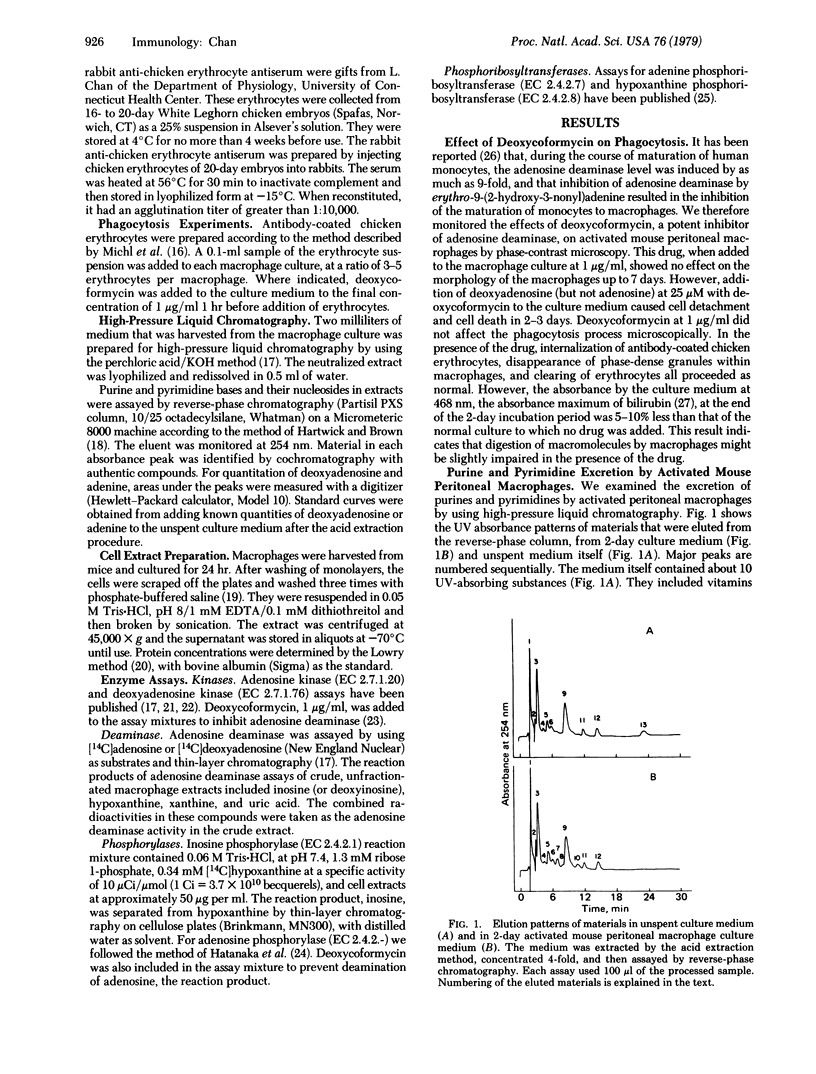
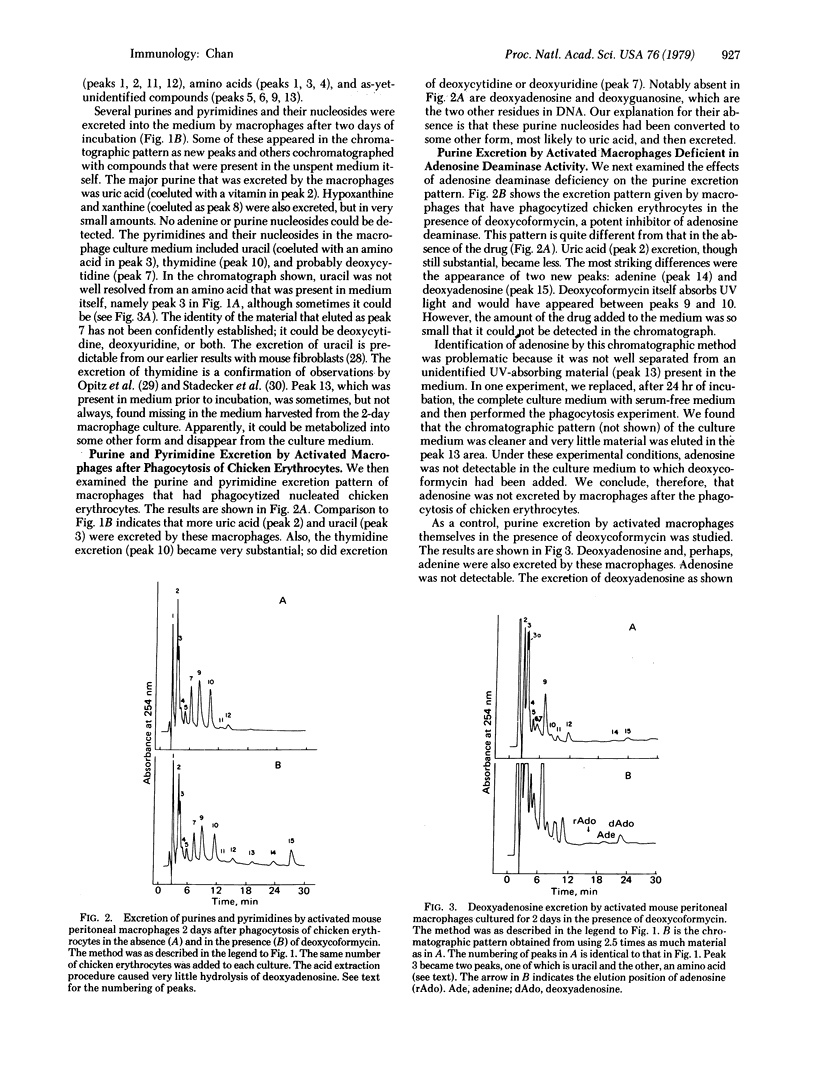
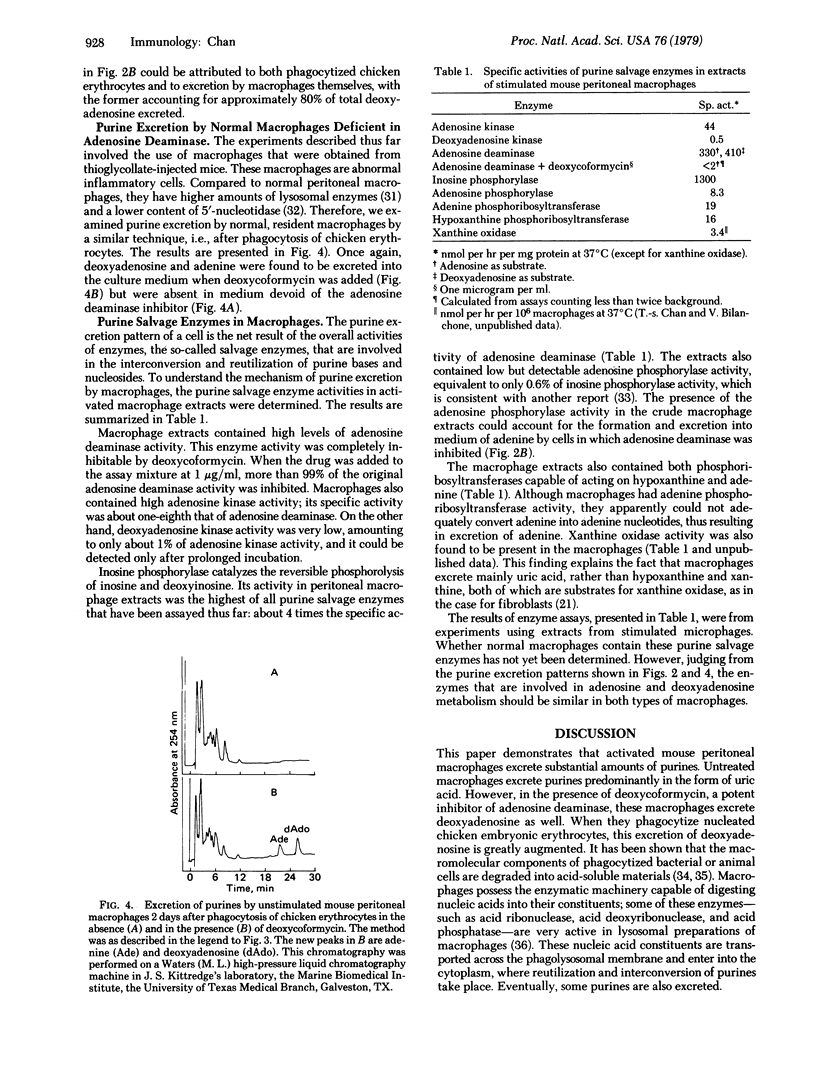
Abstract
Deoxyadenosine, a cytotoxic purine nucleoside, is excreted in large amounts by patients with severe combined immunodeficiency disease associated with deficiency of adenosine deaminase (adenosine aminohydrolase, EC 3.5.4.4). To identify the source of the purine nucleoside, purine excretion by macrophages was studied by using mouse peritoneal macrophages as an experimental model system. Normally, macrophages excrete a large quantity of uric acid into the culture medium. However, in the presence of deoxycoformycin, a potent inhibitor of adenosine deaminase, these macrophages also excreted deoxyadenosine. Furthermore, phagocytosis of nucleated erythrocytes augmented the excretion of deoxyadenosine. Macrophages are involved in the phagocytosis of nuclei that are extruded from normoblasts during erythropoiesis and also of senescent cells in lymphoid organs. A hypothesis is proposed that macrophages of the reticuloendothelial system are a source of deoxyadenosine, which is one of the two cytotoxic purine nucleosides (the other is adenosine) apparently responsible for the suppression of immune functions in patients with adenosine deaminase deficiency.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal R. P., Spector T., Parks R. E., Jr Tight-binding inhibitors--IV. Inhibition of adenosine deaminases by various inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Mar 1;26(5):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballet J. J., Insel R., Merler E., Rosen F. S. Inhibition of maturation of human precursor lymphocytes by coformycin, an inhibitor of the enzyme adenosine deaminase. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. The fate of bacteria within phagocytic cells. I. The degradation of isotopically labeled bacteria by polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:27–42. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., WIENER E. THE PARTICULATE HYDROLASES OF MACROPHAGES. I. COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY, ISOLATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Exp Med. 1963 Dec 1;118:991–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.6.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Kaye J., Seegmiller J. E. Lymphospecific toxicity in adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency: possible role of nucleoside kinase(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5677–5681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Seegmiller J. E. Effect of adenosine deaminase inhibition upon human lymphocyte blastogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):274–282. doi: 10.1172/JCI108278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S., Creagan R. P., Reardon M. P. Adenosine kinase as a new selective marker in somatic cell genetics: isolation of adenosine kinase--deficient mouse cell lines and human--mouse hybrid cell lines containing adenosine kinase. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Jan;4(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01546489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S., Ishii K., Long C., Green H. Purine excretion by mammalian cells deficient in adenosine kinase. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Jun;81(3):315–322. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. S., Meuth M., Green H. Pyrimidine excretion by cultured fibroblasts: effect of mutational deficiency in pyrimidine salvage enzymes. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):263–266. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassin M. M., Chirigos M. A., Johns D. G., Adamson R. H. Adenosine deaminase inhibition for immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 26;296(21):1232–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Benson B. The in vitro differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes. 3. The reversibility of granule and hydrolytic enzyme formation and the turnover of granule constituents. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):455–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Cohn Z. A. 5'-Nucleotidase activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Synthesis and degradation in resident and inflammatory populations. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1581–1595. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich B. A., Cohn Z. A. Fate of hemoglobin pincytosed by macrophages in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):244–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D., Van der Weyden M. B., Snyderman R., Kelley W. N. A role for adenosine deaminase in human monocyte maturation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):399–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI108484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Chan T. Pyrimidine starvation induced by adenosine in fibroblasts and lymphoid cells: role of adenosine deaminase. Science. 1973 Nov 23;182(4114):836–837. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4114.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwick R. A., Brown P. R. Evaluation of microparticle chemically bonded reversed-phase packings in the high-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of nucleosides and their bases. J Chromatogr. 1976 Nov 3;126:679–691. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Del Giudice R., Long C. Adenine formation from adenosine by mycoplasmas: adenosine phosphorylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Sela E. Adenosine deaminase and immunodeficiency: an in vitro model. Cell Immunol. 1977 Aug;32(2):350–360. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Smyth J. F., Allison A. C., Williams S. C. Role of adenosine deaminase in lymphocyte proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Mar;23(3):395–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Green H. Lethality of adenosine for cultured mammalian cells by interference with pyrimidine biosynthesis. J Cell Sci. 1973 Sep;13(2):429–439. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krygier V., Momparler R. L. Mammalian deoxynucleoside kinases. II. Deoxyadenosine kinase: purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2745–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Chan T., Levytska V., Kusano T., Green H. Absence of demonstrable linkage of human genes for enzymes of the purine and pyrimidine salvage pathways in human-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Biochem Genet. 1973 Jul;9(3):283–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00485741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum C. T., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S. Inhibition for immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):819–819. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen H. J., Pollara B., Pickering R. J. Combined immunodeficiency disease associated with adenosine deaminase deficiency. Report on a workshop held in Albany, New York, October 1, 1973. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):169–181. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80463-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michl J., Ohlbaum D. J., Silverstein S. C. 2-Deoxyglucose selectively inhibits Fc and complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Description of the inhibitory effect. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1465–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills G. C., Schmalstieg F. C., Trimmer K. B., Goldman A. S., Goldblum R. M. Purine metabolism in adenosine deaminase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2867–2871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz H. G., Niethammer D., Jackson R. C., Lemke H., Huget R., Flad H. D. Biochemical characterization of a factor released by macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jul;18(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimstone N. R., Tenhunen R., Seitz P. T., Marver H. S., Schmid R. The enzymatic degradation of hemoglobin to bile pigments by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1264–1281. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polmar S. H., Stern R. C., Schwartz A. L., Wetzler E. M., Chase P. A., Hirschhorn R. Enzyme replacement therapy for adenosine deaminase deficiency and severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 9;295(24):1337–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612092952402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds H. A., Panayi G. S., Corrigall V. A role for purine metabolism in the immune response: Adenosine-deaminase activity and deoxyadenosine catabolism. Lancet. 1978 Jan 14;1(8055):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skutelsky E., Danon D. On the expulsion of the erythroid nucleus and its phagocytosis. Anat Rec. 1972 May;173(1):123–126. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091730111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Calderon J., Karnovsky M. L., Unanue E. R. Synthesis and release of thymidine by macrophages. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1738–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Gersten N. B., Ross A. F., Miech R. P. Adenine as substrate for purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Can J Biochem. 1971 Sep;49(9):1050–1054. doi: 10.1139/o71-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



