such processes in large tissue volumes [8, 9].
It is frequently desirable to rapidly image a series of discrete points (e.g. jumping from neuron to neuron) after assessing the entire imaging volume with conventional imaging. This mode of two-photon microscopy is called ‘random-access’, and is implemented using specialized hardware that switches between user-selected imaging points much faster than a conventional galvanometric mirror. For example, acousto-optic deflectors enable positioning of a laser’s focus within a large volume (700 μm × 700 μm × 1400 μm) essentially instantaneously (Fig. 2a–b) [9]. Up to ~2000 points can be scanned in 40 milliseconds, enabling volumetric calcium imaging of activity in hundreds of neurons in the mouse visual cortex at unprecedented speed [9].
Fig. 2.
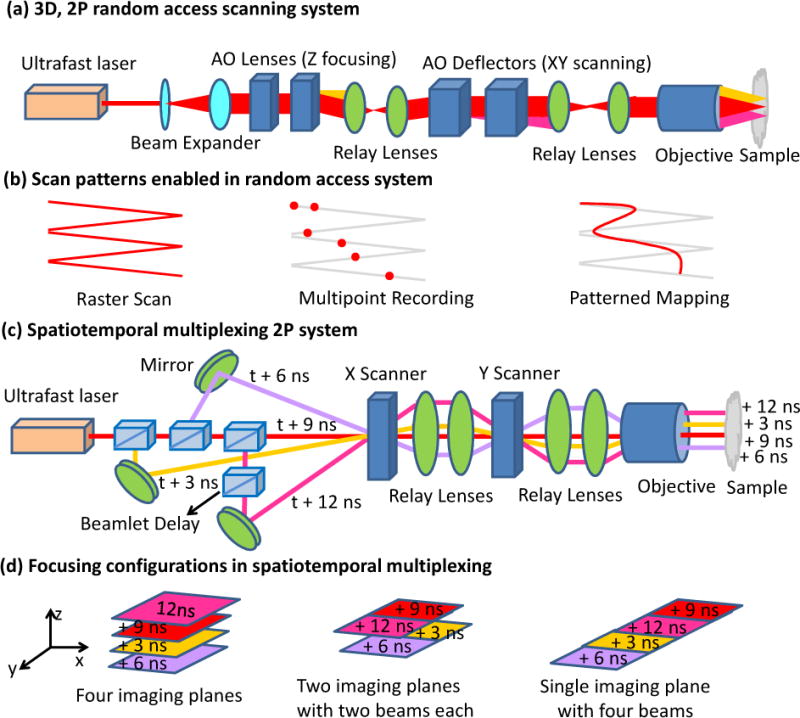
Higher-speed two-photon microscopy. Optical schematic (a) and scanning patterns (b) for 3D random-access scanning. The system allows conventional raster scanning for structural imaging, discrete point sampling for multiunit recording, and pattern mapping for functional imaging. In the high-speed 3D random-access mode, 2000 points can be scanned in 40 ms, enabling volumetric calcium imaging in hundreds of neurons in vivo. Compensating elements must be used because acousto-optical devices generate high spatial and temporal dispersion. Optical schematic (c) and focusing configurations (d) possible in a spatially- and temporally-multiplexed two-photon system. Ultrafast laser pulses are emitted every 12 ns and divided into four beams with 3 ns relative delay that are simultaneously focused at different positions within a sample. Different imaging configurations include a scan of four imaging planes, a single plane scan with four beams, or a scan of two imaging planes with two beams each. When used with a resonant scanning mirror, fast (250 Hz/plane at 500×500 pixels) calcium imaging in four axial planes is possible.
Two-photon microscopy also benefits when multiple excitation beams are used in parallel to increase scanning speed. When simultaneously focusing multiple excitation beams at different positions, a camera may be used to detect the resulting fluorescence, but this approach limits penetration depth relative to conventional two-photon microscopy due to increased sensitivity to scattering [10]. A better approach separates multiple excitation beams not only in space but also in time, using a fast point detector to temporally resolve the resulting fluorescence (Fig. 2c–d) [11]. Four beams with 3 ns relative delay are simultaneously focused at different positions within a sample, increasing speed 4-fold and enabling simultaneous 3D calcium imaging at multiple axial planes to monitor network activity of ensembles of cortical neurons. This strategy only works when the fluorescence decay time is less than 3 ns; further increasing the speed by adding more beams ultimately depends on finding suitable fluorescent dyes.
Finally, axial refocusing may be eliminated entirely by using a diffraction grating to simultaneously record multiple focus-shifted images onto a single camera [12]. Increasing the number of simultaneously recorded planes per volume and improving the light efficiency of the grating are necessary before the technique is widely used in developmental neurobiology.
4. Imaging with Higher Resolution
Many structures within neurons, such as dendritic spines, are small enough that they lie close to or below the diffraction limit for optical microscopy. Given increasing interest in undertanding the cellular compartmentalization of spines and synapses [13], imaging systems capable of sub-diffraction-limited resolution are required. Although the resolution of light microscopy was limited to ~250 nm for several hundred years, a variety of ‘super-resolution’ techniques have emerged in the last decade that are capable of visualizing structures as small as 20 nm [14]. The unifying ability in all these microscopes is the ability to isolate fluorescence from a subdiffractive region inside the sample. We review three of the most popular super-resolution implementations below.
Single-molecule imaging techniques (SMI) [15, 16] repeatedly isolate and localize fluorescence emitted from sparse subsets of photoswitchable molecules, building up a superresolution image from the centers of the fluorescence emitters recorded in thousands of raw images. These techniques provide images with 10–20 nm spatial resolution in ideal conditions [17] but several caveats apply. First, unless enough localizations are obtained, images possess low signal to noise ratio and appear artificially punctate. Second, the acquisition time for a single super-resolution image ranges from seconds to minutes. 3D imaging takes proportionately longer, and is best performed in combination with multiphoton imaging [18] or light sheet microscopy [19] to improve signal to background ratio. Finally, the ~kW/cm2 excitation intensities limit the duration of live applications due to phototoxicity and photobleaching. For these reasons, SMI has been most successfully applied to fixed preparations. Multicolor SMI has enabled ~40 nm imaging of neurites in a hippocampal cell culure model, increasing neural tracing accuracy [20]. SMI also revealed that actin and adducin form periodic ring structures every ~180 nm along axonal shafts in hippocampal cells, a discovery missed previously [21].
Stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) superimposes a donut-shaped ‘depletion’ beam on a focused excitation beam, forcing fluorophores at the perimeter of the excitation beam to preferentially undergo stimulated emission so that fluorescence is emitted only from a subdiffractive region in the center of the focus. Scanning the resulting focus through the sample while collecting the fluorescence in a confocal arrangement enables ‘all-optical’ super-resolution without the need for post-processing required by SMI. STED has been used to image dendritic spines in live nematodes [22] and changes in spine morphology 10–15 μm beneath the surface of the somatosensory cortex in anesthetized mice, at ~70 nm resolution [23]. The resolution in STED scales with the depletion intensity, requiring peak intensities that can lead to phototoxicity over prolonged imaging. If reversible photoactivation is used as the contrast mechanism, similar resolution can be achieved at much lower excitation intensity [24]. Such approaches have been used to study morphological changes in dendritic spines 10–50 μm inside live organotypic brain slices at ~10 s intervals, offering a 3-fold improvement in resolution compared to confocal microscopy [25]. Continued development of multicolor, photostable, faster-switching fluorescent proteins [26] is necessary before these methods are routinely applied in neurobiology.
Linear structured illumination microscopy (SIM) uses spatially patterned excitation light rather than uniform illumination to selectively excite a subset of fluorophores. By shifting the illumination pattern through the sample and mathematically processing the resulting series of diffraction-limited images, it is possible to obtain higher resolution (up to twice the diffraction limit) than can normally be observed in conventional microscopy. While offering a more modest improvement than STED or SMI, SIM is much faster (10 Hz in 2D, ~0.2 Hz in 3D [27]) and uses signficantly lower intensities, enabling volumetric imaging over tens of timepoints. As it is not necessary to use photoswitchable dyes, multicolor imaging [28] is much easier in SIM than in SMI. The recent combination of SIM with confocal pinholing improves background rejection, permitting volumetric imaging of samples ~10x thicker than previously possible [29], and allowing neurodevelopment to be studied in vivo.
5. Imaging Less Invasively
Many neurodevelopmental processes are sensitive to the photobleaching and photodamage that occur during imaging, and that limit the duration over which a given process can be interrogated. Light sheet-based fluorescence microscopes (LSFM) [30–32] minimize photodamage/photobleaching by only illuminating the focal plane (Fig. 3a), and enable 3D acquisition by sweeping the excitation and focal plane through the sample. Since fluorescence is read out with a widefield detector (camera), imaging rates are 10–1000x faster than point-scanning techniques such as confocal or two-photon microscopy.
Fig. 3.
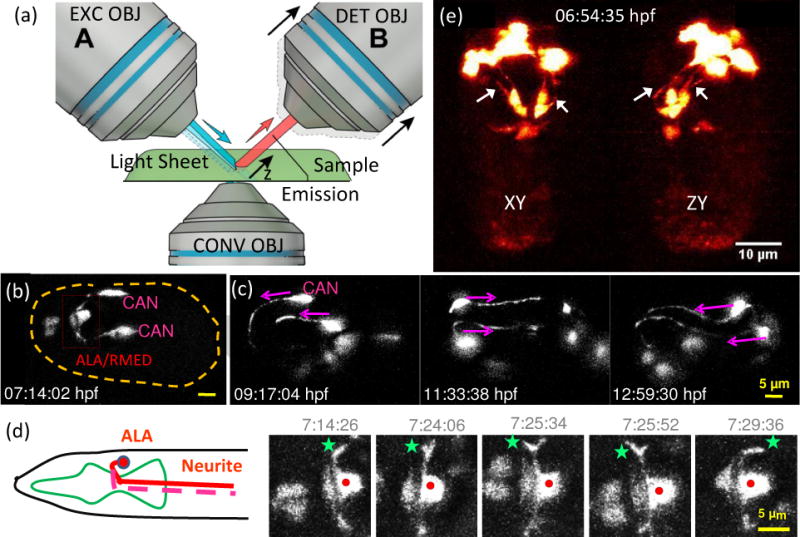
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy enables high-speed, long-term neurodevelopmental imaging during embryogenesis. (a) Inverted selective plane illumination microcopy (iSPIM) schematic. Two long working distance, water immersion objective lenses enable orthogonal SPIM excitation and detection. The excitation objective (EXC OBJ) introduces a light sheet at the sample, and the resulting fluorescence emission is collected by the detection objective (DET OBJ). High-speed volumetric imaging is achieved by sweeping the light sheet and focal plane through the sample, along the detection axis. The bottom objective provides an additional view of the sample and allows other optical modalities. iSPIM enables conventional mounting of specimens. (b–d) Visualization of neuron migration and neurite outgrowths in C.elegans embryos with iSPIM: (b) Maximum-intensity projections of ceh-10p:GFP, highlighting ALA/RMED and CAN neurons before twitching. Scale bar, 5 μm. (c) Time series of the CAN neurite outgrowth through the entire twitching period. (d) The cartoon shows the ALA neuron in the adult worm. Both neurites of ALA project towards the posterior end of the animal. The time-series images display a higher magnification view of the red box in (b). Red dot: ALA soma, green star: left neurite outgrowth. The images show the neuronal outgrowth of ALA through twitching and reveal when the bilateral neurites project towards the posterior end of the embryo. (e) Dual-view iSPIM (diSPIM) imaging highlighting GFP-tagged AIY neurons. Arrows indicate AIY neurites, clearly visible in both lateral projection (left image) and axial projection (right image). Panel c-d are adapted from Y. Wu, et al. [35] with permission from PNAS.
Photobleaching reduction is advantageous in combination with chemical clearing agents that reduce scattering in fixed samples. LSFM has been used in conjunction with clearing agents to investigate development of whole mouse ears over embryonic and postnatal periods [33] and to study monosynaptic connectivity of different neuronal populations in whole adult mouse brains [34]. LSFM can image whole live embryos with spectacular success, as its high speed and low illumination dose enable continuous tracking of neuronal migration and neurite outgrowth in C. elegans [35] (Fig. 3b–d), lineaging of hair cell progenitors in the zebrafish primordium over tens of hours [36], and neuroblast lineaging and observation of subcellular neuronal dynamics in Drosophila [37].
Early LSFM implementations embedded the sample in an agarose gel, rotating and translating the gel as required for 3D acquisition. Although appropriate for samples that do not change shape significantly during development, embedding in agarose can cause severe developmental defects in zebrafish. Systematic evaluation of different mounting agents may help address this problem [38]. Alternatively, mounts such as glass coverslips may be used by placing objectives in an inverted geometry over a microscope stage [35].
Many technical improvements that improve LSFM speed and spatial resolution have occurred recently. Using near-infrared excitation for two-photon LSFM enables imaging 2x deeper than single-photon LSFM and allows imaging rates ~10x faster than conventional two-photon microscopy [39]. Placing two detection objectives at opposite ends of the sample increases penetration depth and light collection, permitting live Drosophila embryos to be imaged every 30 s throughout embryonic development [37]. Combining LSFM with confocal slit detection increases image contrast in thick samples [40], as does combining LSFM with structured illumination and post-processing [8]. Finally, improved spatial resolution is possible if ultrathin light sheets are created from Bessel beams [41] and combined with SIM [42], although such methods significantly increase illumination dose and phototoxicity and are ~5–10x slower than conventional LSFM. A simpler method that provides isotropic 300 nm resolution without these drawbacks relies on acquiring and appropriately combining perpendicular LSFM views (Fig. 3e).
6. Imaging with Intrinsic Contrast
Extraneous fluorescent probes may interfere with neuronal function, eventually bleach, and sometimes are impossible to target specifically, limiting their utility in examining neurodevelopment. Intrinsic, label-free image contrast mechanisms such as autofluorescence imaging [43] (fluorophores include NADH, FAD, collagen and elastin); optical coherence tomography (OCT) [44–46], optical projection tomography [47], optoacoustic tomography [48] (using tissue scattering and absorption for contrast); and second and third harmonic generation [49, 50] (SHG, using noncentrosymmetric structures such as collagen; THG, using lipids) microscopy enable the direct visualization of neurodevelopment without extraneous fluorescent probes.
Optical coherence tomography has been implemented at 200 Hz and up to depths of 500 μm, clearly discriminating dorsal white and gray matter in rodent spinal cord in vivo, as well as resolving vessels with ~10–20 μm diameters in the microvascular network [46]. OCT may thus be an attractive alternative to fluorescence microscopy for studying neurovascular coupling in the developing spinal cord.
Second and third harmonic generation microscopy (Fig. 4a) enables label-free live brain imaging using polarized microtubules inside axons and lipids in neuronal membranes and myelin sheaths surrounding axons (Fig. 4b–c) [50]. In zebrafish embryos, THG signals highlighted cell contours and revealed the yolk-blastoderm interface (Fig. 4d) [51]. Combining THG/SHG with two-photon microscopy in transgenic embryos allows visualization of cytoplasmic streams and mitosis (Fig. 4e) [51]. Also, multichannel imaging of THG with simultaneous three color fluorescence imaging in gastrulating Drosophila embryos revealed the rapid process of mesoderm invagination (Fig. 4f) [52]. These methods may provide an alternate means for reconstructing neuronal connectivity and for tracking cell migrations during embryogenesis.
Fig. 4.
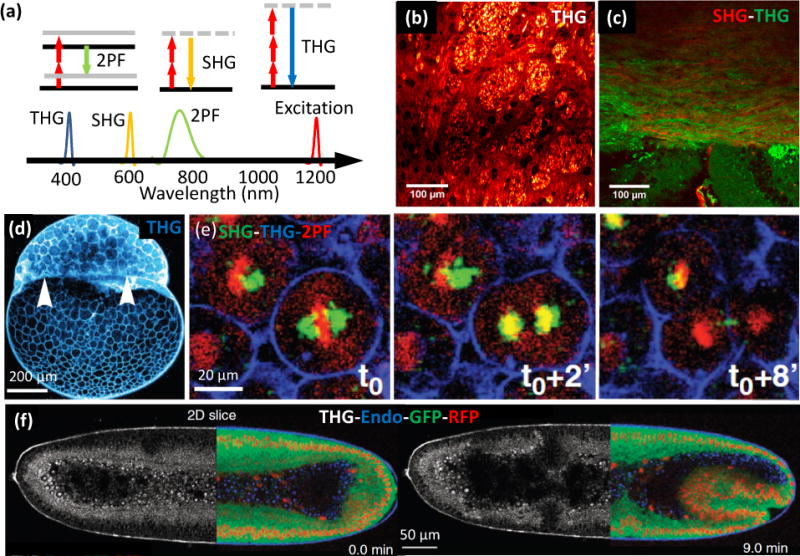
Label free imaging. (a) Energy diagrams and wavelengths in two-photon fluorescence (2PM), second harmonic generation (SHG), and third harmonic generation (THG) imaging. (b) THG image of striatum in a mouse brain (coronal section), showing white-matter fibers and neurons. The bright grainy structures are axon bundles that run perpendicular to the image plane. (c) Merged THG (green) and SHG (red) signal of a mouse corpus callosum. White-matter structures are visible in both SHG and THG images, but gray matter is only visible in the THG image. THG signals originate mostly from the myelin sheaths surrounding axons, whereas SHG signals are produced by polarized microtubules inside the axons. (d) Sagittal THG image of a zebrafish embryo during the 512 cell stage. The THG signal, generated mostly from the lipids in the plasma membrane, highlights cell contours and reveals the yolk-blastoderm interface as indicated by the white arrowheads. (e) Temporal sequence (0, 2 and 8 minutes) of βactin:H2B/mcherry transgenic zebrafish embryo, highlighting mitosis, simultaneously with SHG (green), 2PM (red) and THG (blue). (f) Gastrulating Drosophila embryos with contrast derived from THG (white) and 2PM (mRFP-red, EGFP-green, and autofluorescence-blue) imaging. Panels b-c are adapted from S. Witte, et al. [50] with permission from PNAS; panel d-e are adapted from N. Olivier, et al. [51] with permission from Science; and panel f is adapted from P. Mahou, et al. [52] with permission from Nature.
7. Summary
The technical advantages presented here enable researchers to directly visualize the expression patterns of genes involved in neurodevelopment, examine neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, and synapse formation in living animals, and to examine plasticity in the nervous system throughout the lifespan of an organism. We anticipate that significant discoveries in neuroscience will ensue as these methods are applied to questions well-matched to their unique capabilities.
Highlights.
We describe recent advances in optical imaging of neurodevelopment.
Advances in multi-photon microscopy provide increased imaging depth and speed for investigation of neuronal activity in 3D.
Super-resolution imaging offers resolution down to tens of nm, revealing fine structures in the nervous system.
Light sheet microscopy permits long-term, in toto observation of embryogenesis.
Intrinsic contrast imaging allows direct visualization of neuroanatomy.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Paper of particular interest, published within the period of review, have been highlighted as:
of special interest
of outstanding interest
References and recommended reading
- 1.Kawakami R, et al. Visualizing hippocampal neurons with in vivo two-photon microscopy using a 1030 nm picosecond pulse laser. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1014. doi: 10.1038/srep01014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kobat D, Horton NG, Xu C. In vivo two-photon microscopy to 1.6-mm depth in mouse cortex. J Biomed Opt. 2011;16(10):106014. doi: 10.1117/1.3646209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3**.Horton Nicholas G, Demirhan Kobat KW, Clar Catharine G, Wise Frank W, Schaffer Chris B, Xu Chris. In vivo three-photon microscopy of subcortical structures within an intact mouse brain. Nature Photonics. 2013;7:205–209. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.336. Three-photon fluorescence microscopy with a high-pulse-energy laser at ~1650 nm has enabled the in vivo high-resolution imaging of subcortical structures within an intact mouse brain with a penetration depth of ~1.4 mm. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang YM, et al. Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light. Nature Communications. 2012;3 doi: 10.1038/ncomms1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wang C, Ji N. Pupil-segmentation-based adaptive optical correction of a high-numerical-aperture gradient refractive index lens for two-photon fluorescence endoscopy. Opt Lett. 2012;37(11):2001–3. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6*.Jia N, Sato TR, Betzig E. Characterization and adaptive optical correction of aberrations during in vivo imaging in the mouse cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(1):22–27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109202108. Image-based adaptive optics enables diffraction-limited performance in two-photon imaging up to 450 μm in mouse brain, enabling functional Ca2+ imaging in single neurons. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tang JY, Germain RN, Cui M. Superpenetration optical microscopy by iterative multiphoton adaptive compensation technique. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(22):8434–8439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119590109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keller PJ, et al. Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet-based structured-illumination microscopy. Nature Methods. 2010;7(8):637–U55. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9**.Katona G, et al. Fast two-photon in vivo imaging with three-dimensional random-access scanning in large tissue volumes. Nature Methods. 2012;9(2):201–208. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1851. Acoustic-optics are used to enable high speed, 3D random-access scanning 2P microscopy with a near-cubic millimeter scan range. 3D cacium imaging of action potential backpropagation and dendritic spike forward propagation at sub-milisceond temporal resolution in mouse brain slices is demonstrated, as is in vivo imaging of hundreds of neruosn in the mouse visual cortex. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Andresen V, et al. High-resolution intravital microscopy. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11*.Cheng A, et al. Simultaneous two-photon calcium imaging at different depths with spatiotemporal multiplexing. Nat Methods. 2011;8(2):139–42. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1552. This high-speed two-photon sytsem uses spatiotemporal multiplexing and four excitation beams to enable simultaneous 3D calcium imaging in a variety of imaging configurations. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Abrahamsson S, et al. Fast multicolor 3D imaging using aberration-corrected multifocus microscopy. Nature Methods. 2013;10(1):60–U80. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen Y, Sabatini BL. Signaling in dendritic spines and spine microdomains. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2012;223:389–396. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sigrist SJ, Sabatini BL. Optical super-resolution microscopy in neurobiology. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2012;22(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2011.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kamiyama D, Huang B. Development in the STORM. Developmental Cell. 2012;23(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Thompson MA, Lew MD, Moerner WE. Extending Microscopic Resolution with Single-Molecule Imaging and Active Control. Annual Review of Biophysics. 2012;41:321–342. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-050511-102250. Vol 41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xu K, Babcock HP, Zhuang XW. Dual-objective STORM reveals three-dimensional filament organization in the actin cytoskeleton. Nature Methods. 2012;9(2):185–188. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.York AG, et al. Confined activation and subdiffractive localization enables whole-cell PALM with genetically expressed probes. Nature Methods. 2011;8(4):327–U73. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zanacchi FC, et al. Live-cell 3D super-resolution imaging in thick biological samples. Nature Methods. 2011;8(12):1047–+. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lakadamyali M, et al. 3D multicolor super-resolution imaging offers improved accuracy in neuron tracing. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xu K, Zhong G, Zhuang X. Actin, spectrin, and associated proteins form a periodic cytoskeletal structure in axons. Science. 2013;339(6118):452–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1232251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rankin BR, et al. Nanoscopy in a living multicellular organism expressing GFP. Biophys J. 2011;100(12):L63–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.05.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23*.Berning S, et al. Nanoscopy in a living mouse brain. Science. 2012;335(6068):551. doi: 10.1126/science.1215369. Super-resolution imaging with STED in a living mouse brain is demonstrated, revealing neurons in the cerebral cortex with a resolution less than 70 nm. Changes in dendritic spines are monitored over 30 minutes. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Grotjohann T, et al. Diffraction-unlimited all-optical imaging and writing with a photochromic GFP. Nature. 2011;478(7368):204–208. doi: 10.1038/nature10497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Testa I, et al. Nanoscopy of living brain slices with low light levels. Neuron. 2012;75(6):992–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.07.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grotjohann T, et al. rsEGFP2 enables fast RESOLFT nanoscopy of living cells. eLife. 2012;1:e00248. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shao L, et al. Super-resolution 3D microscopy of live whole cells using structured illumination. Nature Methods. 2011;8(12):1044–+. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fiolka R, et al. Time-lapse two-color 3D imaging of live cells with doubled resolution using structured illumination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(14):5311–5315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119262109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29*.York AG, et al. Resolution doubling in live, multicellular organisms via multifocal structured illumination microscopy. Nature Methods. 2012;9(7):749–U167. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2025. Structured illumination microscopy at depths ~10x thicker than previously possible is demonstrated, enabling resolution doubling 50–60 mm from the coverslip in live embryos. The method is easy to integrate with wide-field microscopes. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hockendorf B, Thumberger T, Wittbrodt J. Quantitative Analysis of Embryogenesis: A Perspective for Light Sheet Microscopy. Developmental Cell. 2012;23(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Santi PA. Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy: A Review. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry. 2011;59(2):129–138. doi: 10.1369/0022155410394857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tomer R, Khairy K, Keller PJ. Shedding light on the system: Studying embryonic development with light sheet microscopy. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 2011;21(5):558–565. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kopecky B, et al. Scanning thin-sheet laser imaging microscopy elucidates details on mouse ear development. Developmental Dynamics. 2012;241(3):465–480. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Niedworok CJ, et al. Charting monosynaptic connectivity maps by two-color lightsheet fluorescence microscopy. Cell reports. 2012;2(5):1375–86. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35**.Wu YC, et al. Inverted selective plane illumination microscopy (iSPIM) enables coupled cell identity lineaging and neurodevelopmental imaging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(43):17708–17713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108494108. LSFM is demonstrated on a conventional microscope, preserving the use of glass coverslips and allowing a variety of samples to be imaged. The technology enables continuous tracking of neuronal migration and neurite outgrowths in C. elegans (every 2 s over the 14 hour period of embryogenesis, a volumetric rate 30x faster than spinning disk confocal microscopy). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Swoger J, et al. 4D retrospective lineage tracing using SPIM for zebrafish organogenesis studies. Journal of Biophotonics. 2011;4(1–2):122–134. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201000087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tomer R, et al. Quantitative high-speed imaging of entire developing embryos with simultaneous multiview light-sheet microscopy. Nat Methods. 2012;9(7):755–63. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kaufmann A, et al. Multilayer mounting enables long-term imaging of zebrafish development in a light sheet microscope. Development. 2012;139(17):3242–7. doi: 10.1242/dev.082586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Truong TV, et al. Deep and fast live imaging with two-photon scanned light-sheet microscopy. Nature Methods. 2011;8(9):757–U102. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Silvestri L, et al. Confocal light sheet microscopy: micron-scale neuroanatomy of the entire mouse brain. Optics Express. 2012;20(18):20582–20598. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.020582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Planchon TA, et al. Rapid three-dimensional isotropic imaging of living cells using Bessel beam plane illumination. Nature Methods. 2011;8(5):417–U68. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gao L, et al. Noninvasive Imaging beyond the Diffraction Limit of 3D Dynamics in Thickly Fluorescent Specimens. Cell. 2012;151(6):1370–1385. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shuttleworth CW. Use of NAD(P)H and flavoprotein autofluorescence transients to probe neuron and astrocyte responses to synaptic activation. Neurochemistry International. 2010;56(3):379–386. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.12.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Srinivasan VJ, et al. Optical coherence microscopy for deep tissue imaging of the cerebral cortex with intrinsic contrast. Optics Express. 2012;20(3):2220–2239. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.002220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mathews MS, et al. Neuroendovascular Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging and Histological Analysis. Neurosurgery. 2011;69(2):430–439. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318212bcb4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46*.Cadotte DW, et al. Speckle variance optical coherence tomography of the rodent spinal cord: in vivo feasibility. Biomedical Optics Express. 2012;3(5):911–919. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.000911. OCT imaging is used to resolve vessels at ~10 μm resolution, demonstrating that OCT may be an attractive tool for studying the dynamic relationship between neural activity and the surrounding blood vessels in the brain. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ragan T, et al. Serial two-photon tomography for automated ex vivo mouse brain imaging. Nature Methods. 2012;9(3):255–U48. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ma R, et al. Non-invasive whole-body imaging of adult zebrafish with optoacoustic tomography. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2012;57(22):7227–7237. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/22/7227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Farrar MJ, et al. In Vivo Imaging of Myelin in the Vertebrate Central Nervous System Using Third Harmonic Generation Microscopy. Biophysical Journal. 2011;100(5):1362–1371. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.01.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50**.Witte S, et al. Label-free live brain imaging and targeted patching with third-harmonic generation microscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(15):5970–5975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018743108. High-contrast imaging of live brain tissue at cellular resolution is achieved without fluorescent probes, using optical third-harmonic generation (THG). The technique enables visualization of neurons, white-matter structures and blood vessels. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Olivier N, et al. Cell Lineage Reconstruction of Early Zebrafish Embryos Using Label-Free Nonlinear Microscopy. Science. 2010;329(5994):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.1189428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mahou P, et al. Multicolor two-photon tissue imaging by wavelength mixing. Nat Methods. 2012;9(8):815–8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


